Read and download the CBSE Class 12 Geography Planning and sustainable Development Assignment Set A for the 2025-26 academic session. We have provided comprehensive Class 12 Geography school assignments that have important solved questions and answers for India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context. These resources have been carefuly prepared by expert teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS syllabus guidelines.
Solved Assignment for Class 12 Geography India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context
Practicing these Class 12 Geography problems daily is must to improve your conceptual understanding and score better marks in school examinations. These printable assignments are a perfect assessment tool for India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context, covering both basic and advanced level questions to help you get more marks in exams.
India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context Class 12 Solved Questions and Answers
Important Notes and Questions for NCERT Class Business Studies 12 Planning and sustainable Development.
CBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 9 Planning and sustainable Development MCQs
Question. Which of the following is the most important objective of planning?
(a) To find out land use areas.
(b) To formulate big plans
(c) To utilise resources in a sustainable manner.
(d) None of these
Answer. C
Question. The planning approach that aims to reduce regional imbalances in development is known as
(a) Sectoral Planning
(b) Target Area Planning
(c) Regional Planning
(d) Target Group Planning
Answer. C
Question. Regional planning relates to which of the following?
(a) Development of various sectors of economy
(b) Area specific approaches of development
(c) Area differences in transportation network
(d) Development of rural areas
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following is not an example of Target Area Programmes?
(a) Drought Prone Area Development Programme
(b) Desert Development Programme
(c) Hill Area Development Programme
(d) Small Farmers Development Agency
Answer. D
Question. The ITDP refers to which of the following?
(a) Integrated Tourism Development Programme
(b) Integrated Travel Development Programme
(c) Integrated Tribal Development Programme
(d) Integrated Transport Development Programme
Answer. C
Question. Arrange the Indira Gandhi Canal Command Area in sequence from North to South.
I. Jaisalme
r II. Bikaner
III. Churu
IV. Ganganagar
Codes
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) IV, III, II, I
(c) III, I, II, IV
(d) IV, I, II, III
Answer. B
Question. Match the following.
Report/Publication Published by
A. Our Common Future 1. Brundtland Commission
B. Limits to Growth 2. P. Ehrlich
C. The Population Bomb 3. D. Meadows
D. 15-years Vision Document 4. NITI Aayog
Codes
A B C D
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 1 3 2 4
(c) 3 2 1 4
(d) 3 1 2 4
Answer. B
CBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 9 Planning and sustainable Development Case Based MCQs
Read the case/source given and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option.
Bharmaur tribal area comprises Bharmaur and Holi tehsils of Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh. It is a notified tribal area since 21st November, 1975. Bharmaur is inhabited by ‘Gaddi’, a tribal community who have maintained a distinct identity in the Himalayan region as they practised transhumance and conversed through Gaddiali dialect.
Bharmaur tribal region has harsh climate conditions, low resource base and fragile environment. These factors have influenced the society and Economy of the region. According to the 2011 census, the total, population of Bharmaur sub-division was 39.113 i.e.. 21 persons per sq km. It is one of the most (economically and socially) backward areas of Himachal Pradesh. Historically, the Gaddis have experienced geographical and political isolation and socio-economic deprivation. The economy is largely based on agriculture and allied activities such as sheep and goat rearing.
Question. Gaddi tribal community is associated with which of the following states/UTs of India?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of Bharmaur tribal region?
(a) Low resource base
(b) Harsh climatic conditions
(c) Fragile environment
(d) Well-developed economic base
Answer. B
Question. Population density is the number of people per unit area. What is population density of the area discussed in the source ?
(a) 17 persons per sq km
(b) 21 persons per sq km
(c) 27 persons per sq km
(d) 35 persons per sq km
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following is the means of livelihood of Gaddi tribal community?
(a) Cultivation of crops
(b) Animal husbandry
(c) Fishing
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer. D
Study the given map carefully and answer the following questions.
