Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Money And Credit Worksheet in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 10 Social Science worksheets for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit
Students of Class 10 should use this Social Science practice paper to check their understanding of Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Worksheet with Answers
DIFFERENT FORMS OF MONEY SUMMARY: The history of money and how various forms were used at different times is an interesting story. At this stage the purpose is to allow students to realize the social situation in which these forms were used. Modern forms of money are linked to the banking system. This is the central idea of the first part of the chapter. Credit is a crucial element in economic life and it is therefore important to first understand this in a conceptual manner. The chapter deals with the benefits and drawbacks of the various credits available to people.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question : Which of the following is a major reason that prevents the poor from getting bank loans?
(a) High rates of interest
(b) Lack of personal connection with banks
(c) Absence of collateral
(d) Lack of proper documents
Answer : (c) Absence of collateral
Question : Match the following: 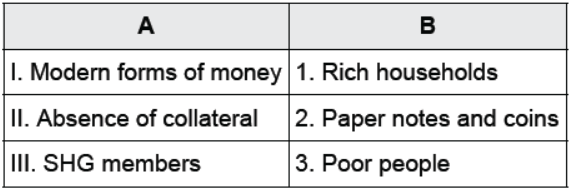
Options:
(a) I-2, II-1, III-3
(b) I-3, II-1, III-2
(c) I-1, II-2, III-3
(d) I-3, II-2, III-1
Answer : (a) I-2, II-1, III-3
Question : Which one of the following is not included under terms of credit ?
(a) Collateral
(b) Documentation
(c) Interest rate
(d) Insurance
Answer : (d) Insurance.
Question : What is the name of the bank that met the credit needs of the poor at reasonable rates in Bangladesh?
(a) Reserve Bank of Bangladesh
(b) Grameen Bank
(c) Cooperative Bank
(d) Sahkari Bank
Answer : (b) Grameen Bank
Question : Which of the following statement best describes the double coincidence of wants?
(a) A person must have double the money if he or she wishes to buy goods or any service.
(b) A person should demand a great amount of a good or service so that another person is willing to produce it.
(c) Two individuals must agree to sell and buy each other's commodities.
(d) Two individuals must be able to produce all goods and services for the entire society.
Answer : (c) Two individuals must agree to sell and buy each other's commodities.
Question : A system where goods are exchanged for other goods is called
(a) barter system
(b) flexible exchange system
(c) fluctuating system
(d) rational trade system
Answer : (a) barter system
Question : The property of money that acts as an intermediary in a transaction, is referred to as _____.
(a) unit of releasing funds
(b) standard of deferred payment
(c) medium of exchange
(d) unit of value
Answer : (c) medium of exchange
Question : Choose the correctly-matched pair about percentage of formal sector in total credit in India in poor households.
(a) Poor- 15%
(b) Middle -20%
(c) Rich- 70%
(d) Very Poor- 80%
Answer : (a) Poor- 15%
Question : Which among the following lenders will possibly not ask the borrower to sign the terms of credit?
(a) Banks
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Cooperatives
(d) Private agencies
Answer : (b) Moneylenders
Question : Which among the following is an example of cooperative society?
(a) Farmers
(b) Workers
(c) Women
(d) All of these
Answer : (d) All of these
Question : _________is used as a substitute for cash. Choose the correct option:
(a) Credit card
(b) Cheque
(c) ATM
(d) Google Pay
Answer : (a) Credit card
Question : Identify the correct statement with regard to banks from the following options:
(a) RBI lays down the norms for other banks.
(b) SBI lays down the norms for other banks.
(c) Syndicate bank lays down the norms for other banks.
(d) PNB lays down the norms for other banks.
Answer : (a) RBI lays down the norms for other banks.
Question : Identify the incorrect statement regarding informal sources of credit:
(a) There is no organisation which supervises the credit activities of lenders.
(b) Their only motive is profit making.
(c) They charge a much higher rate of interest on loans in comparison to formal lenders.
(d) They cover those sources of credit which are registered by the government.
Answer : (d) They cover those sources of credit which are registered by the government.
Question : Identify the one who helps the borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral:
(a) Self-help group (SHG)
(b) State government
(c) Employers
(d) Moneylenders
Answer : (a) Self-help group (SHG)
Question : Identify which one of the following is NOT an informal sector loan provider for poor rural household in India?
(a) Commercial Banks
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Traders
(d) Landlords
Answer : (a) Commercial Banks
Question : Match the following: 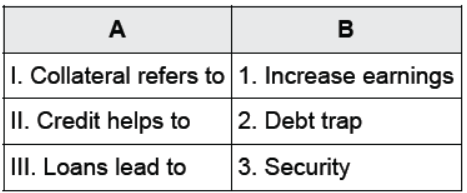
Options:
(a) I-2, II-1, III-3
(b) I-3, II-1, III-2
(c) I-1, II-2, III-3
(d) I-3, II-2, III-1
Answer : (b) I-3, II-1, III-2
Question : Identify the correct statement with regard to agricultural stage:
(a) In agricultural stage, grains were used as money.
(b) In agricultural stage, grains were used as commodity.
(c) In agricultural stage, grains were used as ingredient.
(d) In agricultural stage, grains were used as coins.
Answer : (a) In agricultural stage, grains were used as money.
Question : Which of the following is the most important function of the banks?
(a) Accept deposits and extend loans.
(b) Give loans to government.
(c) Open as many bank accounts as possible.
(d) Give loans to businesses.
Answer : (a) Accept deposits and extend loans.
Question : Identify which one of the following is the newer way of providing loans to the rural poor, particularly women:
(a) Grameen Banks
(b) Self-Help Groups
(c) Cooperative Banks
(d) Moneylenders
Answer : (b) Self-Help Groups
Question : Identify which of the following organisations supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector?
(a) RBI
(b) Commercial banks
(c) Ministry of finance
(d) None of the above
Answer : (d) None of the above
Question : All the banks act as mediator between ______ and ______ .
(a) rural people, urban people
(b) literates, illiterates
(c) people, government
(d) depositors, borrowers
Answer : (d) depositors, borrowers
Question : Which of the following is the term used for method of repayment of loan?
(a) Mode of payment
(b) Method of payment
(c) Mode of repayment
(d) None of the above
Answer : (c) Mode of repayment
Question : Which of the following is Not a part of terms of credit?
(a) Interest rate
(b) Documentation required
(c) Mode of repayment
(d) Functioning of private banks
Answer : (d) Functioning of private banks
Question : Which of the following is a reason for using money to buy goods and services?
(a) Money can be easily exchanged for any goods or service a person wants.
(b) Money is more valuable than any goods or service a person wants.
