Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds Assignment Set D for the 2025-26 academic session. We have provided comprehensive Class 10 Science school assignments that have important solved questions and answers for Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound. These resources have been carefuly prepared by expert teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS syllabus guidelines.
Solved Assignment for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound
Practicing these Class 10 Science problems daily is must to improve your conceptual understanding and score better marks in school examinations. These printable assignments are a perfect assessment tool for Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound, covering both basic and advanced level questions to help you get more marks in exams.
Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound Class 10 Solved Questions and Answers
Very Short answer Type Questions
Question. Write the name and formula of second member of homologous series with general formula CnH2n+2
Answer: C2H6, Ethane
Question. Write the name and formula of second member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n–2.
Answer: C3H4, Propyne
Question. Draw electron dot structure of NH3 molecule. Predict the total no. of bonds around N-atom.
OR
A molecule of ammonia has the formula NH3. Predict the total number of bonds present around nitrogen atom.
Answer:
Question. Write the next homologue of each of the following: (i) C2H4, (ii) C4H6
Answer: (i) C3H6, (ii) C5H8
Question. Write the structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in the molecule.
Answer:
Question. Write the molecular formula of alcohol derived from butane.
Answer: C4H9OH or CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (Butan-1-ol)
Question. Write the molecular formula of an alkyne containing 10 atoms of hydrogen.
Answer: C6H10
Question. Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Answer: C4H10, Butane (CH3CH2CH2CH3)
Question. Which of the following organic compounds belong to the same homologous series:
C2H6, C2H6O, C2H6O2, CH4O
Answer: C2H6O (C2H5OH) and CH4O (CH3OH)
Question. The formula of citric acid is shown below:
State the name of —COOH functional group in citric acid.
Answer: Carboxylic acid
Question. Why covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity?
Answer: It is because covalent compounds do not form ions.
Question. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula, CO2?
Answer:
Question. Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
Answer: Carbon since it forms strong covalent bond, due to smaller atomic size.
Question. Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group Cl.
Answer: The general formula of the compounds having – Cl functional group is CnH2n + 1Cl. Its two members are:
(i) CH3Cl (ii) CH3 – CH2 – Cl
Question. Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and the 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is methane (CH4).
Answer: (i) CH3CH3 (Ethane); where n is 2
(ii) CH3CH2CH3 (Propane); where n is 3
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane (C4H10).
Answer: There are 13 covalent bonds.
Question. State the valency of the carbon atom in (i) an alkane (ii) an alkyne.
Answer: (i) Four, (ii) Four
Question. Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
Answer: Benzene is cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
Question. The molecular formula of ‘A’ is C10H18 and ‘B’ is C18H36. Name the homologous series to which they belong.
Answer: ‘A’ belongs to Alkynes, ‘B’ belongs to Alkenes.
Question. Write the next homologous of CH3CH2OH and HCOOH.
Answer: CH3 – CH2 – CH2OH. Propanol and, CH3COOH ethanoic acid
Short answer Type Questions
Question. How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of ethane, C2H6?
Answer: There are seven covalent bonds in a molecule of ethane:
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compound:
(i) CH3COCH3 (ii) C2H5COOH
Answer: (i) CH3COCH3 —- >C=O ketonic group (ii) C2H5COOH — (-COOH) Carboxylic acid
Question. Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general Formula CnH2n.
Answer: CnH2n: alkene Name: propene(2nd member) formula: C3H6
Question. Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following:
C3H6, C5H10, C4H10, C6H14, C2H4
Answer: Saturated hydrocarbons:
General formula= CnH2n+2
C4H10, C6H14
Question. Write the electron dot structure of ethane molecule, C2H4
Answer:
Question. Draw the structure of ethanoic acid molecule, CH3COOH
Answer: Structure of ethanoic acid molecule:
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds.
(i) C2H5Cl (ii) C2H5OH
Answer: Functional group present in:
(i) C2H5Cl – chloro(halide) (ii) C2H5OH —- Alcohol
Question. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule.
Answer: Name of an alcohol: Propanol
Structure of propanol: H2C – CH2 – CH2 – OH
Question. What are isomers? Draw the structure of two isomers of butane C4H10.
Answer: The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as isomers. Isomers of butane C4H10.
Question. What are homologous series of carbon compounds? Write the molecular formula of two Consecutive members of homologous series of aldehydes.
Answer: A series of carbon compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for Hydrogen on a carbon chain is called homologous series. There is difference of –CH2 in nThe molecular formula of two nearest compounds of a homologous series. Each such Series has same general molecular formula and has a general scientific name. There Is a difference of 14u in the molecular mass of two nearest compound of a series?
Members of homologous series of aldehydes:
H – CHO
CH3 – CHO
C2H5 – CHO
Long answer Type Questions
Question. List two reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Name the type of Bonding found in most of its compounds. Why does carbon form compounds mainly by this kind of bonding?
Answer: Carbon forms a large number of compounds.
The two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds are:
-catenation: it’s a unique property of carbon atoms to form bonds with other atoms of Carbon giving rise to large molecules.
-Tetravalency: Since carbon has four valencies, it is capable of bonding with four other atoms Of carbon or atoms of some other monovalent elements.
Carbon compounds are formed mainly by sharing of electron with covalent bond because carbon atoms have 4 electrons in their outermost shell. So, needs to gain or lose Electrons to achieve inert gas electronic configuration. It could gain four electron forming C4-anion. But it is difficult due to energy consideration. It could lose 4 electrons to form C4+cation. But it is difficult due to energy consideration.
