Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion and Caste Assignment Set A for the 2025-26 academic session. We have provided comprehensive Class 10 Civics school assignments that have important solved questions and answers for Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste. These resources have been carefuly prepared by expert teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS syllabus guidelines.
Solved Assignment for Class 10 Civics Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste
Practicing these Class 10 Civics problems daily is must to improve your conceptual understanding and score better marks in school examinations. These printable assignments are a perfect assessment tool for Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste, covering both basic and advanced level questions to help you get more marks in exams.
Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste Class 10 Solved Questions and Answers
Gender, Religions and Caste
Scheduled Caste: Poor and landless and also socially and economically backward Indians.
Caste Hierarchy: A social structure in which classes are determinds by heredity i.e. the highest to the lowest caste.
Communalism: A belief in which the followers of a particular religion believe that their religion is superior over other religion.
Gender
- Sexual divison of labour — all works inside the home done by women.
- Patriarchal Society — all the power hold by men.
- Less representation in legislatiure (India) — approximately 11% in Lok Sabha in 2014.
- 1/3 reservation in local government.
- Ferminists and other people and many organisations are demanding for reservation of woman in legislative.
Ferminist : A woman or a man who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women and man.
Patriarchy : A system of society in which men hold the power and women are largely excluded from it.
Universal Adult Franchise : After attaining a certain age, all the people are given right to vote without discrimination of caste, class, colour, religions or gender.
Influence of Politics, Gender Caste and Religion on Each Other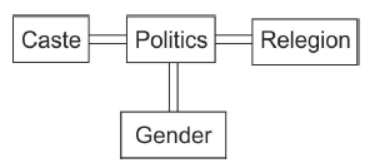
Choose the Appropriate :
Question. When we speak fo gender divison, we usually refer to :
(a) Biological difference between the men and women.
(b) Unequal role assigned by society men and women.
(c) Unequal child sex ratio.
(d) Absence of voting rights for woman in democracy.
Answer. B
Question. In India seats are reserved for women in
(a) Lok Sabha
(b) State Legislative assemblies
(c) Cabinets
(d) Panchayati Raj bodies
Answer. D
Question. Which among the following statements about Indian constitution in wrong ? It ......
(a) Prohibits discrimination on ground of religions
(b) Given official status to one religion.
(c) provides to all individuals freedom to profess any religons
(d) ensures equality of citizens within religious communities.
Answer. B
Question. Social divisons based on ___ are peculiar in India.
(a) disconfort
(b) Religon
(c) Caste
(d) Gender
Answer. C
MCQs
Question. Which one of the following social reformers fought against caste inequalities.
(a) Periyar Ramaswami Naiker
(b) Swami Dayanand Saraswati
(c) Raja Ram Mohan Roy
(d) Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following was the view of Mahatma Gandhi about religion ?
(a) He was in favour of Hinduism.
(b) He was an ardent supporter of Muslim Religion.
(c) By religion, Gandhi meant for moral values that inform all religions.
(d) He said that India should adopt Christianity.
Answer. C
Question. Name any two political leaders who fought against caste inequalities.
(a) Dr. Manmohan Singh and Smt. Pratibha Devi Singh Patil.
(b) Mr. Nitesh Kumar and Mr. Narendra Modi.
(c) Dr.S. Radhakrishnan and Shri Morarji Desai
(d) Mahatma Gandhi and B.R. Ambedkar
Answer. D
Question. What is the average child sex ratio in India ?
(a) 923
(b) 926
(c) 935
(d) 933
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following refers to gender division ?
(a) The hierarchical unequal roles assigned to man and woman by the society.
(b) Biological difference between man and woman.
(c) The ratio of male child and female child.
(d) The division between male labourers and female labourers.
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following is the basis of communal politics?
(a) People of different religions may have the same interests.
(b) People of different religions have different interests that involve conflicts.
(c) People of different religions live in mutual co-operation.
(d) People who follow different religions belong to the same social community.
Answer. B
Question. Name any two countries where women’s participation in public life is very high.
(a) Sri Lanka and Nepal
(b) Pakistan and Bhutan
(c) Sweden and Finland
(d) South Africa and Maldives
Answer. C
Question. What is the literacy rate among women and men respectively in India?
(a) 54% and 76%
(b) 46% and 51%
(c) 76% and 85%
(d) 37% and 54%
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following is a form of communalism?
