Read and download the CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Assignment Set A for the 2025-26 academic session. We have provided comprehensive Class 12 Biology school assignments that have important solved questions and answers for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes. These resources have been carefuly prepared by expert teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS syllabus guidelines.
Solved Assignment for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes
Practicing these Class 12 Biology problems daily is must to improve your conceptual understanding and score better marks in school examinations. These printable assignments are a perfect assessment tool for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes, covering both basic and advanced level questions to help you get more marks in exams.
Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 Solved Questions and Answers
Question: The controlled use of biological agents, such as live organisms or enzymes from organisms to produce products and processes useful to humans is called as
a) biochemistry
b) molecular biology
c) biotechnology
d) microbiology
Answer: c
Question: In the naming of restriction enzymes, the first letter of the name is derived from ..... A .... and next two letters from the ..... B ..... and fourth letters from the name of ..... C .... of .... D .... from which the enzymes are extracted.
A to D in the statement can be
A B C D
a) genus species strain bacteria
b) species genus strain bacteria
c) genus species variety eukaryote
d) species genus variety eukaryote
Answer: a
Question: EFB stands for
a) European Federation of Biotechnology
b) Eurasian Federation of Biotechnology
c) East Asia Federation of Biotechnology
d) Ethiopian Federation of Biotechnology
Answer: a
Question: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) needs
a) DNA template
b) Primers
c) Taq polymerase
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: The cutting of DNA by ……… results in the fragments of DNA. Choose the appropriate option.
a) restriction endonucleases
b) exonuclease
c) endonuclease
d) anhydro L-galactose
Answer: a
Question: The specific sequence of DNA that initiate replication of alien DNA in rDNA technology is called as
a) initiation sequence
b) origin of replication
c) origin of DNA
d) initiation of DNA
Answer: b
Question: The enzymes, commonly used in genetic engineering are
a) restriction endonuclease and polymerase
b) endonuclease and ligase
c) restriction endonuclease and ligase
d) ligase and polymerase
Answer: c
Question: Restriction endonuclease binds to DNA and cuts two strands of double helix at specific points in their
a) sugar-phosphate backbone
b) hydrogen bond
c) glycosidic bonds
d) None of the above
Answer: a
Question: Genetic engineering techniques include
a) altering genetic material
b) sequencing genetic material
c) studying genetic material
d) None of the above
Answer: a
Question: Restriction enzyme cuts the DNA strand a little away from the centre of palindrome site between
a) same two bases on same strand
b) same two bases on opposite strand
c) opposite bases on same strand
d) opposite bases on opposite strand
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following methods(s) is used to introduce foreign DNA into plant host cells?
a) Gene gun method
b) Gel electrophoresis
c) Elution
d) Extension
Answer: a
Question: Which of the following option (s) is not correct regarding Eco RI enzyme?
a) Restriction endonuclease enzyme
b) Isolated from Escherichia coli RY13
c) Cuts at specific position within the DNA
d) None of the above
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following techniques is most commonly used to separate DNA molecules by size?
a) Chromatography
b) PCR
c) RFLP
d) Gel electrophoresis
Answer: d
Question: In gel electrophoresis, the separated bands of DNA are cut out and extracted from the gel piece. This step is called
a) elution
b) origin of replication
c) competency
d) transformation
Answer: a
Question: How many fragments will be generated, if a closed circular DNA molecule is digested using a restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on the DNA?
a) 4
b) 6
c) 7
d) 5
Answer: b
Question: In recombinant DNA technique, the term vector refers to a
a) donor DNA, it is identified and picked up through electrophoresis
b) plasmid transfers DNA into host cell
c) collection of entire genome in the form of plasmid
d) enzyme, cuts the DNA at specific sites
Answer: b
Question: Stirred-tank bioreactors are advantageous over shake flasks because they
a) provide high temperature and pH
b) provide better aeration and mixing properties
c) do not allow the entry of CO2
d) are easy to operate
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following is used in recombinant DNA technique?
a) Cell wall of virus
b) Gene which produces capsid of virus
c) Bacteriophage
d) Capsid of virus
Answer: c
Question: The different basic steps of genetically modifying an organism are given below randomly.
