Access the latest CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles And Processes of Biotechnology Worksheet. We have provided free printable Class 12 Biology worksheets in PDF format, specifically designed for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes. These practice sets are prepared by expert teachers following the 2025-26 syllabus and exam patterns issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS.
Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Biology Practice Worksheet for Class 12
Students should use these Class 12 Biology chapter-wise worksheets for daily practice to improve their conceptual understanding. This detailed test papers include important questions and solutions for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes, to help you prepare for school tests and final examination. Regular practice of these Class 12 Biology questions will help improve your problem-solving speed and exam accuracy for the 2026 session.
Download Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Worksheet PDF
Question. Restriction endonucleases are used as
(a) molecular build up at nucleotides.
(b) molecular degradation to DNA breakup.
(c) molecular knives for cutting DNA at specific sites.
(d) molecular cement to combine DNA sites.
Answer. C
Question. Choose the correct option.
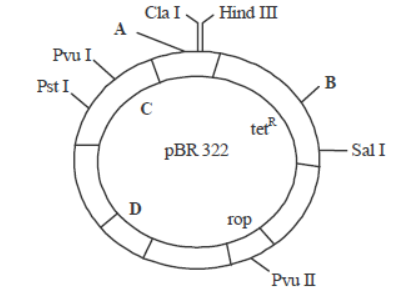
A B C D
(a) Hind I EcoR I ampR ori
(b) Hind I BamH I kanR ampR
(c) BamH I Pst I ori ampR
(d) EcoR I BamH I ampR ori
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzyme?
(a) 5'.............CGTTCG.............3'
3'.............ATGGTA.............5'
(b) 5'.............GATATG.............3'
3'.............CTACTA.............5'
(c) 5'.............GAATTC.............3'
3'.............CTTAAG.............5'
(d) 5'.............CACGTA.............3'
3'.............CTCAGT.............5'
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following statement is not correct about cloning vector ?
(a) ‘Ori’ is a sequence responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
(b) Selectable marker selectively permitting the growth of the non-transformants.
(c) In order to link the alien DNA, the vector needs to have single recognition site for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
(d) The ligation of alien DNA is carried out at a restriction site present in one of the two antibiotic resistance genes.
Answer. B
Question. c-DNA probes are copied from the messenger RNA molecules with the help of
(a) restriction enzymes
(b) reverse transcriptase
(c) DNA polyermase
(d) adenosine deaminase
Answer. B
Question. Electroporation procedure involves
(a) fast passage of food through sieve pores in phloem elements with the help of electric stimulation.
(b) opening of stomatal pores during night by artificial light.
(c) making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs.
(d) purification of saline water with the help of a membrane system.
Answer. C
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA to produce sticky ends.
Reason : Stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : “DNA finger printing” has become a powerful tool to establish paternity and identity of criminals in rape and assault cases.
Reason : Trace evidences such as hairs, saliva and dried semen are adequate for DNA analysis.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : In recombinant DNA technology, human genes are often transferred into bacteria (prokaryotes) or yeast (eukaryote). .
Reason : Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge population, which express the desired gene.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Insertion of recombinant DNA within the coding sequence of β-galactosidase results in colourless colonies.
Reason : Presence of insert results in inactivation of enzyme β-galactosidase known as insertional inactivation.
Answer. A
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question. Name the enzyme used to cut DNA?
Answer: restriction enzymes,
Question. Give the full form of PCR. Who developed it?
Answer: PCR is a polymerase chain reaction. It was developed by Kary Mullis in 1985.
Question. Why is the enzyme cellulase needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and not from animal cells?
Answer: The enzyme cellulase breaks down cellulose which is present in cell walls of plants but absent in animal cells.
Question. Name the first plasmid used as vector.
Answer: pBR322.
Question. Name the bacterium that yields thermostable DNA polymerase.
Answer: The thermostable DNA polymerase can be produced with the help of a bacterium which is named Thermus aquaticus.
Question. What is the role of Ori for cloning vector?
Answer: Ori: It is a genetic sequence that acts as the initiation site for replication of DNA. Any fragment of DNA, when linked to the ori region, can be initiated to replicate.
Question. Name the source organism from which Ti plasmid is isolated. Explain the use of this plasmid in biotechnology.
Answer: (i)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(ii)The desired gene or segment of DNA can be ligated to this plasmid, and it is then used as a vector to introduce gene into the host plant.