(a) Communal Unity and integrity.
(b) Communal fraternity.
(c) Communal violence, riots and massacre.
(d) Communal harmony.
Answer. C
Question. Which one of the following refers to a feminist?
(a) The female labourers
(b) The employer who employs female workers
(c) A woman who does not believe in equal rights for women.
(d) A woman or a man who believes in equal rights and opportunities for woman and man.
Answer. D
Question. Match List I with List Ii and select the correct answer the coes given below the list
List I List II
1. A person who believes in equal A. Communal
rights and opportunities for
women and men
2. A person who says that religion B. Feminist
is the principal basis of community
3. A person who thinks that caste C. Secular
is the principle basis of community
4. A person who does not discriminate D. Castiest
others on the basis of religious believes
1 2 3 4
(a) B C A D
(b) B A D C
(c) D C A B
(d) C A B D
Answer. B
Short Answer Questions
Question. What is Patriarchy ?
Answer. Literally, rule by father or a system that values men more and given them power over women as in Indian society which is still a male dominated, patriarchal society.
Question. What is Urbanisation ?
Answer. In India, hereditary occupetional divison was sanctioned by rituals and,therefore, caste system was based on exclusion of and discrimination against the ''outcaste'' groups.
Question. What was the basis of caste system in India ?
Answer. It implies the shifting of population from rural areas to urban areas in search of jobs and better standard of life in urban areas.
Question. Name the two well known social reformers, who worked for the casteless society in India.
Answer. Gandhi Ji, Jyotiba Phule Ji, B. R. Ambedkar Ji.
Question. How the caste of a person determined in India ?
Answer. By the caste of the family in which he is born.
Question. What is occupational mobility?
Answer. It relates to shift from one occupation to another, usually when a new generation takes up occupations other than those practised by ancestors.
Question. Why are ''Scheduled Castes' and 'Scheduled Tribes' called scheduled or prefix schedule ?
Answer. It is because their castes and tribes have been listed in a official schedule.
Question. What is Gender division ?
Answer. Gender divison : It is a form of hierarchial social division of labour.
Question. How did Gandhi Ji defined religion ?
Answer. For Gandhi Ji, religion was not any particular religion like Hinduism or Islam but moral values that inform all religions.
Question. State the main provision of the ''Equal Weges Act''.
Answer. Equal wages should be paid to equal work to both men and women.
Question. What is a Feminist movement ?
Answer. The radical movements demanding equality in political life, educational and other oppotunities for women are called feminist movements.
Question. Explain the factors responsible for low female literacy rate.
Answer. (1)Indian society is basically a patriarchal society where boys are given preference over the girls.
(2)The parents do not expense equally for both boys and girls. Boys are given more attention.
(3)It is a prevailing stereotype for women that even after getting well education, they have to do household jobs.
Question. What do you mean by secular state ? Give any two provisions that make India a secular state ?
Answer. A nation or state which keeps itself equidistant from different religious issues, and does not give protection to a particular religion.
(1) India is a country of diverse religions. It was the religions on the basis of which India was divided. Unlike Pakistan Buddhism in Sri Lanka. Christianity in England.
(2) The constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess practice and propagate any religion.
Question. In which country was the “Civil Rights Movement” Started? Name any leaders related to this movement? Why did he start this movement?
Answer. America, Martin Luther King.
The purpose of this movement was to give end to the racial discrimination being practiced against the Afro-AmericAnswer.
Question. What do you mean by gender division? How is it linked with division of Labour in most of the societies?
Answer. Gender division simply refers to the division of work between the men and the women. Some work especially the households such as cooking, washing, cleaning, etc. are exclusively meant for the women while the man have some other defined areas of work.
(1) The gender division between the men and women does not mean that men cannot do household works. They simply think that it is for women to attend the household works.(2) The gender division also doesn’t mean that women do not work outside their home.
Question. Give three ill-effects of communalism in the society.
Answer. (1) A communal thought always tends to establish political dominance offer particular religious community.
(2) The country weakens when political parties are formed and political activities are conducted on the communal lines.
(3) One of the most ugly face of communalism emerges out in the form of riots, violence and homicides.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Describe main features of secular state in India.
Answer. (a) No official religons in India.
(b) Freedom of religion in India means the freedom of religion to both individuals and coomunities.
(c) The constitution prohibits discrimination on the grounds of religions.