I. Identification of DNA with desirable genes.
II. Transfer of the DNA to its progeny.
III. Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host.
IV. Introduction of identified DNA into the host.
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of steps?
a) I, II, III and IV
b) I, IV, III and II
c) III, IV, II and I
d) I, III, IV and II
Answer: b
Question: The function of ori in a vector is
a) help in replication of linked DNA
b) control copy number of the linked DNA
c) help in selecting recombinants
d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: d
Question: If recombinant DNA carrying antibiotic resistance gene (e.g. ampicillin) is transferred into E. coli cell, the host cell is transformed into ampicillin resistant cells. The ampicillin resistant gene in this case is called a
a) vectors
b) plasmid
c) selectable marker
d) cloning sites
Answer: c
Question: A single PCR amplification cycle involves
a) denaturation
b) extension
c) annealing
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: The method(s) that is/are used to differentiate recombinants and non-recombinants is/are
a) antibiotic affected gene
b) insertional inactivation
c) gene cloning
d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: b
Question: In insertional inactivation, the recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of
a) b-galactosidase
b) tetracycline resistant gene
c) restriction enzyme
d) ampicillin resistant gene
Answer: a
Question: The different steps involved in the process of recombinant DNA technology are given below randomly? Arrange these in correct order.
I. Extraction of the desired gene product.
II. Amplification of the gene of interest.
III. Isolation of a desired DNA fragment.
IV. Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector.
V. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host.
Correct order is
a) I, II, III, IV and V
b) III, II, IV, V and I
c) II, IV, V, III and I
d) I, IV, V, III and II
Answer: b
Question: Agrobacterium tumefaciens delivers a piece of DNA into dicot plant. The piece of DNA is called as
a) rDNA
b) T-DNA
c) mDNA
d) cDNA
Answer: b
Question: The DNA used as a carrier for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA into a suitable host is called
a) cloning vector
b) vehicle DNA
c) gene carrier
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question: The treatment of host cell with divalent cation leads to the
a) change in permeability of DNA
b) increased efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
c) decreased efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
d) change in permeability of host
Answer: b
Question: RNA is removed by the treatment with
a) ribonuclease
b) protease
c) chitinase
d) cellulase
Answer: a
Question: Protein encoding gene which is expressed in heterologous host is
a) foreign protein
b) heterologous protein
c) recombinant protein
d) alien protein
Answer: c
Question: Having become an expert on gel electrophoresis, you are asked to examine a gel for a colleague. Where would you find the smallest fragments of DNA?
a) Near the positive electrode, farthest away from the wells
b) Near the negative electrode, close to the wells
c) Near the top, near the negative pole
d) Near the middle they tend to slow-down after the first few minutes
Answer: a
Question: Stirred-tank bioreactors have been designed for the
a) purification of the product
b) addition of preservatives to the product
c) availability of oxygen throughout the biorector
d) ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel
Answer: c
Question: The components of a bioreactor are
I. an agitator system.
II. an oxygen delivery system.
III. foam control system.
IV. temperature control system.
V. pH control system.
VI. sampling ports to withdraw cultures periodically.
Choose the correct option.
a) I, II, III, IV and V
b) II, IV, V and VI
c) I, II, III, IV and VI
d) All of these
Answer: d
Question. If the bacterium does not have any insert, then the presence of chromogenic substrate, it gives :
(a) Red coloured colonies
(b) Colourless colonies
(c) Blue colonies
(d) Green colonies
Answer : C
Question. Large vessel in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products, individual enzymes etc using microbial plant, animal or human cell is:
(a) Biotank
(b) Biovessel
(c) Bioreactor
(d) None of the above
Answer : C
Question. The enzymes, which remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA are :
(a) Exonuclease
(b) Endonuclease
(c) Cellulase
(d) Hydrolase
Answer : A
Question. When a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme b-galatosidase, it results into inactivation of the enzyme gene this is called :
(a) Insert inactivation
(b) Insertional inactivation
(c) Insertional activation
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question. Group of letters that form the same words when read both forward and backward is called :
(a) Palindrome
(b) Same words
(c) Opposite words
(d) None of the above
Answer : A
Question. Which type of ends are produced by EcoRI ?
