Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Economics Money And Credit Worksheet Set D in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 10 Social Science worksheets for Chapter 3 Money and Credit, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit
Students of Class 10 should use this Social Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 3 Money and Credit as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Worksheet with Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Why one cannot refuse a payment made in rupees in India?
Answer: Because it is authorized by the Government of India.
Question: What is a cheque?
Answer: A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Question: Give one reason that prevents a rural poor from getting a formal loan.
Answer: Lack of collateral.
Question: How do the deposits with banks become their source of income?
Answer: Banks use a major portion of its deposits to extend loans to people, for which they charge high interests and this is how the deposits with banks become their source of income.
Question: How is double coincidence of wants not appreciable in the contemporary scenario?
Answer: Double coincidence of wants not appreciable: What a person desires to sell is exactly not what the other wishes to buy.
Question: How do the Demand Deposits offer facilities?
Answer: Demand Deposits offer facilities as: It offers essential characteristics of money/Safe transfer of money.
Question: How is money beneficial in transactions?
Answer: Money has made transactions easy as it solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange.
Question: What do terms of credit include?
Answer: The terms of credit include interest rate, collateral, documentation requirement, mode of payment.
Question: Why is money called a medium of exchange?
Answer: Money is accepted as a ‘medium of exchange’ because it acts as an intermediary in the process of exchange. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service.
Question: Which bank issues ‘currency notes’ in India on behalf of the central government?
Answer: The Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes in India on behalf of the federal government.
Question: What can be the alternative mode of payment in place of cash money?
Answer: Cheques and demand deposits are two alternative modes of payment that can be used in place of cash money.
Question: Why do banks ask for collateral while giving loans?
Answer: Banks use collateral as a guarantee until the loan is repaid.
Question: Explain the meaning of ‘Currency’.
Answer: Currency is the form of money: paper notes and coins.
Question: Give one example each of modern currency and older currency.
Answer: Examples of modern currency are paper bills/notes, coins, credit cards etc., whereas examples of older currency are coins made of precious metals like gold or silver and also terracotta coins, etc.
Question: Observe the picture carefully.

Describe this image in your own words.
Answer: This image showcases a meeting of a women self-help group.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Why is it necessary to increase of a large number of banks mainly in rural areas? Explain.
Answer: Increase large number of banks:
(i) To reduce the dependence on informal sector of credit.
(ii) To provide cheaper loans.
(iii) To provide accessibility towards loans for the poor.
(iv) Any other relevant point to be explained.
Question: Describe the significance of the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer: It is the Reserve Bank of India, which controls the functioning and supervises the activities of the formal sectors in India. It also acts as the guardian of all the monetary policies in our country. It monitors the balance kept by banks for day-today transactions. Periodically, banks have to give details about lenders, borrowers and interest rate to RBI. Thus, RBI plays a significant role in our country.
Question: “The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer: (1) There is no organisation which supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector. The informal sector can lend at whatever interest rate they want and there is no one to stop them from using unfair means to get their money back.
(2) Most of the informal moneylenders charge a very high rate of interest on loans in comparison to the formal lenders, which in turn increases the principal ammount which is to be paid back.
(3) Sometimes the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower. It also significantly reduces the income of the borrower, as much of the earnings go into repayment of the loan.
Question: Explain the role of Self Help Groups in the rural economy.
Answer: The role of Self-Help Groups:
(i) Self-Help Groups are small groups (especially from rural areas) who pool their resources and individual savings together to help the others in need of funds.
(ii) Facilitates the members to employ themselves in numerous self-employment opportunities.
(iii) Help in raising the living standards of the concerned members.
(iv) Reduces the dependence on the informal credit sources.
(v) Thus, with the help of SHGs, the rural poor become economically independent and their dependence on the local moneylenders who charge a high rate of interest is also reduced.
Question: ‘‘Credit can play a negative role.’’ Support the statement with arguments.