(c) Money cannot be put to any other use apart from transaction.
(d) Money is less valuable than any goods or service a person wants so people easily give money for the goods and services.
Answer : (a) Money can be easily exchanged for any goods or service a person wants.
True/False
Question : In a SHG, most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by government.
Answer : False.
Question : The main source of income for banks is interest on deposits.
Answer : False.
Question : Gramin Bank is the success story that met the credit needs of the poor at reasonable rates in Bangladesh.
Answer : True.
Question : A ‘debt trap’ means overspending till no money is left.
Answer : False.
Question : The collateral demand that lenders make loans against are vehicle and building of the borrower.
Answer : True.
Fill in the blanks :
Question : Interest rate, collateral and ___________ together comprisewhat is called the terms of credit.
Answer : documentation
Question : __________ issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
Answer : Reserve Bank of India
Question : __________is an asset that the borrower owns and uses asa guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender.
Answer : Collateral
Question : In India, the law legalises the use of ___________ as amedium of payment that cannot be refused in settling any transaction.
Answer : money
Question : ___________help in pooling the savings of their members,who are poor women to meet their credit needs.
Answer : SHGs
Assertion and Reasoning Baseed Questions
Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : The facility of demand deposits makes it possible to settle payments without the use of cash.
Reason : Cheques are paper orders which make it possible to transfer money from one person's account to another person's account.
Answer : (d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : Banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (depositors) and those who are in need of funds.
Reason : Banks hold about 15% of their deposits as cash.
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : In India, no individual can refuse to accept a payment made in rupees.
Reason : Rupee is the legal tender in India.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Debt trap is a situation in which a person is caught in the vicious cycle of debts.
Reason : This debt can be taken from only from informal sources.
Answer : (c) A is true but R is false.
Question : Assertion : Rohan took credit in the form of advance payment from a buyer and he delivered the goods to the buyer on time and also earned profit. The credit made Rohan better off in this situation.
Reason : Credit can never push a person into a debt trap.
Answer : (c) A is true but R is false.
Question : Assertion : The modern currency is used as a medium of exchange; however, it does not have a use of its own.
Reason : Modern currency is easy to carry
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Reason : Lender can sell the collateral to recover the loan amount if the borrower fails to repay the loan.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Which agency is not included in informal loan sector or agency?
Answer : Bank
Question. In SHG most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by __________.
Answer : Non-government organizations
Question. Formal sources of credit include _______________.
Answer : Banks, Co-operatives and LIC
Question. Security (pledge, mortgage) against loan:
Answer : Collateral
Question : In what kind of economic environment, barter system is suitable ?
Answer : Barter was a useful system in an economy which is backward, people live in nearby areas, only a very small number of goods are produced and people have need for only very small number of goods.
Question : What is collateral ?
Answer : Collateral refers to an asset that the borrower owns and mortgages this asset as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Question : How many types of cooperatives are possible ?
Answer : The various types of cooperatives which are possible are farmers cooperatives, weavers cooperatives, industrial workers cooperatives, etc.
Question : How does money act as a medium of exchange ?
Answer : Money acts as a medium of exchange because it acts as an efficient link between the exchange of commodities.
Question : What is credit (loan)?
Answer : Credit (loan) refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment.
Question : What is barter system?
OR
What do you mean by barter system?
OR
What is the meaning of barter system?
Answer : Barter system is an old system of exchange wherein goods or services were directly exchanged for other goods and services without the use of money.
Question : Why is the modern currency accepted as money ?
OR
What is the reason for accepting paper notes as a mediumof exchange ?*
Answer : Modern currency is accepted as a medium of exchange because the modern currency is authorised by the government of the country.
Question : How does a person deposit money with bank ?
Answer : A person deposits money with a bank by opening a bank account in his name.
Question : What in your opinion is the way to break the debt trap ?
Answer : The debt trap can be broken with the help of credit facilities on softer terms from the formal sector like banks, cooperative societies or self help groups.
Question : What are the two benefits of credit?
Answer : 1. Credit helps the people to generate more income.
2. Credit helps the banks to contribute towards the development of country's capital.
Source / Case Based Questions
Question : Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
Grameen Bank of Bangladesh is one of the biggest success stories in reaching the poor to meet their credit needs at reasonable rates. Started in the 1970s as a small project, Grameen Bank in 2018 had over 9 million members in about 81,600 villages spread across Bangladesh. Almost all of the borrowers are women and belong to poorest sections of the society. These borrowers have proved that not only are poor women reliable borrowers, but that they can start and run a variety of small income-generating activities successfully. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(i) The passage given above relates to which of the following options?
(a) Self-help group
(b) Source of credit
(c) Loans for poor
(d) Grameen Bank of Bangladesh
Answer : (d) Grameen Bank of Bangladesh
(ii) According to the given passage, Grameen Bank can be termed as a biggest success story based on which of the following options?
(a) It was started in 1970s
(b) Its member increased to 9 million
(c) The borrowers are poor women
(d) All of the above
Answer : (d) All of the above
(iii) By giving credit to poor women, Grameen Bank wants to:
(a) increase the standard of living
(b) increasing employment opportunities
(c) empower poor women
(d) all of the above
Answer : (c) empower poor women
(iv) What according to you is the reason that Grameen banks is so popular in Bangladesh?
(a) It gives loan only to women.
(b) It provides loan at very affordable rates.
(c) Help women to run a variety of small income-generating activities.
(d) All of the above
Answer : (b) It provides loan at very affordable rates.
Question : Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follow:
Source A - Borrowers and lenders
Every loan agreement specifies an interest rate which the borrower must pay to the lender along with the repayment of the principal. In addition, lenders may demand collateral (security) against loans. Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Source B - Formal sector in India
The various types of loans can be conveniently grouped as formal sector loans and informal sector loans. Among the former are loans from banks and cooperatives. The informal lenders include moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends, etc. The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans. For instance, we have seen that the banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive. The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
Source C - Loan activities of banks
Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. For example, banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash. This is kept as provision to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money from the bank on any given day. Since, on any particular day, only some of its many depositors come to withdraw cash, the bank is able to manage with this cash.
(i) What do you mean by collateral in banking system?
Answer : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestocks, deposit with banks) and uses this to provide guarantee to lender until the loan is repaid.
(ii) Who supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans?
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
(iii) What per cent of deposits is used as cash by banks?
Answer : Banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question : Why should banks and cooperative societies lend more?
Answer : Lending by the banks and cooperative societies has a very positive impact on the income generation and reduction of poverty. Many people may borrow at lower rates of interest.
