Read and download the CBSE Class 10 Biology How Do Organisms Reproduce Worksheet Set F in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 10 Science worksheets for Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce
Students of Class 10 should use this Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Worksheet with Answers
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: Name the life process of an organism which helps in the growth of its population.
Answer: Reproduction
Question: Organisms have a varied body design. Name the property which gives the basic difference in body design.
Answer:Errors in DNA copying.
Question: What is pollination?
Answer: The process of transfer of pollen grains from the stamen to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
Question: Name the type of cells which undergo regeneration.
Answer:Specialised cells called regenerative cells which can make large number of new cells.
Question: Name the nucleic acids.
Answer: DNA and RNA are the two nucleic acids present in the living cells.
Question: What happens when a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length?
Answer:A mature spirogyra filament breaks into smaller fragments and each fragment grows into a new plant.This process of reproduction is called fragmentation.
Question: What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate in the reproduction process?
Answer:DNA copying will lead to variation in populations which helps in evolution of the species.
Question: Name the causative agent of the disease ‘kala-azar’ and its mode of asexual reproduction.
Answer:Leishmania causes ‘kala-azar’. It reproduces by binary fission in a definite orientation.
Question: Regeneration is not possible in all types of animals. Why?
Answer:Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells which are present in few animals which can reproduce by regeneration.
Question: How does Plasmodium reproduce? Is this method sexual or asexual?
Answer:Plasmodium is a single celled organism which reproduces by the process of multiple fission. Multiple fission (i.e. breaking up of a single cell into many daughter cells) is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Question: The mode of reproduction depends on which feature of the organism.
Answer: The mode of reproduction depends on the body design of the organism.
Question: Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessary for the individual?
Answer: Accumulation of variations after several generations results in new set of traits required for survival. As they show results after many generations so they are not important for individual.
Question: What is DNA?
Answer:DNA means deoxyribo nucleic acid. It lies in the cell nucleus, which is the source of information for making proteins and different proteins lead to different body designs.
Question: Name the method by which hydra reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Answer: Hydra reproduces by budding. It is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Question: If a woman is using a copper−T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer: No. Using a copper-T will not provide a protection from sexually transmitted diseases, as it does not prevent the entry of semen. It only prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
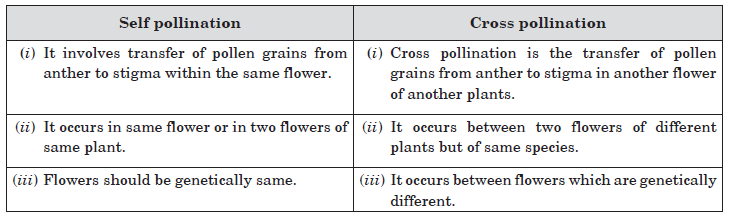
Question: Differentiate between self pollination and cross pollination.
Answer:
Question: List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction.
Answer:
(i) Two parents are involved
(ii) Two dissimilar gametes are formed
(iii) Variations are produced
(iv) Occurs in higher and some of lower organisms
(v) Fertilisation is needed for zygote formation
(vi) It is a slow process.
Question: List three techniques that have been developed to prevent pregnancy. Which one of these is not meant for males? How does the use of these techniques have a direct impact on health and prosperity of a family?
Answer: The three techniques which prevent pregnancy are:
(i) Barrier method, (ii) Chemical method (iii) Surgical method
Chemical methods are not for males.
The use of contraceptive have a direct effect on the health and prosperity of the family.
(i) To avoid unwanted pregnancy–if the woman is not physically or mentally prepared to bear a child her health gets adversely affected.
(ii) Contraception allows the parents to space the birth of two children and helps in family planning.
(iii) This way they can decide how many children to have and allows them to bring them up properly especially in case of limited resources. (or any other)
Question: Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings. Give three reasons in support of the statement.
Answer:Reproduction is an energy consuming process which is not essential for the survival of an individual.But it is the most important characteristic of all living beings, because of the following reasons:
(i) Reproduction helps in increasing the number of members of a population.
(ii) By replacing the dead members with the new ones, it minimises the risk of extinction of a species.
(iii) It brings about variations in species, thus leading to their evolution.
