Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Geography Minerals And Energy Resources Worksheet Set F in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 10 Social Science worksheets for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
Students of Class 10 should use this Social Science practice paper to check their understanding of Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources Worksheet with Answers
Objective Type Questions
Question: Which of the following states is the leading producer of Manganese?
a) Maharashtra
b) Odisha
c) Tamil Nadu
d) Mizoram
Answer: b
Question: The iron ore from Kudremukh mines is exported through this port.
a) Vishakhapatnam
b) Mangalore
c) Mormugao
d) Paradip
Answer: b
Question: Mining depends upon –
a) Concentration of mineral only
b) Ease of extraction
c) Nearness to the market
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following minerals is a fossil fuel?
a) Barium
b) Coal
c) Zircon
d) Uranium
Answer: b
Question: Minerals are deposited and accumulated in the strata of which of the following rocks?
a) Sedimentary rocks
b) Igneous rocks
c) Metamorphic rocks
d) None of the above
Answer: a
Question: Koderma, in Jharkhand is the leading producer of which one of the following minerals?
a) Bauxite
b) Mica
c) Iron ore
d) Copper
Answer: b
Question: Which one of the following mineral is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered material?
a) Coal
b) Bauxite
c) Gold
d) Zinc
Answer: b
Question: Which one of the following states is the largest producer of copper in India?
a) Jharkhand
b) Rajasthan
c) Madhya Pradesh
d) Odisha
Answer: c
Question: Which of the following is an offshore oil field?
a) Ankaleshwar
b) Digboi
c) Kalol
d) Mumbai High
Answer: d
Question: Consider the following statement about Bauxite.
I. From bauxite, a clay like substance alumina is extracted.
II. Jharkhand is largest bauxite producer of India.
III. Ballari-Chitradurga belt is famous for bauxite reserves in India.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
(a) Only I
(b) II and III
(c) I and III
(d) All of these
Answer: a
Question: Arrange the following manganese producing states from highest to lowest production.
I. Odisha
II. Madhya Pradesh
III. Karnataka
IV. Andhra Pradesh
Codes
(a) II, I, III, IV
(b) I, II, III, IV
(c) III, II, I, IV
(d) II, III, IV, I
Answer: a
Case Based Question
Read the case/source given and answer the following questions.
Source A Biogas Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to produce biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas. Decomposition of organic matter yields gas, which has higher thermal efficiency in comparison to kerosene, dung cake and charcoal.
Question: To what extent do you think biogas is better than dung cake for fuel?
Answer: Biogas is much better than dung cakes as it produces no smoke and has more thermal efficiency. Source B Solar Energy India is a tropical country. It has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar energy is fast becoming popular in rural and remote areas.
Question: Why solar energy has more potential to be developed as major fuel in rural areas?
Answer: There is more potential of developing solar energy in rural areas as there are relatively more open spaces. This will reduce the dependence on firewood and dung cakes fuel.
Source C Wind Energy India has great potential of wind power. The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamil Nadu from Nagarcoil to Madurai. Apart from these, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep have important wind farms.
Question: What similarity or trait can be seen in the places idealy suited for setting up wind farm?
Answer: The similarities identified are that the areas should be close to sea where there is lot of potential for blowing of wind or other windy areas.
Read the case/source given and answer the following questions.
Decaying plants in swamps produce peat which has a low carbon and high moisture content and low heating capacity. Lighite is low grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content. The principal lignite reserves are in Neyveli in Tamil Nadu and are used for generation of electricity. Coal that has been buried deep and subjected to increased temperatures is bituminous coal. It is the most popular coal in commercial use. Metallurgical coal is high grade bituminous coal which has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces. Anthracite is the highest quality hard coal. In India coal occurs in rock series of two main geological ages, namely Gondwana, a little over 200 million years in age and in tertiary deposits which are only about 55 million years old. The major resources of Gondwana coal, which are metallurgical coal, are located in Damodar valley (West Bengal, Jharkhand). Jharia, Raniganj, Bokaro are important coalfields. The Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valleys also contain coal deposits. Tertiary coals occur in the North-Eastern states of Meghalya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Question: Which reserves are important for lignite in India?