(a) Blunt ends
(b) Sticky ends
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question. The sequence which is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA is :
(a) Coding sequence
(b) Promoter sequence
(c) Terminator sequence
(d) Ori
Answer : D
Question. In gel electrophoresis the DNA fragments separate according to size (smaller the fragment size, the faster it moves) this effect is called :
(a) Sieving effect
(b) Movement effect
(c) Size effect
(d) Spooling
Answer : A
Question. Extraction, purification and packaging of products is collectively known as :
(a) Upstream processing
(b) Distillation
(c) Downstream processing
(d) Genetic engineering
Answer : C
Question. The enzymes responsible for restricting the growth of bacteriophage in E-coli were isolated in 1963, these enzyme are :
(a) DNA ligases
(b) Alkaline phosphatases
(c) DNA polymerases
(d) Restriction endonuclease
Answer : D
Question. DNA fragments are
(a) negatively charged
(b) neutral
(c) either positively or negatively charged depending on their size
(d) positively charged.
Answer: A
Question. A gene whose expression helps to identify transformed cell is known as
(a) vector
(b) plasmid
(c) structural gene
(d) selectable marker.
Answer: D
Question. What is the criterion for DNA fragments movement on agarose gel during gel electrophoresis ?
(a) The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
(b) Positively charged fragments move to farther end.
(c) Negatively charged fragments do not move.
(d) The larger the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Answer: A
Ques. A foreign DNA and plasmid cut by the same restriction endonuclease can be joined to form a recombinant plasmid using
(a) EcoRI
(b) Taq polymerase
(c) polymerase III
(d) ligase.
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following restriction enzymes produces blunt ends?
(a) SalI
(b) EcoRV
(c) XhoI
(d) HindIII
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is not a feature of the plasmids?
(a) Transferable
(b) Single-stranded
(c) Independent replication
(d) Circular structure
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is a restriction endonuclease?
(a) DNase I
(b) RNase
(c) Hind II
(d) Protease
Answer: C
Question. The introduction of T-DNA into plants involves
(a) exposing the plants to cold for a brief period
(b) allowing the plant roots to stand in water
(c) infection of the plant by Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(d) altering the pH of the soil, then heat-shocking the plants.
Answer: C
Question. Which vector can clone only a small fragment of DNA?
(a) Bacterial artificial chromosome
(b) Yeast artificial chromosome
(c) Plasmid
(d) Cosmid
Answer: C
Question. Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are
(a) T - DNA
(b) BAC and YAC
(c) expression vectors
(d) T/A cloning vectors.
Answer: B
Question. The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of
(a) insertional inactivation of alpha galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
(b) inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
(c) non-recombinant bacteria containing beta galactosidase
(d) insertional inactivation of alpha galactosidase in non-recombinant bacteria.
Answer: C
Question. DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by
(a) electrophoresis
(b) restriction mapping
(c) centrifugation
(d) polymerase chain reaction.
Answer: A
Question. A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called
(a) vector
(b) selectable marker
(c) plasmid
(d) probe.
Answer: D
Question. For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of
(a) silver or platinum
(b) platinum or zinc
(c) silicon or platinum
(d) gold or tungsten.
Answer: D
Question. Biolistics (gene-gun) is suitable for
(a) disarming pathogen vectors
(b) transformation of plant cells
(c) constructing recombinant DNA by joining with vectors
(d) DNA fingerprinting.
Answer: B
Question. In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
(a) as selectable markers
(b) to select healthy vectors
(c) as sequences from where replication starts
(d) to keep the cultures free of infection.
Answer: A
Question. Which one of the following represents a palindromic sequence in DNA?