These loans may be used for a variety of purposes like growing crops, setting up of small-scale industries and business etc. Hence, cheap and affordable credit may be helpful in generating employment and higher incomes.
Question : Why do lenders ask for ‘collateral’ while lending? Analyse the reasons.
OR
Why do banks demand ‘collateral’ while issuing a loan?
Answer : Lenders ask for collateral while lending to borrowers because :
(i) Lenders demand collateral (security) against loans, collateral is an asset that the borrowers owns (such as land, building, vehicles, livestock, deposits with bank).
(ii) Every loan specifies an interest rate which the borrower must pay to the lender alongwith the repayment of theprincipal.
(iii) Lender keeps the collateral as a guarantee until the loan (with interest, if applicable) is repaid.
(iv) If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has a right to sell the asset or collateral to recover his payment.
Question : Why do the farmers take loans?
Answer : Farmers usually take loans for crop production at the beginning of the crop season and they repay the loan after the harvest of crop. Hence, there is an interval of three to four months between the time when the farmers buy these inputs and when they sell the crop to repay the loan.
Question. What do you mean by ‘Barter system’?
Answer : Barter system refers to the system of exchange of goods and services. It is the system by which one commodity or product is exchanged for was introduced, people were practising barter system. [write any one example]
Question. What is meant by double coincidence of wants? What is its inherent problem?
Answer : Double coincidence of wants is a situation when both parties have agreed to sell and buy each other’s products or commodities.
It can only work when both the persons are ready to exchange each other’s goods.
Question : Have you ever wondered why transactions are made in money ?
Answer : Money makes the transactions easier. A person having money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want. So he doesn't have to face the problem of double coincidence of wants involved in the barter system.
Question : How can money be easily exchanged for goods or services? Give an example to explain.
Answer : Money was evolved to remove the inconveniences of barter system, as money has separated the act of purchase from sale. Medium of exchange is the basic or primary function of money. People exchange goods and services through the medium of money. Money acts as a medium of exchange or as a medium of payments. Money by itself has no utility it is only an intermediary. For example, if someone wants buy any grocery or stationery or a car, he can pay the seller with money to purchase the item. If a person wants to avail any service such as train or bus service, he can pay for it with money to the concerned person.
Question : ‘‘The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.’’ Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged because :
(i) 85% of loans taken by the poor households in the urban areas are from informal sources.
(ii) Informal lenders charge very high interest on their loans.
(iii) There are no regulations and restrictions.
(iv) Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
(v) In certain cases, the high interest rate for borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower.
(vi) This could lead to increasing debt and debt trap. Therefore, the credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.
Question : ‘‘Self Help Groups’ help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral.’’ Examine the statement.
Answer : "Self Help Groups" help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(i) In a Self Help Group, most of the important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members.
(ii) Group members are well known to each other. They belong to the same society.
(iii) Also, it is the group which is responsible for the repayment of the loan.
(iv) Any case of non-repayment of loan by any member is followed up seriously by other members in the group.
(v) Due to this feature, banks are willing to lend to the poor women when they get organised in SHGS, even though they have no collateral as such.
Question : How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Answer : Banks act as financial mediator or intermediary between the savers and borrowers. Savers are the people who have surplus money which they do not require in the near future.
They deposit such money by opening an account in the bank. Banks give interest on such deposits. On the other hand, there are people who want credit for business requirements or for meeting their personal needs. Banks provide credit or loan to such people and charge interest on it. The banks charge a higher rate of interest on loans and pay a lower rate of interest on deposits. This difference between rates of interest becomes the source of income for the banks.
Question : What do you understand by double coincidence of wants ?
Answer : Double coincidence of wants is a difficult situation involved in the barter system. Under the barter system, the transactions between two persons were executed through the mutual exchange of goods. For example, person A has got rice and wants a blanket while person B has blanket and wants rice.Both of them have the things which the other one wants. So the transaction here can take place easily.
This is called double coincidence of wants, i.e., what a person desires to sell is exactly what the other wishes to buy.
Question : Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own? Find out the reason.
Answer : The modern currency Rupee in India does not have any value of its own because it is not as precious as gold and silver, it is made up of paper. However, it is used for transaction in exchange for several goods and services. But it is still considered as a medium of exchange as it is authorised by the Government of India.
Question : How are deposits with the banks beneficial for individual as well as for the nation? Explain with examples.
Answer : The deposits with banks are beneficial for individual as well as for the nation:
(i) Banks accept deposit and also pay an amount as interest and in this way people earn money.
(ii) People's money is safe with banks.
(iii) Getting credit is easy for individuals who have savings and current account in the banks.
(iv) Poor people who are engaged in production needs credit.
(v) Credit provided by the banks for government projects helps in the development of the nation.
(vi) Banks provide loans for the promotion of international trade.
(vii) Development of infrastructure is undertaken with the loans provided by the banks.
Question : How does money remove the difficulty of double coincidence of wants ?
Answer : Money has removed the problem of double coincidence of wants by breaking a single exchange transaction for specific goods into two transactions of buying and selling by involving a medium of general acceptability, i.e., money. Everyone involved in a transaction may buy the goods of their requirement from anybody who has got that thing. Now they don't have to look for a person who desires to sell exactly what the other wishes to buy.
Question : How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things ? Give an example.
OR
‘‘The Rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.’’ Explain.
Answer : Money makes the things easier as :
(i) It is in the form of authorised paper currency which gives the guarantee of the mentioned price to the owner.
(ii) It has general acceptability.
(iii) Its price remains constant compared to other commodities.
(iv) Money can be stored easily and it doesn't need much space.
Example : Suppose a foreign touristor visits India. He has currency of his own country. As his currency has value in India he can easily exchange his currency with that of India currency and can enjoy his visit. Hence, use of money makes the buying and selling process an easier one.
Question : How is money used as medium of exchange ? Explain with examples.
Answer : Money makes the transactions easier. It acts as an intermediate in the exchange process that is why it is called a medium of exchange. A person having money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want. So he doesn't have to face the problem of double coincidence of wants involved in barter system.
For Example : If one were to offer a goat as payment for a meal in any restaurant there may be some confusion about the value of the goat.
Question : ‘‘Banks are efficient medium of exchange.’’ Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : We agree with the statement that banks are efficient medium of exchange.
(i) Demand deposits share the essential features of money.
(ii) The facility of cheque against demand deposit makes it possible to directly settle payment without the use of cash.
(iii) Demand deposits are accepted widely as a medium of payment.
Question : What is credit ? What are its importance ?
Answer : Credit (loan) refers to an agreement between a lender and a borrower in which the lender supplies the borrower money, goods or services with the promise from borrower for future repayment.
