Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity Notes. Designed for 2025-26, this advanced study material provides Class 10 Science students with detailed revision notes, sure-shot questions, and detailed answers. Prepared by expert teachers and they follow the latest CBSE, NCERT, and KVS guidelines to ensure you get best scores.
Advanced Study Material for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity
To achieve a high score in Science, students must go beyond standard textbooks. This Class 10 Chapter 8 Heredity study material includes conceptual summaries and solved practice questions to improve you understanding.
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity Notes and Questions
ACCUMULATION OF VARIATION DURING REPRODUCTION
By virtue of being the progeny of the parent, the progeny individual, need not just be the replica of what its parents are. (Inheritance of characters from the parents to the progeny (i.e. , Heredity) ensures the passing of the parental characters to the progeny). The difference or change in the characteristics between the individuals is called Variation. Human population
shows a great deal of variation. Inheritance from the previous generation provides both a common basic body design, and subtle changes in it, for the next generation. The second generation will have differences that they inherit from the first generation, as well as newly created differences.
The below figures shows Creation of diversity over succeeding generations. The original organism at the top will give rise to, say, two individuals, similar in body design, but with subtle differences. Each of them, in turn, will give rise to two individuals in the next generation. Each of the four individuals in the bottom row will be different from each other.
While some of these differences will be unique, others will be inherited from their respective parents, who were different from each other.
Q1. If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Ans: Trait ‘B’. Percentage of any gene in a population increases from generation to generation.
Q2. How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Ans: During reproduction (also inaccuracies in DNA replications), many variations occur in the offspring. Some individuals have more favourable variations than the other. Such individuals survive and pass these variations on their progeny. For example, let us consider the population of beetles. Due to certain conditions, a colour arised during reproduction so that one beetle is green in colour (instead of red). This beetle can pass this colour to its progeny. Crows now cannot see these green-coloured beetles on green leaves and hence, their population become more than that of red-coloured beetles.
HEREDITY
The progeny produced through the reproductive process is similar to its parents, in body design, function etc., The rules of heredity determine the process by which the traits and the
characteristics are relatively inherited. “
The inheritance of characteristics through generation is called heredity”
The inheritable characteristics may be morphological/anatomical/physiological/ reproductive and are also known as traits. If we take a very close look at the rules of inheritance, both father and mother contribute equal amount of genetic material to the child. This means that each trait can be influenced by both paternal and maternal genetic material – i.e, DNA.
RULES FOR THE INHERITANCE OF TRAITS – MENDEL’S CONTRIBUTIONS
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884) worked out the first ever scientific experimental study on heredity. Mendel, an Austrian Augustinian monk observed variations in the characteristics of garden pea plant (Pisum sativum) which he had cultivated in his monastery garden. Mendel was curious to find out the results of crossing of pea plants with the variation in traits. The visible contrasting characters that Mendel observed in the garden pea plants were given below:
MENDEL’S MONOHYBRID CROSS
Mendel selected the garden pea plant, Pisum sativum for his experiments. He selected tall and dwarf plants and allowed them to grow naturally. As pea plants produce seeds only by self pollination, he observed that tall plants produced always tall plants generation after generation under natural condition.Similarly, dwarf plants produced always dwarf plants generation after generation. Hence, he termed the tall and dwarf plants as wild types or pure breeding varieties. Then he crossed a tall plant with a dwarf plant, produced progeny and calculated the percentage of tallness and dwarfness in subsequent generations. When a pure breeding tall plant was crossed with a pure breeding dwarf plant, all plants were tall in the first filial generation (F1) i.e., there was not any medium height plants or dwarf plants. This means that only one of the parental traits were seen and not the mixture of the two. When
such a F1 tall plant was allowed to have self pollination, both the tall and dwarf plants appeared in second filial generation (F2). in the ratio of 3:1.
This indicates that both tallness and dwarfness were inherited in the F1 plants but only tallness trait was expressed.
The first experiment of Mendel considering the inheritance of a single trait (Height of the plant Tall/Dwarf) is called Monohybrid Cross.
Expression of morphological characters as tall or dwarf plant, violet or white flower is called Phenotype.
The expression of gene (or Chromosomal make up) of an individual for a particular trait is called Genotype.
POINTS TO REMEMBER:
- Heredity: The passing of traits from the parents to offspring is called heredity. Genotype: The complete set of genes in an organism’s genome is called genotype.
- Phenotype: The observable characters in an organism make the phenotype. Phenotype is a result of genotype’s interaction with the environment. Due to this reason, many phenotypes are not inheritable.
- Acquired Traits: Traits; which are acquired due to interaction with the environment; are called acquired traits. Acquired traits are not inheritable.