(a) 5′ - GAATTC - 3′ (b) 5′ - CCAATG - 3′
3′ - CTTAAG - 5′ 3′ - GAATCC - 5′
(c) 5′ - CATTAG - 3′ (d) 5′ - GATACC - 3′
3′ - GATAAC - 5′ 3′ - CCTAAG - 5′
Answer: A
Question. Given below is a sample of a portion of DNA strand giving the base sequence on the opposite strands. What is so special shown in it?
5′ _____ GAATTC _____ 3′
3′ _____ CTTAAG _____ 5′
(a) Replication completed
(b) Deletion mutation
(c) Start codon at the 5′ end
(d) Palindromic sequence of base pairs
Answer: D
Question. There is a restriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does “co” part in it stand for?
(a) colon
(b) coelom
(c) coenzyme
(d) coli
Answer: D
Question. Agarose extracted from sea weeds is used in
(a) spectrophotometry
(b) tissue culture
(c) PCR
(d) gel electrophoresis.
Answer: D
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
The term “Biotechnology” refers to the use of living organisms or their products to modify human health and their human environment. For example, ‘testtube’ programme, synthesis of a gene or correcting a defective gene are all part of the biotechnology. The basis of the modern biotechnology are genetic engineering and maintenance of sterile conditions. Genetic engineering is the technique that alter the chemistry of genetic material i.e., DNA and RNA, then this genetic material is introduced into host organisms, which alter the phenotype of the host organism.
Question. The recognition sequence of the first restriction enzyme isolated was ________ base pair long.
(A) four
(B) six
(C) five
(D) two.
Answer : B
Question. The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of :
(A) Ligases
(B) Restriction enzymes
(C) Probes
(D) Selectable markers.
Answer : B
Question. Discovery of _________ molecule made genetic engineering possible.
(A) Restriction exonuclease
(B) Restriction endonuclease
(C) Ribozyme
(D) DNA polymerase
Answer : B
Question. The specific DNA sequence where EcoRI cuts is :
(A) GATTCG
(B) GAATTC
(C) GTTCAA
(D) TTCCAA.
Answer : B
Question. DNA fragments are :
(A) Positively charged
(B) Negatively charged
(C) Neutral
(D) Either positively or negatively charged depending on their size.
Answer : B
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Biotechnologists refer to Agrobacterium tumifaciens as a natural genetic engineer of plants.
Give reasons to support the statement.
Answer. This is because A. tumifaciens can transfer genes naturally by delivering a piece of T-DNA to plant cells. It has a tumour inducing plasmid.
Question. Why is the enzyme cellulase needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and not from the animal cells?
Answer. The enzyme cellulase breaks down cellulose which is present in cell walls of plants but absent in animal cells.
Question. Name the compound used for staining the isolated DNA in the gel electrophoresis.
Answer. Ethidium bromide.
Question. What is gene gun?
Answer. The instrument for bombarding micro-projectile particles (gold/tungsten particles) coated with foreign DNA, with great velocity, into a target cell is called gene gun.
Question. How does an alien DNA gain entry into a plant cell by ‘biolistics’ method?
Answer. In biolistics method, cells are bombarded with high velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA.
Question. Why EtBr is used in gel electrophoresis inspite of it being highly carcinogenic?
Answer. Ethidium bromide (EtBr) exchanges its visible range of wavelength with the invisible wavelength of DNA, to make it visible under UV light.
Question. Why is it not possible for an alien DNA to become part of a chromosome anywhere along its length and replicate normally?
Answer. Alien DNA must be linked to ori or origin of replication site to start replication.
Question. Name the host cells in which micro-injection technique is used to introduce an alien DNA.
Answer. Animal cells.
Question. Write the name of the enzymes that are used for isolation of DNA from bacterial and fungal cells respectively for Recombinant DNA technology.
Answer. Bacterial cell is treated with enzyme lysozyme.
Fungal cell is treated with chitinase.
Question. Which main technique and instrument is used to isolate DNA from any plant cell?
Answer. Centrifugation and centrifuge
Question. By using which vector, the nematode specific genes were introduced into the tobacco host plant.