Answer: The following points elucidate how credit can play a negative role:
(1) The cost of informal loans is much higher and often leads to a debt-trap. In addition budding entrepreneurs who might wish to start a new enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
(2) Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
(3) Credit does no good to the borrower if he/she doesn’t utilise that money in a profitable manner. Sometimes, farmers borrow money to buy raw material to grow crops but due to some factors, the crop turns out to be a failure. The farmer is not able to repay the amount and thus falls into a debt-trap.
Question: Which organisation supervises the functioning of the banks in India and how? Explain.
Answer: The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of the banks in India in the following ways:
(1) The banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive. The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(2) The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, to small borrowers etc.
(3) Banks have to submit information to the RBI periodically on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate etc.
Question: The other form in which people hold money is as deposits with banks. At a point of time, people need only some currency for their day-to-day needs. For instance, workers who receive their salaries at the end of each month have extra cash at the beginning of the month. They deposit this extra cash with the banks by opening a bank account in their name. Why do people deposit their money in bank?
Answer: People deposit money in bank because:
(1) Depositing cash in banks is a wonderful way of keeping the money secure. Bank guarantee the security of your money from being robbed or looted.
(2) The surplus cash leftover after every month expenditure can be deposited in a bank to earn interest over the same. Hence, surplus cash when deposited brings home extra money off interest.
(3) Banks also provide the facility of depositing or withdrawing money at one’s own convenience. It is a good way of saving some money which would otherwise be spent in unnecessary things.
Question: Why is it necessary to increase a large number of banks in rural areas? Explain.
Answer: It is necessary to increase a large number of banks in rural areas. The cost of informal loans is much higher and often leads to a debt trap. People who might wish to start a new enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing in such a case.
Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers Banks can change this..
It is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence of the poor on informal sources of credit reduces.
It is important that formal credit sources like banks are distributed more equally in rural and urban areas so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans.
Question: Dhananjay is a government employee and belongs to a rich household, whereas Raju is a construction worker and comes from a poor rural household. Both are in need and wish to take loan. Create a list of arguments explaining who between the two would successfully be able to arrange money from a formal source. Why?
Answer: Dhananjay will be able to get a loan from a formal source.
Arguments:
- Banks are not present everywhere in rural India.
- Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources.
- Bank loans require proper documents and collateral.
Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans. Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence, are often willing to give a loan without collateral.
Question: What is meant by term of credit? What does it include?
Answer: Terms of credit are the requirements need to be satisfied for any credit arrangements. It includes interest rate, collateral, documentation and mode of repayment. However, the terms of credit vary depending upon the nature of lender, borrower and loan.
Question: Modern forms of money include currency: paper notes and coins. unlike the things that were used as money earlier modern currency is not made of precious metals such as gold silver and copper and unlike green and cattle they are neither of everyday use the modern currency is without any use of its own. Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own?
Answer: Modern currency is accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own because:
(1) Modern currency is authorised by the government of the country because the Reserve Bank of India issues all currency notes on behalf of Central Government.
(2) No other individual or organisation apart from RBI is allowed to issue currency.
(3) Indian law legalises the use of rupee as amedium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
Question: Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own ? Find out the reason.
Answer: Modern currency is accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own because:
(1) Modern currency is authorized by the government of a country.
(2) In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues all currency notes on behalf of central Government.
(3) No other individual or organization is allowed to issue currency.
(4) The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
(5) No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in Rupees.
Question: Explain the role of credit for economic development.
OR
‘‘Credit can play a positive role.’’ Support the statement with arguments.
Answer: Credit plays a crucial role in a country’s development in the following ways –
(1) Credit or loans sanctioned by banks help industrialists as capital investments to revive their failing industry or start up a completely new venture without worrying about the lack of cash. This in turn leads to increase in employment opportunities and economic development of a country.
(2) For farmers, loans help them buy new seeds before the sowing season and becomes their only source of capital in times of urgent need. This helps them grow more and earn more.
(3) Credit also helps to boost various other sectors. It helps to buy houses, vehicles and generate demands which in turn helps to boost economy. The borrower is able to repay this loan in installments.
