Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Making of a global world Assignment Set C for the 2025-26 academic session. We have provided comprehensive Class 10 Social Science school assignments that have important solved questions and answers for India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World. These resources have been carefuly prepared by expert teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS syllabus guidelines.
Solved Assignment for Class 10 Social Science India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World
Practicing these Class 10 Social Science problems daily is must to improve your conceptual understanding and score better marks in school examinations. These printable assignments are a perfect assessment tool for India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World, covering both basic and advanced level questions to help you get more marks in exams.
India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World Class 10 Solved Questions and Answers
The Making Of A Global World
Intoduction- The making of the global world has a long history - of trade, of migration, of people in search of work, the movement of capital, and much else. As we think about the dramatic and visible signs of global interconnectedness in our lives today, we need to understand the phases through which this world in which we live has emerged.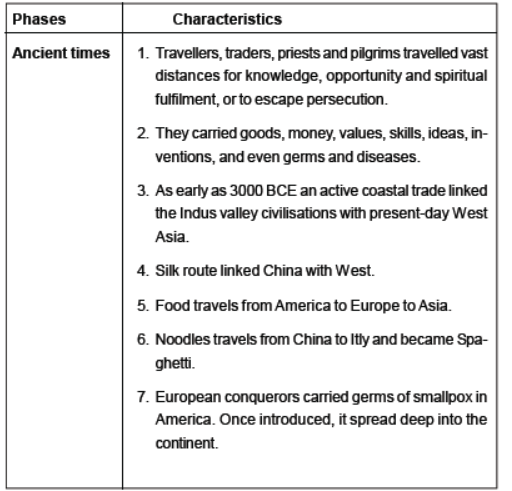
Points to Remember
(1) Globalization- worldwide integration of economic, cultural, political, religious, and social systems. This means that goods and services, capital, and labour are traded on a worldwide basis, and information and the results of research flow readily between countries.
(2) Silk routes- The Silk Route was a historic trade route that dated from the second century B.C. until the 14th century A.D. It stretched from Asia to the Mediterranean, traversing China, India, Persia,Arabia, Greece, and Italy .It was dubbed the Silk Route because of the heavy silk trading that took place during that period.
(3) Corn Law- The laws allowing the government (U.K.) to restrict the import of corn were commonly known as the Corn Laws.
(4) Rinderpest Plague- Rinderpest is a fast spreading cattle plague which hit Africa in the late 1880s.
(5) The Bretton Woods institutions- The International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank were created to bring about orderly development of the world economy in the post-World War II era.
(6) Indentured labour- A bonded labourer under contract to work for an employer for a specific amount of time, to pay off his passage to a new country or home.
(7) Flow of Labour- Migration of people to new areas in search of work.
(8) Hosay- Trinidad the annual Muharram procession was transformed into a riotous carnival called 'Hosay' (for Imam Hussain) in which workers of all races and religions joined.
(9) G-77: G-77 was a group organized by developing countries to de mand a New International Economical Order (NIEO) which would give these countries real control over their national resources, raw material, manufactured goods and their markets.
(10) Veto- A constitutional right to reject a decision or proposal made by a law making body.
(11) Tariff- Tax imposed on a country's imports from the rest of the world. Tariffs are levied at the point of entry, i.e., at the border or the airport.
(12) Exchange Rates- They link national currencies for purposes of international trade. There are broadly two kinds of exchange rates: fixed exchange rate and floating exchange rate.
Short Answer type Questions
Question. Reason for decline of cotton textile export from India to Britain in the early 19th century:
(a) imposition of tariff on cotton import into Britain.
(b) quality of cotton textile was poor.
(c) shortage of raw cotton in India.
(d) cotton producers had found other buyers.
Answer: A
Question. During the First World War women in Europe stepped into jobs which earlier men were expected to do. What was the reason?
(a) because men went to battle.
(b) because men went to other countries in search of jobs.
(c) because of liberalisation of women in society.
(d) because menfolk decided to take charge of the household work.
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following did not take part in the First World War?
(a) Portugal
(b) Germany
(c) France
(d) England
Answer: A
Question. Who adopted the concept of 'assembly line' to manufacture automobiles?