Answer. By using Agrobacterium, the nematode specific genes were introduced into the tobacco host plant.
Question. Why do DNA fragments move towards the anode during gel electrophoresis ?
Answer. DNA fragments are negatively-charged.
Question. Suggest a technique to a researcher who needs to separate fragments of DNA.
Answer. Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments.
Question. Mention the role of Restriction Enzymes in Recombinant DNA technology.
Answer. To cut DNA at specific sites / Molecular scissors
Question. Mention the use of gel electrophoresis in biotechnology experiments.
Answer. Cut fragments of DNA can be segregated / separated.
Question. Name two enzymes that are essential for constructing a recombinant DNA.
Answer. Restriction enzymes / polymerase enzymes / ligase
Question. Write down the correct order of steps in polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Answer. A single PCR amplification cycle involves three basic steps : denaturation, annealing and extension.
PCR stands for a polymerase chain reaction in which multiple copies of the DNA segment, or gene of interest is synthesised in vitro.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Explain with the help of an example the relationship between restriction endonuclease and a palindromic nucleotide sequence.
Answer. Restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
Restriction endonuclease cuts the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of palindromic nucleotide sequence but between the same two bases on the opposite strands, leaving single stranded portions at the end called sticky ends.
Question. Would you like to choose an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule?
Answer. No, as exonuclease acts on the free ends of linear DNA molecule. Therefore, instead of producing DNA fragments with sticky ends, it will shorten or completely degrade the DNA fragment containing the gene of interest, and the circular plasmid (vector) will not get cut as it lacks free ends.
Question. Name the natural source of agarose. Mention one role of agarose in biotechnology.
Answer. The natural source of agarose is sea weed. Agarose is a natural polymer. It is used to develop the matrix for gel electrophoresis. It helps in the separation of DNA fragments based on their size.
Question. Restriction enzymes present in the cloning site of a vector should not have more than one recognition site. Comment.
Answer. If the restriction enzymes have more than one recognition site in a vector, then the vector itself will get fragmented on treatment with the restriction enzyme.
Question. Write any four ways used to introduce a desired DNA segment into a bacterial cell in recombinant technology experiments.
Answer. (i) The desired DNA segment is inserted into a cloning vector and the bacterial cell can be made to take it up after making them competent by treating them with specific concentration of
divalent cations such as calcium.
(ii) Microinjection
(iii) Biolistics
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vector
Question. A plasmid without a selectable marker was chosen as vector for cloning a gene.
Answer. In a gene cloning experiment, first a recombinant DNA molecule is constructed, where the gene of interest is ligated to the vector and introduced inside the host cell (transformation). Since, not all the cells get transformed with the recombinant/plasmid DNA, in the absence of selectable marker, it will be difficult to distinguish between transformants and non-transformants, because role of selectable marker is in the selection of transformants.
Question. How can DNA segments, separated by gel electrophoresis, be visualised and isolated?
Answer. The separated DNA molecules are visualised only after staining DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation. They appear as bright orange coloured bands. The separated bands of DNA (on the gel) are cut from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece. This process is called elution.
Question. Why does the ‘insertional inactivation’ method to detect recombinant DNA is preferred to ‘antibiotic resistance’ procedure?
Answer. In insertional inactivation method, the presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured
colonies in absence of an insert. Presence of an insert in the enzyme site does not produce colour.
This is because insertional inactivation of the β-galactosidase has taken place due to the insert.
Antibiotic resistance method requires duplicate plating. It is a cumbersome procedure to perform.
Question. (a) A recombinant vector with a gene of interest inserted within the gene of a-galactosidase enzyme, is introduced into a bacterium. Explain the method that would help in selection of recombinant colonies from non-recombinant ones.
(b) Why is this method of selection referred to as “insertional inactivation”?
Answer. (a) Bacteria is grown in a medium with chromogenic substrate, blue coloured colonies show no recombinations and colonies with no blue colour show presence of recombinants.