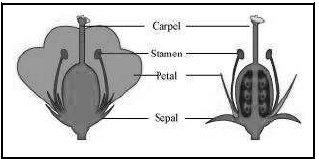
Question: Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.
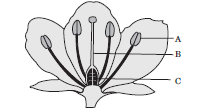
Answer:
‘A’ is anther. It contains pollen grains.
‘B’ is style. It allows growth in pollen tube up to the ovary from the stigma.
‘C’ is ovary. It contains ovules.
Question: Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located? Explain in brief the structure of female reproductive parts.
Answer:
The male reproductive part of an angiosperm is stamen. The female reproductive part is pistil/carpel,which consist of stigma, style and ovary.
Stigma: It is the site for deposition of pollen grains after pollination.
Style: It is a tube that allows growth of pollen tube to reach the ovary.
Ovary: It contains ovules that develops into seeds.
Question: Why are testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Mention the endocrine and exocrine functions of the testes.
Answer:
Sperm formation takes place at a lower temperature than body temperature therefore testes are located outside the body and its temperature is 2°C below the body temperature.
Functions of Testes:
Endocrine Function: The production of testosterone hormone.
Exocrine Function: The production of sperms.
Question: (a) State in brief the functions of following female reproductive system
(i) Ovary, (ii) Fallopian tube, (iii) Uterus
(b) State in brief the functions of following male reproductive system
(i) Scrotum, (ii) Testes, (iii) Vas deferens
Answer:
(a) (i) Ovary: It produces ova and female sex hormones.
(ii) Fallopian tube: It is the site of fertilisation and transfer of female gamete from the ovary.
(iii) Uterus: Implantation of zygote and it keeps foetus till complete development.
(b) (i) Scrotum: It protects testes.
(ii) Testes: It produces sperms.
(iii) Vas deferens: It delivers sperms from testes to urethra.
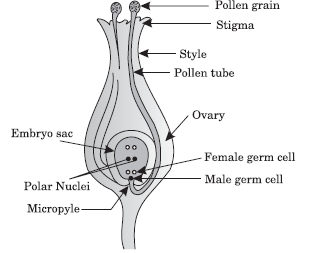
Question: Why must pollination occur before fertilisation? How is pollination different from fertilisation? What does a pollen contain inside?
Answer: Pollination must occur before fertilisation as it has to reach the male gametes present in pollen grain which will germinate to form a pollen tube and carry the male gametes to the ovum. Pollination is different from fertilisation because here the pollen grain with its male gametes just reaches the stigma, whereas fertilisation of male gamete to ovum results in formation of diploid zygote which is the foundation of new generation.
Question: Define the term pollination. Differentiate between self pollination and cross pollination. What is the significance of pollination?
Answer: Pollination: The process in which pollen is transferred from stamen to the stigma is called pollination.
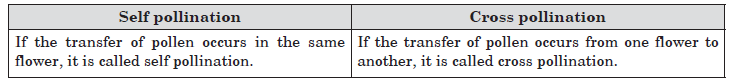
Significance: After the pollen lands on suitable stigma, it needs to reach the female germ cells in the ovary where fertilisation takes place, zygot is formed. Zygot divides several times to form embryo with in ovule which develops a tough coat around it called seed coat and seed is formed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form fruit.
Question: (a) List in tabular form two differences between binary fission and multiple fission.
(b) What happens when a mature spirogyra filament attains considerable length.
Answer:
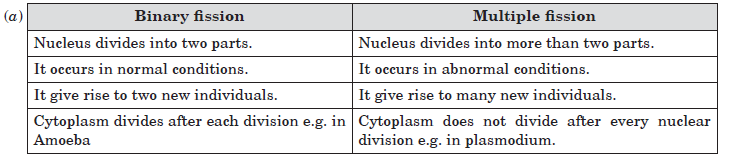
(b) A mature spirogyra filament breaks into smaller fragments and each fragment grows into a new plant. This process of reproduction is called fragmentation.
Question: In the context of reproduction of species state the main difference between fission and fragmentation.Also give one example of each.
Answer:
Question: How do sperms reach the female genital tract? Where fertilisation and implantation of the embryo does take place? For how long does the embryo remain attached to uterine walls?