(a) T. Cuppola
(b) Henry Ford
(c) Samuel Morse
(d) Christopher Columbus
Answer: B
Question. Thousands of people fled Europe for America in the 19th century due to
(a) poverty and widespread deadly diseases
(b) natural calamity
(c) outbreak of a war among nations
(d) outbreak of plague
Answer: A
Question. Who was V.S.Naipaul?
Answer: a writer, whose forefather migrated as indentured worker.
Question. How were human societies interlinked in ancient times ?
Answer: interlinked by travellers, traders, priests and pilgrims who travelled vast distances for knowledge, opportunity and spiritual fulfillment
Question. Mention one example of vibrant pre-modem trade and cultural link between distant parts of the world.
Answer: The silk routes are a good example
Question. What is Al-Dorado in Latin America?
Answer: City of Gold.
Question. Give any two factors which helped in making of global world?
Answer: (1) Trade (2) In search of work (3) Money
Fill in the blanks
Question. ................ is a fast spreading cattle plague which hit Africa in the late 1880s.
Answer: Rinderpest
Question. The First World War (1914-18) was mainly fought in ...... (continent)
Answer: European.
Question. America was discovered by ..........
State whether the following statements are True or False-
Answer: Christopher Columbus
Question. People livelihood and local economy of Asia was badly affected by the disease named Rinderpest.
Answer: False
Question. Carribbean island was an important destination for indentured migrants?
Answer: True
Question. Europeans were attracted to Africa by its natural beauty.
Answer: False
Question. In the question given below,there are two statements marked as Assertion
(A) and Reason (R).Mark your answer as per the codes provided below :
(A) Chutney music, popular in Trinidad and Guyana,is another creative contemporary expression of the post-indenture experience.
(R) Some of the Naipaul's early novels capture their sense of loss and alienation.
Options :
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of
(3) A is true but R is False.
(4) A is false but R is true.
Answer: B
Question. (A) Over the nineteenth century,British manufactures flooded the Indian market.
(R) The value of Indian exports to Britain was much higher than the value of British imports to India.
Options:
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of
(3) A is true but R is False.
(4) A is false but R is true.
Answer: C
Question. (A) The Portuguese and Spanish conquest and colonisation of America was decisively under way by the mid-sixteenth century.
(R) The most powerful weapon of the Spanish conquerors was atom bombs.
Options :
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of
(3) A is true but R is False.
(4) A is false but R is true.
Answer. C
Short/Long Answer Type Questios
Question. What are 'canal colonies' ?
Answer: The British Indian government built a network of irrigation canals in Punjab. The Colonies situated around the areas irrigated by the new canals were called, Canal Colonies.
Question. Why is it said that there was no other war earlier like first world war? State in three points.
Answer:
(a) Involved almost all countries in one or the other way.
(b) Weapons used had a deadly potential to kill and destroy whatever came in their way.
(c) There was an immense loss of young and productive population.
(d) Economies of the countries round the world crashed beyond the level of recovery.
Question. Why did Europeans flee to America in the 19th Century? Give three reasons.
Answer: (a) Poverty and hunger were common and widespread in Europe in the beginning of the 19th century.
(b) Cities were overcrowded and people feared deadly diseases.
(c) Religious conflicts were frequent as dissenters were persecuted on a large scale.
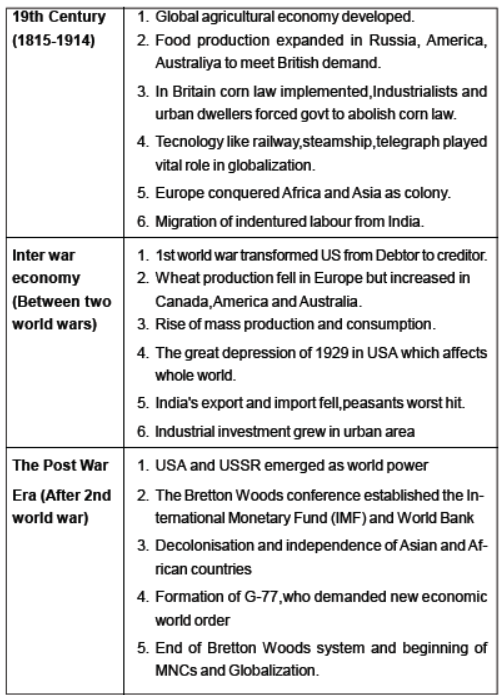
Question. How did the withdrawals of US loans during the phase of the Great Depression affect the rest of the world? Explain in three points.
