Access the latest CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet Set C. We have provided free printable Class 12 Biology worksheets in PDF format, specifically designed for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction. These practice sets are prepared by expert teachers following the 2025-26 syllabus and exam patterns issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS.
Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Biology Practice Worksheet for Class 12
Students should use these Class 12 Biology chapter-wise worksheets for daily practice to improve their conceptual understanding. This detailed test papers include important questions and solutions for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction, to help you prepare for school tests and final examination. Regular practice of these Class 12 Biology questions will help improve your problem-solving speed and exam accuracy for the 2026 session.
Download Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction Worksheet PDF
Long Answer Questions
Question: (i) Draw a sectional view of seminiferous tubule of a human. Label the following cells in the seminiferous tubule:
(a) Cells that divide by mitosis to increase their number.
(b) Cells that undergo Meiosis I.
(c) Cells that undergo Meiosis II.
(d) Cells that help in the process of spermiogenesis.
(ii) Mention the role of Leydig cells.
OR
Draw a labelled sectional view of seminiferous tubule of a human male.
Answer: (i) Refer to Fig. 3.8.
(a) Cells that divide by mitosis to increase their number—Spermatogonia
(b) Cells that undergo Meiosis I—Primary spermatocytes
(c) Cells that undergo Meiosis II—Secondary spermatocytes
(d) Cells that help in the process of spermiogenesis—Sertoli cells
(ii) Role of Leydig cells: They synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens.
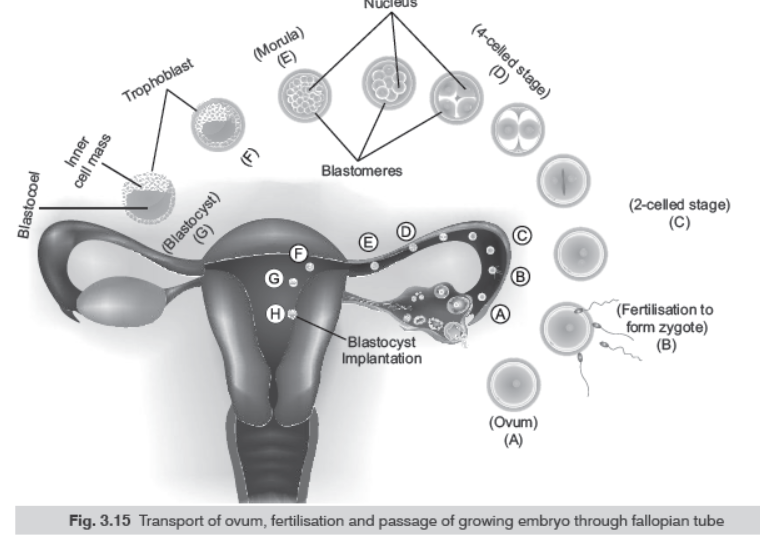
Question: (i) Explain the events taking place at the time of fertilisation of an ovum in a human female.
(ii) Trace the development of the zygote up to its implantation in the uterus.
(iii) Name and draw a labelled sectional view of the embryonic stage that gets implanted
Answer: (i) Fertilisation: Refer to Basic Concepts Point 5. (Image 111)
(ii) Implantation: Refer to Basic Concepts Point 6.
Question: (i) Draw a diagrammatic labelled sectional view of a seminiferous tubule of a human.
(ii) Describe in sequence the process of spermatogenesis in humans.
Answer: (i)
 Diagrammatic sectional view of a seminiferous tubule (enlarged)
Diagrammatic sectional view of a seminiferous tubule (enlarged)(ii) Spermatogenesis
• The process of formation of spermatozoa (sperms) from diploid spermatogonia is called spermatogenesis. It occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes after attaining puberty.
• It includes the following phases:
(a) Multiplication phase: The male germ cells (spermatogonia) present on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules multiply by mitotic division and increase in numbers.
(b) Growth phase: Spermatogonia grow and increase in size and form primary spermatocytes. Each spermatogonium is diploid and contains 46 chromosomes.
(c) Maturation phase or formation of spermatids: Some of the spermatogonia called primary spermatocytes periodically undergomeiosis. Aprimaryspermatocyte completes the first meiotic division (reduction division) leading to formation of two equal haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes, which have only 23 chromosomes each. The secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to produce four equal haploid spermatids.