Answer: Neyveli reserves in Tamil Nadu are important lignite reserves in India.
Question: In what extent do you agree that bituminous coal is metallurgical coal? State its one property.
Answer: Bituminous coal is a high grade coal and thus, is a metallurgical coal. This type of coal has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces. Important Property of Bituminous Coal. Bituminous coal is buried deep under the earth’s surface and is subjected to increased temperature. It makes it unique to use in smelting iron-ore in blast furnaces.
Question: Why is coal associated with geological ages? State where it is found?
Answer: Coal is associated with geological ages because coal is formed due to compression of plant material and takes million of years to come into existence. In India, coal occurs in rock series of two main geological ages, namely Gondwana rock series which is a little over 200 million years in age and in tertiary deposits rock series which are only about 55 million years old. Distribution of Coal Gondwana coal deposits are found in Damodar valley (West Bengal, Jharkhand), Jharia, Raniganj, Bokaro, coalfields. The Godavari,Mahanadi, Son andWardha valleys also contain coal deposits. Tertiary coal deposits are found in the North-Eastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Read the case/source given and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct options.
Energy is required for all activities. It is needed to cook, to provide light and heat, to propel vehicles and to drive machinery in industries. Energy can be generated from fuel minerals like coal, petroleum, natural gas, uranium and from electricity. Energy resources can be classified as conventional and non-conventional sources. Conventional sources include: firewood, cattle dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity (both hydel and thermal). Non-conventional sources include solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy. Firewood and cattle dung cake are most common in rural India. According to one estimate more than 70 per cent energy requirement in rural households is met by these two; continuation of these is increasingly becoming difficult due to decreasing forest area. Moreover, using dung cake too is being discouraged because it consumes most valuable manure which could be used in agriculture.
Question: Which of the following statement is true about conventional energy resources?
(a) They cause minimum pollution.
(b) They are available in limited quantity.
(c) Cattle dung is the most used energy in the world.
(d) There are sufficient reserves of conventional energy sources.
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following resources does not generate energy?
(a) Coal
(b) Fuel
(c) Natural gas
(d) None of the above
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following energy is non-conventional source of energy?
(a) Firewood
(b) Tidal energy
(c) Natural gas
(d) Petroleum
Answer: b
Question: Firewood and cattle dung cake are most common energy in rural India because
(a) they are easily available
(b) they are non-conventional
(c) they produces high energy
(d) None of the above
Answer: a
Question: How India can reduce its dependence over countries for energy?
(a) Promoting non-conventional source of energy
(b) Promoting efficient use of resources
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer: c
Question: Assertion (A) About 70 per cent energy required in countryside households are met by firewood and cattle dung cake.
Reason (R) Cattle dung cake is valuable for use as manure in agriculture.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer: b
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Why do you think that solar energy has a bright future in India?
Answer: Solar energy has a bright future in India due to the following reasons
(i) Solar energy is an inexhaustible source of energy that is produced from sunlight. India is a tropical country thus, there is enough scope for the development of solar energy.
(ii) Many parts (regions) of the country receive sunlight at least 300 days annually and so, it becomes possible to generate 20 MW solar energy per square kilometer in such areas.
(iii) It is easy to establish solar plants in urban and rural areas.
(iv) By setting up solar plants in rural areas, the dependence of people on fire wood can be reduced.
(v) Solar energy is also becoming popular as it is used for cooking, heating water, lighting, etc.
Question: Describe any three non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer: Non-conventional sources of energy are :
(i) Solar Energy: India is a tropical country. It has enormous possibilities for trapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar energy is becoming popular in rural and remote areas.
(ii) Wind Energy: India now ranks as a ‘wind super power’ in the world. The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamil Nadu from Nagercoil to Madurai. Apart from these, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep have important wind farms. Nagercoil and Jaisalmer are well- known for effective use of wind energy in the country.
(iii) Biogas: Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to produce biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas. Biogas plants using cattle dung are known as ‘Gobar Gas Plants’ in rural India. These provide twin benefits to the farmer in the form of energy and improved quality of manure.
Question: What efforts are required to use mineral resources in a planned and sustainable manner? Explain in three points.
