Access the latest CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set B. We have provided free printable Class 12 Biology worksheets in PDF format, specifically designed for Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases. These practice sets are prepared by expert teachers following the 2025-26 syllabus and exam patterns issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS.
Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Biology Practice Worksheet for Class 12
Students should use these Class 12 Biology chapter-wise worksheets for daily practice to improve their conceptual understanding. This detailed test papers include important questions and solutions for Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases, to help you prepare for school tests and final examination. Regular practice of these Class 12 Biology questions will help improve your problem-solving speed and exam accuracy for the 2026 session.
Download Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Worksheet PDF
Question. Name two diseases whose spread can be controlled by the eradication of Aedes mosquitoes.
Answer. Dengue/Chikungunya/yellow fever/Eastern equine encephalitis/West Nile fever/Zika virus disease. (Any two)
Question. Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
Answer. Primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus. Secondary lymphoid organs are spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, Peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix.
Question. “Pranay suffered from measles at the age of 10 years. There are rare chances of his getting infected with the same disease for the rest of his life.” Give reason for the statement.
Answer. First exposure to the infection works as vaccination, the immune system of the body gets familiar with the nature of microorganisms and specific antibodies can be produced against infection.
Question. In what way are monocytes a cellular barrier in immunity?
Answer. Monocytes can phagocytose (by the process called phagocytosis) and thereby destroy the pathogens.
Question. How does colostrum provide initial protection against diseases to new born infants? Give one reason.
Answer. Colostrum contains several antibodies which are absolutely essential for developing resistance in the new-born babies.
Question. High fever, loss of appetite, stomach pain and constipation are some of the symptoms seen in a patient. How would the doctor confirm that the patient is suffering from typhoid and not amoebiasis?
Answer. By performing Widal test.
Question. Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Answer. Yes, friends can influence a person to take alcohol or drugs. It can be avoided by (i) avoiding addicted friends.
(ii) avoiding experimental use of alcohol/drug just for curiosity and pressure.
Question. What is it that prevents a child to suffer from a disease he/she is vaccinated against? Give one reason.
Answer. The immunological memory induced by the vaccine in a child prevents the recurrence of a disease.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the two types of immune systems in a human body. Why are cell-mediated and humoral immunities so called?
Answer. The two types of immune systems in a human body are innate and adaptive immunity.
Humoral immunity is called so because it consists of antibodies that are present in humors or body fluids, whereas cell-mediated immunity is provided by T-cells and defends body against viruses, fungi and some bacteria which enter host cells. T-cells recognise non-self cells and kill them.
Question. Describe the role of lymph nodes in providing immunity.
Answer. Lymph nodes trap microorganisms or other antigens. These trapped antigens activate lymphocytes present in the lymph and cause an immune response.
Question. What are the various routes by which transmission of human immunodeficiency virus takes place?
Answer. Various routes by which transmission of HIV takes place:
(i) Transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products.
(ii) By sharing infected needles in case of intravenous drug abusers.
(iii) Sexual contact with an infected person.
(iv) From mother to child through placenta.
Question. Name the plant source of cocaine. How does it affect the human body?
OR
Name the drug obtained from Erythroxylum coca and write its effects on the human body.
Answer. Plant source of cocaine is Erythroxylum coca. It has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
Question. State the functions of primary and secondary lymphoid organs in humans.
Answer. Primary lymphoid organs are the sites where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen sensitive lymphocytes.
Secondary lymphoid organs are the sites where the lymphocytes interact with antigens and proliferate to become effector cells.
Question. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Answer.
| S.No. | Benign tumour | Malignant tumour |
| (i) | It is a non-cancerous tumour. | It is a cancerous tumour. |
| (ii) | Benign tumour does not show metastasis and is non-invasive. | It shows metastasis and thus invades other body parts. |
| (iii) | It stops growth after reaching a certain size. | Malignant tumour shows indefinite growth as proliferating cells, called Neoplastic or tumor cells, grow rapidly, invade and damage other tissues. |
| (iv) | Limited adherence occurs amongst cells of benign tumour. | There is no adherence amongst cells. They tend to slip past one another. |
| (v) | It is less fatal to the body. | It is more fatal to the body. |
Question. Write the biological (binomial) names of causal organisms of the following diseases:
(a) Typhoid (b) Pneumonia
Answer. (a) Salmonella typhi
(b) Streptococcus pneumoniae
Question. (a) Name one primary and one secondary lymphoid organ in the human body.