- Inheritable Traits: Traits; which can be expressed in subsequent generations; are called inheritable traits. Such traits bring a change in the genotype of the organism and hence become inheritable.
MENDEL'S FIRST LAW
Law of Segregation: Every individual possesses a pair of alleles for a particular trait. During gamete formation, a gamete receives only one trait from the alleles. A particular trait can be dominant or recessive in a particular generation.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution MCQs
Question. When a red flowered homozygous pea plant is crossed with a white flowered plant what colour is produced in F1 generation in mirabilis jalapa.
(A) Red
(B) White
(C) Pink
(D) Red and white
Answer : B
Question. Analogous organs have a :
(A) Common embryonic origin but perform different functions
(B) Different embryonic origin and perform different functions
(C) Common embryonic origin and perform similar functions
(D) Different embryonic origin but perform similar functions
Answer : D
Question. The evidence of evolution is based on
(A) paleontology
(B) embryology
(C) anatomically
(D) all of these
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following is a vestigial structure in python ?
(A) Teeth
(B) Scales
(C) Hind limbs
(D) Poison glands
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following can you call atavism ?
(A) Wings of bat
(B) Fins of fish
(C) Cervical fistula of man
(D) Flippers of whale
Answer : C
Question. Mendel formulated the law of purity of gametes on the basis of
(A) dihybrid cross
(B) monohybrid cross
(C) back cross
(D) test cross
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following is a pair of homologous organs ?
(A) Lungs of rabbit and gills of rohu
(B) Wings of bat and wings of butterfly
(C) Pectoral fin of whale and fore limb of horse
(D) Wings of grasshopper and wings of crow
Answer : C
Question. The character that proves that frogs have evolved from fishes is :
(A) The ability to swim in water
(B) The tadpole larva in frogs which resembles the fishes in many characters
(C) Similarity in the shape of the head
(D) None of these
Answer : B
Question. The term for similarity in organ structure seen in great diversity is :
(A) Homology
(B) Identical
(C) Analogy
(D) Symmetrical
Answer : A
Question. The term evolution in biology means that
(A) fossils are old
(B) life began in Sea
(C) living things constantly change
(D) none of the above
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is used for dating the bones ?
(A) C14
(B) I121
(C) K32
(D) All of these
Answer : A
Question. Analogous structures are :
(A) Structurally similar
(B) Functionally similar
(C) Structurally and functionally similar
(D) Normally non-functional
Answer : B
Question. Homologous structures have
(A) similar origin & dissimilar functions
(B) dissimilar origin but similar functions
(C) similar origin & similar functions
(D) dissimilar origin and dissimilar structures
Answer : A
Question. Fossils are
(A) fovea in the retina of vertebrate eye
(B) remains of organisms presents in the rocks
(C) the fossa present in the bones
(D) foramens through which nerves pass
Answer : B
Question. Connecting link between Reptiles and Birds is
(A) Dimetrodon
(B) Dodo
(C) Archaeopteryx
(D) Sphenodon
Answer : C
Question. In a dihybrid cross four phenotypes form in the ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1, because of
(a) dominance of one phenotype in each pair of contrasting traits
(b) independent assortment of the genes of contrasting traits
(c) crossing over of genes
(d) mixed effect of dominance and independent assortment.
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following represents the characteristic of a pleiotropic gene?
(a) Controls sexual characters.
(b) Present only in prokaryotes.
(c) Controls one character in association with the other.
(d) Control more than one character.
Answer. D
Question. Fossils are dated now by
(A) stratigraphic position
(B) amount of calcium residue
(C) association with other animals
(D) radioactive carbon contents
Answer : D
Question. Evolution is the best defined by
(A) inheritance of acquired characters
(B) descent with modifications
(C) spontaneous generation
(D) struggle for existence
Answer : B
Question. Mendel conducted his famous breeding experiments by working on
(a) Drosophila
(b) Pisum sativum
(c) Escherichia coli
(d) all of these.
Answer. B
Question. The main reason for Mendel’s success in discovering the principles of inheritance was
(a) he considered each character separately
(b) he was lucky not to encounter with linkage problem
(c) the plant was pure breeding
(d) all of these.
Answer. D
Question. Why were pea plants more suitable than dogs for Mendel’s experiments ?
(a) There were no pedigree records of dogs.
(b) Pea plants can be self-fertilised.
(c) All pea plants have only two chromosomes.
(d) Dogs have many genetic traits.
Answer. B
Question. Which one is not a vestigial organ in man ?
(A) Vermiform appendix
(B) Plica semilunaris
(C) Ear muscles
(D) Epiglottis
Answer : D
Question. A segment of DNA providing information for a protein is called
(a) nucleus
(b) chromosomes
(c) trait
(d) gene.
Answer. D
Question. Which one of these is likely to have been absent in free form at the time of origin of life ?
