Access the latest CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Population Worksheet Set B. We have provided free printable Class 12 Biology worksheets in PDF format, specifically designed for Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations. These practice sets are prepared by expert teachers following the 2025-26 syllabus and exam patterns issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS.
Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations Biology Practice Worksheet for Class 12
Students should use these Class 12 Biology chapter-wise worksheets for daily practice to improve their conceptual understanding. This detailed test papers include important questions and solutions for Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations, to help you prepare for school tests and final examination. Regular practice of these Class 12 Biology questions will help improve your problem-solving speed and exam accuracy for the 2026 session.
Download Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations Worksheet PDF
Question. The maintenance of internal favourable conditions, by a self regulated mechanisms inspite of the fact that there are changes in environment, is known as
(a) entropy
(b) enthalpy
(c) homoeostasis
(d) steady state
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following would necessarily decrease the density of a population in a given habitat?
(a) Natality> mortality
(b) Immigration > emigration
(c) Mortality and emigration
(d) Natality and immigration
Answer : C
Question. A protozoan reproduces by binary fission.
What will be the number of protozoans in its population after six generations?
(a) 128
(b) 24
(c) 64
(d) 32
Answer : C
Question. Snails escape from stressful time in summers by
(a) Hibernation
(b) Aestivation
(c) Diapause
(d) Homeostasis
Answer : B
Question. Salt concentration (salinity) of the sea measured in parts per thousand is
(a) 10–15
(b) 30–70
(c) 0 – 5
(d) 30– 35
Answer : D
Question. What parameters are used for tiger census in our country’s National parks and sanctuaries?
(a) Pug marks only
(b) Pug marks and faecal pellets
(c) Faecal pellets only
(d) Actual head counts
Answer : B
Question. The rate of formation of new organic matter by rabbit in a grassland, is called
(a) Net productivity
(b) Secondary productivity
(c) Net primary productivity
(d) Gross primary productivity
Answer : B
Question. If 4 individuals in a laboratory population of 40 fruitflies died during a specified time interval (i.e., a week), the death rate in the population during that period is
(a) 1
(b) 0.1
(c) 0.01
(d) 0.4
Answer : B
Question. Territoriality occurs as a result of
(a) competition
(b) parasitism
(c) predation
(d) co-operation
Answer : A
Question. July 11 is observed as
(a) World Population Day
(b) No Tobacco Day
(c) World Environment Day
(d) World Health Day
Answer : A
Question. Keystone species deserve protection because these
(a) are capable of surviving in harsh environmental conditions.
(b) indicate presence of certain minerals in the soil.
(c) have become rare due to overexploitation.
(d) play an important role in supporting other species.
Answer : D
Question. Which one of the following correctly represents an organism and its ecological niche ?
(a) Vallisneria and pond
(b) Desert locust (Schistocerca) and desert
(c) Plant lice (aphids) and leaf
(d) Vultures and dense forest
Answer : C
Question. Carrying capacity is
(a) the capacity of an individual to produce young ones.
(b) availability of resources in a given habitat to support a certain no of individuals of population, beyond which no further growth is possible.
(c) gene frequency from one generation to next.
(d) gene frequency in same generation.
Answer : B
Question. A lizard-like member of reptila is sitting on a tree with its tail coiled around a twig. This animal could be
(a) Hemidactylus showing sexual dimorphism
(b) Varanus showing mimicry
(c) Garden lizard (Calotes) showing camouflage
(d) Chamaeleon showing protective colouration
Answer : D
Question. Which one of the following is a matching pair of certain organism(s) and the kind of association?
(a) Shark and sucker fish - Commensalism
(b) Algae and fungi in lichens - Mutualism
(c) Orchids growing on trees - Parasitism
(d) Cuscuta (dodder) growing on other - flowering plants - Epiphytism
Answer : B
Question. A population of 500 that experiences 55 births and 5 deaths during a one-year period. What is the reproductive rate for the population during the one-year period ?
(a) 0.01/year
(b) 0.05/year
(c) 0.1/year
(d) 50/year
Answer : C
Question. The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of response of organisms to abiotic factors. What do A, B and C represent respectively?