Answer: (a) It led to some major banks crashing and the collapse of currencies.
(b) It led to a fall in agricultural productivity and raw material prices in Latin America.
(c) Unemployment became rampant as no jobs could be generated.
Question. How did rinderpest become instrumental in subjugating the Africans?
Answer: (a) It affected the livelihood, economy , the social peace and harmony of the Africans.
(b) About ninety-nine per cent of the cattle were killed, which forced Africans to work for the Europeans in the plantations.
(c) It enabled the Europeans to colonies and subdue Africa. The colonial government forced Africans into labour - market.
Question. How did technology help to solve hardship of food availability throughout the world in the late-nineteenth century? Explain with example.
Answer: (a) Because of improvements in transport, like faster railways with lighter wagons and large ships, food moved quickly and cheaply from farms to final markets.
(b) Now perishable food could travel long distances easily through refrigerated ships.
(c) Animals could be slaughtered and easily packed for long distances.
Cost of transportation also reduced.
(d) The poor could now consume more varied diet including meat as it was available in plenty and at reduced costs.
Question. Explain the impact of First World War on the British economy.
Answer: (a) 15 - 25 percent of Britain's wealth was spent on the war.
(b) It had borrowed heavily from the United States and after the war, the debts mounted.
(c) British industries could not produce goods for exports.
(d) Being unable to modernize its industries and compete with the United States, Germany and Japan, British economy crumbled.
Question. Describe the effects of abolishing the Corn Laws.
Answer: (a) Food could be imported into Britain more cheaply than it could be produced within the country.
(b) British agriculture was unable to compete with imports.
(c) Vast areas of land were now left uncultivated and thousands of men and women were thrown out of work.
(d) Peasants flocked to the cities or migrated overseas.
Question. When was the Bretton Woods Conference convened? State the main aim of the conference.
Answer: (a) In July 1944 , New Hampshire, US.
(b) To preserve the economic stability of Europe and ensure full employment in the industrial world.
(c) To control the influence of the outer world on flow of capital, goods and labour.
Question. How did the Great Depression of 1929 affect the farmers and the middle classes in India in different ways?
Answer: (a) Agricultural prices began to fell and finally collapsed in 1930.
(b) It became difficult for the peasants to sell their harvest and pay revenues.
(c) Peasants ran into huge debts who had mortgaged their land and used their savings.
(d) This depression however did not hit the urban areas where the middle class lived and had fixed incomes.
(e) Middle class salaried people were not affected and rather they could buy goods at a cheaper rate.
Question. How did the global transfer of disease in pre-modern world helped in colonisation of the Americas?
Answer: (a) Due to the long isolation from the world, American inhabitants had no knowledge and immunity against diseases of Europe.
(b) The Spanish conquerors used their instance to introduce germs of smallpox through their smallpox-infected person.
(c) It spread deep into the continent and killed and decimated whole communities.
Question. What do you mean by surplus trade? Why the balance of trade is always favourable for Britain in terms of India?
Answer: When export value is more than import value is known as surplus value
(a) The excess of goods in the market of Britain.
(b) Increase in export of grains and raw material to Britain and other countries from India.
(c) The goods imported to India cost very high whereas the goods exported to Britain cost very less.
Question. What is Globalization? Explain the three types of movements or flows within international economic exchange.
Answer: Globalization is an economic system with the free movement of goods,
capital, services, technology and people across the globe.
(a) Flow of capital-investment of capital
(b) Flow of goods- trade in goods
(c) Flow of labour- migration of people to new areas in search of work.
Question. What were the causes of Economic Depression?