(b) How do they differ in their functions?
Answer. (a) Primary lymphoid organ: Bone marrow/thymus. (Any one)
Secondary lymphoid organ: Spleen/Lymph nodes/Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). (Any one)
(b) Primary lymphoid organs are the sites where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen sensitive lymphocytes.
Secondary lymphoid organs are the sites where the lymphocytes interact with antigens and proliferate to become effector cells.
Question. (a) Name the lymphoid organ in humans where all the blood cells are produced.
(b) Where do the lymphocytes produced by the lymphoid organ mentioned above migrate and how do they affect immunity?
Answer. (a) Bone marrow.
(b) The lymphocytes produced migrate to secondary lymphoid organs like spleen, lymph nodes,etc. They trap the microorganisms thereby activating the lymphocytes present in the lymph nodes and produce an immune response.
Question. Write the scientific names of the causal organisms of elephantiasis and ringworm in humans.
Mention the body parts affected by them.
Answer.
| Disease | Causal Organism | Body parts affected |
| Elephantiasis | Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi. | Lymph vessels of lower limbs and genital organs |
| Ringworm | Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton | Skin, nails and scalp. |
Question. A young boy when brought a pet dog home started to complain of watery eyes and running nose. The symptoms disappeared when the boy was kept away from the pet.
(a) Name the type of antibody and the chemicals responsible for such a response in the boy.
(b) Mention the name of any one drug that could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Answer. (a) Antibody: IgE; chemicals: Histamine and serotonin
(b) Drugs: Antihistamine, adrenalin, steroids. (Any one)
Question. (a) Highlight the role of thymus as a lymphoid organ.
(b) Name the cells that are released from the above mentioned gland. Mention how they help in immunity.
Answer. (a) Immature lymphocytes differentiate into mature T-lymphocytes and become antigensensitive in thymus.
(b) T-lymphocytes are released from thymus. T-cells help B-cells to produce antibodies and provide cell-mediated immunity.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Under polio prevention programme, infants in India were given polio vaccines on a large scale at regular intervals to eradicate polio from the country.
(a) What is a vaccine? Explain how does it impart immunity to the child against the disease.
(b) With the help of an example each, differentiate between active and passive immunity.
Answer. (a) Vaccination is the process of introduction of weakened or inactivated pathogens or proteins (vaccine) into a person to provide protection against a disease.
• Vaccines are weakened or inactivated pathogens or proteins introduced into a person to provide protection against a disease.
• Immunisation is the process by which the body produces antibodies against the vaccine (primary response) and develops the ability to neutralise pathogens during actual infection (secondary response).
• Vaccination provides immunisation after a time gap.
• Vaccination and immunisation are based on the property called ‘Memory’ of the immune system.
(b) • It is the ability of an organism to resist or defend itself from the development of a disease.
(i) Innate immunity
• It is present from the birth and is inherited from parents.
• It is non-specific type of defence.
• It is accomplished by providing different types of barriers to entry of foreign agents 4 types of barriers are:
Question. (a) What precaution(s) would you recommend to a patient requiring repeated blood transfusion?
(b) If the advise is not followed by the patient, there is an apprehension that the patient might contract a disease that would destroy the immune system of his/her body. Explain
with the help of schematic diagram only how the immune system would get affected and destroyed.
Answer. (a) A patient requiring repeated blood transfusion must ensure that the donor’s blood has been screened for HIV and other pathogens before transfusion.
Question. During a school trip to ‘Rohtang Pass’, one of your classmate suddenly developed ‘altitude sickness’. But, she recovered after sometime.
(a) Mention one symptom to diagnose the sickness.
(b) What caused the sickness?
(c) How could she recover by herself after sometime?
Answer. (a) Nausea/fatigue/heart palpitation
(b) The sickness was caused due to low atmospheric pressure at high altitude because of which the body was deprived of oxygen.