Answer: Sperms travel upwards through uterus to oviduct where they may meet an ovum and hence fertilise it. Fertilisation takes place in oviduct to give rise to single celled zygote. The zygote
divides to become multicellular embryo which gets fixed in uterus. The embryo remains attached to uterine walls throughout gestation period which is about 40 weeks in humans.
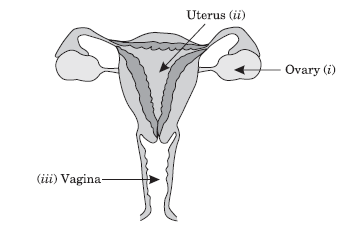
Question: Draw the diagram of a female reproductive system and label the part which:
(i) Produces egg in female germ cell (ii) Part where zygote is implanted.
(iii) Path for entry of sperms.
Answer: (i) Ovary produces eggs
(ii) Zygote is implanted in womb or uterus
(iii) Entry of sperms through vagina.
Question: What are the two roles of testosterone?
Answer: (i) Testosterone regulates formation of sperms.
(ii) The appearance of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty like beard, genital hair, change in voice is due to testosterone.
Question: Draw a labelled diagram of longitudinal section of pistil of flower showing germination of pollen grains on the stigma.
Answer:
Question: List any four steps involved in sexual reproduction and write its two advantages.
Answer:
The four main steps involved in sexual reproduction are:
(i) In the first stage of sexual reproduction, meiosis process occurs and the number of chromosomes reduces from diploid (2n = 46) to haploid (n = 23) for each gamete.
(ii) In the second stage, there is transfer of male gametes into the female body.
(iii) In the third stage, the two gametes will fuse together after fertilisation, a single male gamete will fuse with a female gamete. i.e. fertilisation process takes place.
(iv) After fusion of male and female gametes, they form a zygote, in which the number of chromosomes is restored to diploid (2n = 46).
The two main advantages of sexual reproduction are:
(i) There are more variations, which leads to better adaptability of the offsprings in the environment.
(ii) Promotes the diversity in the characteristics of offspring, because it results by fusion of gametes.
Question: List three distinguishing features between sexual and asexual types of reproduction in tabular form.
Answer:
Question: Mention the changes observed in flower after fertilisation.
Answer:
(i) Ovary ripens and developed into fruit.
(ii) Ovules develop into seed.
(iii) Petals and sepals wither and drop.
(iv) Stigma, style and stamens dry up and fall off.
Question: Describe the structure and function of placenta.
Answer: Structure of placenta: It is a special disc like tissue embedded in mother’s uterine wall and connected to the foetus/embryo.
Functions of placenta: It provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen/nutrients to pass from mother’s body to the developing/developed embryo/foetus and also helps in passing the waste from the foetus/embryo to the mother’s body.
Question: What is the role of following in reproduction?
(i) DNA (ii) Ovulation (iii) Fertilisation
(iv) Puberty (v) Contraception
Answer: (i) Variation (ii) Egg production (iii) Zygote formation
(iv) Attainment of sexual maturity (v) Birth control
Question: Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer:
Question: (a) (i) Write full form of DNA.
(ii) State the role of DNA in the cell nucleus.
(iii) What will be the effect if the information of the DNA is changed?
(b) Explain the importance of DNA copying in reproduction.
Answer:
(b) (i) Deoxy Ribonucleic Acid
(ii) It helps in synthesis of protein and transfer of genetic characteristics.
(iii) Proteins will be changed.
(b) Body designs are similar due to DNA copying.
DNA cell nucleus carry information for synthesis of protein.
If DNA copying will not take place then body design will change.
Question: What is STD? Name two STDs.
Answer: STD is Sexually Transmitted Disease. Two STDs are syphilis and gonorrhoea.
Question: What is vegetative propagation? State two advantages and two disadvantages of this method.
Answer:Vegetative propagation is a mode of asexual reproduction in which new plants are obtained from vegetative parts of the plants. It does not involve the production of seeds or spores for the propagation of new plants.
Two advantages of vegetative propagation are:
(i) Plants which do not produce seeds are propagated by this method, for example sugarcane, potato, etc.
(ii) Vegetative propagation is a cheaper, easier, rapid method of propagation in plants than growing plants from their seeds. For example, lilies grow very slowly and take 4 to 7 years to develop flowers when grown through their seeds, but flowers are produced only after a year or two when grown vegetatively.
