Learning Objectives:-
The learner will be able to,
• Explore the parts of the flowering plants
• Differentiate vegetative morphology and reproductive morphology
• Compare various root systems and their modifications
• Understand the stem modifications and functions
• Interpret the structure of leaf and functions of leaf
Chapter Outline
3.1 Habit
3.2 Plant habitat
3.3 Life Span
3.4 Parts of a flowering plant
3.5 Root System
3.6 Shoot system
3.7 Leaf
The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Plant morphology also known as external morphology deals with the study of shape, size and structure of plants and their parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds). Study of morphology is important in taxonomy. Morphological features are important in determining productivity of crops. Morphological characters indicate the specific habitats of living as well as the fossil plants and help to correlate the distribution in space and time of fossil plants. Morphological features are also significant for phylogeny.
Plant Morphology can be studied under two broad categories:
A. Vegetative morphology – It includes shoot system and root system
B. Reproductive morphology – It includes Flower/inflorescence, Fruit and Seed
A. Vegetative morphology
Vegetative morphology deals with the study of shape, size and structure of plants and their parts roots, stems and leaves. To understand the vegetative morphology the following important components are to be studied. They are,
1) Habit, 2) Habitat and 3) Lifespan.
3.1 Habit
The general form of a plant is referred to as habit. Based on habit plants are classified into herbs, shrubs, climbers (vines) and trees.
I. Herbs
Herbs are soft stemmed plants with less wood or no wood. According to the duration of their life they may be classified as annuals, biennials and perennials.Perennial herbs having a bulb, corm, rhizome or tuber as the underground stem are termed as geophytes. Example: Phyllanthus amarus, Cleome viscosa.
II. Shrubs
A shrub is a perennial, woody plant with several main stems arising from the ground level. Example: Hibiscus
III. Climbers (Vine)
An elongated weak stem generally supported by means of climbing devices are called Climbers (vines) which may be annual or perennial, herbaceous or woody. Liana is a vine that is perennial and woody.Liana’s are major components in the tree canopy layer of some tropical forests.Example: Ventilago, Entada, Bougainvillea.
IV. Trees
A tree is a stout, tall, perennial, woody plant having one main stem called trunk with many lateral branches. Example: mango, sapota, jack, fig, teak. If the trunk remains unbranched it is said to be caudex. Example: Palmyra, coconut.
3.2 Plant habitat
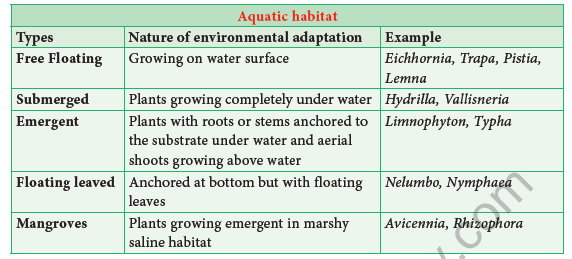
Depending upon where plants grow habitats may be classified into major categories: I. Terrestrial and II.Aquatic.
I. Terrestrial
Plants growing on land are called terrestrial plants. The following table illustrate the types of terrestrial plants classified based on their environmental adaptation.
II. Aquatic
Plants that are living in water environment are called aquatic plants or hydrophytes.
3.3 Life Span
Based on life span plants are classified into 3 types. They are annual, biennial and perennial

I. Annual (Therophyte or Ephemerals)
A plant that completes its life cycle in one growing season. Example: Peas, maize,water melon, groundnut, sunflower, rice and so on.
II. Biennial
A plant that lives for two seasons, growing vegetatively during the first season and flowering and fruiting during the second season. Example: Onion, Lettuce, Fennel, Carrot, Radish, Cabbage and Spinach.
III. Perennial (Geophyte)
A plant that grows for many years that flowers and set fruits for several seasons during the life span. When they bear fruits every year, they are called polycarpic. Example: mango, sapota. Some plants produce flowers and fruits only once and die after a vegetative growth of several years. These plants are called monocarpic. Example: Bamboo, Agave, Musa, Talipot palm.
3.4 Parts of a flowering plant
Flowering plants are called “Angiosperms” or Magnoliophytes. They are sporophytes consisting of an axis with an underground “Root system” and an aerial “Shoot System”. The shoot system has a stem, branches and leaves. The root system consists of root and its lateral branches.
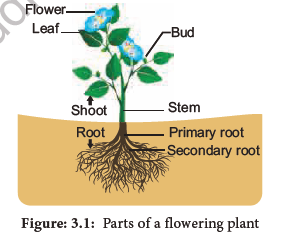
3.5 Root System
The root is non-green, cylindrical descending axis of the plant that usually grows into the soil (positively geotropic).It develops from the radicle which is the first structure that comes out when a seed is placed in the soil. Root is responsible for absorption of water and nutrients and anchoring the plant.
I. Characteristic features
• Root is the descending portion of the plant axis.
• Generally non-green in colour as it lacks chlorophyll.
• Does not possess nodes, internodes and buds (Exception in sweet potato and members of Rutaceae, roots bear buds which help in vegetative propagation)
• It bears root hairs (To absorb water and minerals from the soil)
• It is positively geotropic and negatively phototropic in nature.
II. Regions of root
Root tip is covered by a dome shaped parenchymatous cells called root cap.It protects the meristematic cells in the apex. In Pandanus multiple root cap is present. In Pistia instead of root cap root pocket is present. A few millimeters above
the root cap the following three distinct zones have been classified based on their meristematic activity.
1. Meristematic Zone
2. Zone of Elongation
3. Zone of Maturation