Question: Draw a diagram of the microscopic structure of human sperm. Label the following parts in it and write their functions.
(i) Acrosome (ii) Nucleus (iii) Middle piece
OR
Draw a diagram of a human sperm. Label only those parts along with their functions, that assist the sperm to reach and gain entry into the female gamete.
OR
Draw a diagram of a mature human sperm. Label any three parts and write their functions.
Ans. For diagram
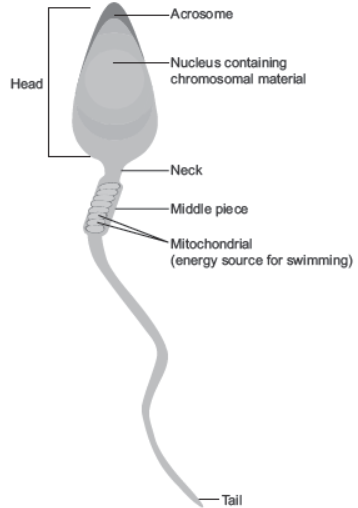
(i) Acrosome: Contains hydrolytic enzymes that help in dissolving membranes of the ovum for fertilisation.
(ii) Nucleus: Carries genetic material of male.
(iii) Middle piece: Contains a number of mitochondria that provide energy for the movement of the tail that facilitate sperm motility.
Question: Study the figure given below:
(i) What is being depicted in the diagram?
(ii) Name ‘a’ and ‘b’ cells. What is the difference between them with reference to the number of chromosomes?
(iii) Pick out and name the motile cells.
(iv) What is ‘f’ cell? Mention its function.
(v) Name the structure of which the given diagram is a part.
Answer: (i) The seminiferous tubule is being depicted in the diagram.
(ii) a—Spermatogonium, b—Primary spermatocyte
They both are diploid and have 46 chromosomes each.
(iii) e—Spermatozoa
(iv) f—Sertoli cell. It provides nutrition to the germ cells.
(v) Seminiferous tubule.
Question: Name the hormones influencing (i) ovulation, (ii) development of corpus luteum.
Answer: (i) Ovulation: Gonadotropins like luteinising hormone and follicular stimulating hormone, and estrogen.
(ii) Development of corpus luteum: Luteinising hormone and progesterone.
Question: Draw the following diagrams related to human reproduction and label them.
(i) The zygote after the first cleavage division
(ii) Morula stage
(iii) Blastocyst stage (sectional view)Answer:
Question: (a) How is ‘oogenesis’ markedly different from ‘spermatogenesis’ with respect to the growth till puberty in the humans?
Answer: (a) Oogenesis is initiated at the embryonic stage whereas spermatogenesis begins only at puberty.
Question: Describe the change that occur in ovaries and uterus in human female during the reproductive cycle.
Answer:
 Diagrammatic presentation of various events during a menstrual cycle
Diagrammatic presentation of various events during a menstrual cycleQuestion: Name the stage of human embryo at which it gets implanted. Explain the process of implantation.
OR
Draw a labelled diagram of a human blastocyst. How does it get implanted in the uterus?
Answer:
The human embryo gets implanted at blastocyst stage.
The trophoblast layer of the blastocyst get attached to the endometrium and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo. After attachment the uterine cell divides rapidly and covers the blastocyst. As a result the blastocyst becomes embedded in the endometrium of the uterus.
Question: Name the source of gonadotropins in human females. Explain the changes brought about in the ovary by these hormones during menstrual cycle.
OR
Describe how the changing levels of FSH, LH and progesterone during menstrual cycle induce changes in the ovary and the uterus in human female.
Answer: Gonadotropins (LH and FSH) are secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
- Gonadotropins (LH and FSH) increase gradually during the follicular phase (proliferative phase) of menstrual cycle and stimulate follicular development as well as secretion of estrogen by the growing follicles.
- LH and FSH attain a peak level in the middle of the cycle (about 14th day) and rapid secretion of LH induces rupture of Graafian follicle followed by ovulation (release of ovum).
- LH stimulates transformation of Graafian follicle into corpus luteum.