Question. Name the technique used for amplification of DNA?
Answer: The DNA amplification can be done by the technique named the Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Question. Biotechnological techniques can help to diagnose the pathogen much before the symptoms of the disease appear in the patient. Suggest any two such techniques?
Answer: 1. PCR – Polymerase chain reaction
2. ELISA – Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Question. How many PCR cycles are adequate for proper amplification of DNA segment?
Answer: 20-30 cycles.
Question. What are selectable markers? What is their use in genetic engineering?
Answer: A gene or other identifiable portion of DNA whose inheritance can be followed and used in the process of selection of transformed cells from non-transformed ones is called selectable marker.
A selectable marker is a gene inserted into a cell, in particular a bacterium or a cultured cell, which confers a trait appropriate for artificial selection.
Question. Name the source of the DNA polymerase used in PCR technique.
Answer: The DNA polymerase used in PCR is Taq polymerase extracted from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus.
Question. Study the given diagram and answer the questions
A) Name the restriction enzyme that recognises this palindrome.
B) Name the enzyme that link the DNA fragments.
Answer: A] EcoR1
B] DNA ligase
Question. Write the function of a bioreactor.
Answer: Bioreactors are required to produce large volumes (100 - 1000 litres) of recombinant proteins / desired protein / enzymes.
Question. How the introduction of an alien DNA into plant host cell is achieved ?
Answer: Introduction of an alien DNA into the plant host cell is achieved by using a gene gun, coated with gold or tungsten particles.
Question. Name the technique that is used to alter the chemistry of genetic material (DNA, RNA) to obtain desired result.
Answer: Genetic Engineering / Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology.
Question. What is the name of the process given to separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing?
Answer: After completion of the biosynthetic stage, the product has to be subjected to a series of processes before it is ready for marketing as a finished product.
The processes include separation & purification, which are collectively referred to as downstream processing.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is an “origin of replication” (ori) in a chromosome ? State its function.
Answer: This is the point on DNA where replication originates / starts.
It controls the copy number of linked DNA.
Question. b-galactosidase enzyme is considered a better selectable marker. Justify the statement.
Answer: Non-recombinant can be differentiated from recombinant on the basis of colour change (from colourless to blue), when grown on a chromogenic substrate, whereas the recombinant will not be able to show any colour change (due to insertional inactivation of the gene responsible for b galactosidase).
Non-cumbersome procedure / does not require simultaneous plating having different antibiotics / single step / easy process.
Question. What is EcoRI ? How does EcoRI differ from an exonuclease ?
Answer: EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease enzyme.
Exonuclease removes nucleotides from the ends of DNA.
EcoRI makes cuts at a specific position within the DNA.
Question. How is continuous culture system maintained in bioreactors and why ?
Answer: Used medium is drained out from one side of the bioreactor and fresh medium is added from the other side. This type of culturing method produces a larger biomass leading to higher yields (of desired protein).
Question. Explain the process of gel electrophoresis technique.
Answer: Separation of DNA fragments under an electric field in agarose gel, negatively charged DNA move towards anode and smaller fragments move farther, separated DNA fragments are stained with ethidium bromide followed by UV radiations, extraction of DNA bands by elution.
Question. All cloning vectors do have a ‘selectable marker’. Describe its role in recombinant DNA-technology.
Answer: The role of a selectable marker in rDNA technology is to identify and distinguish the bacterial cells that have taken up the recombinant vector during the transformation process.
Question. How are DNA fragments visualised during gel electrophoresis ? What is elution ?
Answer: Separated DNA fragments stained with ethidium bromide, followed by exposure to UV radiations.
Removal of DNA bands from agarose gel, and its extraction from the gel is elution.
Question. Why is the ‘insertional inactivation’ method to detect recombinant DNA preferred to ‘antibiotic resistance’ procedure?
Answer: The presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured colonies, in absence of an insert/ in non-transformants, presence of an insert (in the enzyme site), results into (insertional inactivation of the b-galactosidase) colonies which do not produce colour.
Antibiotic resistance method requires duplicate plating/cumbersome procedure.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Why are engineered vectors preferred ?
(b) A vector is engineered with some features which help in cloning within the host cell.
List the features and explain all of them.
Answer: (a) Engineered vectors help in the easy linking of foreign DNA and the selection of recombinants from non-recombinants.
(b) Following are the four features, which are required to facilitate cloning into a vector.