Credit plays a vital and positive role in the following ways :
(i) Credit helps people in meeting the ongoing expenses of production.
(ii) It also helps people to complete tasks in given period of time.
(iii) It helps people to earn more profits.
(iv) It helps in increasing economic activities of the country, thus, help in its development.
Question : How do banks play an important role in the economy of India ? Explain.
Answer : Banks play an important part in India's economy by providing a safe foundation for individuals and businesses to invest or deposit their money, which allows the bank to use the money in its possession for loans. The ability for the public to receive these loans enables them to make purchases, which drives the economy at different levels. The bank is able to take the deposits, which start out as liabilities, and turn them into assets. This is accomplished by the banks through investing the money that is deposited in a way that benefits them in the form of higher returns than what is being paid to the depositor's account when they receive interest.
Question. State the role of Reserve Bank of India.
Answer : (i) In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
(ii) The RBI supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
(iii) The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(iv) The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators.
(v) Any other relevant point.
Question. Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own ? Point out the reasons.
Answer : Modern currency is accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own due to reasons as :
• In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the central government.
• As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency.
• The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
• No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
• (Any other relevant point).
Question. How do the demand deposits share the essential features of money ?
Answer : The demand deposits share the essential features of money:
The facility of cheques against demand deposits make it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
Since demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment, along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy.
Question. Why is money called a medium of exchange?
Answer : In an economy where money is in use, money by providing the crucial intermediate step eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants. Since money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, it is called a medium of exchange
Question. How do banks play an important role in the economy of India?
Answer : (a) (i) Banks provide people the facility to deposit their surplus money byopening a bank account in their name. Banks also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest. Thus, banks add to the income of the family.
(ii) Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans to the needy. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks, thus, mediate between those who have surplus money and those who are in need of this money.
(iii) Banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers, etc. Thus, they empower these people and help indirectly in the country’s development.
(iv) The rate of interest that banks demand from the borrowers is always cheap and affordable. This helps people to improve their condition. Banks also give loans to industrialists. These industrialists use these loans to expand their industries. In this way, they contribute in country’s development.
(v) By employing a large number of people banks solve the problem of unemployment to a great extent.
Question. What is meaning of Barter system? Why is double coincidence of wants is an essential feature of a Barter system?
Answer : Meaning of Barter system: A system in which goods are directly exchanged without the use of money is called barter system.
Double coincidence of wants means when both the parties – seller and purchaser – agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities. It implies that what a person desires to sell is exactly what the other wishes to buy. No money is used in such an arrangement. Therefore it is an essential feature of barter system.
Question. Why are deposits with banks are called demand deposits?
Answer : Depositors have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question : In India, about 80 per cent of farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(i) Why might banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(ii) What are the other sources from which the small farmers can borrow?
(iii) Explain with an example how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer.
(iv) Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
Answer : (i) Banks need proper documentation and reasonable collateral to provide any kind of loan. Small farmers many not have necessary documentation and reasonable collateral because his collateral may already have been mortgaged or he may be a tenant on the land or may be very poor. In all these situations, his chances of getting loans from the bank are very less.
(ii) The other sources through which the farmers can take loan from are the cooperative society, moneylenders, agricultural traders and Self Help Groups etc.
(iii) Suppose, Gopal is a farmer who wants loan from a local moneylender for the purpose of crop production. Now the moneylender extends him loan on 5 % rate of interest per
month on cumulative basis. As collateral, the moneylender keeps the papers of his land. Another condition the moneylender puts before him is that after this crop season, Gopal will be allowed to use his land only when he repays the whole loan or repays loan by selling his land or does "Begar" for the money lender till he repays the entire loan.
(iv) Small farmers can get cheap credit from banks, cooperative societies or self help groups.
Question. Describe the organization, working and importance of Self-Help Groups.
Or
What are the Self-Help Groups? How do they work?Explain.
Or
What is meant by Self Help Group? Explain is working.
Answer : (1) SHGs are the groups created by the needy persons themselves, especially women to fulfil their credit and loan needs. A typical SHG has 15-20 members, who meet and save regularly.
(2) Saving of per member varies from 25 to Z 100 or more depending on the ability of the people to save.
(3) Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
(4) The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the money-lenders charge.
(5) If the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. The loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
Question. Why are informal sources of credit preferred in rural areas? Give five reasons.
Answer : (1) There is no need for collateral such as land; building, vehicles, deposits with banks. The rural poor people are unable to provide collateral.
(2) Also, there is no need for complicated paperwork which the rural poor are not capable of providing.
These moneylenders, traders and rich landlords continue to extend loans to defaulters even if the previous loan is unpaid.
(4) They are hesitant and unsure about the functioning of the banks.
(5) They may not have access to banks in their villages.
(6) The procedure for giving credit is often very simple.
Question : How does SHG manage its finances?
Answer : Self Help Groups manage their finances in the followingmanner:
(i) A SHG collects small savings from its members depending on the ability of the people to save.
(ii) These savings make the resource pool for the SHG.
(iii) Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
(iv) The group charges reasonable interest on these loans which is very less in comparison to what the moneylenders charge.
(v) All the important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities of the members are taken collectively by the group members. The group decides, keeping in mind the purpose,
amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule etc. regarding the loans to be granted.
(vi) If the group is regular in savings, after some years, it becomes eligible for availing loan from a bank without any collateral.
Question : What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers?
Answer : The banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers due to the following reasons:
(i) The borrower might not having proper guarantee or collateral.
(ii) The previous track record of the borrower regarding loan repayment is not good.
(iii) The purpose for which the borrower wants to take loan involves very high risks or uncertainty and the bank has the doubt of getting its loan back.
(iv) The bank is not satisfied with the purpose for which the borrower is taking the loan.
(v) The borrower is not able to present a proper project report showing convincing returns on investment.
(vi) If the amount of the loan is very high which the bank is not willing to lend to a single borrower.
(vii) The RBI has put restrictions on the bank to lend to certain category of borrowers.
Question : What is money? What are the modern forms of money? How has it removed the difficulties of barter system?
OR
‘‘Money has made transactions easy.’’ Justify.
Answer : Money is anything which is generally acceptable as a medium of exchange. Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process, that is why it is called a medium of exchange. Currency (paper notes and coins), debit cards, credit cards and demand deposits withdrawable by cheques are modern forms of money. Money has removed the problem of double coincidence of wants involved in the Barter system. Under the barter system, the transactions between two persons were executed through the mutual exchange of goods. For example, person A has got rice and wants a blanket, while person B has blanket and wants rice. Both of them have things which the other one wants. So, the transaction here can take place easily. The situation becomes difficult when one of them wants something which the other one does not have. For example, person B has got blanket but he wants milk instead of rice. Now he will have to search for a third person who has milk and wants rice. This is highly difficult. Money has made this situation easier by breaking a single exchange transaction for specific goods into two transactions of buying and selling by involving a medium of general acceptability, i.e., money. For example, person A may buy blanket from person B by giving him money, while person B may buy milk from someone else who may or may not want rice by paying him that money any time. So, the transaction become easier for everyone and one does not have to care for mutual coincidence of wants of goods.