(c) The body compensates low oxygen availability by increasing RBC production decreasing the binding capacity of haemoglobin and by increasing breathing rate.
Question. A heavily bleeding bruised road accident victim was brought to a nursing home. The doctor immediately gave him an injection to protect him against a deadly disease.
(a) Write what did the doctor inject into the patient’s body.
(b) How do you think this injection would protect the patient against the disease?
(c) Name the disease against which this injection was given and the kind of immunity it provides.
Answer. (a) Tetanus antitoxins/Tetanus toxoid.
(b) The preformed antibody injected act on the pathogen immediately to provide protection.
(c) This injection was given against tetanus and it provides passive immunity.
Question. Write the source and the effect on the human body of the following drugs:
(i) Morphine (ii) Cocaine (iii) Marijuana
Answer. (i) Morphine: It is obtained from poppy plant Papaver somniferum. It binds to specific opioid receptors present in central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
(ii) Cocaine: It is obtained from coca plant Erythroxylum coca. It interferes with the transport of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
(iii) Marijuana: It is obtained from Cannabis sativa. It affects the cardiovascular system of the body.
Question. On a visit to a Hill station, one of your friend suddenly become unwell and felt uneasy.
(a) List two symptoms you would look for the term it to be due to allergy.
(b) Explain the response of the body to an allergen.
(c) Name two drugs that can be recommended for immediate relief.
Answer. (a) Sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing are symptoms of allergy.(Any two)
(b) In response to an allergen, the body releases antibodies of IgE type.
(c) Antihistamine, adrenalin, steroids. (Any two)
Question. (a) All human beings have cellular oncogenes but only a few suffer from cancer disease. Give reasons.
(b) How is a malignant tumour different from a benign tumour?
Answer. (a) All humans have cellular oncogenes or proto-oncogenes, but only a few suffer from cancer because cancer only occurs on activation of oncogenes. This activation is induced by
carcinogens which can be physical, chemical or biological. The chemical carcinogens present in tobacco and smoke have been identified as a major cause of lung cancer.
Question. Prior to a sports event, blood and urine samples of sports persons are collected for drug tests.
(a) Why is there a need to conduct such tests?
(b) Name the drugs the authorities usually look for.
(c) Write the genetic names of two plants from which these drugs are obtained.
Answer. (a) Such tests are conducted to detect drug abuse to ensure fair game.
(b) The authorities look for cannabinoids, cocaine, coca alkaloid, coke, crack, hashish, charas, ganja and hemp plant extract.
(c) These drugs are obtained from Cannabis, Atropa, Erythroxylum, Datura. (Any two)
Question. (a) Name a drug used (i) as an effective sedative and pain killer (ii) for helping patients to cope with mental illnesses like depression, but often misused.
(b) How does the moderate and high dosage of cocaine affect the human body?
Answer. (a) (i) Morphine
(ii) Lysergic acid diethyl amides (LSD).
(b) Cocaine has a potent simulating action on central nervous system producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
Question. A farmer while working on his farm was bitten by a poisonous snake. The workers in the farm immediately rushed him to the nearby health centre. The doctor right away gave him an injection to save his life. What did the doctor inject and why? Explain.
Answer. The doctor injected an antivenom. The antivenom contains preformed antibodies which when injected act on the pathogen immediately provide protection by providing passive immunity.
Question. Explain the role of the following in providing defence against infection in human body:
(i) Histamines
(ii) Interferons
(iii) B-cells
Answer. (i) Histamines: These are chemicals which cause inflammatory responses.
(ii) Interferons: These are glycoproteins which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
(iii) B-cells: These produce proteins called antibodies in response to pathogens into the blood to fight with them.
Question. A group of youth were having a ‘rave party’ in an isolated area and was raided by police. Packets of ‘smack’ and syringes with needles were found littered around.
(a) Why is taking ‘smack’ considered an abuse?
(b) Write the chemical name of ‘smack’ and the name of its source plant.
(c) Syringes and needles used by the youth for taking the drug could prove to be very fatal.Why?
Answer. (a) Taking smack is considered as abuse because it is highly addictive. It is a depressant and slows down body functions. It causes psychological and physical dependance.