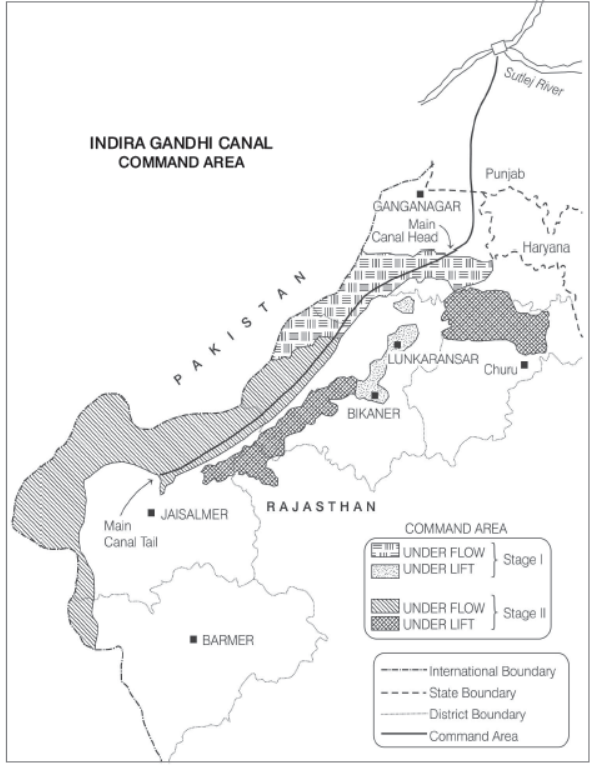
Question. Mention the source of origin of this canal.
Answer. The source of origin of Indira Gandhi Canal is the Harike Barrage in Punjab.
Question. Why is the area to the East of the canal under lift irrigation? Name the areas.
Answer. The area of the East of the Indira Gandhi Canal is under lift irrigation as it comprises of desert land dotted with shifting sand dunes. With the help of lift irrigation system, the water is lifted up to make it to flow against the slope of the land. The areas of the East of the canal are parts of Jaisalmer, Bikaner, Lunkaransar, Churu.
Question. Explain the economic significance of this canal for the command area.
Answer. The economic significance of this canal is that the irrigation through this canal led to increase in cultivated land and intensity of cropping. Main commercial crops i.e. wheat, rice, cotton, groundnut replaced the drought resistant crops like gram, bajra, and jowar. But intensive irrigation has also become a cause of waterlogging and soil salinity. So, in the near future it may interrupt the sustainability of agriculture.
CBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 9 Planning and sustainable Development Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Point out some salient features of Hill Area Development Programme.
Answer. Features of Hill Area Development Programme are
- It was started in Fifth Five Year Plan and in the begining it covered 15 districts comprising all the hilly districts of Uttarakhand, Mikir hills and North Cachar hills of Assam, Darjeeling district of West Bengal and Nilgiri district of Tamil Nadu.
- Development of horticulture, plantation agriculture, animal husbandry, poultry, forestry and small scale and village industry were the main objectives of the programme through which efficient use of local resources may become possible.
- National Committee on the Development of Backward Area recommended in 1981 that all the hill areas having a height above 600 m and not covered under tribal sub-plan be treated as backward hill areas.
Question. Write in brief about the physical setting of Bharmaur region.
Answer. Bharmaur region lies between 32° 11' N and 32° 41' N latitudes and 76° 22' E and 76° 53' E longitudes. Spread over an area of about 1818 sq km, the region mostly lies between an altitude of 1500 m to 3700 m above the mean sea level.
This region is popularly known as the homeland of Gaddis (a tribal community) and is surrounded by lofty mountains on all sides.
It has Pir Panjal Range in the North and Dhaula Dhar Range in the South. In the East, the extension of Dhaula Dhar Range converges with Pir Panjal near Rohtang pass.
Question. Explain the main aims of Bharmaur Tribal Area Development plan.
Answer. The main aims of Bharmaur Tribal Area Development Plan were
- Improving the quality of life of the Gaddis.
- Narrowing the gap in the level of development between Bharmaur and other districts of Himachal Pradesh.
- The highest priority was on development of transport and communication, agriculture and allied activities as well as social and community services.
- To utilise local resources in the efficient manner.
- To create new opportunities for the people.
CBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 9 Planning and sustainable Development Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain in brief the purpose of Target Area Programme with suitable examples from India.
Answer. The main purpose of the Target Area Programme is to develop the economically backward areas. There are regional imbalances in economic development which is lagging behind the economic sector. In order to combat both regional and social disparities, the planning commission introduced the target area and target group approach to planning.
Some of the examples of these are
Target Area Programme
(i) Command Area Development Programme.
(ii) Drought Prone Area Development Programme.
(iii) Desert Development Programme.
(iv) Hill Area Development Programme.
Target Group Programmes
(i) The Small Farmers Development Agency (SFDA).
(ii) Marginal Farmers Development Agency (MFDA).