(b) Gene for the enzyme is inactivated by insertion of foreign DNA.
Question. While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Answer. If denaturation of double-stranded DNA does not take place, then primers will not be able to anneal to the template, no extension will take place, hence no amplification will occur.
Question. Why and how bacteria can be made ‘competent’?
Answer. Bacteria are made competent to accept the DNA or plasmid molecules. This is done by treating them with specific concentration of a divalent cation such as calcium to increase pore size in cell wall. The cells are then incubated with recombinant DNA on ice, followed by placing them briefly at 42°C and then putting it back on ice.
Question. DNA being hydrophilic cannot pass through the cell membrane of a host cell. Explain how does recombinant DNA get introduced into the host cell to transform the latter.
Answer. DNA being a hydrophilic molecule, cannot pass through cell membranes.
- Therefore, the bacteria should be made competent to accept the DNA molecules.
- Competency is the ability of a cell to take up foreign DNA.
- The cell is made competent by the following methods:
(i) Chemical method (ii) Physical method
Question. What modification is done in the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to convert it into a cloning vector?
Answer. T-DNA is the only essential part required to make Ti plasmid a cloning vector. The plasmid is disarmed by deleting the tumour inducing genes in the plasmid so that it becomes an effective cloning vector and remove it harmful effect.
Question. What would happen when one grows a recombinant bacterium in a bioreactor forget to add antibiotic to the medium in which the recombinant is growing bacterium?
Answer. In the absence of antibiotic, there will be no pressure on recombinants to retain the plasmid (containing the gene of your interest). Since, maintaining a high copy number of plasmids is a metabolic burden to the microbial cells, it will thus tend to lose the plasmid.
Question. Rearrange the following in the correct sequence to accomplish an important biotechnological reaction:
(a) In vitro synthesis of copies of DNA of interest
(b) Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides
(c) Enzyme DNA-polymerase
(d) Complementary region of DNA
(e) Genomic DNA template
(f) Nucleotides provided
(g) Primers
(h) Thermostable DNA-polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(i) Denaturation of dsDNA
Answer. Correct sequence is
i→ e→ b/g→ g/b→ c/b→ h/c→ f→d→ a
Question. How can the following be made possible for biotechnology experiments?
(a) Isolation of DNA from bacterial cell.
(b) Reintroduction of the recombinant DNA into a bacterial cell.
Answer. (a) By treating cell with lysozyme
(b) Microinjection/gene gun
Question. Name the source organism that possesses Taq polymerase. What is so special about the function of this enzyme?
OR
Name the organism from where the thermostable DNA polymerase is isolated. State its role in genetic engineering.
Answer. Source organism: Thermus aquaticus
The enzyme can tolerate high temperature and is thus thermostable. It does not get denatured during PCR at high temperature.
Question. How are recombinant vectors created? Why is only one type of restriction endonuclease required for creating one recombinant vector?
Answer. The construction of recombinant DNA is done by linking a gene encoding antibiotic resistance with a native plasmid. These plasmid DNA act as vectors to transfer the piece of DNA attached to it.
Only one type of restriction endonuclease is required for creating recombinant vector because when cut by the same enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have the same sticky ends, which can be joined together using DNA ligases.
Question. Name the type of bioreactor shown. Write the purpose for which it is used.
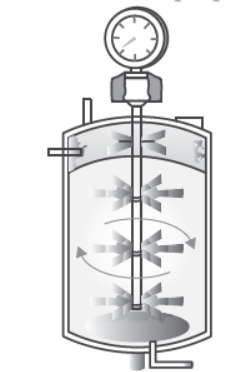
Answer. The given bioreactor is the simple stirred tank bioreactor.
Its purpose is large scale production of recombinant protein or enzymes, using microbial plants/ animals/human cells.
Question. (a) Explain how to find whether an E.coli bacterium has transformed or not when a recombinant
DNA bearing ampicillin resistant gene is transferred into it.
(b) What does the ampicillin resistant gene act as in the above case?