Question. Why are credit arrangements not fair for all sections of society? Give three reasons. Suggest two remedies for the problem.
Or
Why is the share of formal sector credit higher for the richer households compared to the poorer households ? Give any three reasons responsible for this.
Answer : (1) Undoubtedly, credit arrangements are not very fair for all sections of society The share of formal sector credit is higher for the richer households as compared to the poorer households. This has the following reasons:
(i) Poverty affects poor households’ capacity to borrow. Formal sector credit requires proper documents and collateral as security against loans. Collateral is an asset. So, poor people lack in providing such things which affect their capacity to borrow.
(ii) The poor people do not repay
(iii) The people in villages may not have access to banks in their village. Also, they are R. loan on time because of the various day-to-day needs. - hesitant and unsure about the functioning of the banks.
(2) (i) More credit facilities should be made available in rural areas by opening more banks there.
(ii) The procedure of giving loans should be made easier and simpler.
Question : Why is it necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas? Explain.
Answer : In rural areas, people often borrow from moneylenders which comprise the unorganised sector. This usually involves higher cost of borrowing which means a larger part of the earnings of the borrower is used to repay the loan. Hence, borrowers have less income left for themselves. This could lead to increasing debt. Thus, it is necessary that banks and cooperatives should increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that dependence on informal sources of credit reduces. Borrowing from organised sector like banks and co-operatives would lead to higher incomes and many people could then be able to borrow cheaply for a variety of needs. They could grow crops, do business, set up small-scale industries etc. They could set up new industries or trade in goods. Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country's development. Thus, the formal sector loans need to expand, and it is also
necessary that everyone has access to these loans.
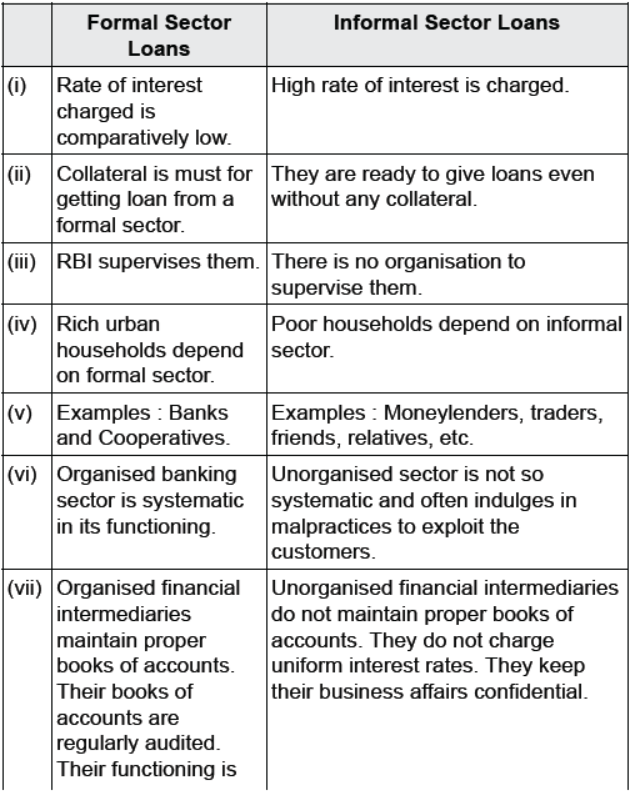
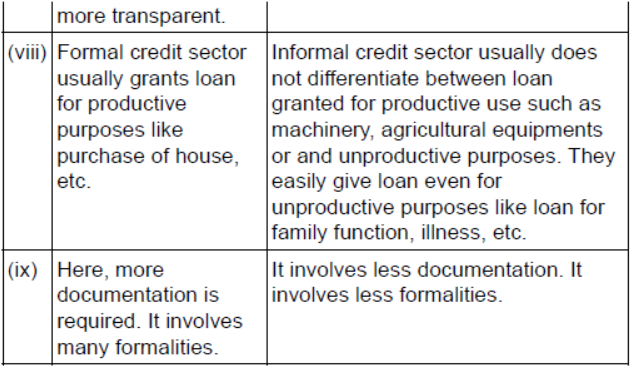
Question : Compare Formal Sector Loans with Informal Sector Loans regarding interest only.
Answer :
Question : What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
OR
Answer : a note on Self Help Groups (SHGs).
Ans A Self Help Group organises the rural or urban poor, in particular women, into small group of normally 15-20 members and pool or collect their savings. The members usually belong to one neighbourhood, who meet and save regularly. These members contribute their savings which may vary from ₹ 25 to ₹ 100 or more per member per day or per month, depending on the ability of the people to contribute into the pool of the group. This pool is utilised for its members in the form of small loans to meet their needs. The group charges interest on these loans but this is very less than what the informal sources of loans such as moneylenders or traders charge. After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it
becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members. The members may utilise such credit for buying equipments like sewing machines, handlooms, hammers, axe, shovel etc. for their works, seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, raw materials, cattle, house etc. The group is responsible for the repayment of the loan. Because of this feature, banks are willing to lend to the SHGs, even though they have no collateral.
Question : Write a note on the “Cooperative”.
Answer : Cooperative or the cooperative society is an organisation of persons which is based on the principle of mutual cooperation. The concept of cooperation refers to the superiority or unity of weaker sections or consumers over the exploitative powers of the lenders, traders or middlemen. It is generally an organisation of people from the same profession and not necessarily formed by poor people only. These are generally the registered bodies. The agriculturists and labourers may form such cooperative society for their welfare. The objective of such cooperative society may be to :
(i) Promote a sense of security among its members.
(ii) Stop the exploitation of the members from the exploitative practices of informal sector loans.
(iii) Provide a formal source of credit to its members.
(iv) Make credit available on favourable terms to its members.
The capital of the cooperative society is generated by the contribution of members in the form of deposits. With these deposits as collateral, the cooperative can obtain a loan from
the bank. These funds can be used to provide loans to members. Once these loans are repaid, another round of lending can take place. These loans can be provided to its members for the purchase of equipment, crop production, construction of houses etc.
Question : Apart from medium of exchange function, what more functions does money perform?