As part of target area planning in the Eighth Five Year Plan, special programmes were designed to develop infrastructure in hill areas. North Eastern states, tribal areas and backward areas integrated tribal development project of Bharmaur region in Himachal Pradesh, Indira Gandhi Canal Command Area Project in Rajasthan are some examples of such programmes.
Question. ‘‘Hill Area Development Programmes in India were drawn keeping in view their topographical, ecological,social and economic conditions.’’ Support this statement with suitable explanation.
Answer. Yes, it is true that Hill Area Development Programmes in India were drawn keeping in view their topographical, ecological, social and economic conditions because the main objectives of these programmes were to develop horticulture, plantation agriculture, animal husbandry, poultry, forestry, small scale and village industry. By this, efficient use of local resources may become possible. National Commitee on the Development of Backward Area (1981) set a criterion that the hill areas having a height above 600 m and not covered under tribal sub-plan be treated as backward hill areas. The programme covered all the hilly districts of Uttar Pradesh (present Uttarakhand),Mikir hill and North hills of Assam, Darjeeling district ofWest Bengal and Nilgiri district of Tamil Nadu.
In drawing up the plans for the region, ecological elements were kept in mind. The aim of plan was to harness local resources without environmental degradation. In the regard deforestation was prohibited and pollution of different type was discharged.
Along with economic, topographical and ecological sphere, social sphere was also given due attention in implementation of the plan. The objective of plan was to promote marginalised and socially backward classes.
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Fundamental of Human Geography Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Fundamental of Human Geography Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography The world Population Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography The world Population Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Human Development Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Human Development Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Primary Activities Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Primary Activities Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Secondary Activities Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Secondary Activities Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Tertiary and Quaternary Activities Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Tertiary and Quaternary Activities Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Transport and Communication Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Transport and Communication Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Transport and Communication Assignment Set C |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography International Trade Assignment |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Population Distribution Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Population Distribution Density Growth and Composition Assignment |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Human Settlements Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Human Settlements Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Migration Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Migration Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Land Resources and Agriculture Assignment |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Water Resources Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Water Resources Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Mineral and Energy Resources Assignment |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Planning and sustainable Development Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Planning and sustainable Development Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Geographical Perspective Assignment Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Geographical Perspective Assignment Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Question Bank in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 12 Geography Population Composition Assignment |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Class 12 Geography India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context Assignment
Access the latest India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context assignments designed as per the current CBSE syllabus for Class 12. We have included all question types, including MCQs, short answer questions, and long-form problems relating to India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context. You can easily download these assignments in PDF format for free. Our expert teachers have carefully looked at previous year exam patterns and have made sure that these questions help you prepare properly for your upcoming school tests.
Benefits of solving Assignments for India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context
Practicing these Class 12 Geography assignments has many advantages for you:
- Better Exam Scores: Regular practice will help you to understand India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context properly and you will be able to answer exam questions correctly.
- Latest Exam Pattern: All questions are aligned as per the latest CBSE sample papers and marking schemes.
- Huge Variety of Questions: These India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context sets include Case Studies, objective questions, and various descriptive problems with answers.
- Time Management: Solving these India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context test papers daily will improve your speed and accuracy.
How to solve Geography India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context Assignments effectively?
- Read the Chapter First: Start with the NCERT book for Class 12 Geography before attempting the assignment.
- Self-Assessment: Try solving the India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context questions by yourself and then check the solutions provided by us.
- Use Supporting Material: Refer to our Revision Notes and Class 12 worksheets if you get stuck on any topic.
- Track Mistakes: Maintain a notebook for tricky concepts and revise them using our online MCQ tests.
Best Practices for Class 12 Geography Preparation
For the best results, solve one assignment for India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context on daily basis. Using a timer while practicing will further improve your problem-solving skills and prepare you for the actual CBSE exam.
You can download free PDF assignments for Class 12 Geography Chapter India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets have been updated for the 2025-26 session covering all concepts from latest NCERT textbook.
Yes, our teachers have given solutions for all questions in the Class 12 Geography Chapter India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context assignments. This will help you to understand step-by-step methodology to get full marks in school tests and exams.
Yes. These assignments are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus for 2026. We have included huge variety of question formats such as MCQs, Case-study based questions and important diagram-based problems found in Chapter India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context.
Practicing topicw wise assignments will help Class 12 students understand every sub-topic of Chapter India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context. Daily practice will improve speed, accuracy and answering competency-based questions.
Yes, all printable assignments for Class 12 Geography Chapter India People And Economy Chapter 6 Planning And Sustainable Development In Indian Context are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format.