Answer:
(a) Agricultural overproduction
(b) Falling agricultural prices
(c) Agricultural income declined
(d) Countries that depended on US loans now faced an acute crisis.
(e) The withdrawal of US loans affected much of the rest of the world
(f) Thousands of banks became bankrupt
Source Based Questions
1. Read the following passage and answer the questions.
All through history, human societies have become steadily more interlinked. From ancient times, travellers, traders, priests and pilgrims travelled vast distances for knowledge, opportunity and spiritual fulfilment, or to escape persecution. They carried goods, money, values, skills, ideas, inventions, and even germs and diseases. As early as 3000 BCE an active coastal trade linked the Indus valley civilisations with present-day West Asia. For more than a millennia, cowries (the Hindi cowdi or seashells, used as a form of currency) from the Maldives found their way to China and East Africa. The long distance spread of disease-carrying germs may be traced as far back as the seventh century. By the thirteenth century it had become an unmistakable link.
Question. In ancient times,Why people travelled vast distances?
Answer. For knowledge, opportunity and spiritual fulfilment, or to escape persecution,
Question. What was cowries?
Answer. Seashells, used as a form of currency.
Question. What was the negative impact of travel?
Answer. They carried germs with them.
2. Read the following passage and answer the questions at the end.
The Portuguese and Spanish conquest and colonisation of America was decisively under way by the mid-sixteenth century. European conquest was not just a result of superior firepower. In fact, the most powerful weapon of the Spanish conquerors was not a conventional military weapon at all. It was the germs such as those of smallpox that they carried on their person. Because of their long isolation, America's original inhabitants had no immunity against these diseases that came from Europe. Smallpox in particular proved a deadly killer. Once introduced, it spread deep into the continent, ahead even of any Europeans reaching there. It killed and decimated whole communities, paving the way for conquest.
Question. What was the most powerful weapon of the Spanish conquerors?
Answer. The germs such as those of smallpox
Question. Why America's original inhabitants infected easily by the germs that came from Europe?
Answer. They were isolated from the rest of the world and had no immunity.
Question. How Europeans carried germs in America?
Answer. With infected person.
Answer: C
Question. What did indentured labour mean?
(a) Cheap Labour
(b) Free Labour
(c) Bonded Labour
(d) None of these
Answer: C
Question. What were ‘Canal Colonies’?
(a) Large Colonies
(b) Sea Ports
(c) Large Canals
(d) Irrigated areas
Answer: D
(b) Groundnuts
Answer: D
(b) Small pox
(d) None of these
Answer: A
(b) Mexico
(d) Spain
Answer: C
(b) Henry Ford
(d) Imam Husain
(d) Ram Naresh Sarwan
Answer: B
(b) 1928
(c) 1929
(d) 1930
Answer: C
(b) South America
Answer: B
(b) Cattle disease in China
Answer: A
(b) Flow of Capital
(d) Flow of Trade
Answer: C
More Questions and Answers for NCERT Class 10 The Making of a Global World
Question. Elucidate any three factors that let to the Great Depression.
Answer: (i) Agricultural overproduction remained a problem and it was made worse by falling agricultural prices.
(ii) As prices slumped and agricultural incomes declined, farmers tried to expand production and bring a large volume of produce to the market but it pushed down prices.
(iii) In the mid 1920s, many countries financed their investments through loans from the US, it was extremely easy to raise loans in the US when the going was good.
(iv) But in the first half of the 1920’s, countries that depended crucially on US loan faced an acute crisis.
(v) The withdrawal of the US loans affected the rest of the world in different ways. In Europe, it led to the failure of small major banks and the collapse of currencies, such as the British Pound Sterling.
Question. The multinational companies (MNCs) choose China as an alternative location for investment? Explain the statement.
Answer: (i) Since the revolution in 1949, China gradually came in the field of world economy. It attracted the foreign MNC’s because of its economic structure.
(ii) Wages were relatively low.
(iii) China has the largest population besides labour, that formed a larger consumer base.
Question. Explain why economy of USA was strong in the early 1920s? Would you agree that the roots of the Great Depression lay in the ‘boom’? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer: (i) Mass production became a characteristic feature of industrial production in the USA.