Two disadvantages of vegetative propagation are:
(i) As there is no genetic variation, there is no chance of development of new and better varieties.
(ii) The vegetatively propagated plants are more prone to diseases that are specific to the species. This can result in the destruction of an entire crop.
Question: Why does menstruation occur ?
Answer: Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flows out every month through the vagina. This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg. Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg does not get fertilised, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly and gets released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina.
Question: List any two differences between pollination and fertilisation
Answer:
Pollination Fertilisation
1. Transfer of pollen grain from anther to stigma of a flower. Fusion of pollen nucleus and ovule in the ovary.
2. Its types are self pollination and cross pollination. Its types are internal and external fertilisation.
Question: Suggest three contraceptive methods for birth control, which is essential for the health and prosperity of a country. State the basic principle involved in each.
Answer:
(i) Barrier method: Condom is placed on the erect penis of male before sexual intercourse. In female,a thin rubber disc is placed in the vagina, which covers the opening of cervix.
(ii) Oral pills: Birth control pills can be taken to prevent pregnancy.
(iii) Surgical methods: Use of copper-T in females, surgically implanted at the opening of the cervix, prevents entry of sperms.
Vasectomy in males, tubectomy in females can also help in population control. In vasectomy, sperm ducts are cut. In tubectomy, oviducts are tied, blocked or cut. Sperms cannot reach the ova and thus pregnancy is avoided.
Question: Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your Answer:
Answer:Any one of the following differences:
(i) In sexual reproduction two opposite sexes are involved whereas in asexual reproduction only one individual is involved.
(ii) In sexual reproduction male and female gametes formation take place whereas in asexual reproduction no gamete formation occurs.
- Sexually reproducing organisms have better chances of survival.
- This is because more variations are generated.
Question: State the basic requirements for sexual reproduction. Write the importance of such reproduction in nature.
Answer: The basic requirements for sexual reproduction to take place are involvement of two parents and fusion of their haploid gametes. In the sexual reproduction, a new individual is formed by the fusion of two haploid gametes, one from the male parent and the other from the female parent. Since the new individual formed is diploid in nature, the gametes must be formed by meiosis, so that chromosome number can be reduced to half. When fusion of gametes occurs, the two nuclei of these two gametes fuse and the chromosome number is restored to normal. The zygote, thus formed is diploid in nature.
Importance of sexual reproduction:
Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes coming from both the parents. The fusion of these gametes results in genetic variations in the offsprings. This way sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in offsprings by providing genetic variations. These genetic variations, thus lead to evolution of species as well as allow the organisms to become better adapted in the changing environment.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: (a) Name the organ that produces sperms as well as secretes a hormone in human males. Name the hormone it secretes and write its functions.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs.
(c) Explain how the developing embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Answer:
(a) The organ that produces sperms as well as secretes male hormone is testis. The hormone secreted by it is testosterone. Its important functions are as follows:
It stimulates sperm production.
It stimulates the development of secondary sexual characters in males like growth of beard hairs,low pitch voice, etc. It involves in the development, maturation and functioning of the male accessory sex organs like vas deferens and seminal vesicles
(b) In human female reproductive system, the process of fertilisation takes place in one of the fallopian tubes.
(c) The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. Placenta is a vascular membranous organ that connects the developing foetus to the uterine wall of the mother. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. The placenta draws nutrients and oxygen, which it supplies to the foetus, from the maternal circulation. In turn, the placenta receives carbon dioxide and wastes of foetal metabolism and discharges them into the maternal circulation for disposal.
Question: Draw a well labelled diagram of the female reproductive system in humans :
Answer:
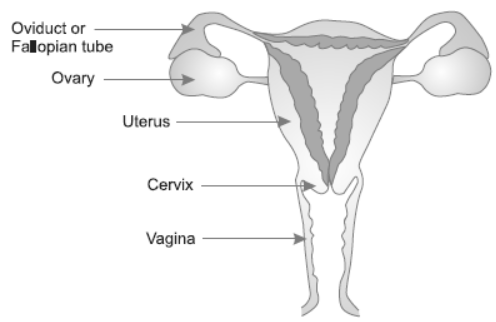
Question: State the functions of the following:
(a) testis (b) ovaries (c) vas deferens (d) stamen (e) pistil
Answer: (a) Testis: Form the male gametes the sperms and secrete the male sex hormone testosterone
(b) Ovaries: Form the female gamete ovum or the egg cell and secrete the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
(c) Vas deferens: Transport the sperms from the testis to the exterior.