Answer : Apart from medium of exchange functions, money performs the following functions:
(i) Under barter system, there was the problem of the logical measurement of value of goods and each and every good had to be valued against each and every other good. So, there was the possibility of existence of many values of a single commodity in terms of different commodities. Money has solved this problem. Now any commodity can be valued in terms of money, no matter how small it is.
(ii) In barter system, commodities used to be stored as future purchasing power but commodities were perishable in a short period of time. So they would lose value. Money has solved this problem. Currency can be stored and used at any time as and when the need arises. Money does not perish.
(iii) Money helps in the determination and distribution of national income. National income can be determined because the production can be summed up in money. National income can be distributed among the various factors of production in monetary form which was not at all easy to be distributed in the form of physical goods and services under barter system.
Question : “Focuses of currency have undergone several changes since early times.” Elucidate.
Answer : (i) Before the introduction of coins, a variety of objects were used as money.
(ii) For example, since the very early ages, Indians used grains and cattle as money.
(iii) Thereafter, the use of metallic coins-gold, silver, copper coins-a phase which continued well into the last century.
(iv) Modern forms of money include currency-paper notes and coins.
(v) Modern currency is not made of precious metal, it is without any use of its own.
Question : Why do you think that richer section of the society has better access to formal sector loans while poor section does not?
Answer : The richer section of the society, whether urban or rural, has better access to the formal sources of credit due to the following reasons:
(i) The richer section of the society is comparatively better educated and it can understand very well the formal procedures of getting credit from formal sources of credit.
Poor people lack such understanding.
(ii) The richer section of the society has proper documents, guarantees or collateral which it can offer to the bank or any other institution. Poor section generally lacks all such things.
(iii) The richer section of the society has better repayment capacity. So its chances of back tracking on the repayment are lesser. In the case of poor section, such chances of failure of repayments may be higher.
(iv) The richer section of the society has regular interaction with the formal sector institutions in terms of deposits and withdrawals. Such kind of interaction increases the trust of
the formal sector in richer section of the society. Poor section of the society lacks such interaction and hence the trust too.
Important Questions for NCERT Class 10 Social Science Money And Credit
Question : Why did Salim need credit?
Answer : Salim needed credit to purchase the raw materials for the manufacture of shoes.
Question : Why did Swapna need credit?
Answer : Swapna needed credit to meet the expenses of cultivation.
Question : Why is it necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas? Explain.
Answer : Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers. Hence, it is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
While formal sector loans need to expand, it is also necessary that everyone receives these loans. At present, it is the richer households who receive formal credit whereas the poor have to depend on the informal sources. So, it is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans.
Question : People obtain loans from various sources. Name them.
Answer : • Banks and cooperatives (formal sector)
• Moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends (informal sector).
Question : How does the use of money make exchange of things easier? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Money means wealth around which the whole economic activities of every country move. Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process and therefore it is called a medium of exchange.
(ii) In our day to day transactions, goods are being bought and sold with the use of money. At times we do exchange services with money.
(iii) Use of money has made things easier to exchange as we can exchange it for any commodity we need.
(iv) The transactions are made in money because a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she wants.
(v) Thus, the main function of money in an economic system is to facilitate the exchange of goods and services. Without exchange of money nobody can fulfil his all needs and requirements.
Question : Give some common examples of collateral used for borrowing.
Answer : Property such as land titles, deposits with banks, livestock are some common examples of collateral used for borrowing.
Question : What portions of bank deposits are kept by the banks for day to day transactions?
(a) 11% of the deposits
(b) 15% of the deposits
(c) 18% of the deposits
(d) 17% of the deposits.
Answer : B
Question : While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. What do is this mean?
Answer : This means low interest rate, easy conditions for repayment and less collateral and documentations requirements.
Question : Throw light on the various sectors of the economy.
Answer : People obtain loan from various sources. The various types of loans can be grouped as formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
Formal sector: It Includes banks and cooperatives. The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loan. The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance. Similarly, the RBI sees that these banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers etc. Periodically banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending and to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Informal sector: It includes moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends etc. There is no one to supervise their credit activities. It can charge whatever interest rate they choose. There is no one to stop them from using unfair means to get their money back.
Question : How do the informal lenders take undue advantage of the borrowers helplessness?
Answer : They charge high interest on loans. As a result, the cost to the borrower of informal loans is also very high.
Question : What would the lender do in case the borrower fails to repay the loan?
Or
Why do lender ask for collateral while lending?
Answer : If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to obtain payment.
Question : People obtain loans from various sources. Name them.
Answer : • Banks and cooperatives (formal sector)
• Moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends (informal sector).
Question : What are the benefits that you can get by depositing your extra money in the banks?
Answer : (i) Safety
(ii) Earn interest
(iii) Can make payments easily through cheques.
Question : How do the SHGs help borrowers?
Answer : The SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
Question : How do the informal lenders take undue advantage of the borrowers helplessness?
Answer : They charge high interest on loans. As a result, the cost to the borrower of informal loans is also very high.
Question : What is known as double coincidence of wants?
Answer : When in the exchange, both parties agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities, it is known as double coincidence of wants.
Question : What is it that can act as a medium of exchange in transactions?
Answer : It is money that can act as a medium of exchange in transactions.
Question : “Most of the poor households still depend on the informal sector for loans, both in rural and urban areas of India”. Support the statement with three examples.
Answer : (i) Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources.
(ii) Bank loans require proper document and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
(iii) Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence are often willing to give a loan without collateral. The borrowers can, if necessary, approach the moneylenders even without repaying their earlier loans.
Question : Define the term’ Money’. How does money serve as a medium of exchange? OR How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things?
Answer : 1. Money may be defined as anything which is generally accepted as a medium of exchange of goods and services or in payment of debts.
2. Medium of exchange or medium of payment is the basic function of money. People exchange goods and services through the medium of money.
3. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or services he might want.
4. Money solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange.
Question : Explain ‘Barter System’. What were its demerits?
Answer : Barter system was the direct exchange of goods against goods without the use of money.
Eg. When a weaver gives clothes to the farmer in return for getting wheat from the farmer.
Demerits of Barter System.
1. Lack of double coincidence of wants
2. Absence of common measure of value
3. Lack of divisibility
4. Difficulty in storing wealth
5. Lack of satisfactory unit to engage in contracts
Question : What are the functions of money?
Answer : 1. Money acts as a medium of exchange in goods and services and in payment of debts.
2. Money is used as a measure of value.
3. It is a Standard of Demand Payments.
4. It acts as store of value.
Question : What is double coincidence of wants? Why is the „lack of double coincidence of wants‟ a main demerit of barter system? Explain with an example.