Question: How is money transferred from one bank account to another bank account? Explain with an example.
Answer: Money can be transferred from one bank account to another in many ways like cheque payments, net banking, etc.
For example – A shoe manufacturer, M. Salim, has to make a payment to the leather supplier and writes a cheque for a specific amount. This means that the shoe manufacturer instructs his bank to pay this amount to the leather supplier.
The leather supplier takes this cheque, and deposits it in his own account in the bank. The money is transferred from one bank account to another bank account in a couple of days. The transaction is complete without any payment of cash.
Question: Why is credit a crucial element in the economic development?
Answer: Credit is a crucial element in economic development of a country because:
(i) It helps to meet the ongoing expenses of production
(ii) It helps in increasing earnings
(iii) It helps in completing production in time.
Question: How do demand deposits have the essential features of money? Explain.
Answer: The most essential feature of money is that it becomes a medium of exchange to buy things. Demand deposits, like cheque, also fulfill this role.
A cheque is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the other person or to the account holder.
Thus this facility involving cheques makes the settlement of payments possible without using cash. Since they are widely used alongside money as a medium of exchange, demand deposits have this feature, which is similar to money.
Question: Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India? Explain.
Answer: Expand formal sources
(1) To save people from the exploitation of Informal sector
(2) Formal charge a low interest on loans.
(3) To save from debt trap.
(4) It provides cheap and affordable credit.
(5) RBI also supervises the formal sector credit through various rules and regulations which ensures that banks give loans to small cultivators, small borrowers, etc. and not just to profit making business and traders.
Question: Explain any three functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer: Functions of the Reserve Bank of India are:
(1) The RBI is the only authorized body that can issue currency in the country.
(2) They print, distribute and regulate the flow of currency in the economy.
(3.) The RBI provides central and state governments with banking facilities.
(4) The Reserve Bank of India also supervises all other commercial banks in the country. It provides financial assistance to these banks, like short-term loans and advances.
(5) To maintain the value of the rupee in the global economy, the RBI acts as the custodian of foreign exchange reserves in the country.
(6) The primary function of the Reserve Bank of India is the control of credit and money in the market.
Question: How is the concept of self help groups important for poor people ? Give your view point.
Answer: Self help groups for poor people:
(1) Help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(2) Get timely loans for a variety of purposes (releasing mortgaged land, buying seeds, fertilizers, cattle, etc.) and at a reasonable interest rate.
(3) Help women to become financially selfreliant.
(4) The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to its members to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
Question: Examine any three situations in which credit pushes the borrower into a debttrap.
Answer: Credit and debt-trap:
(1) Loans from informal sector could lead to debt trap.
(2) Lack of planning results in debt.
(3) Diffculty in repaying loans due to certain circumstances.
(4) Higher interest rate.
Question: Why is it diffcult for poor people to get loan from banks?
Answer: Limited availability of banks makes it diffcult for poor people in rural areas to get loans from banks. Poor people don’t have sufficient collateral and required documents to present to banks while borrowing.
Question: “Banks are eficient medium of exchange.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer: Banks are effcient m ediusm o f exchang because:
(1) Demand deposits share the essential features of money.
(2) The facility of cheque against demand deposit makes it possible to directly settle payment without use of cash.
(3) Demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment.
Question: Describe the utility of Cheque.
Answer: The utility of cheque is as follows:
(1) Cheques have the same features as money.
(2) They settle payments without the use of cash.
(3) They are widely accepted as a means of payment.
(4) There pose the least risk in transactions.
(5) In a fair dealing, it is the most appropriate means of money transactions.
Question: Why are formal sources of credit preferred over the infomal source of credit? Give three reasons.
Answer: Formal sources of credit preferred over Informal sources of credit because:
(1) Formal sources have low cost of borrowing
(2) Higher Income through cheap borrowing
(3) No exploitation and debt trap.
Question: Explain the three important terms of credit.
Answer: The important terms of credit are as follows:
(1) Collateral: Collateral refers to an asset like a building or vehicle owned by the borrower, which acts as a guarantee against which the loan is given to the borrower.