(A) Oxygen
(B) Hydrogen
(C) Ammonia
(D) Methane
Answer : A
Question. An allele is said to be dominant if
(a) it is expressed in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions
(b) it is expressed only in second generation
(c) it is expressed only in heterozygous condition
(d) it is expressed only in homozygous condition.
Answer. A
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Case Based MCQs
Case : Read the following and answer the following questions.
Refer to the schematic representation of the albinism that is an inherited condition caused by recessive allele (a). ‘A’ is the dominant allele for the normal condition. The inheritance of certain genetic traits for two or more generations is represented in a pedigree or family tree.
Study the given pedigree chart and answer the following questions.
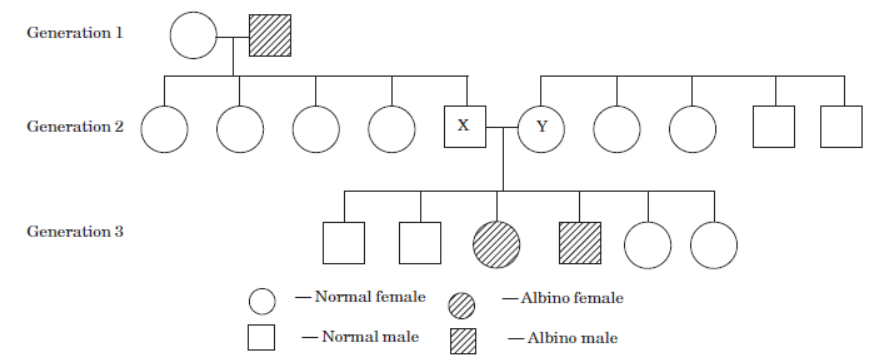
Question. Which of the following could be the genotypes of X and Y?
X Y
(a) AA AA
(b) AA Aa
(c) Aa Aa
(d) aa aa
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following could be the genotype of generation - 1 male and female?
Male Female
(a) AA aa
(b) aa AA
(c) Aa aa
(d) AA AA
Answer. B
Question. If X married an albino female, then what is the probability that their children would be albino?
(a) 0
(b) 0.125
(c) 0.25
(d) 0.5
Answer. D
Question. If Y married a normal homozygous male, then what is the probability that their children would be albino?
(a) 0
(b) 0.125
(c) 0.25
(d) 0.5
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following could be the genotype of offsprings produced by cross of X and Y?
(a) AA, Aa, aa
(b) aa, aa
(c) Aa, Aa
(d) AA, AA
Answer. A
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name two human traits that show variations.
Answer. Colour of eyes and shape of external ears.
Question. What is a gene?
Answer. Gene is the unit of inheritance. It is a segment of the chromosome which controls hereditary characteristics.
Question. Give an example where sex determination is regulated by environmental factors.
Answer. In garden lizards, sex of the organism is determined by environmental factor such as temperature.
Question. How do genes control traits?
Answer. Genes carry information for the the production of proteins which, on the other hand, control the various body characteristics.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and evolution Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Differentiate between inherited and acquired traits.
Answer. Differences between inherited and acquired traits are as follows
| Inherited traits | Acquired traits |
| These are obtained from the parents. | These are developed during the life of an individual. |
| These are genetic variations. | These are somatic variations. |
| These develop due to crossing over phenomenon and mutations. | These develop due to use and disuse of organs and direct effect of environment. |
| These are passed on from one generation to the other. | These are lost with the death of the individual. |
Question. Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome?
Answer. Genotype of human female is 44 + XX. Human female is homogametic. During meiosis, at the time of gamete formation, only one X chromosome enters in each gamete.
Hence, all female gametes have genotype (22 + X).
Question. An individual inherits different traits from his parents. On what basis classification of traits as dominant and recessive is done?
Answer. A trait which is able to express itself both in homozygous as well as heterozygous conditions is called a dominant trait,e.g., tallness is a dominant trait in pea plant. A trait which expresses itself only in homozygous condition, but remains suppressed in heterozygous condition is called recessive trait, e.g., dwarfness is the recessive trait in a pea plant.
Question. Which type of organisms will have more variations – sexually or asexually reproducing organisms? Justify.
Answer. Sexually reproducing organisms will show more variations as genetic material is exchanged between homologous pair of chromosomes during crossing over. However, during asexual reproduction, mutations are the only means of variations during DNA replication which are not very common and thus may lead to very little variation.
Question. “The chromosome number of the sexually reproducing parents and their offspring is the same.” Justify this statement.