Answer : 1. Double coincidence of wants is an essential feature of barter exchange system.’ Simultaneous fulfillment of mutual wants by buyers and sellers ‘is known as double coincidence of wants.
2. It means, what a person desires to sell is what the other person wishes to buy.
3. In barter exchange, this double coincidence of wants is often lacking. Eg. The producer of wheat may want to buy shoes in exchange of his wheat. But he may find it difficult to get a shoe maker who is willing to exchange his shoes for wheat. Thus a seller has to find out a person who wants to buy the seller’s goods and the same time who must have what the seller wants.
Question : How does money eliminate the problem of lack of double coincidence of wants? Give an example.
Answer : 1. Double coincidence wants is the most difficult problem of barter system.
2. If wants do not match between two persons, no exchange of goods will take place.
3. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or services he might want.
4. Money solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange.
5. E.g. If a shoe manufacturer wants wheat he can sell his shoes that he has produced for money and then exchange the money for wheat.
Question : Name a few modern forms of money.
Answer : Currency-Paper and Coins, Cheque, Demand Draft/ Demand Deposits, Postal Order , Credit and Debit Cards etc.
Question : How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Answer : (i) Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves, as a provision to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw from the bank on any given day.
(ii) They use their major portion of the deposits to extend loans, mediate between those people who have surplus funds (depositors) and those who are in need of those funds (the borrowers).
(iii) They charge higher rate of interest on the loans than what they offer on deposits. The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Question : What are the drawbacks of informal sources of credit?
Answer : (i) Most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans. Thus the cost to the borrower of the informal loans is much higher.
(ii) Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of earning of the borrowers is used to repay the loan and they have less income left for themselves.
(iii) The high rate of interest of borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower and it can lead to increasing debt and debt-trap.
(iv) People who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
Question : What does credit mean? What are the terms of the credit?
Answer : Credit refers to an agreement in which lender supplies the borrowers with money, goods and services in return for the promise of future payments.
Terms of credit includes the following:
(i) Interest rate
(ii) Collateral
(iii) Documentation requirement
(iv) Mode of payment.
These terms of credit vary substantially from one credit arrangement to another. They may vary depending on the nature of lender and borrower. Every loan agreement specifies an interest rate which the borrower has to pay to the lender along with the repayment of the principal. In addition to this lenders may demand collateral (security) against the loans.
Question : How is the facility of cheque useful?
Answer : A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from a person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The payer, who has an account with the bank, makes out a cheque for a specific amount. The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
Question : What is credit? Why is there a need for credit in rural areas?
Answer : Credit refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. There is a need for credit in rural areas for the following reasons.
(i) In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production.
(ii) crop production involves considerable costs on seeds fertilisers, pesticides, water electricity, repair of equipment, etc.
(iii) Farmers usually takes crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest.
(iv) Rural people also take loans for starting small business and for the marriage of their daughters.
Question : Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender? Discuss.
Answer : Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. Manav will decide on whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender on the basis of various factors:
(i) Firstly, he must have a collateral or asset which can guarantee his loan. If he lacks such an asset, he cannot get a loan from the bank. In this scenario, he will have to go to a moneylender, even though the latter charges a higher interest rate.
(ii) Secondly, if Manav is not aware of the banes of borrowing from the informal sector, he might not even consider taking a bank loan.
(iii) Thirdly, if there are no banks in or near his area of residence or work place, then he will borrow from a moneylender.
Question : Grameen Bank of Bangladesh has done a great job in the rural areas of the country. Which values according to you is it able to support?
Answer : Grameen Bank of Bangladesh was started in the 1970s as a small project. But soon it achieved grand success in removing poverty from the country. It helps the poor to meet their credit needs at reasonable rates. Almost all of the borrowers are women who belong to poorest sections of the society. These borrowers have proved themselves very reliable. They use the money in a number of income generating activities and thus empower themselves and their families.
The values that Grameen Bank of Bangladesh supports are:
(i) Removal of poverty.
(ii) Women empowerment.
(iii) Self-sufficiency.
Question : What is the role of SHGs? What are the reasons of its growing popularity?
Or
What are Self-Help Groups? Describe, in brief, their functioning.
Answer : Self-Help Groups consist of certain members who pool their savings and constitute a fund which is further used in making finance and advances to other members. A typical Self-Help Group has 15 to 20 members. The members pool their savings and after some time, it becomes a large amount which is used to give loans to the needy ones at a very nominal rate of interest. This helps to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit.
After a year, if such a group is regular in its savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members. Loans are provided for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs as buying seeds, fertilisers, raw materials, for acquiring assets like sewing machine, handlooms, cattle, etc. Important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members. The group decides the purpose, amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule etc. Non-repayment is taken seriously. Because of this feature, banks are willing to lend loan especially to the poor women when organised in SHG.
SHGs are becoming popular for the following reasons:
(i) They help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(ii) They can get timely loans for variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate.
(iii) They are building blocks of the organisation of the rural poor.
(iv) It helps women to become self-reliant.
(v) The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on various social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
Question. „The modern currency like paper notes and coins is without any use of its own.‟ Then why is it accepted as a medium of exchange?
Answer: 1. It is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorized by the government of the country.
2. In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
3. As per Indian law, no other individual or organization is allowed to issue currency.
4. The law legalizes the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
5. No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees.
Question. What is a demand deposit? Why is it considered as money?
Answer: 1. Deposits in a bank which are payable to the depositor on demand are called demand deposits.
2. The people need only some currency for their daily needs, the surplus money can be deposited with banks by opening a bank account in their name.
3. Demand deposits are payable on demand through cheques or withdrawal slips.
4. The facility of cheques against the withdrawal makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
5. Since demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment, they are considered money in the modern economy.
Question. Define a cheque. How does it act as money? ANS.
Answer: 1. A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been made.
2. For payment through a cheque , the payer who has an account with the bank makes out a cheque for a specific amount.The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
3. Eg. if a Shoe manufacturer has to make a payment to the leather supplier, then he writes a cheque for a specific amount. This means that the shoe manufacturer instructs his bank to pay this amount to the leather supplier. The leather supplier takes this cheque and deposits it in his own account in the bank. The money is transferred from one bank account to another bank account in a couple of days. The transaction is complete without any payment of cash.
Question. List out some details that are to be filled in a cheque.
Answer: The Cheque is a document in which the following details are to be filled by the person issuing the cheque : name of the person to whom it is drawn, date , amount in rupees ( both in figures and words) account number, bank branch , and signature.
Question. How do the banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who are in need of money? OR What do the Banks do after accepting the deposits from the public?