(ii) Mass production lowered costs and prices of engineered goods.
(iii) There was a spurt in the purchase of refrigerators, washing machines, etc., through hire purchase.
(iv) It was fuelled by a boom in house construction and home ownership, financed once again by loans. Yes, the roots of the Great Depression lies in this boom because of the overproduction in industrial and agricultural sector and liberal credit facility.
Question. Mention three reasons for the creation of International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
Answer: (i) The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank were created to meet the financial needs of the industrial countries.
(ii) When Japan and Europe rapidly rebuilt economies, they became less dependent on the IMF and the World Bank.
(iii) Thus, from the late 1950s the Bretton Woods institutions, WB and IMF, began to turn their attention towards newly developing countries.
(iv) The newly independent countries facing problems of poverty came under the guidance of international agencies dominated by the former colonial powers.
Question. Describe the social and economic effects of the World War on England and USA.
Answer: Social Effects : (i) Most of the killed and maimed people were of the working age and this affected the work force in England.
(ii) Household income declined and women stepped in to take up jobs usually done by men.
(iii) Role and position of women changed forever in England. Economic Effects :
(i) Economic links between some of the major economic powers of the world were snapped.
(ii) England borrowed large sums of money from the US Banks.
(iii) USA emerged as an international creditor. (iv) USA owned more assets in foreign countries than foreign countries owned in the USA.
Question. How did the use of technology transform food availability in Europe?
Answer: (i) Faster railway, lighter wagons and larger ships helped food to reach more cheaply and quickly from far away farms to markets.
(ii) Earlier the animals were shipped live from America to Europe, many died on the way or became unfit to eat. Thus meat became expensive.
(iii) Refrigerated ships : The animal could be slaughtered at the starting point of America, Australia or New Zealand and transported to Europe as frozen meat.
(iv) This reduced the shipping cost and lowered prices in Europe.
(v) The poor could add variety to their food and it improved their living condition.
Question. How did the Great Depression of 1929 affect the Indian trade? Explain
Answer: The Great Depression affected the Indian trade in many ways.
(i) India’s exports and imports were halved between 1928 and 1934.
(ii) As international prices crashed, prices in India also plunged.
(iii) Peasants and farmers suffered more than urban dwellers.
(iv) Peasants producing for the world market were the worst hit.
(v) Town-dwelling land owners and middle-class salaried employees found themselves better off as everything cost less for them.
Question. Which one of the following groups of the countries was known as the 'Central Powers' in Europe? (a) Germany, Russia and France (b) Russia, Germany and Britain (c) Germany, Austria-Hungary and ottoman- Turkey (d) Britain, Germany and Russia
Answer: (c) Germany, Austria-Hungary and Ottoman Turkey
Question. Explain the three impacts of the first World War on the British economy.
Answer: (i) After the war, Britain found it difficult to recapture its earlier position of dominance in the colonial market.
(ii) To finance war expenditures, Britain had borrowed from the U.S. At the end of the war Britain was burdened with huge external debts.
(iii) The war had led to a huge increase in demand, production and employment.
(iv) The government reduced bloated war expenditures to bring them at par with peace time revenues.
(v) These developments led to huge job losses. In 1921, one in every five British worker was out of work.
Question. Why did most of the developing countries organise themselves as a group - the Group of 77 (G-77)?
Answer: (i) The developing countries came under the guidance of IMF and World Bank which were dominated by the former colonial powers in order to uplift their economies.
(ii) Former colonial powers exploited the natural resources of developing nations through IMF and World Bank.
(iii) The developing nations organised themselves into G-77 so as to gain real control over their natural resources, to get more development assistance and fairer prices for raw materials.
(iv) They also wanted a better opportunity for their manufactured good in the markets of developing nations.
Question. Describe any three effects of the Great Depression of 1929 on the Indian economy.
Answer: (i) India’s exports and imports nearly halved.
(ii) As international prices crashed, prices in India also plunged.
(iii) Wheat prices in India fell by 50 percent. (iv) Peasants and farmers suffered more than urban dwellers.