(b) Its chemical name is diacetylmorphine and is obtained from poppy plant, Papaver Somniferum.
(c) Drugs taken intravenously (direct injection into the vein using a needle and syringe) are much likely to acquire serious infections like AIDS and hepatitis B. The viruses, which are responsible for these diseases are transferred from one person to another by sharing infected needles and syringes.
Question. Identify A, B, C and D in the replication of HIV (retrovirus).
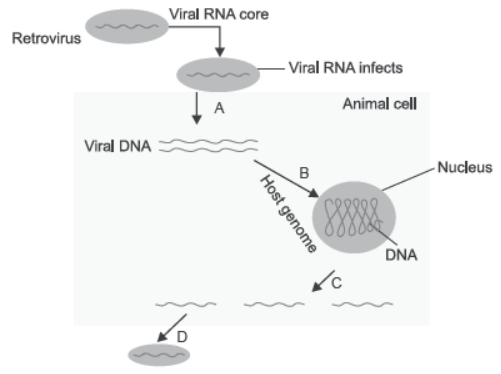
Answer. (A) Reverse transcription.
(B) Viral DNA incorporates into host genome.
(C) New viral RNA produced by infected cell.
(D) New viruses can infect other cells.
Question. Many microbial pathogens enter the gut of humans along with food. What are the preventive barriers to protect the body from such pathogens? What type of immunity do you observe in this case?
Answer. Preventive barrier to protect body are:
(i) The mucus coating of the epithelium lining of the gut helps in trapping microbes entering the body.
(ii) Saliva in the mouth and hydrochloric acid in gastric juice secreted by stomach prevent microbial growth.
This type of immunity is innate immunity.
Question. When someone buys packets of cigarettes, cannot miss the statutory warning that is present on the packing which warns against smoking and says how it is injurious to health. Yet, smoking is very prevalent in our society, both among young and old. Advise the adolescents about the importance of avoiding smoking. (Mention any six points.)
Answer. (i) Tobacco in cigarettes contains a large number of chemical substances including nicotine, an alkaloid. Nicotine stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood circulation, both of which raise blood pressure and increase heart rate.
(ii) Smoking is associated with increased incidence of cancers of lung, urinary bladder, throat and oral cavity.
(iii) It is responsible for bronchitis and emphysema.
(iv) It is associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease, gastric ulcer, etc.
(v) Smoking increases carbon monoxide (CO) content in blood and reduces the concentration of haem-bound oxygen. This causes oxygen deficiency in the body.
Question. Name the two intermediate hosts which the human liver fluke depends on to complete its life cycle so as to facilitate parasitisation of its primary host.
Answer. Snail and fish.
Question. Why is Gambusia introduced into drains and ponds?
Answer. Gambusia is a larvivorous fish. It feeds on mosquito larvae, so introduced in drains and ponds to check spread of mosquito borne diseases.
Question. How does haemozoin affect the human body when released in blood during malarial infection?
Answer. Haemozoin is a toxic substance released by rupturing of RBCs into blood during malarial infection. It causes chill and high fever recurring every 3-4 days.
Question. Malaria, typhoid, pneumonia and amoebiasis are some of the human infectious diseases. Which one of these are transmitted through mechanical carriers?
Answer. Mechanical carrier is one that simply carries pathogens to a susceptible individual and is not essential to the development of the pathogen. The pathogens are simply carried on the mouthparts, legs, body surface of the carrier from an infected to a susceptible host. Amoebiasis and typhoid are carried through mechanical carriers like housefly.
Question. Name any two techniques that serve the purpose of early diagnosis of some bacterial/ viral human diseases.
Answer. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) are used for early diagnosis of some bacterial/viral diseases.
Question. How does malaria differ from chikungunya with reference to their vectors?
Answer. Malaria is a protozoan disease, transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito while chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquito.
Question. Recently chikungunya cases were reported from various parts of the country. Name the vector responsible.
Answer. Aedes aegypti
Question. What causes swelling of the lower limbs in patients suffering from filariasis?
Answer. Filariasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti. They normally affect the lymph vessels of the lower limbs causing them to swell like that of an elephant.
Question. List the symptoms of ascariasis. How does a healthy person acquire this infection?