Question. Write a short note on communalism.
Answer. Prepare on the basis of notes.
Question. Describe the role of caste politics in India.
Answer. (a) The caste politics in India has helped SKs, STs and OBC's to gain better access to decision making.
Question. Caste can take various form in politics. Describe any five forms.
Answer. The caste can take following forms in politics :
(a) Sometimes candidates are chosen on the basis of their caste
(b) In many places, voters on the basis of caste and fail to choose suitable condidates.
(c) Political parties appeal to caste sentiments during election.
(d) To gain support poltical parties, raise caste based issues during elections.
(e) The castes considered inferior or low until now have been made conscious of their rights by the political parties.
Question. How can religion influence politics ?
Answer. Prepare on the basis of notes.
Question. Give the reason which have contributed to changes in caste and caste system in India.
Answer. Reasons :
(a) Efforts of political leaders and social reformers like Gandhi ji and Ambedker Ji who advocated and worked to establish a society in which caste inequalties are absent.
(b) Socio economic reasons like urbanisation, growth of literaxy and education, Occupational mobility, weakening of land lord's position in the village have led to the breaking down of caste hierarchy.
(c) The constitution of India prohibits any caste based discrimination that lays down the foundation of politics to end the injustices of the caste system.
Question. What steps have been taken by the government of India to improve the conditions of women in society ?
Answer. Following schemes and steps have been taken up by the govt. of
India for women empowerment.
(a) Act prohibiting the practice of sati.
(b) The hindu widow remarriage Act
(c) The married women's property Act
(d) Indira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog Yojna.
(e) Kishori Shakti Yojna
(f) The Dowry Prohibition Act.
(g) The Protection of woman from Domestic Violence Act 2005
(h) The Pre-Natal Diognostic Techniques Act.
(i) The equal Remuneretion Act.
Question. Religion can never be separated from politics. Explain the statement
Answer. Prepare from Notes
Question. What is the proportion of women in Indian legislative ? What can be done to improve the representation of women in legislative ?
Answer. (a) In Lok Sabha women are approx 11.23%
(b) In state assemblies women are approx. 5%
(c) In panchayat 1/3 seats are reservered for women.
Question. Explain the reasons behind change in caste and caste system in modern India.
Answer. Caste and caste system in modern India have undergone great changes became of .....
— Economic development
— Large scale urbanisation
— Growth of Literacy and education
— Occupational Mobility.
— Weakning of the position of landlords in the village.
Question. Which factors are responsible for miserable and poor conditions of women in India? Explain.
Answer. (1) Sexual division of Labour. (2) Illiteracy
(3) Lack of Representation in politics. (4) Discrimination in Job.
Question. Write two positive and two negative impacts each of caste-politics relation in India.
Answer. (1) Positive Impacts
(i) Caste Politics relationship has helped people from Dalits and OBCs to gain better access to decision making.
(ii) Now people are making voice for the end of discrimination against particular castes for more dignity and more access to land, other resources and opportunities.
(2) Negative Impacts
(i) It can divert attention from other pressing issues like poverty, development and corruption. Sometimes a few underprivileged castes get more benefit while other underprivileged classes remain deprived.
(ii) Sometimes it also disrupts social harmony.
Question. What is feminist movement? What are the results of political expressions of gender divisions?
Answer. The feminist movement refers to the agitation demanding enhancing the political and legal status of movement.
(1) The gender issues or equality of men and women, as a result of feminist movement was raised in politics.
(2) The political expressions and political mobilization helped improve women’s role in public life.
(3) As a result of the expression of gender division in politics many legislations were passed by which women were empowered in the social, economic and political feels.
Question. Discuss any four facilities are given by the government to the backward classes.
Answer. (1) The people from the backward classes have been given reservation in the government jobs as per the their proportion in the population.
(2) To give them fair representation in the Vidhan Sabha and the Lok Sabha.
(3) To help them move forward in the field of higher education. The seats have been reserved for them.
(4) The constitution also prohibits any type of caste discrimination.
Question. Discuss any four steps taken by the government towards women empowerment and gender inequality.
Answer. (1) Women have less than 10% representation in the Indian legislature. In the State legislature their representation is even less than 5%.
(2) The provision of equal wages for women without any discrimination has been made under the Equal Wages Act.
(3) There is a tendency of female infanticide in many parts of the country.
