Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sectors of the Indian Economy Assignment Set B for the 2025-26 academic session. We have provided comprehensive Class 10 Economics school assignments that have important solved questions and answers for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy. These resources have been carefuly prepared by expert teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS syllabus guidelines.
Solved Assignment for Class 10 Economics Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy
Practicing these Class 10 Economics problems daily is must to improve your conceptual understanding and score better marks in school examinations. These printable assignments are a perfect assessment tool for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy, covering both basic and advanced level questions to help you get more marks in exams.
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy Class 10 Solved Questions and Answers
Sectors of Indian Economy
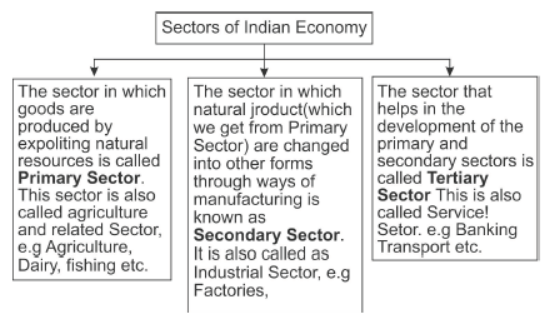
Gross Domestic Product(GDP): The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year and the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the GDP.
Problem of Double Counting: The problem of double counting arises when the production value of all the products is added to calculate in the National Income as raw material value is also added to it. Hence only the value of the final product should be calculated for the solution.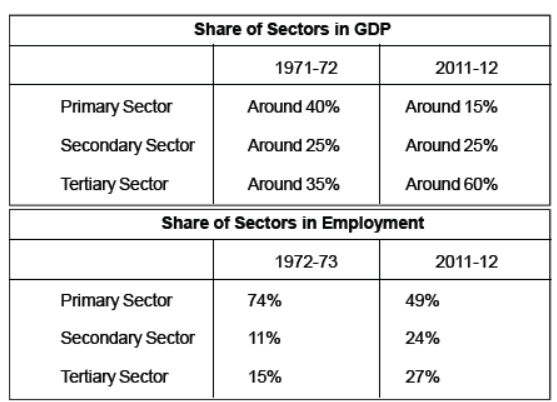
- It is clear from the above tables that, the secondary and tertiary sectors produce three-fourth of GDP whereas they employ around half the people.
- The contribution of primary sector over the years has decreased but still around half of workers are working in Primary Sector, mainly in agriculture. It means that there are more people in agriculture than is necessary. It is others words, workers in the agricultural sector are underemployed. This kind of underemployment is hidden. It is called Disguised Unemployment.
- We can see that around half of the workers work in the primary sector whereas its contribution is very low (around 15%). The contribution of Secondary and tertiary Sector is around 85% in the GDP but they employ only around half of the workers. There is considerable underemployment in agriculture. There are people who are not employed at all. Considering this situation, there is a need to create more employment.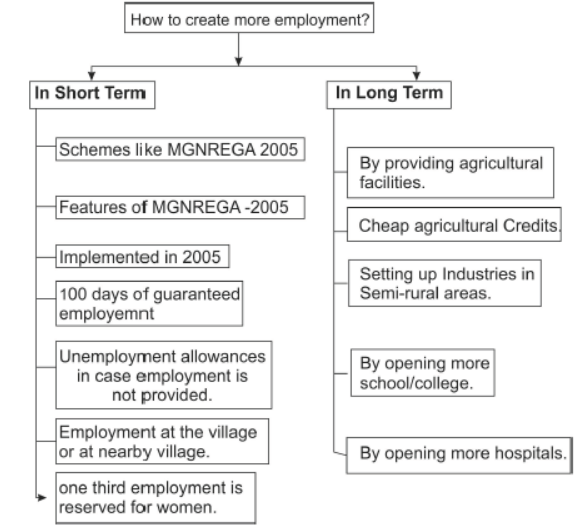
- There are other ways of classifying economics activities. It can be classified as Public Sector and Private Sector and Organized sector and Unorganized sector.

MCQs
Question. During the period between 1973 to2003, the production has increased most in the
(a) primary sector
(b) secondary sector
(c) tertiary sector
(d) all the three sectors
Answer : C
Question. GDP is the value of……….. produced during a particular year :
(a) All goods & services
(b) All final goods & services
(c) All intermediate goods &services
(d) All intermediate & final goods and services
Answer : B
Question. The sectors are classified in to public and private sectors on the basis of
(a) Employment conditions
(b) The nature of economic activity
(c) Ownership of enterprises
(d) Number of workers employed in the enterprises
Answer : C
Question. NREGA 2005 guarantees work for how many days in a year
(a) 100
(b) 120
(c)150
(d) 90
Answer : A
Question. Which one of the following is a public sector enterprise?
