Read and download the CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity And Conservation Worksheet Set B in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 12 Biology worksheets for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation
Students of Class 12 should use this Biology practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Worksheet with Answers
BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION
1 What does the term ‘Frugivorous’ mean?
2 What is the expanded form of IUCN?
3 How is the presently occurring species extinction different from the earlier mass extinctions?
4 A species-area curve is drawn by plotting the number of species against the area. How is it that when a very large area is considered the slope is steeper than that for smaller areas?
5 Why are the conventional methods not suitable for the assessment of biodiversity of bacteria?
6 What is co-extinction? Explain with a suitable example?
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Biodiversity and Conservation
Question. Term "biodiversity" was popularised by-
(a) Edward Wilson
(b) Humboldt
(c) Tilman
(d) Paul Ehrlich
Answer : A
Question. According to IUCN (2004), how many plant and animal species have been described so far -
(a) <1.5 billion
(b) >1.5 million
(c) 7.1 million
(d) 7.1 billion
Answer : B
Question. When large habitats are broken up in to small fragments due to human activities, which of the following get badly affected -
(a) Mammals and birds requiring large territories
(b) Animals with migratory habitats
(c) Animals with large bodysize
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer : D
Question. Which method is thought to be best for estimation of mirobial biodiversity -
(a) Bio statistical method
(b) Bio chemical or molecular method
(c) Paleobotanical method
(d) Culture method
Answer : B
Question. What is the contribution of India in global species diversity -
(a) 2.4 %
(b) 12 %
(c) 8.1 %
(d) 7.1 %
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is not the reason of great biodiversity in tropics ?
(a) Undisturbed climate for millions of years
(b) Less seasonal variations
(c) More nutritive soil
(d) More solar energy
Answer : C
Question. Find out the wrong match -
(a) Bioshpere reserves - 14
(b) National parks - 85
(c) Wild life sanctuaries - 448
(d) Indian Biodiversity hot spot - 3
Answer : B
Question. 'Sacred groves is also one of the important mean of Biodiversity conservation. In respect of this find out the odd one -
(a) Khasi and Jaintia - Meghalaya
(b) Aravalli hills - Rajasthan
(c) Sarguja, Chanda and Bastar - Mizoram
(d) Western Ghat - Maharashtra
Answer : C
Ques. Which one of the following is not a method of in situ conservation of biodiversity ?
(a) Sacred grove
(b) Biosphere reserve
(c) Wildlife sanctuary
(d) Botanical garden
Answer: D
Ques. Western Ghats have a large number of plant and animal species that are not found anywhere else. Which of the following terms will you use to notify such species?
(a) Endemic
(b) Vulnerable
(c) Threatened
(d) Keystone
Answer: A
Ques. All of the following are included in ‘ex-situ conservation’ except
(a) wildlife safari parks
(b) sacred groves
(c) botanical gardens
(d) seed banks.
Answer: B
Ques. Which one of the following is related to ex-situ conservation of threatened animals and plants?
(a) Biodiversity hotspots
(b) Amazon rainforest
(c) Himalayan region
(d) Wildlife safari parks
Answer: D
Ques. The region of biosphere reserve which is legally protected and where no human activity is allowed is known as
(a) buffer zone
(b) transition zone
(c) restoration zone
(d) core zone.
Answer: D
Ques. How many hotspots of biodiversity in the world have been identified till date by Norman Myers?
(a) 17
(b) 25
(c) 34
(d) 43
Answer: C
Ques. Which of the following national parks is home to the famous musk deer or hangul?
(a) Keibul Lamjao National Park, Manipur
(b) Bandhavgarh National Park, Madhya Pradesh
(c) Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary, Arunachal Pradesh
(d) Dachigam National Park, Jammu and Kashmir
Answer: D
Ques. The species confined to a particular region and not found elsewhere is termed as
(a) endemic
(b) rare
(c) keystone
(d) alien.
Answer: A
Ques. In which of the following, both pairs have correct combination?
(a) In-situ conservation : Seed Bank
Ex-situ conservation : National Park
(b) In-situ conservation : Tissue culture
Ex-situ conservation : Sacred groves
(c) In-situ conservation : National Park
Ex-situ conservation : Botanical Garden
(d) In-situ conservation : Cryopreservation
Ex-situ conservation : Wildlife Sanctuary
Answer: C
Ques. Cryopreservation of gametes of threatened species in viable and fertile condition can be referred to as
(a) in situ conservation by sacred groves
(b) in situ cryo-conservation of biodiversity
(c) in situ conservation of biodiversity
(d) advanced ex situ conservation of biodiversity.