(v) The colonial government refused to reduce revenue demands. (vi) India’s peasants’ indebtedness increased.
(vii) They used up their savings and sold jewellery and precious metals. The Great Depression helped the urban people, especially the fixed income earners.
Question. The relocation of industry to low-wage countries stimulated world trade and capital flows. Justify the statement.
Answer: (i) MNCs shifted their production units to Asian countries because of cheap labour and low wages.
(ii) Availability of raw materials and a large market.
(iii) Effects : It stimulated world trade and flow of capital. Countries like India, China and Brazil underwent rapid economic transformation. It generated employment opportunities and introduced competition in the domestic markets.
Question. What is Group 77? Why did Group 77 countries demand a New International Economic Order? Explain.
Answer: As colonies, many of the less developed regions of the world had been part of Western empires. As newly independent countries facing urgent pressures to lift their populations out of poverty, they came under the guidance of international agencies that was dominated by the former colonial powers. The former colonial powers still controlled vital resources such as minerals and land in many of their former colonies.
Even the large corporations of other powerful countries, for example the US, also often managed to secure rights to exploit developing countries’ natural resources very cheaply.
At the same time, most developing countries did not benefit from the fast growth the Western economies experienced in the 1950s and 1960s. Therefore, they organised themselves as a group – the Group of 77 (or G-77) – to demand a new international economic order (NIEO). By the NIEO they meant a system that would give them real control over their natural resources, more development assistance, fairer prices for raw materials. and better access for their manufactured goods in developed countries’ markets.
Question. China becomes an attraction destination for investment by foreign MNCs in the 19th and 20th century. Justify the statement.
Answer: (i) Since the revolution in 1949, China gradually came in the field of world economy. It attracted the foreign MNC’s because of its economic structure.
(ii) Wages were relatively low.
(iii) China has the largest population besides labour, that formed a larger consumer base.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Social Science
CBSE Class 10 Social Science India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World Assignment
Access the latest India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World assignments designed as per the current CBSE syllabus for Class 10. We have included all question types, including MCQs, short answer questions, and long-form problems relating to India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World. You can easily download these assignments in PDF format for free. Our expert teachers have carefully looked at previous year exam patterns and have made sure that these questions help you prepare properly for your upcoming school tests.
Benefits of solving Assignments for India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World
Practicing these Class 10 Social Science assignments has many advantages for you:
- Better Exam Scores: Regular practice will help you to understand India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World properly and you will be able to answer exam questions correctly.
- Latest Exam Pattern: All questions are aligned as per the latest CBSE sample papers and marking schemes.
- Huge Variety of Questions: These India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World sets include Case Studies, objective questions, and various descriptive problems with answers.
- Time Management: Solving these India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World test papers daily will improve your speed and accuracy.
How to solve Social Science India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World Assignments effectively?
- Read the Chapter First: Start with the NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science before attempting the assignment.
- Self-Assessment: Try solving the India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World questions by yourself and then check the solutions provided by us.
- Use Supporting Material: Refer to our Revision Notes and Class 10 worksheets if you get stuck on any topic.
- Track Mistakes: Maintain a notebook for tricky concepts and revise them using our online MCQ tests.
Best Practices for Class 10 Social Science Preparation
For the best results, solve one assignment for India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World on daily basis. Using a timer while practicing will further improve your problem-solving skills and prepare you for the actual CBSE exam.
You can download free PDF assignments for Class 10 Social Science Chapter India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets have been updated for the 2025-26 session covering all concepts from latest NCERT textbook.
Yes, our teachers have given solutions for all questions in the Class 10 Social Science Chapter India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World assignments. This will help you to understand step-by-step methodology to get full marks in school tests and exams.
Yes. These assignments are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus for 2026. We have included huge variety of question formats such as MCQs, Case-study based questions and important diagram-based problems found in Chapter India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World.
Practicing topicw wise assignments will help Class 10 students understand every sub-topic of Chapter India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World. Daily practice will improve speed, accuracy and answering competency-based questions.
Yes, all printable assignments for Class 10 Social Science Chapter India And Contemporary World II Chapter 3 The Making Of A Global World are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format.