Answer: Following efforts have to be made to use mineral resources in a planned and sustainable manner :
(i) Recycling of metals: We should recycle the metal or metal-made products to prevent its scarcity.
For example: Used steel blade should be sent for recycling, so that the steel can be used again for other purposes.
(ii) Improved technologies need to be evolved: Traditional technologies should be replaced with new and improved technologies, so that the wastages can be minimised.
(iii) Use of substitute or alternative resources : The resources which cannot be recycled or reused should be replaced with the recyclable resources, e.g., use of green gas instead of coal for cooking purpose.
Question: Why is it essential to use renewable sources of energy?
Answer: (i) Non-renewable sources are going to exhaust such as coal, petroleum, natural gas, etc. They can cause environmental pollution; therefore, we have to use renewable resources.
(ii) India has abundance of solar energy, wind, water, and biomass.
(iii) Rising prices of oil and gas and their shortage have raised uncertainties about energy resources in the future.
Question: Which state is the largest producer of manganese in India? Mention any two uses of manganese.
Answer: Odisha is the largest producer of manganese in India.
Two uses of manganese are:
(i) Manganese compounds are used in dry-cell batteries, matches, fireworks, etc.
(ii) Manganese is used as an alloying agent for aluminium.
Question: Describe any three characteristics of Bellary-Chitradurga- Chikmaglur-Tumkur iron ore belt in India.
Answer: (i) Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt in Karnataka has large reserves of iron ore.
(ii) The Kudermukh mines located in the Western Ghats of Karnataka are a 100 per cent export unit.
(iii) Kudremukh deposits are known to be one of the largest in the world.
(iv) The ore is transported as slurry through a pipeline to a port near Mangalore.
Question: Why is energy required for all activities? How can energy be generated?
Answer: (a) (i) Energy is a basic requirement for economic development.
(ii) Every sector of the national economy needs the input of energy.
(iii) Consumption of energy in all forms has been steadily rising all over the country.
(iv) Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortage have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in the future.
(b) Energy can be generated from fuel minerals like coal, petroleum, natural gas, uranium and from electricity.
Question: Describe any three characteristics of the Durg-Bastar- Chandrapur Iron-ore belt in India.
Answer: (i) Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt: It lies in Chhattisgarh and
Maharashtra and comprises of high grade hematite iron ore.
(ii) Very high grade hematites are found in the famous Bailadila range of hills in the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh.
(iii) The range of hills comprises of 14 deposits of super high grade hematite iron ore.
(iv) Iron ore from these mines is exported to Japan and South Korea via Vishakhapatnam port.
Question: Why is conservation of minerals important? How can we conserve minerals?
Answer: Conservation of minerals is important for the following reasons :
(i) Minerals are exhaustible.
(ii) They are limited.
We can conserve minerals by:
(i) Using minerals properly.
(ii) Improvement in technology so that low grade order can be used profitably.
(iii) By recising and recycling methods.
Question: Describe any three characteristics of Odisha-Jharkhand belt of iron ore in India.
Answer: Odisha-Jharkhand belt :
(i) In Odisha, high grade hematite ore is found.
(i) It is found in Badampahar mines in the Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar districts.
(iii) In the adjoining Singbhum district of Jharkhand, hematite iron ore is mined in Gua and Noamundi.
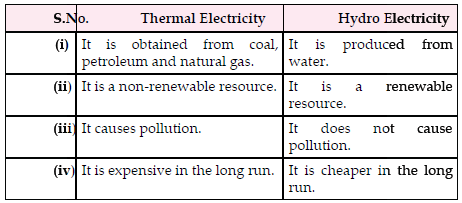
Question: What are the two main ways of generating electricity? How are they different from each other ?
Answer:
Question: Name the non-metallic mineral which can split easily into thin sheets. Mention its uses.
Answer: Mica is the non-metallic mineral which can be split easily into thin sheets.
Its uses:
(i) electric and electronic: Mica is used in industries due to its excellent dielectric strength, low power loss factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage.
(ii) Plastic industry uses mica as an extender and filler.
Question: “Natural gas is an important source of energy.” Support the statement.