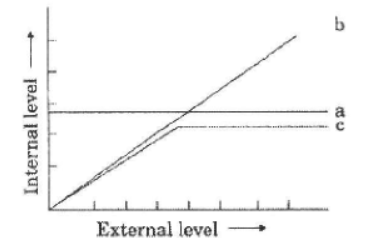
A B C
(a) conformer regulator partial regulator
(b) regulator partial conformer
regulator
(c) partial regulator conformer
regulator
(d) regulator conformer partial regulator
Answer : D
ASSERTION REASON QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Question. Assertion : Thick cuticle is mostly present in disease resistant plants.
Reason : Disease causing agents cannot grow on cuticle and cannot invade the cuticle.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : In sigmoid growth curve, population finally stabilizes itself.
Reason : Finally, the death rate increases than the birth rate.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : Tropical rain forests are disappearing fast from developing countries such as India.
Reason : No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : Flora contains the actual account of habitat and distribution of plants of a given area.
Reason : Flora helps in correct identification.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Species are groups of potentially interbreeding natural populations which are isolated from other such groups.
Reason : Distinctive morphological characters are displayed due to reproductive isolation.
Answer : B
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question. Mention the term used to describe a population interaction between an orchid growing on a forest tree.
Answer : Commensalism.
Question. Name the type of interaction seen between fig and wasps.
Answer : Mutualism.
Question. In a pond there were 200 frogs. 40 more frogs were born in a year. Calculate the birth rate of the population.
Answer : Birth rate = 40/200 = 0.2 frogs/yr or 20%.
Question. Very small animals are rarely found in polar regions. Give two reasons.
Answer : Small animals have a larger surface area relative to their volume, lose heat very fast, due to small size, expend much energy to generate body heat through metabolism.
Question. Name the interaction that exists between sucker fish and shark.
Answer : Commensalism.
Question. Provide an instance where the population size of a species can be estimated indirectly, without actually counting them or seeing them.
Answer : Tiger census in National parks and Tiger reserves was done based on counting pug marks /faecal pellets.
Question. Name the type of interaction that exists between barnacles and whale.
Answer : Commensalism.
Question. Name the interaction that exists between Cuscuta and shoe-flower plant.
Answer : Parasitism
Question. Give two reasons as to why a weed such as calotropis flourishes in abandoned fields.
Answer : Dry hairy seeds helps in dissemination/having xerophytic adaptations (thick hair on leaves and stems) not grazed by animals as it produces poisonous substances/cardiac glycosides.
Question. State the type of interaction that exists between ticks and dogs.
Answer : Ectoparasitism.
Question. Give example of an organism that enters ‘diapause’ and why.
Answer : Bombyx mori (silk moth) is an insect that enters diapause due to some adverse environmental conditions such as drought, extreme temperature, reduced food availability; which, in turn, delays the overall development. The physiological and metabolic activities diminish at this particular time.
Question. Why are green algae not likely to be found in the deepest strata of the ocean?
Answer : Green algae are photosynthetic in nature. In the deepest strata of the ocean i.e., benthic zone, light does not penetrate therefore, this zone is in perpetual darkness and photosynthetic organisms such as green algae cannot survive in this region.
Question. Mention how do bears escape from stressful time in winter.
Answer : Bears undergo hibernation to escape from stressful time in winter. In hibernation, they seek a warm shelter and remain dormant, their respiration rate turns low and they consume stored food.
Question. How do seed bearing plants tide over dry and hot weather conditions?
Answer : Mesophytic seed bearing plants sometimes have to face hot and dry weather conditions. They survive such adverse conditions by forming underground perennating structures such as corms, rhizomes, tubers, etc. Xerophytic plants on the other hand have to face hot and dry conditions throughout the year. They show various adaptations like sunken stomata, fleshy organs, leaves reduced to spines, extensive root system, etc.
Question. How do snails escape from stressful time in summers?
Answer : Snails undergo aestivation to escape from stressful time in summers.
Question.Why are some organisms called as eurythermals and some others as stenohaline?
Answer : Some organisms can tolerate a wide range of temperature variations, e.g., most mammals and birds. They are called eurythermals while other organisms live within narrow range of temperature because of their requirement of nearly constant tempeture throughout the year e.g., polar bear, lizards, amphibians, and are called stenothermals
Question. Why green plants are not found beyond a certain depth in the ocean?