(a) TISCO
(b) RIL
(c) Indian Railway
(d) WIPRO
Answer : C
Question. Which was the largest producing sector in 1973?
(a) Primary sector
(b) Secondary sector
(c) Tertiary sector
(d) Public sector
Answer : A
Question. Fill in the blanks using the correct option given in the bracket:
(i) Employment in the service sector _________ increased to the same extent as production. (has / has not)
(ii) Workers in the _________ sector do not produce goods. (tertiary / agricultural)
(iii) Most of the workers in the _________ sector enjoy job security. (organised / unorganised)
(iv) A _________ proportion of labourers in India are working in the unorganised sector. (large / small)
(v) Cotton is a _________ product and cloth is a _________ product. (natural / manufactured)
(vi) The activities in primary, secondary and tertiary sectors are _________. (independent /interdependent)
Answer :
(i) has not
(ii) tertiary
(iii) organised
(iv) large
(v) natural
(vi) interdependent
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the differences between public and private sectors?
Answer : Public Sector :-
(i) The government owns most of the assets and provides all the services.
(ii) The purpose of the public sector is not just to earn profit, but also to raise the welfare of the economy.
(iii) Railways or post office is an example of the public sector.
Private Sector :-
(i) Ownership of assets and delivery of services is in the hands of private individuals or companies.
(ii) Activities in the private sector are guided by the motive to earn profit.
(iii) Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited or Reliance Industries Limited are privately owned.
Question. Though maximum share of GDP is coming from tertiary sector, but still the share of employment in the primary sector is maximum. Discuss.
Answer :
(a) This situation is because not enough jobs are created in the secondary and tertiary sectors.
(b) Though the industrial production of goods went up by eight times, but employment in the industry went up by only 2.5 times.
(c) Similarly in the tertiary sector, production rose by 11 times but employment rose less than three times. As a result, more than half of the population is dependent on the primary sector which contributes only a quarter of GDP.
Question. Why does only final goods and services are included while calculating National Income?
Answer : Only final goods and services are included while calculating National Income because:
(a) Final goods are those goods which have crossed the boundary line of production and are ready for final consumption and investment.
(b) The value of final goods already includes the value of all the intermediate goods that are used in making the final goods. This would lead to the problem of double counting if all the goods of the economy will be included while calculating national income.
(c) This should be avoided because if the value of any commodity is counted more than once it will result in overestimation of national income.
Question. What is the meaning of under employment? In which economic sector is under employment conditions more prevalent? & Why?
Answer : A condition in which each individual appears working but no one is fully employed. This is the situation of under employment. People under such type of employment cannot utilize their potential and capacity in full.
It is in primary sector because-
(i) This sector comprises the poorest section of society in majority.
(ii) People engaged in this sector are illiterate or semi-literate.
Question. Match the following:
| Problems faced by farming sector | Some possible measures |
| 1. Unirrigated land | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 2. Low prices for crops | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
| 3. Debt burden | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 4. No job in the off season | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
Answer :
| Problems faced by farming sector | Some possible measures |
| 1. Unirrigated land | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 2. Low prices for crops | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 3. Debt burden | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
| 4. No job in the off season | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
Question. A research scholar looked at the working people in the city of Surat and found the following.
| Place of work | Nature of employment | Percentage of working people |
| In offices and factories registered with the government | Organised | 15 |
| Own shops, office, clinics in marketplaces with formal license | – | 15 |
| People working on the street, construction workers, domestic workers | – | 20 |
| Working in small workshops usually not registered with the government | – | – |
Complete the table. What is the percentage of workers in the unorganised sector in this city?
Answer :
| Place of work | Nature of employment | Percentage of working people |
| In offices and factories registered with the government | Organised | 15 |
| Own shops, office, clinics in marketplaces with formal license | Organised | 15 |
| People working on the street, construction workers, domestic workers | Unorganised | 20 |
| Working in small workshops usually not registered with the government | Unorganised | 50 |
The percentage of workers in the unorganised sector in this city is 70%.
Question. For each of the sectors that we came across in this chapter why should one focus on employment and GDP? Could there be other issues which should be examined? Discuss.
Answer : For each of the sectors that we came across in this chapter, one should focus on employment and GDP because these determine the size of a country’s economy. A focus on employment and GDP helps determine two important things- per capita income and productivity. Hence, in each of the three sectors, employment rate and status as well as its contribution to the GDP help us understand how that particular sector is functioning and what needs to be done to initiate further growth in it.
