Learning Objectives
The learner will be able to,
• Recognize the stages of glucose breakdown and its redox system.
• Differentiate aerobic respiration from anaerobic respiration.
• Describe the conditions under which respiration occurs.
• Realize the role of mitochondria as power house of the cell.
• Understand, how ATP molecules are generated during respiration.
Chapter Outline
14.1 Gaseous exchange
14.2 Structure of ATP
14.3 Redox reactions
14.4 Types of Respiration
14.5 Stages of Respiration
14.6 Respiratory Quotient
14.7 Anaerobic Respiration
14.8 Factors Affecting Respiration
14.9 Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Plant and Animal Interdependence
In biosphere, plants and animals are complementary systems which are integrated to sustain life. In plants, oxygen enters through the stomata and it is transported to cells, where oxygen is utilized for energy production. Plants require carbon dioxide to survive, to produce carbohydrates and to release oxygen through photosynthesis. These oxygen molecules are inhaled by human through the nose, which reaches the lungs where oxygen is transported through the blood and it reaches cells. Cellular respiration takes place inside the cell. A specialized respiratory system is present in animals but is absent in plants for delivering oxygen inside the cell. But the cellular respiration stages are similar in both plants and animals which hint at evolutionary divergence.
If you are sleeping under a tree during night time you will feel difficulty in breathing. During night, plants take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide and as a result carbon dioxide will be abundant around the tree. This process of CO2 evolution is called respiration. This process takes place during day time also (Figure 14.1). It is accompanied by breakdown of substrates and release of energy. In this chapter, respiration process in plants at cellular level will be dealt with.
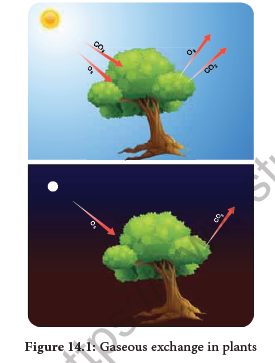
14.1 Gaseous Exchange
14.1.1 Respiration
The term respiration was coined by Pepys (1966). Respiration is a biological process in which oxidation of various food substances like carbohydrates,proteins and fats take place and as a result of this, energy is produced where O
2 is taken in and CO
2is liberated. The organic substances which are oxidised during respiration are called respiratory substrates. Among these, glucose is the commonest respiratory substrate. Breaking of C-C bonds of complex organic compounds through oxidation within the cells leads to energy release. The energy released during respiration is stored in the form of ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate) as well as liberated heat. Respiration occurs in all the living cells of organisms. The overall process of respiration corresponds to a reversal of photosynthesis.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (686 K cal or 2868 KJ)
Depending upon the nature of respiratory substrate, Blackman divided respiration into,
1. Floating respiration
2. Protoplasmic respiration
When carbohydrate or fat or organic acid serves as respiratory substrate and it is called floating respiration. It is a common mode of respiration and does not produce any toxic product. Whereas respiration utilizing protein as a respiratory substrate,it is called protoplasmic respiration.Protoplasmic respiration is rare and it depletes structural and functional proteins of protoplasm and liberates toxic ammonia.
14.1.2 Compensation point
At dawn and dusk the intensity of light is low. The point at which CO2 released in respiration is exactly compensated by CO2 fixed in photosynthesis that means no net gaseous exchange takes place, it is called compensation point. At this moment, the amount of oxygen released from photosynthesis is equal to the
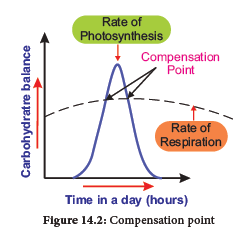
amount of oxygen utilized in respiration.The two common factors associated with compensation point are CO2 and light (Figure 14.2). Based on this there are two types of compensation point.They are CO2 compensation point and
light compensation point. C3 plants have compensation points ranging from 40-60 ppm (parts per million) CO2 while those of C4 plants ranges from 1-5 ppm CO2.
14.2 Structure of ATP
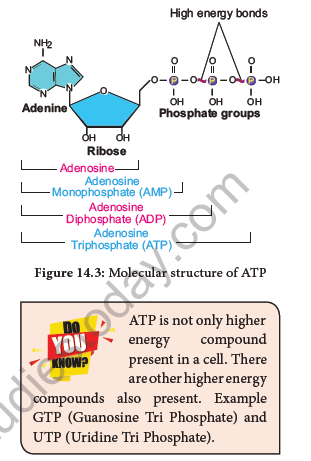
Respiration is responsible for generation of ATP. The discovery of ATP was made by Karl Lohman (1929). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of a base-adenine, a pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups.Out of three phosphate groups the last two are attached by high energy rich bonds (Figure 14.3). On hydrolysis, it releases energy (7.3 K cal or 30.6 KJ/ATP) and it is found in all living cells and hence it is called universal energy currency of the cell. ATP is an instant source of energy within the cell. The energy contained in ATP is used in synthesis carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. The energy transformation concept was established by Lipman (1941).
14.3 Redox Reactions
NAD+ + 2e -+ 2H+ → NADH + H+
FAD + 2e- + 2H+ → FADH2
When NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide-oxidised form) and FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) pick up electrons and one or two hydrogen ions (protons), they get reduced to NADH + H+ and FADH2 respectively. When they drop
electrons and hydrogen off they go back to their original form. The reaction in which NAD+ and FAD gain (reduction) or lose (oxidation) electrons are called redox reaction (Oxidation reduction reaction). These reactions are important in cellular respiration.

14.4 Types of Respiration
Respiration is classified into two types as aerobic and anaerobic respiration (Figure 14.4)
14.4.1 Aerobic respiration
Respiration occurring in the presence of oxygen is called aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration, food materials like carbohydrates, fats and proteins are completely oxidised into CO2, H2O and energy is released. Aerobic respiration is a very complex process and is completed in four major steps:
1. Glycolysis
2. Pyruvate oxidation (Link reaction)
3. Krebs cycle (TCA cycle)
4. Electron Transport Chain (Terminal oxidation).
14.4.2 Anaerobic respiration
In the absence of molecular oxygen glucose is incompletely degraded into either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid (Table 14.1). It includes two steps:
1. Glycolysis
2. Fermentation
14.5 Stages of Respiration
1. Glycolysis-conversion of glucose into pyruvic acid in cytoplasm of cell.
2. Link reaction-conversion of pyruvic acid into acetyl coenzyme-A in mitochondrial matrix.
3. Krebs cycle-conversion of acetyl coenzyme A into carbon dioxide and water in the mitochondrial matrix.