Answer : Green plants are photosynthetic and show autotrophic mode of nutrition. They require sunlight to photosynthesise. Light does not penetrate beyond a certain depth in oceans and hence very deep layers remain in perpetual darkness. In the absence of sunlight green plants cannot manufacture their food and hence cannot survive. Therefore, they are found in those regions of the ocean where sunlight is available.
Question. Mention any two activities of animals which get cues from diurnal and seasonal variations in light intensity.
Answer : Most animals are active during a particular period of the day, e.g., butterflies and most birds are active during day time hence called diurnal whereas few animals like rat, cockroaches and birds like owl are active during night hence called nocturnal. Various activities like flowering in plants and migration in birds and animlas are affected by seasonal variations.
Question. How does camouflage help an insect?
Answer : Camouflage is the ability of an organism to blend with the surroundings or background. It is the most common type of adaptation in animals. It is advantageous to insects whether they act as prey or predator. Prey insects can easily hide from their predators and escape from them whereas predator insects can also hide from their prey and remain unnoticed so that easily attack their prey.
Question. When and why do some animals like frogs hibernate?
Answer : Hibernation or winter sleep is quite common in ectothermal (cold blooded) animals like frog. This is because they are unable to regulate their body temperature which changes with the fluctuating external environment. Such animals pass the winter period in dormant condition, resting in warm places. Hibernation is necessary for these animals to prevent their metabolic rate from slowing down to levels which could be harmful to them.
Question. Which one of the two, stenothermals or eurythermals, show wide range of distribution of earth and why?
Answer : Eurythermal organisms are those organisms which can tolerate wide range of temperature variations and thus show wide distribution on earth.
Question. When and why do some animals like snails go into aestivation?
Answer : When animals like snails are exposed to very high temperatures, they go into aestivation to avoid the heat of summer.
Question. Why is the polar region not a suitable habitat for tiny humming birds?
Answer : Polar region is not a suitable habitat for humming bird. Because of larger surface area relative to volume it tends to lose heat very fast in comparision to large sized animals hence it will have to spend more energy in maintaining its body temperature.
Question. Between amphibians and birds, which will be able to cope with global warming? Give reason.
Answer : Birds are better able to cope with global warming then amphibians because birds are eurythermal and can tolerate wide range of temperature whereas amphibians are stenothermal and cannot tolerate much fluctuation in the ambient temperature.
Question. How do herbs and shrubs survive under the shadow of big canopied trees in forests?
Answer : Herbs and shrubs survive under the shadow of big canopied trees in forests as they are perfect shade tolerant plants showing better growth in lower level of light intensity and are arranged in different strata according to their shade tolerance.
Question. List any two physiological responses that help you to gradually get acclimatised to high altitudes when you go from the planes.
Answer : (i) Enhancement in RBCs production to compensate low oxygen availability
(ii) Increase in breathing rate.
Question. When an organism is called a ‘conformer’?
Explain with the help of an example.
Answer : The organism in which osmotic concentration of body fluids and body temperature changes according to ambient conditions is called conformer. E.g. in aquatic animal Asterias, the osmotic concentration of body fluids changes according to the osmotic concentration of the surrounding water.
Question. Write the normal body temperature of humans.
How is it maintained during summers?
Answer : Normal body temperature of humans is about 37°C. Humans maintain constant body temperature by homeostasis. During summer, when external temperature rises, we begin to sweat profusely. As sweat evaporates, cooling of body occurs.
Short Answer type Questions
Question. How do desert lizards cope with temperature variations in their environment? Explain.
Answer : Desert lizards lack the physiological ability that mammals have to deal with the high temperature. They keep their body temperature fairly constant by behavioural means. They enjoy in the sun and absorb heat when their body temperature drops below the comfort zone, but move into shade when the surrounding temperature starts increasing. Some species are capable of burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from too much heat.
Question. Bear hibernates whereas some species of zooplanktons enters diapause to avoid stressful external conditions. How are these two ways different from each other?
Answer : Bears undergo hibernation during winters to escape extreme cold. It is characterised by low body temperature, slow breathing and heart rate and low metabolic rate. However, diapause is a stage of suspended development or growth occurring in many insects and other invertebrates during which metabolism is greatly decreased. Diapause is often triggered by seasonal changes and regulated by inborn rhythm.
