Practice CBSE Class 10 Physics Light Reflection and Refraction MCQs Set E provided below. The MCQ Questions for Class 10 Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction Science with answers and follow the latest CBSE/ NCERT and KVS patterns. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for CBSE Class 10 Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction
Class 10 Science students should review the 50 questions and answers to strengthen understanding of core concepts in Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction
Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction MCQ Questions Class 10 Science with Answers
Question: A man runs towards the plane mirror at 2 ms–1. The relative speed of his image with respect to him will be
a) 2 ms–1
b) 4 ms–1
c) 8 ms–1
d) 10 ms–1
Answer: b
Question: A ray of light travelling in air falls obliquely on the surface of a calm pond. It will
a) Go into the water without deviating from its path
b) Deviate away from the normal
c) Deviate towards the normal
d) Turn back on its original path
Answer: c
Question: Choose the incorrect statement.
a) The height of the object is taken to be positive as the object is usually placed above the principal axis.
b) The height of the image should be taken as positive for both virtual and real image.
c) A negative sign in the value of the magnification indicates that the image is real.
d) A positive sign in the value of the magnification indicates that the image is virtual.
Answer: b
Question: A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed
a) At the focus
b) Between focus and centre of curvature
c) Between focus and pole
d) Beyond the centre of curvature
Answer: c
Question: Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
b) Convex mirror as well as concave lens
c) Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other
d) Concave mirror as well as concave lens
Answer: a
Question: The diameter of the reflecting surface of spherical mirror is called its
a) Aperture
b) Focal length
c) Radius of curvature
d) None of the options
Answer: a
Question: The image of the distant object is obtained on a screen by using a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror can be determined by measuring the distance between
a) The object and the mirror
b) The object and the screen
c) The mirror and the screen
d) The mirror and the screen as well as that between the object and the screen
Answer: c
Question: A ray of light that strikes a plane mirror PQ at an angle of incidence of 30°, is reflected from the plane mirror and then strikes a second plane mirror QR placed at right angles to the first mirror. The angle of reflection at the second mirror is
a) 30°
b) 45°
c) 60°
d) 90°
Answer: c
Question: If the magnification of a lens has a negative value, the image is
a) Real and inverted
b) Virtual
c) Erect
d) None of the options
Answer: a
Question: A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. He finds the image of his head bigger, the middle portion of his body to be of same size and that of the legs smaller. Which of the following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top?
a) Plane, convex and concave
b) Convex, concave and plane
c) Concave, plane and convex
d) Convex, plane and concave
Answer: c
Question: If the magnification of a lens has a positive value, the image is
a) Real
b) Virtual and erect
c) Inverted
d) None of the options
Answer: b
Question: Which position of the object will produce a magnified virtual image, if a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm is being used?
a) 10 cm
b) 20 cm
c) 30 cm
d) 35 cm
Answer: a
Question: Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
c) Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
d) More than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer: b
Question: An object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between the image and the pole is
a) Equal to f
b) Greater than f but less than 2f
c) Equal to 2f
d) Greater than 2f
Answer: c
Question: Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form a real image larger than the actual object?
a) When the object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of curvature
b) When object is kept at a distance less than its focal length
c) When object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
d) When object is kept at a distance greater than its radius of curvature
Answer: c
Question: Two lenses of power +2.50 D and –3.75 D are combined to form a compound lens. Its focal length in cm will be
a) 40
b) –40
c) 80
d) –80
Answer: d
Question: You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
a) Kerosene
b) Water
c) Mustard oil
d) Glycerine
Answer: d
Question: The focal length, f R2 = is valid
a) For convex mirror but not for concave mirror
b) For concave mirror but not for convex mirror
c) For both convex and concave mirrors
d) Neither for convex mirror nor for concave mirror
Answer: c
Question: Which one of the following ray diagrams is c orrect for the ray of light incident on a lens as shown in figure?