Answer: D
Ques. An example of ex-situ conservation is
(a) national park
(b) seed bank
(c) wildlife sanctuary
(d) sacred grove.
Answer: B
Ques. Which one of the following is not used for ex-situ plant conservation?
(a) Shifting cultivation
(b) Botanical gardens
(c) Field gene banks
(d) Seed banks
Answer: A
Ques. The largest tiger reserve in India is
(a) Valmiki
(b) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam
(c) Periyar
(d) Nagarhole.
Answer: B
Ques. Which one of the following areas in India, is a hotspot of biodiversity?
(a) Eastern Ghats
(b) Gangetic Plain
(c) Sunderbans
(d) Western Ghats
Answer: D
Ques. Select the correct statement about biodiversity.
(a) The desert areas of Rajasthan and Gujarat have a very high level of desert animal species as well as numerous rare animals.
(b) Large scale planting of Bt cotton has no adverse effect on biodiversity.
(c) Western ghats have a very high degree of species richness and endemism.
(d) Conservation of biodiversity is just a fad pursued by the developed countries.
Answer: C
Ques. Sacred groves are specially useful in
(a) generating environmental awareness
(b) preventing soil erosion
(c) year-round flow of water in rivers
(d) conserving rare and threatened species.
Answer: D
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
India is divided into 10 biogeographical regions.
Varying physical conditions and species grouping.
India has rich species diversity. Tropics are rich centre of biodiversity. Warm temperature, high humidity in tropical areas provide favourable conditions throughout the years. Rich diversity is important for stability, productivity for ecosystems.
Question. Which among the following represents diversity at ecosystem level ?
(A) Genetic diversity
(B) Ecological diversity
(C) Species diversity
(D) Species evenness
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following taxon shows maximum species diversity ?
(A) Fishes
(B) Beetles
(C) Orchids
(D) Ants.
Answer : B
Question. What is the approximate ratio of animals and plant species in our country ?
(A) 3 : 1
(B) 2 : 1
(C) 1 : 3
(D) 1 : 2
Answer : B
Question. Which group represents minimum species diversity among vertebrates ?
(A) Birds
(B) Mammals
(C) Reptiles
(D) Amphibians
Answer : D
Directions : In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
(A) Both Assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A) : Tropics have more biodiversity.
Reason (R) : Climate of tropical region is more seasonal.
Answer : C
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What is the expanded form of IUCN?
Answer. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.
Question. Name the type of biodiversity represented by the following:
(i) 50,000 different strains of rice in India
(ii) Estuaries and alpine meadows in India.
Answer. (i) Genetic diversity
(ii) Ecological diversity
Question. Eichhornia crassipes is an alien hydrophyte introduced in India. Mention the problems posed by this plant.
Answer. When an alien hydrophyte Eichhornia crassipes were introduced unintentionally, they turned invasive and caused decline or extinction of indigenous species.
Question. Give an example of a plant which came into India as a contaminant and is a cause of pollen allergy.
Answer. Parthenium / Carrot grass.
Question. Why are mango trees unable to grow in temperate climate?
Answer. Because temperature affects the basal metabolism/ physiological function of the plant not adapted to low temperature of temperate climate. Mango trees are not able to grow in temperate below 30 degree, thus cannot grow in temperate climate.
Question. Name the type of biodiversity represented by the following :
(i) 1000 varieties of mangoes in India.
(ii) Variations in terms of potency and concentration of reserpine in Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different regions of Himalayas.
Answer. (i) Genetic diversity.
(ii) Genetic diversity.
Question. Write the importance of cryopreservation in conservation of biodiversity.
Answer. By cryopreservation, the reproductive parts of rare species can be preserved.
Question. Name the unlabelled areas ‘a’ and ‘b’ of the pie chart representing biodiversity of vertebrates showing the proportionate number of species of major taxa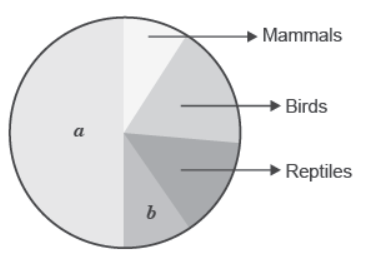
Answer. a → Fishes;
b → AmphibiAnswer.