Answer. Ascariasis is caused by the common round worm Ascaris lumbricoides, a giant intestinal worm. Symptoms of this disease include internal bleeding, muscular pain, fever, anemia and blockage of the intestinal passage. A healthy person acquires infection through contaminated water, vegetables, fruits, etc.
Question. A patient showed symptoms of sustained high fever, stomach pain and constipation, but no blood clot in stools. Name the disease and its pathogen. Write the diagnostic test for the disease. How does the disease get transmitted?
Answer. Bacterial disease typhoid, caused by Salmonella typhi is characterised by sustained high fever (39° - 40°C), stomach pain and constipation. Typhoid fever is diagnosed by Widal test and is transmitted through contaminated food and water.
Question. (a) Name the protozoan parasite that causes amoebic dysentery in humans.
(b) Mention two diagnostic symptoms of the disease.
(c) How is this disease transmitted to others?
Answer. (a) Entamoeba histolytica.
(b) Abdominal pain and blood in faeces.
(c) Amoebic dysentery is transmitted through contaminated food and water.
Question. Name the parasite that causes filariasis in humans. Mention its two diagnostic symptoms.How is this disease transmitted to others?
Answer. Filariasis is a helminthic disease caused by Wuchereria (W. bancrofti and W. malayi). It causes swelling of lymphatic vessels of lower limbs resulting in swelling of feet, legs, scrotal sacs and thighs. It spreads from one human being to other through the bite of female mosquito, Culex.
Question. Explain what causes chill in humans during malarial attack. Name the causative organism of malignant malaria.
Answer. Haemozoin released by rupturing of RBCs causes chill in humans during malarial attack. Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
Question. Name the causative organism, two symptoms and mode of transmission of amoebiasis.
Answer. Entamoeba histolytica is a protozoan parasite in the large intestine of human which causes amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery). Symptoms of this disease include diarrhoea alternating with constipation, abdominal pain and cramps, stool with excess mucus and blood clots. Houseflies act as mechanical carriers and serve to transmit the parasite from faeces of infected person to food and food products, thereby contaminating them. Drinking water and food contaminated by the faecal matter is the main source of infection.
Question. Name the causative organism, two symptoms and mode of transmission of ringworms.
Answer. Ringworm is a fungal disease caused by dermatophytes, which include Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton. Symptoms of ringworm are appearance of dry, scaly lesions on skin, nails, scalp. Ringworm infection is acquired by sharing towels or clothes or comb with infected person.
Question. Write the scientific names of the causal organisms of elephantiasis and ringworm in humans.
Mention the body parts affected by them.
Answer. Elephantiasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti and mainly affects lower limbs.
Ringworm is caused by Trichophyton and affects skin, hair and nails.
Question. Name the host and the site where the following occur in the life-cycle of a malarial parasite:
(a) formation of gametocytes
(b) fusion of gametocytes.
Answer. (a) Formation of gametocytes takes place in human host in red blood cells.
(b) Fusion of gametocytes takes place in mosquito, in its stomach.
Question. Define the term ‘health’. Mention any two ways of maintaining it.
Answer. Health is defined as a state of complete physical, mental and social well being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. Balanced diet, personal hygiene and regular exercise are very important to maintain good health.
Question. List the specific symptoms of pneumonia. Name the causative organism.
Answer. Pneumonia is a serious disease of lungs characterised by accumulation of mucus/fluid in alveoli and bronchioles to that extent that breathing becomes difficult. It is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Diplococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Question. (a) State what happens in the human body when malarial parasites infected RBCs burst to release the parasites in the blood.
(b) Mention the specific sites in the host body where production of
(i) sporozoites and
(ii) gametocytes takes place in the life cycle of the malarial parasites.
Answer. (a) When RBCs infected with malarial parasites burst, they release toxin called haemozoin which causes chill and high fever recurring every three or four days.
(b) (i) Production of sporozoites occurs in female Anopheles mosquito, inside oocyst on the surface of stomach.
(ii) Gametocytes formation takes place in human host inside RBCs.
Question. Mention any two human diseases caused by round worms. Name their causative agents and their mode of transmission into the human body.
Answer. Round worms are nematodes, responsible for helminthic diseases in humans.