Domestic violence against women, their exploitation etc. always have been the part of daily news. In this regards, the government has brought Domestic Violence Act which proves and effective steps.
Source Based Questions
Source-I
Boys and girls are brought up to believe that the main responsibility of women is housework and bringing up children. This is reflected in a SEXUAL DIVISION OF LABOUR in most families : women do all work inside the home such as cooking, cleaning, washing clothes, tailoring, looknig after children, etc., and men do all the work outside the home. It is not that men cannot do housework; they simply think that it is for women to attend to these things. When these jobs are paid for, men are ready to take up these works. Most tailors or cooks in hotels are men. Similarly, it is not that women do not work outside their home. In villages, women fetch water, collect fuel and work in the fields. In urban areas, poor women work as domestic helper in middle class homes, while middle class women work in offices. In fact the majority of women do some sort of paid work in addition to domestic labour. But their work is not valued and does not get recognition.
Questions
Question. Define Sexual Division of Labour.
Answer. Sexual divison of labour is a system in which all work inside the home is eitehr done by the women of the family, or organised by them through
domestic helpers.
Question. Give one instance of sexual labour.
Answer. Give answer on the basis of your reading.
Question. Name the work, which men wishfully do when they are paid for it.
Answer. Job of Tailor, Cooks in hotel etc.
Source II
Communal politics is based on the idea the religion is the principal basis of social community. Communalism involves thinking along the following lines. The followers of a particular religion must belong to one community. Their fundamental interests are the same. Any difference that they may have is irrelevant or trivial for community life. It also follows that people who follow different religions cannot belong to the same social community. If the followers of different religions have some commonalities these are superficial and immaterial. Their intrests are bound to be different and involve a conflict. In its extreme form communalism leads to the belief that people belonging to different religions cannot live as equal citizens within one nation. Either, one of them has to dominate the rest or they have to form different nations.
Questions
Question. Define Communal politics.
Answer. Communal Polities : The use of religon in politics where one religion in shown as superior to other religions in called communal politics.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science History The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Hindi Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer Rights Hindi Assignment |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Social Science
CBSE Class 10 Civics Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste Assignment
Access the latest Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste assignments designed as per the current CBSE syllabus for Class 10. We have included all question types, including MCQs, short answer questions, and long-form problems relating to Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste. You can easily download these assignments in PDF format for free. Our expert teachers have carefully looked at previous year exam patterns and have made sure that these questions help you prepare properly for your upcoming school tests.
Benefits of solving Assignments for Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste
Practicing these Class 10 Civics assignments has many advantages for you:
- Better Exam Scores: Regular practice will help you to understand Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste properly and you will be able to answer exam questions correctly.
- Latest Exam Pattern: All questions are aligned as per the latest CBSE sample papers and marking schemes.
- Huge Variety of Questions: These Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste sets include Case Studies, objective questions, and various descriptive problems with answers.
- Time Management: Solving these Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste test papers daily will improve your speed and accuracy.
How to solve Civics Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste Assignments effectively?
- Read the Chapter First: Start with the NCERT book for Class 10 Civics before attempting the assignment.
- Self-Assessment: Try solving the Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste questions by yourself and then check the solutions provided by us.
- Use Supporting Material: Refer to our Revision Notes and Class 10 worksheets if you get stuck on any topic.
- Track Mistakes: Maintain a notebook for tricky concepts and revise them using our online MCQ tests.
Best Practices for Class 10 Civics Preparation
For the best results, solve one assignment for Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste on daily basis. Using a timer while practicing will further improve your problem-solving skills and prepare you for the actual CBSE exam.
You can download free PDF assignments for Class 10 Civics Chapter Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets have been updated for the 2025-26 session covering all concepts from latest NCERT textbook.
Yes, our teachers have given solutions for all questions in the Class 10 Civics Chapter Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste assignments. This will help you to understand step-by-step methodology to get full marks in school tests and exams.
Yes. These assignments are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus for 2026. We have included huge variety of question formats such as MCQs, Case-study based questions and important diagram-based problems found in Chapter Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste.
Practicing topicw wise assignments will help Class 10 students understand every sub-topic of Chapter Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste. Daily practice will improve speed, accuracy and answering competency-based questions.
Yes, all printable assignments for Class 10 Civics Chapter Democratic Politics II Chapter 3 Gender Religion And Caste are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format.