(i) Origin of replication (ori) : It is a sequence of DNA from where replication starts. Any piece of alien/foreign DNA when linked to it can be made to replicate within the host cells. This sequence also controls the copy number of the linked DNA.
(ii) Selectable marker : They help in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and permitting the growth of the transformants. Transformation is a process by which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium.
(iii) Cloning sites : The vector must have a few, preferable one recognition site to link the alien DNA, presence of a particular cloning/ recognition site enables the particular restriction enzyme to cut the vector DNA.
(iv) Size of Vector : It should be small as large molecules tend to breakdown during purification.
CASE STUDY -I
When you insert a piece of alien DNA into a cloning vector and transfer it into a bacterial, plant or animal cell, the alien DNA gets multiplied. In almost all recombinant technologies, the ultimate aim is to produce a desirable protein. Hence, there is a need for the recombinant DNA to be expressed. The foreign gene gets expressed under appropriate conditions. The expression of foreign genes in host cells involve understanding many technical details. After having cloned the gene of interest and having optimised the conditions to induce the expression of the target protein, one has to consider producing it on a large scale. Can you think of any reason why there is a need for large-scale production?
If any protein encoding gene is expressed in a heterologous host, it is called a recombinant protein. The cells harbouring cloned genes of interest may be grown on a small scale in the laboratory. The cultures may be used for extracting the desired protein and then purifying it by using different separation techniques.
Question. Genetically engineered bacteria is used for the production of:
(a) Thyroxine
(b) Human insulin
(c) growth hormone
(d) None of the above
Answer: B
Question. Construction of recombinant DNA involves:
(a) cleaving and joining of DNA segments with endonuclease
(b) cleaving DNA segments with endonuclease and re-joining with ligase
(c) cleaving and re-joining DNA segments with ligase
(d) cleaving DNA segments with ligase and re-joining with endonuclease
Answer: B
Question. Any DNA molecule that has the ability to replicate in an appropriate host cell, to which the desired gene are integrated for cloning:
(a) Plasmid
(b) Linker
(c) Vector
(d) adapter
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following should be chosen for best yield if one were to produce a recombinant protein in large amounts?
(a) A continuous culture system
(b) A stirred-tank bioreactor without in-lets and out-lets
(c) Laboratory flask of the largest capacity
(d) None of the above
Answer: A
Question. The process of separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing is called
(a) upstream processing
(b) downstream processing
(c) bioprocessing
(d) postproduction processing
Answer: B
CASE STUDY-II
The cells can also be multiplied in a continuous culture system wherein the used medium is drained out from one side while fresh medium is added from the other to maintain the cells in their physiologically most active log/exponential phase. A stirred-tank reactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor. Alternatively, air can be bubbled through the reactor. If you look at the figure closely you will see that
the bioreactor has an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system and a foam control system, a temperature control system, pH control system and sampling ports so that small volumes of the culture can be withdrawn periodically.
Question. The bioreactor is not capable of:
(a) Producing aseptic conditions
(b) Meeting containment regulations
(c) Controlling pH
(d) Produce electricity
Answer: D
Question. The small-scale bioreactors have volume of:
(a) 5-10 litres
(b) 10-20 litres
(c) 1-10 litres
(d) 1-20 litres
Answer: A
Question. Sparger in stirred tank bioreactor helps in:
(a) Proper gas distribution
(b) Proper mixing of medium
(c) Measuring temperature of medium
(d) Better sterility
Answer: A
Question. Micro-organisms can be grown in the bioreactors by
(a) Support growth system
(b) Agitated growth system
(c) Suspended. growth system
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer: D
Question. The components of a bioreactor are:
(a) An agitator system
(b) An oxygen delivery system
(c) A foam control system
(d) All of these
Answer: D
Question. (a) Why are restriction endonucleases so called?
Answer : Restriction endonucleases are so called because they cut DNA duplex at specific points. Their single stranded free ends are called ‘sticky ends’ which can be joined end to end by DNA ligases.
Question. EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease. How is it named so? Explain.
Answer : Enzyme EcoRI is named as follows :
The capital letter E comes from the genus Escherichia : The letters co are derived from the species name coli. The letter R is from RYI3 (strain). The Roman number I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from the bacterium E. coli RYI3.
Question. Name and explain the technique used in the separation and isolation of DNA fragments to be used in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer : After the cutting of DNA by restriction enzyme, fragments of DNA are formed. Separation of DNA
rop : rop codes for protein involved in the replication of plasmid ampR: gene for ampicillin resistance which help in selecting transformants.