OR
Explain the loan activities of banks.
Answer:
1. After the Banks accept deposits from the public they keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
2. For example, banks in India these days hold about 15% of their deposits as cash. This is kept as provision to pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money from the bank on any given day.
3. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people. In this way, banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers).
4. Banks charge a higher rate of interest on loans than what they offer to the public for deposits.
5. The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Question. What is credit (loan)? Analyze the role of credit for development.
Answer:
1. Credit (loan) refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods, or services in return for the promise of future payment.
2. The credit helps the people to meet the ongoing expenses of production, or complete production on time and increase earning.
3. In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves considerable costs on seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, water, electricity etc.
4. The progress of business activity is fully linked with credit system.
5. The credit helps the farmers and businessmen to increase production and increase the national income.
Question. “Credit Helps as well as harms and pushes the farmers into a debt trap”. Explain.
Answer:
1. In one situation credit helps to increase earning and therefore the person is better off than before.
2. In another situation, because of the crop failure, credit pushes the person into a debt trap
3. For instance for a forth coming festival season if a shoe manufacturer has received an order from a large trader in town for 3000 pairs of shoes to be delivered in a month time.
4. In this case he obtains credit to meet the working capital needs of production. If he is able to supply goods on time, he gets profit and credit is useful to him.
5. When a Farmer takes a loan or Credit, the repayment has to be made from the income from farming; sometimes due to failure of the crop the repayment of the loan becomes impossible. The farmers may have to sell a part of their land to repay the loan or may have to take another credit from another source. Credit in this case pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is painful.
Question. Define the term „Collateral ?
Answer: Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns -such as land, building, vehicle, live stock , deposits with banks ’- and uses as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is paid.
Question. What does „terms of credit „mean?
Answer:
1. While giving loan, the lender specifies certain terms and conditions relating to the loan to be followed by the borrower. This known as terms of credit.
2. It includes interest rate, collateral, and documents required and mode of payment.
3. Depending on the nature of the borrower and the lender, these terms may differ.
Question. Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending?
Answer:
1. Every loan agreement specifies an interest rate which the borrower has to pay with the principal amount. In addition, lenders may demand collateral as security against loans.
2. Collateral refers to use of assets by the borrower as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is paid. Eg.Land, Deposits with banks etc.
3. The lender asks for collateral to safeguard his money. Without security, a lender may face loss if the borrower does not pay the loan back. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to obtain the payment.
Question. What are the two sources of credit? Describe any sources of formal and informal credit in India.
OR
What are the differences between Formal Source of Credit and Informal Source of Credit?
Answer: FORMAL SECTOR/ SOURCE OF CREDIT:
i) It includes loans from bank and cooperatives. Interest rate is low.
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA supervises the functions of the formal sector.
ii)The urban households depend largely on formal sector.
INFORMAL SECTOR/ SOURCE OF CREDIT:
iii) It includes traders, money lenders, relatives, land lords, etc.
iv)The rate of interest is higher compared to formal sector. There is no organization to supervise the lending activities of informal sector of credit.
v) In rural area , people dependant on informal sector of credit.
Question. Why is the demand for Credit high in Rural Areas? Explain.
Answer:
1. In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves considerable costs on seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, water, electricity, repair of equipment, etc.
2. There is minimum stretch of three to four months between the time when the farmers buy these inputs and when they sell the crop.
3. Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest.
4. Repayment of the loan is crucially dependent on the income from farming. The failure of the crop can make the repayment almost impossible.
Question. In what way does the RBI supervise the functions of Banks in India?
Answer: 1. The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans. For instance, the banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive. The RBI monitors that the banks actually maintain the cash balance.
2. The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, to small borrowers etc.
3. Periodically banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending to whom, at what interest rate etc. Central Bank is the lender or the last resort. Whenever banks are short of funds, they take loans from the Central Bank.
Question. „The cost to the borrower of informal sector is much higher‟ Explain the statement.
OR
What are the drawbacks of borrowing from the informal lenders? Explain.
Answer: 1. Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of earning of the borrower is used for repaying the loan.
2. Informal lenders charge a higher rate of interest compared to the formal lenders. There is no Organization to supervise their credit activities. There is no one to stop them from using unfair means to get their money back.
3. Due to the high rate of interest the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower, leading the borrower into a debt trap.
Question. Why are the poor households dependent upon the informal sources of credit?
Answer: 1. Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Getting loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources because of the necessity of various documents.
2. Absence of Collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans
3. On the other hand the moneylenders know them personally hence are willing to give the loan without a collateral. The Borrowers may be able to approach the moneylenders even without repaying their previous loans.
Question. Why do we need to expand the formal sources of credit in India? OR Why should credit be available at reasonable rates?
OR
What are the advantages of borrowing from formal sector?
Answer: 1. Banks and Cooperative Societies are the main source of formal sector of credit. The rate of interest charged by formal lenders is much less compared to the informal lenders. If people can borrow at cheaper rates it leads to increase in income.
2. People can grow crops, set up small-scale industries, do business or trade in goods. Hence cheap and affordable credit provided by the formal lenders is crucial for the country’s development.
3. The credit provided by the formal sector meets only about half of the total credit needs of the rural people. The remaining credit needs are met from informal sources; most loans from informal sources carry high interest rates and do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
4. While formal sector loans need to expand, it is also necessary that everyone receives these loans.
5. At present only rich households are getting formal credit. It is important that formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from cheaper loans.
Question. What are Self Help Groups? Briefly explain the role played by SHG‟s in providing credit to the poor rural households.
Answer: 1. SHG’s are a new source of providing loans to the rural poor particularly women. It may consist of 15-20 members belonging to a neighborhood who meet and save regularly. Their savings may vary from Rs 25 to Rs 100 or more depending on the ability to save. They provide loans to its members according to necessity.
2. The rate of interest charged by SHG’s is lesser than that charged by money the lender. The SHG helps the borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
3. Small loans are provided to members for instance meeting working capital needs such as buying seeds, raw materials, fertilizers or cloth.
4. The group decides on the loans to be granted- the purpose, amount, interests to be charged, repayment schedule etc.
5. The reason why banks are lending to these groups even without collateral is that in any case of non-repayment of loan, the members of the group seriously follow it up.
6. They are the building blocks of organization of the rural poor. They also discuss certain social issues such as health, nutrition and domestic violence.
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Consumer Awareness Worksheet |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Social Science
CBSE Social Science Class 10 Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 10. We suggest that Class 10 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Social Science.
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Social Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 10 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 10 Social Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 10 Social Science worksheets for Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 10 Social Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Understanding Economic Development Chapter 3 Money and Credit, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