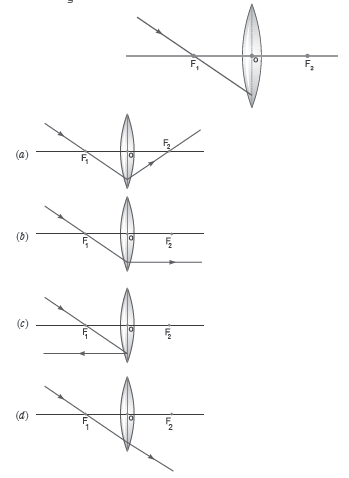
Answer: b
Question: In optics, an object which has higher refractive index is called
a) Optically rarer
b) Optically denser
c) Optical density
d) Refractive index
Answer: b
Question: One of the following does not apply to a concave mirror. This is:
a) Focal length is negative
b) Image distance can be positive or negative
c) Image distance is always positive
d) Height of image can be positive or negative
Answer: c
Question: A concave mirror cannot be used as:
a) A magnifying mirror
b) A torch reflector
c) A dentist’s mirror
d) A rear view mirror
Answer: d
Question: A lens of focal length 12 cm forms an erect image, three times the size of the object. The distance between the object and image is
a) 8 cm
b) 16 cm
c) 24 cm
d) 36 cm
Answer: b
Question: A ray of light passes from a medium X to another medium Y. No refraction of light occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium Y at an angle of
a) 120°
b) 90°
c) 45°
d) 0°
Answer: b
Question: An object is placed 20 cm in front of a plane mirror. The mirror is moved 2 cm towards the object. The distance between the positions of the original and final images seen in the mirror is
a) 2 cm
b) 4 cm
c) 10 cm
d) 22 cm
Answer: b
Question: A concave mirror gives real, inverted and same size image if the object is placed
a) At F
b) At infinity
c) At C
d) Beyond C
Answer: c
Question: A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab for three different values of angle of incidence (∠i) namely 30°, 45° and 60°. He extends the direction of incident ray by a dotted line and measures the perpendicular distance ‘l’ between the extended incident ray and the emergent ray. He will observe that
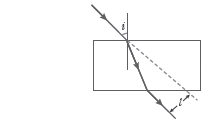
a) ‘l’ keeps on increasing with increase in angle of incidence
b) ‘l’ keeps on decreasing with increase in angle of incidence
c) ‘l’ remains the same for all three angles of incidence
d) ‘l’ is the maximum for ∠i = 45° and is less than this value for ∠i = 30° and ∠i = 60°
Answer: a
Question: A ray of light is travelling in a direction perpendicular to the boundary of a parallel glass slab. The ray of light
a) Is refracted towards the normal
b) Is refracted away from the normal
c) Is reflected along the same path
d) Does not get refracted
Answer: d
Question: Image formed by plane mirror is
a) Real and erect
b) Real and inverted
c) Virtual and erect
d) Virtual and inverted
Answer: c
Question: Focal length of plane mirror is
a) At infinity
b) Zero
c) Negative
d) None of the options
Answer: a
Question: The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence:
a) Always
b) Sometimes
c) Under special conditions
d) Never
Answer: a
Question: In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at:
a) A flat surface
b) A bent-in surface
c) A bulging-out surface
d) An uneven surface
Answer: c
Question: A concave mirror is used to obtain a magnification of –2. The object should be placed
a) Between pole and focus
b) Between focus and centre of curvature
c) At the centre of curvature
d) Beyond the centre of curvature
Answer: b
Question: The figure shows the image of a clock as seen in a plane mirror. The correct time is:
a) 2.25
b) 2.35
c) 6.45
d) 9.25
Answer: d
Question: A boy is standing in front of and close to a special mirror. He finds the image of his head bigger than normal, the middle part of his body of the same size, and his legs smaller than normal. The special mirror is made up of three types of mirrors in the following order from top downwards:
a) Convex, Plane, Concave
b) Plane, Convex, Concave
c) Concave, Plane, Convex
d) Convex, Concave, Plane
Answer: c
Question: If an object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens, the image formed is slightly smaller than the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 19 cm from the lens, the image formed is slightly larger than the object. The approximate focal length of the lens is
a) 20 cm
b) 18 cm
c) 10 cm
d) 5 cm
Answer: c
Question: Two big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he finds that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B remains the same
a) Mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
b) Mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
c) Mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
d) Mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
Answer: c
Question: A student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get a correct measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by following the labelling indicated in figure 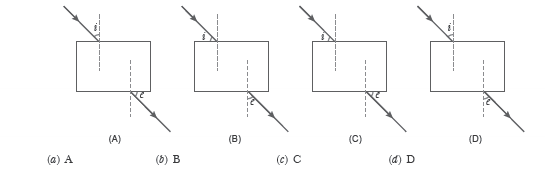
Answer: d
Question: A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
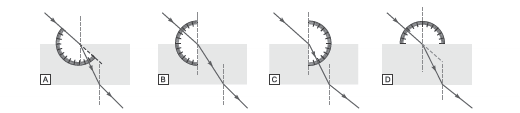
Answer: b
More free study material for Science
MCQs for Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction Science Class 10
Students can use these MCQs for Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction to quickly test their knowledge of the chapter. These multiple-choice questions have been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Our expert teachers suggest that you should practice daily and solving these objective questions of Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction to understand the important concepts and better marks in your school tests.
Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT Based Objective Questions
Our expert teachers have designed these Science MCQs based on the official NCERT book for Class 10. We have identified all questions from the most important topics that are always asked in exams. After solving these, please compare your choices with our provided answers. For better understanding of Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science created by our team.
Online Practice and Revision for Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction Science
To prepare for your exams you should also take the Class 10 Science MCQ Test for this chapter on our website. This will help you improve your speed and accuracy and its also free for you. Regular revision of these Science topics will make you an expert in all important chapters of your course.
You can get most exhaustive CBSE Class 10 Physics Light Reflection and Refraction MCQs Set E for free on StudiesToday.com. These MCQs for Class 10 Science are updated for the 2025-26 academic session as per CBSE examination standards.
Yes, our CBSE Class 10 Physics Light Reflection and Refraction MCQs Set E include the latest type of questions, such as Assertion-Reasoning and Case-based MCQs. 50% of the CBSE paper is now competency-based.
By solving our CBSE Class 10 Physics Light Reflection and Refraction MCQs Set E, Class 10 students can improve their accuracy and speed which is important as objective questions provide a chance to secure 100% marks in the Science.
Yes, Science MCQs for Class 10 have answer key and brief explanations to help students understand logic behind the correct option as its important for 2026 competency-focused CBSE exams.
Yes, you can also access online interactive tests for CBSE Class 10 Physics Light Reflection and Refraction MCQs Set E on StudiesToday.com as they provide instant answers and score to help you track your progress in Science.