56.
ClaI HindIII
fragments according to their size or length is done by a technique called agarose gel electrophoresis.
It is a technique of separation of molecules such as DNA, RNA or protein, under the influence of an electrical field, so that they migrate in the direction of electrode bearing the opposite charge, viz., positively charged molecules move towards cathode (–ve electrode) and negatively charged molecules travel towards anode (+ve electrode) through a medium/matrix. Most commonly used matrix is agarose. DNA fragments separate according to size through the pores of agarose gel. Hence the smaller, the fragment size, the farther it moves.
The separated DNA fragments can be seen only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide (EtBr) followed by exposure to UV radiation. The fragments are visible as bright orange coloured bands.
Question. Why are genes encoding resistance to antibiotics considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector? Explain with the help of one example.
Answer : Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics are considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector because they help in selecting transformant cell from non-transformant ones.
The genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as tetracycline, ampicillin, kanamycin or chloramphenicol etc. are useful selectable markers for E. coli. The common E. coli cells are not resistant to any of these antibiotics. Plasmid pBR322 has two antibiotic resistance genes – ampicillin resistance (ampR) and tetracycline resistance (tetR) which are considered useful for selectable markers.
The presence of restriction sites within the markers tetR and ampR permits an easy selection for cells transformed with the recombinant pBR322. For example, insertion of the DNA fragment into the plasmid using enzyme PstI or PvuI places the DNA insert within the gene ampR. This makes ampR nonfunctional. Bacterial cells containing such a recombinant pBR322 will be unable to grow in the presence of ampicillin, but will grow on tetracycline.
Question. Name the endonuclease that was first discovered.
Answer : The first discovered restriction endonuclease was HindII.
Question. Why is Agrobacterium tumefaciens a good cloning vector? Explain.
Answer : Agrobacterium tumifacines is considered as a good cloning vector because it is used for introducing genes of desirable traits into plants. Properties of Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium are as follows :
(i) They are self replicating.
(ii) They possess sites for insertion of foreign gene which needs to be introduced.
(iii) They possess selectable markers.
Question. DNA being hydrophilic cannot pass through the cell membranes of a host cell. Explain how does recombinant DNA get introduced into the host cell to transform the latter.
Answer : Competent host is essential for biotechnology experiment. Since DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, it cannot pass through membranes, so the bacterial cells must be made capable to take up DNA i.e., made competent.
This can be achieved by :
(i) treatment of DNA with divalent cation of CaCl2 or rubidium chloride. Treating them with a specific concentration of a divalent cation, increases the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall.
(ii) Heat shock treatment of DNA. Recombinant DNA (rDNA) can then be forced into such cells by incubating the cells with recombinant DNA on ice, followed by placing them briefly at 42°C (heat shock) and then putting them back on ice. This enables the bacteria to take up the recombinant DNA.
Question. Explain any three methods to force ‘alien’ or recombinant DNA into host cells.
Answer : The three methods which force ‘alien’ or recombinant DNA into host cells are: electroporation, biolistic method and microinjection.
(i) Electroporation : In this method, electrical impulses induce transient pores in the plant cell membrane through which foreign DNA molecules are incorporated into cells.
(ii) Biolistic Method : Biolistic is a means of introducing DNA into cells that involves bombardment of cells with high-velocity microprojectiles coated with DNA. In biolistic method tungsten or gold particles, coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity.
(iii) Microinjection : It is the introduction of foreign gene into plant cell or animal cell by using microneedles or micropipettes.
Question. Name the enzymes that are used for the isolation of DNA from bacterial and fungal cells for recombinant DNA technology.
Answer : In recombinant DNA technology, enzymes that are used for isolation of DNA from bacterial and fungal cells are lysozyme and chitinase respectively.
Question. (a) Describe the characteristics a cloning vector must possess.
(b) Why DNA cannot pass-through the cell membrane? Explain. How is bacterial cell made ‘competent’ to take up recombinant DNA from the medium?
Answer : (a) A cloning vector must possess the following characterstics:
(i) Origin of replication (Ori) : Ori is a sequence from where replication starts and is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA. (ii) Selectable marker : Selectable markers help in selecting transformant host cell from non- transformant ones.