Because of this reason carbon Share their electron to form covalent bond only.
Question. What are covalent compounds? Why are they different from ionic compound? List any Three characteristics properties.
Answer: (i) The chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms is known as a covalent bond. The molecules formed by sharing of electrons between two or more same atoms or between two or more non-metals are called covalent compound.
(ii)Covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds as ionic compounds are Formed by transfer of electrons.
Characteristics of covalent compound:
(i) Covalent compounds usually have low melting and boiling point because force Of attraction between molecules is very weak.
(ii) Covalent compounds are usually insoluble in water but they are soluble in organic compound.
(iii) Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity as they do not contain ions.
Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound
Case/Passage – 1
There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the waist. A waste product Q formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in the liver is brought into organ P through blood by an artery R. The numerous tiny filters S present in organ P clean the dirty blood y removing the waste product Q. The clean blood goes into circulation through a vein T. The waste substance Q, other waste salts, and excess water form a yellowish liquid U which goes from organ P into a bag-like structure V through two tubes W. This liquid is then thrown out of the body through a tube X.
Question: What are tiny filters S known as?
Answer: c
Question: What is (i) organ P, and (ii) waste substance Q?
Answer: a
Question: Name
(i) liquid U
(ii) structure V
(iii) tubes W, and
(iv) tube X.
Answer: d
Question: Name (i) artery R, and (ii) vein T.
Answer: b
Case/Passage – 2
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
Question: The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a peak at point D.
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race.
Respiration in athletics
The blood of an athlete was tested before, during and after a 400m race:
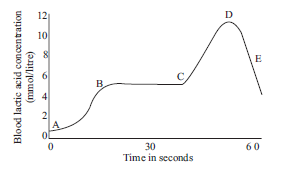
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event?
Which of the following processes explains this event?
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(c) Fermentation
(d) Breathing
Answer: b
Question: Study the graph below that represents the amount of energy supplied with respect to the time while an athlete is running at full speed
Choose the correct combination of plots and justification provided in the following table.
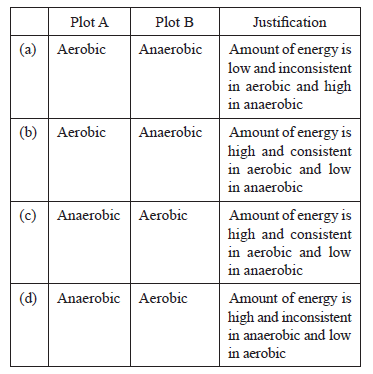
Answer: b
Question: The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration are:
(i) presence of oxygen
(ii) release of carbon dioxide
(iii) release of energy
(iv) release of lactic acid
(a) (i), (ii) only
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) only
(c) (ii), iii), iv) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer: c
Question: Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by
(a) Breathing
(b) Tissue respiration
(c) Organ respiration
(d) Digestion of food
Answer: b
Question: Study the table below and select the row that has the incorrect information.
Aerobic Anaerobic
(a) Location Cytoplasm Mitochondria
(b) End Porduct CO2 and H2O Ethanol and CO2
(c) Amount of ATP High Low
(d) Oxygen Needed Not needed
Answer: a
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Revision Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Revision Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Assignment |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Assignments Collection |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Energy Crossword Puzzle Assignment |
More free study material for Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound Assignment
Access the latest Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound assignments designed as per the current CBSE syllabus for Class 10. We have included all question types, including MCQs, short answer questions, and long-form problems relating to Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound. You can easily download these assignments in PDF format for free. Our expert teachers have carefully looked at previous year exam patterns and have made sure that these questions help you prepare properly for your upcoming school tests.
Benefits of solving Assignments for Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound
Practicing these Class 10 Science assignments has many advantages for you:
- Better Exam Scores: Regular practice will help you to understand Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound properly and you will be able to answer exam questions correctly.
- Latest Exam Pattern: All questions are aligned as per the latest CBSE sample papers and marking schemes.
- Huge Variety of Questions: These Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound sets include Case Studies, objective questions, and various descriptive problems with answers.
- Time Management: Solving these Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound test papers daily will improve your speed and accuracy.
How to solve Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound Assignments effectively?
- Read the Chapter First: Start with the NCERT book for Class 10 Science before attempting the assignment.
- Self-Assessment: Try solving the Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound questions by yourself and then check the solutions provided by us.
- Use Supporting Material: Refer to our Revision Notes and Class 10 worksheets if you get stuck on any topic.
- Track Mistakes: Maintain a notebook for tricky concepts and revise them using our online MCQ tests.
Best Practices for Class 10 Science Preparation
For the best results, solve one assignment for Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound on daily basis. Using a timer while practicing will further improve your problem-solving skills and prepare you for the actual CBSE exam.
You can download free PDF assignments for Class 10 Science Chapter Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets have been updated for the 2025-26 session covering all concepts from latest NCERT textbook.
Yes, our teachers have given solutions for all questions in the Class 10 Science Chapter Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound assignments. This will help you to understand step-by-step methodology to get full marks in school tests and exams.
Yes. These assignments are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus for 2026. We have included huge variety of question formats such as MCQs, Case-study based questions and important diagram-based problems found in Chapter Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound.
Practicing topicw wise assignments will help Class 10 students understand every sub-topic of Chapter Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound. Daily practice will improve speed, accuracy and answering competency-based questions.
Yes, all printable assignments for Class 10 Science Chapter Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compound are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format.