Question. Why do we experience shivering during winters when the temperature is very low?
Answer : When the ambient temperature is very low, our body starts shivering. It is an exercise that raises body temperature and helps to maintain constant internal body temperature at about 37°C, by mechanism of homeostasis.
Question. Humming birds live among the bushes in tropics while penguins live on icebergs. They cannot survive if their habitats are reversed. Justify.
Answer : Hummingbird is a small animal that has large surface area as compared to volume. In colder environment, it will lose heat very fast and will have to spend more energy in maintaining internal body temperature as compared to large sized animals. It is because of this reason small sized animals like humming bird do not occur in polar regions. Penguins found in polar regions have narrow and acuminate wings as compared to broader wings of birds of warmer areas and possess thick fur, subcutaneous fat and small extremities which help in conservation of heat so if they inhabit warm tropical areas they won’t be able to dessipate extra heat and will suffocate and die.
Question. How does the human body maintain constant temperature both in summers and winters? Explain.
Answer : When the ambient temperature is very low, our body starts shivering. It is an exercise that raises body temperature and helps to maintain constant internal body temperature at about 37°C, by mechanism of homeostasis.
Question. Name the interaction in each of the following:
(a) Ascaris worms living in the intestine of human
(b) Sucker fish attached to the shark
(c) Smaller barnacles disappeared when Balanus dominated in the coast of Scotland
(d) Wasp pollnating fig inflorescence
Answer : (a) Endoparasitism
(b) Commensalism
(c) Competition
(d) Mutualism
Question. What does S-shaped pattern of population growth represent? How is J-shaped pattern different from it and why?
Answer : S-shaped pattern of population growth represents logistic growth, in which population grows in sigmoid fashion as resources are limited. Population growth is slow initially, then becomes very rapid and finally slows down as environmental resistance increases.
J-shaped pattern shows exponential growth. In this, population increases rapidly and at the peak, population growth ceases abruptly due to environmental resistance.
Question. Name and explain the type of interaction that exists in mycorrhizae and between cattle egret and cattle.
Answer : Mycorrhiza is a mutualistic interaction between fungus and roots of higher plants. The root provides food and shelter to the fungus. The fungus helps the plant in solubilisation and absorption of minerals, water uptake and protection against pathogenic fungi.
The egret and grazing cattle in close association is an example of commensalism. Commensalism is the interaction in which one organism is benefitted and other organism is neither harmed nor benefitted. The egrets always forage close to where the cattle are grazing because the cattle, as they move, stir up and flush out from the vegetation insects that otherwise might be difficult for the egrets to find and catch.
Question. Predation is usually referred to as detrimental association. State any three positive roles that a predator plays in an ecosystem.
Answer : Predators play important role in ecosystem. These are discussed as follows:
(i) Maintaining prey population : In nature, the population of predator is quite small as compared to that of the prey. The prey has high reproductive potential. If, for some time, the prey population is allowed to grow without predation, then it would grow beyond the carrying capacity of the environment. The predator keeps the population of the prey under check so that an equilibrium is maintained. Example, the prickly pear cactus introduced in Australia in the early 1920’s caused havoc by spreading rapidly into millions of hectares of rangeland. Finally, the invasive cactus was brought under control only after a cactus-feeding predator (a moth) from its natural habitat was introduced into the country.
(ii) Maintaining species diversity : Predators also help in maintaining species diversity in a community, by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species. Example, in the rocky intertidal communities of the American Pacific Coast, the starfish Pisaster is an important predator.
When all the starfish were removed from an enclosed intertidal area, more than 10 species of invertebrates became extinct within a year because of interspecific competition.
(iii) Vegetation : Predation helps in growth of vegetation all over the globe by restricting population of herbivores.
Question.Explain parasitism and coevolution with the help of one example of each.
Answer : Parasitism is the interspecific interaction where one of species (called parasite) depends on the other species (host) for food and shelter and damages the host. E.g., malarial parasite in blood cells of humans. Coevolution in parasitism refers to the process in which parasite evolves mechanism to interact and neutralise the mechanism evolved by the host to reject or resist parasite.
Question. Differentiate between mutualism, parasitism and commensalism. Provide one example for each of them.