Question. Name the alien fish species which is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes in our rivers.
Answer. Clarias gariepinus (African catfish)
Question. What is mass extinction?
Answer. Due to natural calamities like volcanic eruptions, prolonged drought, heavy rains, earthquakes, asteroid collision, etc., a large number of species become extinct at the same time which is called mass extinction.
Question. What is meant by alien species?
Answer. Non-native powerful species which invade a new area are known as alien species.
Question. What is genetic diversity?
Answer. It is the measure of variation in genetic information contained in the organisms.
Question. Why is genetic variation important in the plant Rauwolfia vomitoria?
Answer. Genetic variation affects the variation in potency and concentration of the drug reserpine in the medicinal plant Rauwolfia.
Question. According to David Tilman, greater the diversity greater is the primary productivity. Can you think of a very low diversity man-made ecosystem that has high productivity.
Answer. Agricultural fields like wheat field or paddy field which are also examples of monoculture practices.
Question. Identify ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the figure given below representing proportionate number of major vertebrate taxa.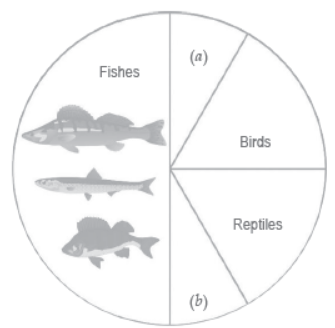
Answer. a → Mammals
b → Amphibians
Question. Define biodiversity.
Answer. The occurrence of different types of genes, gene pools, species, habitats and ecosystems in a particular place and various parts of earth is called biodiversity.
Question. Name any two sanctuaries in India.
Answer. Keoladeo Ghana bird sanctuary, Bharatpur (Rajasthan) and Periyar sanctuary (Kerala).
Question. About 200 species of Cichlid fish became extinct when a particular fish was introduced in Lake Victoria of Africa. Name the invasive fish.
Answer. Nile perch.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Justify with the help of an example where a deliberate attempt by humans has led to the extinction of a particular species.
Answer. The Nile perch introduced into Lake Victoria in East Africa, eventually led to the extinction of an ecologically unique assemblage of more than 200 species of cichlid fish in the lake // Abingdon tortoise in Galapagos islands became, extinct, after goats were introduced due to greater browsing efficiency of goats // Connell’s field experiment showed that the competitively superior barnacle Balanus, excludes smaller barnacle Chathamalus // Over exploitation by man, caused extinction of Stellar’s sea cow / Passenger pigeon.
Question. Where would you expect more species diversityin tropics or in polar regions? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Answer. Tropics have more species biodiversity than that of the polar regions. The maximum biodiversity in the tropical regions is due to the following reasons :
(i) Prolonged evolutionary time : The tropics have remained undisturbed in the past and therefore evolved more species diversity.
(ii) High productivity : There is more solar energy available in tropics which contributes directly to more productivity, population sizes and indirectly to greater species diversity.
Question. List the features that make a stable biological community.
Answer. The features of a stable community are as follows :
(i) Communities should have greater biodiversity for greater stability.
(ii) It should be able to prevent invasion by alien species.
(iii) It should be able to restore itself in a short period of time.
(iv) Variations should be minimal in the community.
Question. How does over-exploitation of beneficial species affect biodiversity ? Explain with the help of one example.
Answer. Humans have always depended on nature for food and shelter, but when need turns to ‘greed’, it leads to over-exploitation of natural resources. Many species extinctions in the last 500 years (Steller’s sea cow, passenger pigeon) were due to overexploitation by humans.
Presently, many marine fish populations around the world are over harvested, endangering the continued existence of some commercially important species.
Question. Write what was the percentage of forest cover of India at the beginning and at the end of the twentieth century. How different is it from the one recommended by the National Forest Policy of our country ?
Answer. Beginning of 20th century – 30%
End of 20th century – 19.4%
Recommendations were 33% for the plains and 67% for the hills (thus forest cover shrunk substantially)
Question. Co-extinction and introduction of alien species too are responsible for the loss of biodiversity. Explain, how.