Answer: Natural gas :
In a power-deficient country, natural gas is a precious gift.
(i) It can be used as a source of energy. It takes less time to build a power plant based on natural gas.
(ii) It can be used as an industrial raw material in petrochemical industry.
(iii) It can be used in building the fertiliser plants and thereby encouraging the use of fertilizers. It can boost agricultural production.
(iv) Through easy transportation by way of pipelines, its utility is further increased.
(v) Use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles to replace liquid fuels is gaining wide popularity in the country.
Question: What are ‘placer deposits’? Give examples of minerals found in such deposits.
Answer: (i) Certain minerals may occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors and base of hills. These deposits are called ‘placer deposits’.
(ii) They generally contain minerals which are not corroded by water.
(iii) Gold, silver, tin and platinum are examples of some important minerals found in ‘placer deposits’.
Question: There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development. Give two broad measures for it. As concerned citizens, how can you help to conserve energy?
Answer: Twin planks/measures :
(i) Promotion of energy conservation.
(ii) Increased use of renewable energy sources.
As concerned citizens, we can do our bit by :
(i) Using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles.
(ii) Switching off electricity when not in use.
(iii) Using power–saving devices.
(iv) Using non-conventional sources of energy.
Question: How is mining activity hazardous? Explain.
OR
How is the mining activity injurious to the health of the miners and environment? Explain.
OR
“Mining affects health and environment both.” Comment.
Answer: The mining activity is injurious to the health of the miners and environment as :
(i) The dust and noxious fumes inhaled by miners make them vulnerable to pulmonary diseases.
(ii) The risk of collapsing mine roofs.
(iii) Inundation and fires in coal mines are a constant threat to miners.
(iv) The water sources in the region get contaminated due to mining.
(v) Dumping of waste and slurry leads to degradation of land, soil and increase in stream and river pollution.
Question: What are the uses of copper? Name the two leading copper producing states of India.
Answer: Uses of copper :
(i) In manufacturing electrical cables.
(ii) In electronic industries.
(iii) In chemical industries.
The two leading copper producing states of India are Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Question: How can solar energy solve the energy problem to some extent in India? Give your opinion.
OR
Why is solar energy fastly becoming popular in rural and remote areas of India? Explain.
Answer: (i) India is a tropical country, therefore it receives sunlight in abundance throughout the year.
(ii) Solar plant can be easily established in rural and remote areas.
(iii) It will minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes which in turn will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate quantity of manure.
(iv) Solar energy is an important alternate source. Use of solar energy will reduce the pressure on conventional sources of energy.
Question: Describe any three importance of coal as a source of energy.
Answer: Importance of coal as a source of energy in India are :
(i) Coal is the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India.
(ii) It provides a substantial part of the nation’s energy needs.
(iii) It is used for power generation.
(iv) It supplies energy to the industry as well as for domestic needs.
Question: Why is mica considered the most important mineral in electric and electronic industries? Give three reasons.
OR
How is mica one of the most indispensable minerals? Explain any three points.
Answer: Mica is :
(i) Excellent dielectric in strength and has a low power loss factor.
(ii) It has insulating properties and resistance to high voltage.
(iii) Most indispensable mineral used in electric and electronic industries.
Question: “Natural gas is considered an environment–friendly fuel.” Explain the statement in two points.
Answer: Natural gas is used as a source of energy as well as an industrial raw material.
(i) It can be transported easily through pipelines.
(ii) Pipelines have helped in setting up fertilizer plants and power plants on their way.
(iii) Natural gas is a clean source of energy.
(iv) It is an environment–friendly fuel because of the low carbon emission.
Question: How is geothermal energy produced? Explain.
Answer: The earth grows progressively hotter with increasing is high, high temperatures are found at shallow depths. Groundwater in such areas absolute hot.
It is so hot that when it rises to the earth’s surface, it drive turbines electricity.
Question: Which are the potential sources of biogas? State any four benefits of biogas.
Answer: Potential sources of biogas are: Shrubs, farm wastes, animal and human wastes, etc.
Four benefits of biogas are :
(i) Its calorific value is high.
(ii) It burns without smoke, causing no pollution.