(2) Documentation: Before lending money, the lender checks all the documents, like income and employment records, etc.
(3) Interest rate: While borrowing or lending money, both the parties decide the rate of interest on which the amount is being lent. The borrower pays the principal amount added to the interest amount while repaying the loan. Document is specified for the same.
(4) Mode of payment: It refers to the mode of payment in which the borrower will return the money to the lender. The duration of time for which the amount is being given also comes under this term.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question: “Bank plays an important role in the economic development of the country.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer: Bank plays an important role in the economic development of the country in many ways:
(i) Bank provides loan in rural area for crop production ultimately resulting in the development of many places.
(ii) Bank provides loan to create fixed assets that will create employment opportunities.
(iii) It acts as a link between savers and investors i.e. people who have surplus money and those who are in need of money.
(iv) Banks accepts the deposit and pay an amount as interest on the deposit which mobilizes savings.
(v) Bank uses major portion of these deposits to extend loan for the industrial and agricultural sector. They also provide funds to different organisations.
Question: Why is it necessary for banks and cooperatives to increase their lending in rural areas? Explain.
Answer: Necessity for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas:
(i) Dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
(ii) To provide more loan facilities to rural households.
(iii) To save rural people from exploitation.
(iv) It is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans.
(v) The bank and the cooperative societies have to increase the lending facilities to improve the livelihood of the people in the rural areas.
Question: What are demand deposits? Explain any three features of it.
OR Which type of deposits with the banks are called demand deposits? State some important features of demand deposits.
Answer: People save their money in banks by opening an account. The deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, so these deposits are called demand deposits.
(i) Banks accept the deposits and also pay an interest rate on the deposits. In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it also earns interest. (ii) The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash. Since, demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment, along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy.
(iii) It is authorised by the government of the country.
Question: How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Answer: (i) Banks keep a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
(ii) Major portion of deposits is used for extending loans.
(iii) The banks mediate between depositors and borrowers in this way.
(iv) They charge high rate of interest on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Question: ‘‘The rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.’’ Explain.
Answer: The rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange because:
(i) The currency is authorised by the government of the country.
(ii) In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the central government.
(iii) The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
(iv) No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
Question: Which are the two major sources of formal sectors in India? Why do we need to expand the formal sources of credit?
Answer: The two major sources of formal sources of credit are:
(i) Banks and
(ii) Cooperatives. Need to expand formal sources of credit are:
(i) To save the poor farmers and workers from the exploitation by the informal sector credit.
(ii) Informal sector charges a higher interest on loans which means that a large part of the earnings is used to repay the loan.
(iii) Formal credit can fulfil various needs of the people by providing cheap and affordable credit.
Question: Why is it necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending in rural areas? Explain.
Answer: Banks and cooperatives should increase their lending in rural areas because:
(1) India largely depends on agriculture for export revenues. Farmers and agricultural workers in rural areas deserve special attention as they lack capital and resources to invest in their work.
(2) Most of the people in rural areas are illiterate and informal money lenders exploit and cheat them for their benefit. People need a reliable source for credit.
(3) Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
(4) Banks and co-operative societies provide loans to the rural households at cheap rates and are backed by the government, which helps them boost their income. Incentives are also given to farmers for quick repayment.
(5) Most of the people in urban areas depend upon the rural people for their food and raw material requirements. For better production and to boost their income sources, easy credit is required.
(6) High rate of interest and repayment of such high amount to informal sources, make farmers fall in a debt trap. Formal sources are monitored and backed by the government. Help is given to them readily in dire times.
Question: “Credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a ‘situation from which recovery is very painful.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer: Yes, it is true that credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful. It can be further understood through the following points :
(1) Sudden calamities cannot be predicted. In rural areas, if crops fail due to any natural factors, then it becomes dificult for the borrower to repay the loan. For example, thunderstorms, hailstorms, etc. destroy crops and farmer’s source of income. Loan repayment becomes impossible for the farmer.