Answer. Co-extinction : When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in the obligatory way, also becomes extinct Introduction of alien species : When alien species are introduced, some of them turn invasive (because of not having their predator there), and hence cause decline / extinction of indigenous species.
Question. Alien species are highly invasive and are a threat to indigenous species. Substantiate this statement with any three examples.
Answer. (i) Nile perch introduced into Lake Victoria in East Africa led to the extinction of Cichlids fish.
(ii) Parthenium/Lantana/Eichhornia are invasive plants and pose a threat to indigenous species.
(iii) Introduction of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) to aquaculture is a threat to Indian catfishes.
Detailed Answer :
(i) The Nile perch introduced into Lake Victoria in east Africa led eventually to the extinction of an ecologically unique assemblage of more than 200 species of cichlid fish in the lake.
Since, cichlid fish became extinct and so the Nile perch, not finding any food for itself, died too.
(ii) The environmental damage caused a threat to our native species by invasive weed species like carrot grass (Parthenium), Lantana and water hyacinth (Eichhornia).
(ii) The recent illegal introduction of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus for aquaculture purposes is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes in our rivers.
Question. With the help of one example, explain how does alien species invasion cause biodiversity loss.
Answer. When alien species are introduced, some of them become invasive, compete with the native species and cause extinction of indigenous species.
(i) Partheniun, Lantana and Eichhornia are the exotic species of plants that have invaded India and caused environmental damage. They pose threats to the survival of many of our native species.
(ii) Introduction of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) for aquaculture purposes is posing a threat to our indigenous catfish Clarias batrachus.
Question. Why certain regions have been declared as biodiversity ‘hot spots’ by environmentalists of the world ? Name any two (hotspot) regions of India.
Answer. Faced with the conflict between development and conservation, many nations find it unrealistic and economically not feasible to conserve all their biological wealth. Invariably, the number of species waiting to be saved from extinction far exceeds the conservation resources available.
Hence, conservationists have declared certain regions as “hot spots” for maximum protection of these regions which have high levels of species richness and high degree of endemism.
Example, Western Ghats, Sri Lanka and Himalaya.
Question. (a) “India has greater ecosystem diversity than Norway.” Do you agree with the statement ?
Give reasons in support of your answer.
(b) Write the difference between genetic biodiversity and species biodiversity that exists at all levels of biological organization.
Answer. (a) Yes
India / tropical region : (i) are less seasonal / more constant / more predictable.
(ii) promote niche specialisation leading to greater bio-diversity.
(iii) Species diversity increases as we move towards equator.
(iv) More number of species exist.
Norway / temperate region : (i) more seasonal / less constant / less predictable.
(ii) do not promote niche specialisation leading to low bio-diversity.
(iii) Species diversity decreases as we move away from equator.
(iv) Less number of species exist.
(b) (i) Genetic diversity : Diversity / variation within a species over its distributional range/ (same explanation with the help of a correct examples)
(ii) Species diversity : Diversity / variation at a species level (same explained with the help of a correct example).
Detailed Answer :
(a) Yes, India has greater ecosystem diversity than Norway. It is because India lies primarily in the tropical and sub-tropical zone while Norway lies near the Arctic region. This exposes the India to greater amounts of sunlight and thus greater level of ecosystem diversity.
(b) Difference between genetic diversity and species diversity :
Genetic diversity Species diversity
It refers to the number of genes and their alleles found in organisms. It refers to the numbers of species per unit area.
It increases as we move up the biological organization. It may or may not increase to a greater extent as we move up the biological organization.
Long Answer Questions
Question. (i) Taking one example each of habitat loss and fragmentation, explain how are two responsible for biodiversity loss.
(ii) Explain two different ways of biodiversity conservation.
Answer. (i) Habitat loss—Amazon rain forest destroyed for soya beans cultivation for growing grass land, for grazing cattle / colonisation of Pacific islandsextinction of 2000 species of native birds.
Fragmentation—By human activity— migratory birds and animals are affected.
(ii) Ex situ, Threatened organism are taken out from the natural habitat and placed in special setting with care and protection. e.g., Zoological park / botanical garden / wild safari.
In situ, Threatened organisms are conserved in their natural habitat e.g. National park / Biosphere reserves.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Populations Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Populations Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Biology Class 12 Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 12. We suggest that Class 12 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Biology.
Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Biology to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 12 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 12 Biology study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 12 Biology worksheets for Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 12 Biology test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