Yes, the other issues which should be examined are –
- Balanced regional development
- Equality in income and wealth among the people of the country.
- How to eradicate poverty
- Modernization of technology
- Self-reliance of the country
- How to achieve surplus food production in the country.
Question. How is the tertiary sector different from other sectors? Illustrate with a few examples.
Answer : The tertiary sector different from other two sectors. This is because other two sectors produce goods but, this sector does not produce goods by itself. But the activities under this sector help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities are an aid or support for the production process. For example, transport, communication, storage, banking, insurance, trade activities etc. For this reason this sector is also known as service sector.
Question. Distinguish between open unemployment and disguised unemployment.
Answer :
| Open Unemployment | Disguised unemployment |
| When a country’s labour force do not get opportunities for adequate employment, this situation is called open unemployment. | This is a kind of unemployment in which there are people who are visibly employed but actually they don’t have full employment. In such a situation more people are engaged in a work than required. |
| This type of unemployment is generally found in the industrial sector of our country. This is also found among the landless agricultural labourers in rural areas. | This type of unemployment is generally found in unorganized sector where either work is not constantly available or too many people are employed for the same work that does not require so many hands. |
Question. Service sector in India employs two different kinds of people. Who are these?
Answer : The service sector in India employs the following two different kinds of people. They are:
- The people involved in the services that may directly help in the production of goods. For example, people involved in the transportation, storage, communication, finance etc.
- The people involved in such services that may not directly help in the production of goods e.g. teachers, doctors, barbers, cobblers lawyers etc. They may be termed as ancillary workers means those who give services to the primary service providers.
Question. How are the activities in the economy classified on the basis of employment conditions?
Answer : On the basis of employment conditions, the activities in the economy are classified into organized and unorganized sectors.
- Organized Sector This sector covers those enterprises which are registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations. For example, Reliance Industries Ltd., GAIL etc.
- Unorganized Sector It includes those small and scattered units which are largely outside the control of the government. Though there are rules and regulations but these are never followed here. For example, casual workers in construction, shops etc. In this sector there is no job security and the conditions of employment are also very tough.
Question. Explain the objective of implementing the NREGA 2005.
Answer : The objective of implementing the NREGA 2005 are:
- To increase the income and employment of people.
- Every state/region can develop tourism, regional craft, IT etc. for additional employment.
- The central government made a law implementing the right to work in 200 districts.
- NREGA aims to provide employment of 100 days. If it fails to do so, it will give unemployment allowances to the people.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
More free study material for Social Science
CBSE Class 10 Economics Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy Assignment
Access the latest Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy assignments designed as per the current CBSE syllabus for Class 10. We have included all question types, including MCQs, short answer questions, and long-form problems relating to Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy. You can easily download these assignments in PDF format for free. Our expert teachers have carefully looked at previous year exam patterns and have made sure that these questions help you prepare properly for your upcoming school tests.
Benefits of solving Assignments for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy
Practicing these Class 10 Economics assignments has many advantages for you:
- Better Exam Scores: Regular practice will help you to understand Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy properly and you will be able to answer exam questions correctly.
- Latest Exam Pattern: All questions are aligned as per the latest CBSE sample papers and marking schemes.
- Huge Variety of Questions: These Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy sets include Case Studies, objective questions, and various descriptive problems with answers.
- Time Management: Solving these Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy test papers daily will improve your speed and accuracy.
How to solve Economics Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy Assignments effectively?
- Read the Chapter First: Start with the NCERT book for Class 10 Economics before attempting the assignment.
- Self-Assessment: Try solving the Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy questions by yourself and then check the solutions provided by us.
- Use Supporting Material: Refer to our Revision Notes and Class 10 worksheets if you get stuck on any topic.
- Track Mistakes: Maintain a notebook for tricky concepts and revise them using our online MCQ tests.
Best Practices for Class 10 Economics Preparation
For the best results, solve one assignment for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy on daily basis. Using a timer while practicing will further improve your problem-solving skills and prepare you for the actual CBSE exam.
You can download free PDF assignments for Class 10 Economics Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets have been updated for the 2025-26 session covering all concepts from latest NCERT textbook.
Yes, our teachers have given solutions for all questions in the Class 10 Economics Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy assignments. This will help you to understand step-by-step methodology to get full marks in school tests and exams.
Yes. These assignments are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus for 2026. We have included huge variety of question formats such as MCQs, Case-study based questions and important diagram-based problems found in Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy.
Practicing topicw wise assignments will help Class 10 students understand every sub-topic of Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy. Daily practice will improve speed, accuracy and answering competency-based questions.
Yes, all printable assignments for Class 10 Economics Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format.