Two human diseases caused by round worms are :
(i) Ascariasis - It is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides and spreads through contaminated fruits, water, vegetables etc.
(ii) Filariasis - It is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, and W. malayi. It is transmitted by the bite of female Culex mosquito.
Question. At what stage is Plasmodium picked up by the female Anopheles? Describe the life cycle of the parasite in this insect.
Answer. Female Anopheles mosquito picks up Plasmodium as gametocytes with blood meal. Life cycle of Plasmodium in mosquito is as follows :
The gametocytes come out of the RBCs into the lumen of the stomach of the mosquito. Inside the stomach of the mosquito, the male and female gametocytes change into male and female gametes respectively. The gametes fuse (fertilise) to form zygote called oocyst. The nucleus of oocyst divides first by meiosis and subsequently by mitosis, forming large number of small haploid nuclei. At the same time, spindle shaped bodies called sporozoites are formed. When mature oocysts rupture, the sporozoites are liberated into the haemocoel (body cavity filled with blood) of the mosquito. Being motile, the sporozoites move to different organs in the body cavity of the mosquito, but many of them penetrate the salivary glands. The mosquito now becomes infective. When the female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy person, the sporozoites are injected in his/her blood along with saliva. These sporozoites start the cycle again in human body.
Question. At what stage does Plasmodium gain entry into the human body? Write the different stages of its life cycle in the human body.
Answer. The malarial parasite, Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites (infectious form) through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito (vector). From the human blood sporozoites enter liver cells and multiply here and then attack the red blood cells (RBCs) resulting in their rupture. The rupture of RBCs is associated with release of a toxic substance, haemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days. The released parasites from the ruptured RBCs infect new RBCs and develop into gametocytes (male and female). When a female Anopheles mosquito sucks the blood of an infected human host, it receives RBCs containing gametocytes.
Question. (a) Name the causative organisms for the following diseases:
(i) Elephantiasis,
(ii) Ringworm,
(iii) Amoebiasis
(b) How can public hygiene help control such diseases?
Answer. (a) (i) Elephantiasis – Wuchereria bancrofti
(ii) Ringworm – Microsporum
(iii) Amoebiasis – Entamoeba histolytica (b) Maintenance of public hygiene is very important for prevention and control of many infectious diseases. Public hygiene includes proper disposal of waste and excreta, periodic cleaning and disinfection of water reservoirs, pools, and tanks and observing standard practices of hygiene in public catering. These measures are particularly essential where the infectious agents are transmitted through food and water such as typhoid, amoebiasis and ascariasis.
Question. (a) Write the scientific names of the two species of filarial worms causing filariasis.
(b) How do they affect the body of infected person(s)?
(c) How does the disease spread?
Answer. a) Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi. (b) The filarial worms are deposited near the site of mosquito (Culex) bite. They pass through the punctured skin and reach the lymphatic system where they slowly develop and cause chronic inflammation. They usually infect lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs. The inflammation of lymph nodes and lymph vessels leads to obstruction of lymph vessels which causes thickening of subcutaneous tissues and skin so that swelling of feet, legs, thighs, scrotal sacs occurs.
(c) The pathogens are transmitted to the healthy persons through the bite of the female mosquito Culex.
Question. (a) Name the respective forms in which the malarial parasite gains entry into
(i) human body and
(ii) body of female Anopheles.
(b) Name the hosts where the sexual and the asexual reproductions of malarial parasite occur respectively.
(c) Name the toxin responsible for the appearances of symptoms of malaria in humans.
Why do these symptoms occur periodically?
Answer. (a) (i) Sporozoites, (ii) Gametocytes
(b) Sexual phase of malarial parasite occurs in the mosquito, the primary host of malarial parasite and asexual phase occurs in man, the secondary host.
(c) The release of merozoites and toxin haemozoin from the bursting of schizont in RBCs causes chill and high fever. The released merozoites then attack fresh RBCs leading to the formation of trophozoites causing decrease in fever. The trophozoites then grow in size to become schizont that causes increase in temperature. The schizonts again develop merozoites inside themselves thus causing recurrence of fever with the release of merozoites after few days e.g. at regular intervals of 48 hours in case of P. vivax malaria.