Answer. Gametes formation involves meiosis or reduction division. The gamete mother cell is diploid (2n), i.e., it has two sets of chromosomes. This single diploid cell divides by meiosis to form 4 haploid (n) daughter cells. Each daughter cell becomes a gamete, either male or female. Each gamete possesses single set of chromosomes. Fusion of these gametes results in the formation of a zygote having a double set of chromosomes i.e., diploid (2n) (one set of paternal and the other set maternal). Thus the number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remains constant.
Question. Crossing of a pea plant with purple flower and pea plant with white flowers, produces 50 plants with only purple flowers. On selfing, the plants produced 470 plants with purple flowers and 160 with white flowers. Explain the genetic mechanism accounting for the above results.
Answer. In this breeding experiment, ratio of purple to white flowers is approximately 3 : 1 in F2 generation. So the ratio is according to Mendelian monohybrid cross. The cross further explains the following facts:
(i) F1 is represented only by dominant trait, i.e., purple flowered plants.
(ii) Both the traits, i.e., purple and white flower colour show segregation and thus appear in F2 generation.
Question. In which generation does the segregation of allelic phenotype takes place?
Answer. In F1 generation both alleles come together in hybrid but only dominant character is expressed. In F2 generation, on selfing of F1 hybrids, these alleles segregate. As a result,dominant (pure and hybrid) and recessive (pure) phenotypes are segregated.
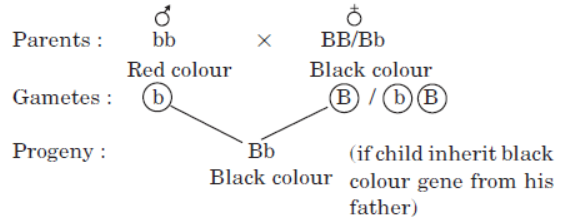
Question. The gene for red hair is recessive to the gene for black hair. What will be the hair colour of a child if he inherits a gene for red colour from his mother and a gene for black hair from his father? Express with the help of flow chart.
Answer. The hair colour of child will be black. This can be illustrated as follows:
Question. Differentiate between genotype and phenotype.
Answer. Differences between genotype and phenotype are as follows :
| Characters | Genotype | Phenotype |
| Definition | Genotype is the gene complement of an organism, i.e. TT or Tt for a tall plant. | It is the expression of a character, e.g. tall plant. |
| Change | Genotype remain unchanged. | Phenotype may change under the effect of environment. |
| Observation | It cannot be studied directly. It can be ascertained from ancestry or by studying progeny obtained by mating. | Phenotype can be observed directly. |
| Similarity | Organisms with different genotypes may have similar phenotypes, e.g. tallness with TT or Tt genotypes. | Organisms with different phenotypes are usually with different genotypes. |
Question. Explain the law of purity of gametes.
Answer. Principle of purity of gametes is also known as principle or law of segregation. According to this law, the two unit factors of a character which remains together in an individual do not get mixed up and keep their distinct identity. They separate during gamete formation so that each gamete receives only one factor or gene for each character and is always pure.
Please click the link below to download CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity and evolution Notes.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Notes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Sure Shot Questions A |
| Class 10 Science Electricity Exam Notes |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity Study Material
Students can find all the important study material for Chapter 8 Heredity on this page. This collection includes detailed notes, Mind Maps for quick revision, and Sure Shot Questions that will come in your CBSE exams. This material has been strictly prepared on the latest 2026 syllabus for Class 10 Science. Our expert teachers always suggest you to use these tools daily to make your learning easier and faster.
Chapter 8 Heredity Expert Notes & Solved Exam Questions
Our teachers have used the latest official NCERT book for Class 10 Science to prepare these study material. We have included previous year examination questions and also step-by-step solutions to help you understand the marking scheme too. After reading the above chapter notes and solved questions also solve the practice problems and then compare your work with our NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science.
Complete Revision for Science
To get the best marks in your Class 10 exams you should use Science Sample Papers along with these chapter notes. Daily practicing with our online MCQ Tests for Chapter 8 Heredity will also help you improve your speed and accuracy. All the study material provided on studiestoday.com is free and updated regularly to help Class 10 students stay ahead in their studies and feel confident during their school tests.
Our advanced study package for Chapter Chapter 8 Heredity includes detailed concepts, diagrams, Mind Maps, and explanation of complex topics to ensure Class 10 students learn as per syllabus for 2026 exams.
The Mind Maps provided for Chapter Chapter 8 Heredity act as visual anchors which will help faster recall during high-pressure exams.
Yes, teachers use our Class 10 Science resources for lesson planning as they are in simple language and have lot of solved examples.
Yes, You can download the complete, mobile-friendly PDF of the Science Chapter Chapter 8 Heredity advanced resources for free.
Yes, our subject matter experts have updated the Chapter Chapter 8 Heredity material to align with the rationalized NCERT textbooks and have removed deleted topics and added new competency-based questions.