Answer. (a) E.coli bearing transferred recombinant DNA are first grown on ampicillin containing medium and then transferred on to a medium containing tetracycline. The transformants will grow only in ampicillin containing medium and not in tetracycline containing medium. The nontransformants,on the other hand, will grow in both the mediums.
(b) Ampicillin resistant gene acts as a selectable marker and helps in selecting the transformants.
Question. “Cotton bollworms enjoy feeding on cotton plants, but get killed when feed on Bt cotton plant”. Justify the statement.
Answer. Bt-cotton plant is a transgenic plant that produces an insecticide for bollworm. Bacillus thuringiensis is the bacterium that has a Bt gene or Cry gene
which is incorporated in the cotton plant through biotechnological methods and thus, it produces a crystalline product Bt. The product acts as a toxin when ingested by the pests as it gets activated after reaching the alkaline gut of pests and creates pores in the intestine and kills the pests. The gene protects the GMO against budworm, bollworm, beetle, borer, etc.
Question. Explain the role(s) of the following in Biotechnology :
(i) Restriction endonuclease
(ii) Gel - electrophoresis
(iii) Selectable markers in pBR322.
Answer. (i) Cuts at specific position within the DNA / cuts DNA at specific nucleotide / cuts at palindromic nucleotide sequence.
(ii) Separation of DNA fragments (under the influence of electric field).
(iii) Helps in identifying and eliminating nontransformants from transformants / selection of transformants.
Question. When the gene product is required in large amounts, the transformed bacteria with the plasmid inside the bacteria are cultured on a large scale in an industrial fermenter which then synthesizes the desired protein. This product is extracted from the fermenter for commercial use.
(a) Why is the used medium drained out from one side while fresh medium is added from the other? Explain.
(b) List any four optimum conditions for achieving the desired product in a bioreactor.
Answer. (a) To maintain the cells in their physiologically most active log/exponential phase.
(b) Temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen.
Question. (i) Why must a cell be made ‘competent’ in biotechnology experiments ? How does calcium ion help in doing so ?
(ii) State the role of ‘biolistic gun’ in biotechnology experiments.
Answer. (i) To take up the (hydrophilic) DNA from the external medium.
Divalent calcium ions increase the efficiency of the cell to take up foreign DNA through pores in the cell wall.
(ii) To introduce alien DNA into the plant cell by bombarding them with high velocity microparticles (gold or tungsten coated with DNA).
Question. Name the most commonly used bioreactor in biotechnology labs. Mention the most essential components this bioreactor must
have so as to provide the optimum conditions to the culture medium, resulting in production of large volume of desired product.
Answer. Stirred-type Agitator system, O2 delivery system, foam control system, temperature control system, pH control system.
Question. Name and explain the technique that helps in the separation of DNA fragments for
DNA recombinant technology experiments.
How can these separated DNA fragments be visualised ?
Answer. Gel electrophoresis, Since DNA fragments are negatively charged, they move towards anode (under an electric field) through a medium / matrix / agarose gel. The fragments separate (resolve) according to their sizes through sieving effect provided by agarose gel. The separated DNA fragments can be visualised after staining the DNA with ethidium bromide, followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Question. (i) Explain the significance of ‘palindromic nucleotide sequence‘ in the formation of recombinant DNA.
(ii) Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
Answer. (i) The palindromic nucleotide sequence is the recognition (specific) sequence present both on the vector and on a desired / alien DNA for the action of the same (specific) restriction endonuclease to act upon.
Question. Write the functions of the following in biotechnology.
(i) Polymerase chain reaction technique
(ii) Restriction endonucleases
(iii) Bacterium Thermus aquaticus.
Answer. (i) Multiple copies of gene of interest can be obtained.
(ii) They can cut DNA molecule at a particular point by recognizing a specific sequence of base pairs. Thus they are useful in forming recombinant DNA.
(iii) Thermus aquaticus is the source of Taqpolymerase
which remains active during high temperature induces denaturation of DNA
in PCR technique and therefore allows chain reaction to proceed.