Question. A person is suffering from ascariasis. Mention the pathogen causing the disease and an organ of the body affected, three symptoms and one mode of transmission of the disease.
Answer. Ascariasis is caused by a round worm, Ascaris lumbricoides. It is an endoparasite of small intestine of human beings. Symptoms of ascariasis are abdominal discomfort, fever, anaemia. It is transmitted through contaminated food, water, vegetables etc.
Very Short Answer
Question. What are opioids?
Answer. Opioids are the drugs which bind to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal.
Question. What is primary response?
Answer. When our body encounters a pathogen for the first time produces a response is called primary response.
Question. What are antibodies?
Answer. An army of proteins in response to pathogens into our blood to fight with them, these proteins are called antibodies.
Question. What are light chains and heavy chains?
Answer. Each antibody molecule has four peptide chains, two small called light chains and two longer called heavy chains
Question. What is humoral immune response?
Answer. Antibodies are found in the blood the response is called humoral immune response.
Short Answer
Question. What are the causes of cancer?
Answer. Cancer is caused by accumulated damage to genes. Such changes may be due to chance or to exposure to a cancer causing substance. The substances that cause cancer are called carcinogens. A carcinogen may be a chemical substance, such as certain molecules in tobacco smoke.
Question. What do you mean by tumors?
Answer. Cancerous cells just continue to divide giving rise to masses of cells called tumors. They are of two types’ benign tumors and malignant tumors. Benign tumors normally remain confined to their original location and do not spread to other parts of the body and cause the little damage. The malignant tumors are a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic or tumor cells.
Question. What do you mean by passive immunisation?
Answer. Immunity produced by the transfer to one person of antibodies that were produced by another person, for example: antibodies passed from the mother to the baby before birth confers passive immunity to the baby for the first 4-6 months of life. Passive immunisation is the term used when antibody formed in one individual is given to another individual who is at risk of infection the protection is temporary.
Question. Distinguish between vaccination and immunization?
Answer. Vaccination is the term used for getting a vaccine that is, actually getting the injection or taking an oral vaccine dose whereas immunisation refers to the process of both getting the vaccine and becoming immune to the disease following vaccination.
Question. What do you mean by auto immunity?
Answer. Autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells and tissues. Any disease that results from such an aberrant immune response is termed an autoimmune disease.
Long Answer
Question. State the difference between active immunity and passive immunity?
Answer. 1. Active immunity refers to immunity, which results from the production of antibodies by the person’s own immune system in response to a direct contact of an antigen whereas passive immunity refers to a short-term immunity which results from the introduction of antibodies from the outside.
2. Active immunity does not generate a rapid response whereas passive immunity generates a rapid response.
3. Active immunity generates an immunological memory whereas passive immunity does not generate an immunological memory.
4. Active immunity may last for a long time or lifelong whereas Passive immunity may not last for a long time (2 to 3 days).
5. Active immunity is mediated by the antibodies produced by the person’s own cells whereas passive immunity is mediated by the antibodies produced outside the body.
Question. Write short note on AIDS?
Answer. AIDS stands for Acquires Immuno Deficiency Syndrome. Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV or AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The virus can enter your body through mouth sores or small tears that sometimes develop in the rectum or vagina during sexual activity. AIDS happens after someone has had HIV for many years. In AIDS, the immune system is severely weakened. People with AIDS get serious infections and health problems. AIDS is a set of symptoms and illnesses that develop as a result of advanced HIV infection which has destroyed the immune system. There is always a time-lag between the infection and the appearance of AIDS symptoms. This period may vary from a few months to many years usually 5 to 10 years. Protecting yourself from HIV begins with understanding how the virus is spread. The virus can be passed in only certain ways:
1. During sex with a person infected with HIV
2. By sharing a contaminated needle, such as through illicit drug use.
3. From HIV mother to child either during pregnancy, labour or breastfeeding.
4. Through a contaminated blood transfusion.
Question. Explain about the immune system in the body?