(iii)It is the cheapest gaseous fuel.
(iv) Its plants provide twin benefits to the farmers in the form of energy and improved quality of manure.
Question: Which are the two main minerals used to obtain nuclear energy? Name any two states where these minerals are found.
Answer: Nuclear or atomic energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms. When such an alteration is made, much energy is released in the form of heat and this is used to generate electric power.
(i) Uranium and Thorium are used for generating atomic or nuclear power.
(ii) They are available in Jharkhand and Rajasthan.
Question: State the importance of petroleum as an energy resource. Mention any four oil fields of India.
Answer: Importance of petroleum can be seen through the following points ! Petroleum or mineral oil is the next major energy source in India after coal. ! It provides fuel for heating and lighting, lubricants for machinery and raw materials for a number of manufacturing industries. ! It is a fuel used in all the automobiles. Four major oil fields of India are
(i) Mumbai High (ii) Ankleshwar and Kalol in Gujarat
(iii) Digboi, Naharkatiya and Moran is Assam
(iv) Rajasthan, Mangala, District Barmer
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: Why is energy needed? How can we conserve energy resources? Explain.
Answer: Energy is required for all activities. It is needed to cook, to provide light and heat, to propel vehicles and to drive machinery in industries.
We can conserve energy resources by:
(i) Developing a sustainable path of energy development, i.e., energy development but not at the cost of environment or needs of future generation.
(ii) Judicious use of limited energy resources.
(iii) Wastage of minerals should be minimised.
(iv) Modern technology should be used for the exploitation of energy resources.
(v) Export of energy resources should be minimised.
Question: “Conservation of minerals is the need of the hour”. Support the statement with five facts.
Answer: Conservation of minerals is the need of the hour :
(i) Minerals are considered to be the backbone of the economy.
(ii) Industry and agriculture depend on mineral deposits.
(iii) The substances manufactured from them also depend on mineral deposits.
(iv) Total volume of workable mineral deposits is very less- only 1% of the earth’s crust.
(v) Mineral resources are being consumed rapidly, and minerals require millions of years to be created and concentrated.
(vi) The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that the rates of replenishment are infinitely small in comparison to the present rates of consumption.
(vii) Minerals resources are finite and non-renewable.
(viii) The rich mineral deposits of our country are extremely valuable but short-lived possessions.
Question: Which minerals are used to obtain nuclear energy? Name all the six nuclear power stations of India.
Answer: The minerals which are used to obtain this energy are :
(i) Uranium and
(ii) Thorium.
The six nuclear power stations of India are :
(i) Narora nuclear power station
(ii) Kakrapar nuclear power station
(iii) Tarapur nuclear power station
(iv) Kaiga nuclear power station
(v) Kalpakkam nuclear power station
(vi) Rawat Bhata nuclear power station
Question: ‘Energy saved is energy produced’. Assess the statement.
Answer: Energy saved is energy produced:
India is presently one of the least energy efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for judicious use of our limited energy resources.
For example:
(i) As concerned citizens we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles.
(ii) Switching off electricity when it is not in use.
(iii) Using power saving devices.
(iv) Using non-conventional sources of energy.
(v) After all “energy saved is energy produced”
Question: Highlight the importance of petroleum. Explain the occurrence of petroleum in India.
Answer: Importance of Petroleum :
(i) Petroleum is the major energy source in India.
(ii) Provides fuel for heat and lighting.
(iii) Provides lubricant for machinery.
(iv) Provides raw material for a number of manufacturing industries.
(v) Petroleum refineries act as nodal industry for synthetic, textile, fertilizer and chemical industries.
Its occurrence :
(i) Most of the petroleum occurrences in India are associated with anticlines and fault traps.
(ii) In regions of folding, anticline or domes, it occurs where oil is trapped in the crest of the up fold.
(iii) Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous and non-porous rocks.
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Consumer Awareness Worksheet |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Social Science
CBSE Social Science Class 10 Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 10. We suggest that Class 10 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Social Science.
Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Social Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 10 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 10 Social Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Chapter Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 10 Social Science worksheets for Chapter Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Chapter Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 10 Social Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Contemporary India Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