Restriction Enzymes Questions and Answers
Ques. Which Enzyme Produces sticky Ends in DNA for Foreign DNA Insertion?
Ans. Restriction Endonuclease
Ques. Name the enzyme that joins the sticky ends to form recombinant DNA.
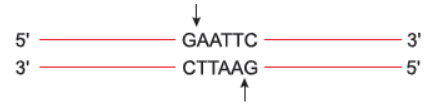
5' —— G↓AATTC —— 3'
Ans. DNA Ligase
Ques. 3' —— CTTAA↑G —— 5'
Name the Enzyme that cuts at the points marked in arrows.
Ans. EcoRI
Ques. Match the following:
a)Ti Plasmid i)Removes wall of Fungus.
b)Biolistics or gene gun ii)Beta galactosidase gene
c)Insertional inactivation iii)insertion of recombinant DNA in Plant cell
d)Chitinase iv)Agarobacterium tumifaciens.
Ans.
a)Ti Plasmid iv)Agarobacterium tumifaciens
b)Biolistics or gene gun iii)insertion of recombinant DNA in Plant cell
c)Insertional inactivation ii)Beta galactosidase gene
d)Chitinase i)Removes wall of Fungus.
Ques. Ori sequence is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.True/False
Ans. True
Cloning Vectors Questions and Answers
Ques. Name two selectable markers used in cloning vector.
Ans. Amp-r & tet-r
Ques. Extention /Denaturation/annealing ,arrange the steps of PCR in proper order according to their occurance.
Ans. Denaturation/annealing/ Extention
Ques. Exonucleases remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA.True/False
Ans. True
Ques. Chomogenic substance produces blue colour by the action of beta galactosidase in non recombinant colony. True/False
Ans. True
Ques. Match the followings:-
For the removal of cell wall
a)Lysozyme i)Plant cells
b)Cellulase ii)Fungus
c)Chitinase iii)Bacteria
Ans.
a)Lysozyme iii)Bacteria
b)Cellulase i)Plant cells
c)Chitinase ii)Fungus
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Assignment Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Biology
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Assignment
Access the latest Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes assignments designed as per the current CBSE syllabus for Class 12. We have included all question types, including MCQs, short answer questions, and long-form problems relating to Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes. You can easily download these assignments in PDF format for free. Our expert teachers have carefully looked at previous year exam patterns and have made sure that these questions help you prepare properly for your upcoming school tests.
Benefits of solving Assignments for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes
Practicing these Class 12 Biology assignments has many advantages for you:
- Better Exam Scores: Regular practice will help you to understand Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes properly and you will be able to answer exam questions correctly.
- Latest Exam Pattern: All questions are aligned as per the latest CBSE sample papers and marking schemes.
- Huge Variety of Questions: These Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes sets include Case Studies, objective questions, and various descriptive problems with answers.
- Time Management: Solving these Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes test papers daily will improve your speed and accuracy.
How to solve Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Assignments effectively?
- Read the Chapter First: Start with the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology before attempting the assignment.
- Self-Assessment: Try solving the Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes questions by yourself and then check the solutions provided by us.
- Use Supporting Material: Refer to our Revision Notes and Class 12 worksheets if you get stuck on any topic.
- Track Mistakes: Maintain a notebook for tricky concepts and revise them using our online MCQ tests.
Best Practices for Class 12 Biology Preparation
For the best results, solve one assignment for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes on daily basis. Using a timer while practicing will further improve your problem-solving skills and prepare you for the actual CBSE exam.
You can download free PDF assignments for Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets have been updated for the 2025-26 session covering all concepts from latest NCERT textbook.
Yes, our teachers have given solutions for all questions in the Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes assignments. This will help you to understand step-by-step methodology to get full marks in school tests and exams.
Yes. These assignments are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus for 2026. We have included huge variety of question formats such as MCQs, Case-study based questions and important diagram-based problems found in Chapter Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes.
Practicing topicw wise assignments will help Class 12 students understand every sub-topic of Chapter Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes. Daily practice will improve speed, accuracy and answering competency-based questions.
Yes, all printable assignments for Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format.