Answer. The immune system protects the body against disease or other potentially damaging foreign bodies. When functioning properly, the immune system identifies and attacks a variety of threats, including viruses, bacteria and parasites, while distinguishing them from the body's own healthy tissue. The immune system is made up of organs that control the production and maturation of certain defence cells, the lymphocytes. Bone marrow and the thymus, a gland situated above the heart and behind the breast bone, are so-called primary lymphoid organs. The bone marrow produces defence cells. When the body senses foreign substances called antigens, the immune system works to recognize the antigens and get rid of them. B lymphocytes are triggered to make antibodies. These specialized proteins lock onto specific antigens. The immune system protects us from disease caused by bacteria, viruses and toxins, and helps remove foreign bodies and malignant cells from our system. In addition, the immune system is responsible for down-regulating immune responses against external harmless triggers such as food, or against the body’s own tissue. Feeling tired and achy, overheating and glands swelling are all signs that our immune system is busy fighting something. Our immune system has evolved to naturally detect and eliminate viral infections and we can actively strengthen our immunity and natural defences by looking after ourselves.
Question. Write short note on cancer?
Answer. Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Cancer is caused by accumulated damage to genes. Such changes may be due to chance or to exposure to a cancer causing substance. The substances that cause cancer are called carcinogens. A carcinogen may be a chemical substance, such as certain molecules in tobacco smoke. A number of forces can cause gene mutations, such as smoking, radiation, viruses, cancer-causing chemicals (carcinogens), obesity, hormones, chronic inflammation and a lack of exercise. Certain foods, such as animal foods high in fat and protein, as well as highly processed foods, are most likely to produce these harmful compounds when subjected to high temperatures. These include meat particularly red meat certain cheeses, fried eggs, butter, margarine, cream cheese, mayonnaise, oils and nuts. We can prevent cancer by adding diets high in nonstarchy vegetables, such as broccoli, spinach, and beans, may help protect against stomach and oesophageal cancer. Eating oranges, berries, peas, bell peppers, dark leafy greens and other foods high in vitamin C may also protect against oesophageal cancer. When we chop, chew, and digest cruciferous veggies like cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, and bok choy, they break down into biologically active compounds that both protect our cells from DNA damage and kill cancer cells, at least in animal tests.
Question. State the difference between drugs and medicine?
Answer. 1. Drug is any substance other than food which has a physiological effect when ingested or otherwise introduced into the body whereas medicine is a substance that is used in treating disease or relieving pain.
2. Drug may have either positive or negative effect whereas medicine usually has a positive effect on the health.
3. Drugs are used for different purposes such as treating disease, relieving pain, recreation and improving cognitive abilities whereas medicine is mainly used to treat disease or relieve pain.
4. Drug is associated with negative connotations whereas medicine is not associated with negative connotations.
5. All drugs are not medicines whereas all medicines are drugs.
6. Drugs do not have any definite form and dose whereas medicine has a definite form and dose.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Disease Worksheet Set B
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
More free study material for Biology
Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
Students can use the Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases practice sheet provided above to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This solved questions and answers follow the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12 Biology. You can easily download the PDF format and solve these questions every day to improve your marks. Our expert teachers have made these from the most important topics that are always asked in your exams to help you get more marks in exams.
NCERT Based Questions and Solutions for Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create this practice material for students. After solving the questions our teachers have also suggested to study the NCERT solutions which will help you to understand the best way to solve problems in Biology. You can get all this study material for free on studiestoday.com.
Extra Practice for Biology
To get the best results in Class 12, students should try the Biology MCQ Test for this chapter. We have also provided printable assignments for Class 12 Biology on our website. Regular practice will help you feel more confident and get higher marks in CBSE examinations.
You can download the teacher-verified PDF for CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set B from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets for Class 12 Biology are designed as per the latest CBSE academic session.
Yes, our CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set B includes a variety of questions like Case-based studies, Assertion-Reasoning, and MCQs as per the 50% competency-based weightage in the latest curriculum for Class 12.
Yes, we have provided detailed solutions for CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set B to help Class 12 and follow the official CBSE marking scheme.
Daily practice with these Biology worksheets helps in identifying understanding gaps. It also improves question solving speed and ensures that Class 12 students get more marks in CBSE exams.
All our Class 12 Biology practice test papers and worksheets are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format. You can access CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet Set B without any registration.