(2) In informal sectors, the rate of interest is not fixed and is usually very high. In case the credit is not repaid then the interest rates further mounts leading the borrower in a debt trap.
(3) There are cases when people have to sell their land and fixed assets to repay loan.
(4) The borrower is often pushed into painful situation in case of high risk activities failure and specially when there is no support.
(5) Some borrowers also commit suicide if they fail to repay the loan.
Question: ‘‘Bank plays an important role in the economic development of a country.” Support the state-ment with examples.
Answer: ‘‘Banks plays an important role in the economic development of the country’’. This statement can be supported by:
(1) Loan is provided by banks to workers of the agriculture sector for all stages of crop production which results in the development of many households.
(2) Employment opportunities are created when banks provide loan to create fixed assets like buildings, industries and factories.
(3) Banks acts as a link between savers and investors. They mediate between those who have surplus money and those who are in need of it.
(4) One can easily rely and trust banks when it comes to keeping money safe. Banks provide a percentage of interest on the deposited money to the people which boosts their demands as well.
(5) Banks encourage entrepreneurs, native craftsmen and industrialists to work, produce and develop without worrying about capital or credit which in turn helps to make country economically sound. Banks help to distribute money allotted by various government schemes to beneficiaries in the remotest areas of the country.
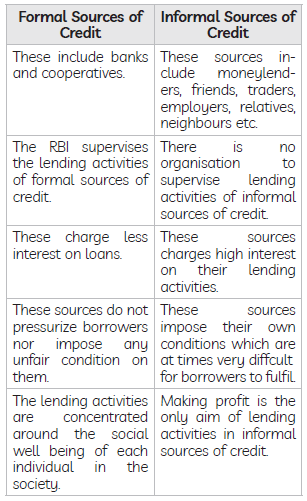
Question: What are the differences between formal and informal sources of credit? Mention five points.
Answer: The difference between formal and informal sources of credit is as follows:
Question: Explain any two features each of formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
Answer: Formal Sector
Loans: Include loans from banks and cooperatives. Features of formal sector loans are:
(i) Formal sectors provide cheap and affordable loans and their rate of interest is monitored by Reserve Bank of India.
(ii) Formal sector strictly follows the terms of credit, which include interest rate, collateral, documentation and the mode of repayment. Informal Sector Loans: Include loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc. Features of informal sector loans are:
(i) Their credit activities are not governed by any organisation, therefore they charge a higher rate of interest.
(ii) Informal sector loan providers know the borrowers personally, and hence they provide loans on easy terms without collateral and documentation.
Question: Review any three merits and any two demerits of ‘formal sector of credit’ in India.
Answer: Merits :
(1) Formal sector of credit helps to meet the working capital needs of production.
(2) It also helps in completing production on time.
(3) It offers loans at low rates of interest.
(4) It helps in increasing earnings by making more investment.
(5) It helps in meeting on going expenses of production activities.
Demerits:
(1) The formal sector of credit lacks credibility in rural areas.
(2) People face difficulty in obtaining loans.
(3) People don’t always have collateral or required documents.
Question: How do banks play an important role in the economy of India? Explain.
Answer: Banks play an important role in developing the economy of India:
(i) They keep the money of the people in their safe custody.
(ii) They give interest on the deposited money to the people.
(iii) They mediate between those who have surplus money and those who are in need of money.
(iv) They provide loan to a large number of people at the low interest rate.
(v) They promote agricultural and industrial sector by providing loans.
(vi) They also provide funds to different organisations.
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography Water Resources Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Political Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion And Caste Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture Modern World Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Consumer Awareness Worksheet |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Social Science
CBSE Social Science Class 10 Chapter 3 Money and Credit Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 3 Money and Credit to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 10. We suggest that Class 10 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Social Science.
Chapter 3 Money and Credit Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Social Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 10 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 10 Social Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 3 Money and Credit difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Chapter Chapter 3 Money and Credit for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 10 Social Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 3 Money and Credit focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 10 Social Science Chapter Chapter 3 Money and Credit to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 10 Social Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 3 Money and Credit, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