Answer : Differences between mutualism, commensalism and parasitism are as follows:
| Mutualism | Commensalism | Parasitism |
| It is an association between two organisms in which both are benefitted. |
It is an association between two organisms in which only one is benefitted. The second is neither benefitted nor harmed. |
It is an interaction between two living organisms of di erent species in which one organism called parasite obtains its food from another living organism called host, i.e., one is benefitted and other is harmed. |
| Contact between the two organisms is obligatory. |
Contact between commensal and its benefactor may be periodic or continuous. |
Contact between host and parasite may be temporary or permanent. |
| Nitrogen fixing blue-green alga or cyanobacterium called Anabaena is associated with water fern Azolla in a mutualistic interaction. |
Many epiphytes, e.g., orchids, are found growing on the branches and in the forks of trees. These epiphytes use the trees only for attachment and manufacture their own food by photosynthesis. |
e.g., Cuscuta is a total stem parasite, malarial parasite is found intracellulary (endoparasite) etc. |
Question. Egrets are often seen along with grazing cattle. How do you refer to this interaction? Give a reason for this association.
Answer : The egret and cattle grazing in close association is an example of commensalism. Commensalism is the interaction in which one organism is benefitted and other organism is neither harmed nor benefitted. The egrets always forage close to where the cattle are grazing because the cattle, as they move, stir up and flush out from the vegetation insects that otherwise might be difficult for the egrets to find and catch.
Question. (a) What is “r” in the population equation given below:
dN/dt = rN
(b) How does the increase and the decrease in the value of ‘r’ affect the population size?
Answer : (a) In the population equation dN/dt = rN , ‘r’ is the intrinsic rate of natural increase. dt
(b) It is a very important parameter chosen for assessing impacts of any biotic or abiotic factor on population growth. Its value depends upon the birth rates and death rates.
Question. In a pond there were 40 lotus plants. After a year the number rose to 56. Calculate birth rate of a lotus plant.
Answer : Initial number of lotus plants = 40
Current population = 56
No. of lotus plants added = 16
Birth rate = 16/40 = 0.4 lotus plants per year
Question. Name the interaction in each of the following:
(a) Cuckoo lays her eggs in the crow’s nest.
(b) Orchid grows on a mango tree.
(c) Ticks live on the skin of dogs.
(d) Sea anemone is often found on the shell of hermit crab.
Answer : (a) Brood parasitism
(b) Commensalism (c) Ectoparasitism (d) Commensalism
Question. Name the interaction in each of the following:
(a) Cuscuta growing on a shoe flower plant
(b) Mycorrhizae living on the roots of higherplants
(c) Clown fish living among the tentacles of sea anemone
Answer : (a) Parasitism
(b) Mutualism
(c) Mutualism
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Population Worksheet Set B
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Biology
Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
Students can use the Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations practice sheet provided above to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This solved questions and answers follow the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12 Biology. You can easily download the PDF format and solve these questions every day to improve your marks. Our expert teachers have made these from the most important topics that are always asked in your exams to help you get more marks in exams.
NCERT Based Questions and Solutions for Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create this practice material for students. After solving the questions our teachers have also suggested to study the NCERT solutions which will help you to understand the best way to solve problems in Biology. You can get all this study material for free on studiestoday.com.
Extra Practice for Biology
To get the best results in Class 12, students should try the Biology MCQ Test for this chapter. We have also provided printable assignments for Class 12 Biology on our website. Regular practice will help you feel more confident and get higher marks in CBSE examinations.
You can download the teacher-verified PDF for CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Population Worksheet Set B from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets for Class 12 Biology are designed as per the latest CBSE academic session.
Yes, our CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Population Worksheet Set B includes a variety of questions like Case-based studies, Assertion-Reasoning, and MCQs as per the 50% competency-based weightage in the latest curriculum for Class 12.
Yes, we have provided detailed solutions for CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Population Worksheet Set B to help Class 12 and follow the official CBSE marking scheme.
Daily practice with these Biology worksheets helps in identifying understanding gaps. It also improves question solving speed and ensures that Class 12 students get more marks in CBSE exams.
All our Class 12 Biology practice test papers and worksheets are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format. You can access CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Population Worksheet Set B without any registration.