(d) Stamen: Form the pollen grains in flowers. The pollen grains bear the male gametes.
Question: Trace the changes that take place in a flower from gamete formation to fruit formation.
Answer: [Diagram drawn and annotated with the following points will also be considered]
– Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains.
- The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
- The pollen needs to be transferred from the stamen to the stigma.
- If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination./ On the other hand, if the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as crosspollination.
After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ-cells which are in the ovary. For this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary/Figure
- The male germ-cell produced by pollen grain fuses with the female gamete present in the ovule.
- This fusion of the germ-cells or fertilisation gives the zygote.
- After fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
- The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
- Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
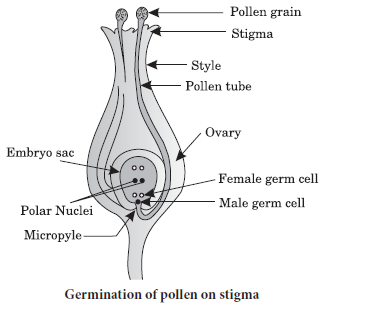
Question: Write two causes of human population explosion. Explain with the help of a suitable examples how this explosion can be checked.
Answer:
Two causes of human population explosion are:
(i) Reduced mortality rate due to better medical facilities.
(ii) Desire for male child.
(iii) Less awareness of birth control methods.
(iv) Illiteracy and poverty. (Any two)
Methods to check population explosion are:
(i) By using contraception methods.
(ii) Awareness among people of the advantage of small family.
Question: (a) Draw the diagram of female reproductive system and match and mark the part (s):
(i) Where block is created surgically to prevent fertilisation.
(ii) Where CuT is inserted. (iii) Inside which condom can be placed.
(b) Why do more and more people prefer to use condoms? What is the principle behind use of condoms?
Answer:
(a) (i) Fallopian Tube/Oviduct
(ii) Uterus
(iii) Vagina
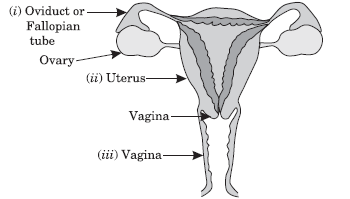
(b) People prefer use of condoms as it prevents STDs/gives privacy to the user. Condoms help create a mechanical barrier preventing meeting of sperms and ovum.
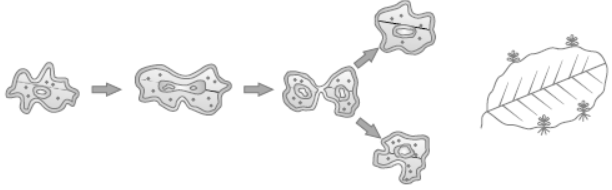
Question: Illustrate the following with the help of suitable diagram
(i) Binary fission in Amoeba
(ii) Leaf of Bryophyllum with buds
Answer: (i) Binary fission in Amoeba (ii) Bryophyllum leaf
Question: What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer:The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
1. Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting of sperms and ovum. In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high.
2. Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females. Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover penis in males and vagina in females.
3. Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus fertilization cannot occur.
4. Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods can also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperms known as vasectomy. Similarly, fallopian tubes of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus known as tubectomy.
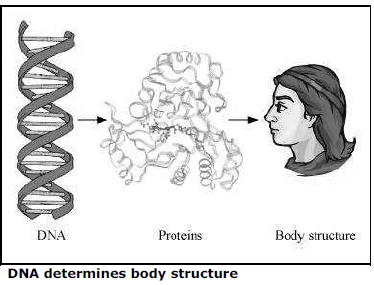
Question: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction ?
Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus of a cell. The DNA is the information site for making proteins and each specific type of protein leads to a specific type of body design.
Thus, it is the DNA molecule that determines the body design of an individual. Therefore, it can be concluded that it is the DNA that gets transferred from parents to offsprings and makes them look similar.
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Science
CBSE Science Class 10 Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 10. We suggest that Class 10 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Science.
Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 10 Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 10 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 10 Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 10 Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 10 Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