(iii) Cloning sites : A vector must have unique recognition site to link foreign DNA. Presence of a particular cloning/recognition site enables the particular enzyme to cut the vector DNA.
Question. Write the importance of the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in polymerase chain reaction.
Answer : Taq DNA polymerase is isolated from thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus. It is used to synthesise the segment of DNA between the primers (extension) in polymerase chain reaction at high temperatures.
Question. Mention the source of thermostable DNA polymerase.
Answer : Thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus is the source of thermostable DNA Taq polymerase.
Question. Why is Taq polymerase preferred in PCR?
Answer : Taq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase isolated from thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus. Taq polymerase is heat stable enzyme and is able to withstand high temperature induced denaturation of DNA during PCR hence it is preferred in PCR reactions.
Question. Name two commonly used bioreactors. State the importance of using a bioreactor.
Answer : Two commonly used bioreactors are : (i) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
(ii) Sparged strirred-tank bioreactor
Bioreactors are used for large scale production of biological products.
Question. (a) Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Write the role of primers and DNA polymerase in PCR.
Answer : (a) The two sets of primers (small chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA) are required in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction. Primers hybridise to target DNA region and allow synthesis of the DNA towards one another whereas DNA polymerase synthesise DNA region between the primers using dNTPs and Mg2+.
Question. What is genetic engineering ? List the steps in rDNA technology.
Answer : Genetic engineering refers to artificial synthesis, isolation, modification, combination, addition and repair of genetic material (DNA) to alter the phenotype of the host organism to suit human needs. It includes formation of recombinant DNA, use of gene cloning in gene transfer. Process of rDNA technology involves (i) Isolation of genetic material, (ii) Cutting of DNA at specific locations, (iii) Amplification of gene of interest using PCR, (iv) Preparation and insertion of rDNA, into host cell and (v) obtaining desirable gene product.
Question. Name the organism from where the thermostable DNA polymerase is isolated. State its role in genetic engineering.
Answer : Taq DNA polymerase isolated from thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus synthesises the DNA region from gene of interest between the primers, using dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates) and Mg2+. The primers are extended towards each other so that the DNA segment lying between the two primers is copied. It is stable even at high temperatures.
Question. What are recombinant proteins? How do bioreactors help in their production?
Answer : Recombinant protein is a protein obtained by introducing recombinant DNA into a heterologous host and causing it to produce the gene product.
Bioreactors are vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products. A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions (temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen). To maintain a higher yield, optimum temperature must be maintained and suitable pH must be provided.
Question. Mention the three steps involved in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). How is repeated amplification of DNA made possible during PCR?
Answer : Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique of synthesising multiple copies of the desired gene (DNA segment) in vitro. The basic requirements of PCR are DNA template, two oligonucleotide primers usually 20 nucleotides long, dNTPs and DNA polymerase which is stable at high temperature (usually Taq polymerase). Working mechanism of PCR is as follows :
(i) Denaturation : The target DNA (DNA segment to be amplified) is heated to high temperature (94°C). Heating results in the separation of two strands of DNA. Each of the two strands of the target DNA now act as template for synthesis of new DNA strand.
(ii) Annealing : During this step, two oligonucleotide primers hybridise to each of single stranded template DNA in presence of excess of synthetic oligonucleotides.
(iii) Extension : During this step, the enzyme DNA polymerase synthesises the DNA segment between the primers. Taq DNA polymerase, isolated from a thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus, is used in most of the cases. This step requires presence of deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) and Mg2+ and occurs at 72°C.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles And Processes of Biotechnology Worksheet
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Biology
Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
Students can use the Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes practice sheet provided above to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This solved questions and answers follow the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12 Biology. You can easily download the PDF format and solve these questions every day to improve your marks. Our expert teachers have made these from the most important topics that are always asked in your exams to help you get more marks in exams.
NCERT Based Questions and Solutions for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create this practice material for students. After solving the questions our teachers have also suggested to study the NCERT solutions which will help you to understand the best way to solve problems in Biology. You can get all this study material for free on studiestoday.com.
Extra Practice for Biology
To get the best results in Class 12, students should try the Biology MCQ Test for this chapter. We have also provided printable assignments for Class 12 Biology on our website. Regular practice will help you feel more confident and get higher marks in CBSE examinations.
You can download the CBSE Practice worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes for the latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the Practice worksheets issued for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology have been made available here for the latest academic session
There is no charge for the Practice worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all the latest Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles and Processes test practice sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session