Question: Pouch in which testes are suspended outside the abdominal cavity, is
a) tunica albuginea
b) inguinal canal
c) epididymis
d) scrotum
Answer: d
Question: Compartments in mammalian testes are called
a) testicular lobules
b) seminiferous tubules
c) Sertoli cells
d) interstitial cells
Answer: a
Question: Region outside the seminiferous tubules is called
a) interdigital space
b) interferous space
c) interstitial space
d) blind space
Answer: c
Question: Trophoblast of blastocyst attaches to the
a) endometrium
b) myometrium
c) perimetrium
d) mesoderm
Answer: a
Question: ……… provide nutrition to the male germ cells.
a) Interstitial cells
b) Leydig cells
c) Sertoli cells
d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: c
Question: Function of scrotum is to maintain the
a) temperature of testes
b) body temperature
c) level of growth hormone
d) level of male hormone
Answer: a
Question: Funnel-shaped part of oviduct closer to the ovary is called
a) fimbriae
b) infundibulum
c) ampulla
d) isthmus
Answer: b
Question: Identify the accessory glands found in males.
a) Seminal vesicles
b) Prostate gland
c) Bulbourethral gland
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: The seminiferous tubules of the testis is lined on its inside by
a) spermatocytes
b) spermatogonia
c) cells of Sertoli
d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer: d
Question: Spermatogenesis starts at puberty due to significant increase in the secretion of
a) GnRH
b) prolactin
c) testosterone
d) oestrogen
Answer: a
Question: Human Fallopian tube is about
a) 8-9 cm long
b) 9-10 cm long
c) 10-12 cm long
d) 12-17 cm long
Answer: c
Question: The main function of fimbriae of Fallopian tube is
a) help in development of ovary
b) help in collection of the ovum after ovulation
c) help in development of ova
d) help in fertilisation
Answer: b
Question: Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla, which is connected to
a) lactiferous duct
b) seminiferous duct
c) seminiferous tubules
d) nipple
Answer: a
Question: Choose the incorrect pair.
a) Finger-like projections – Fimbriae
b) Narrow part of oviduct – Ampulla
c) Part of oviduct joining the uterus – Isthmus
d) None of the above
Answer: b
Question: The main tissue present in breast is ……… tissue.
a) glandular
b) squamous
c) ciliated
d) epithelium
Answer: a
Question: Which of the following undergoes meiosis-I division during spermatogenesis?
a) Primary spermatocytes
b) Secondary spermatocytes
c) Sertoli cell
d) Leydig cell
Answer: a
Question: Testicular lobules contain
a) 3-5 seminiferous tubules
b) 2-6 seminiferous tubules
c) 5-7 seminiferous tubules
d) 1-3 seminiferous tubules
Answer: d
Question: A sectional view of mammary gland shows
I. nipple and areola.
II. mammary lobes (alveolus) and duct.
III. ribs.
IV. ampulla and lactiferous duct.
Choose the correct option from the above.
a) I, II, III and IV
b) I, II and III
c) III, IV and II
d) I, IV and III
Answer: a
Question: Choose the incorrect pair.
a) Cushion of fatty tissue covered by pubic hair –Mons pubis
b) Membrane covering opening of vagina–Hymen
c) Finger-like structure above the urethral opening –Clitoris
d) Uterine layer exhibiting strong contraction during delivery–Endometrium
Answer: d
Question: Which cells come earliest in the sequence of spermproduction?
a) Spermatozoa
b) Spermatocyte
c) Spermatid
d) Spermatogonia
Answer: d
Question: Approximate length and width of testis are
a) 4-5 cm and 2-3 cm
b) 5-6 cm and 3-4 cm
c) 6-7 cm and 4-5 cm
d) 7-8 cm and 8-9 cm
Answer: a
Question: Which one of the following cells have haploid number of chromosome?
a) Primary spermatocytes
b) Secondary spermatocytes
c) Spermatid
d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer: d
Question: In an ideal menstrual cycle, the menstrual phase last for
a) 3-5 days
b) 5-6 days
c) 1-3 days
d) 2-3 days
Answer: a
Question: During spermatogenesis, which cells are the first to contain haploid number of chromosomes?
a) Spermatogonium
b) Primary spermatocyte
c) Secondary spermatocyte
d) Spermatid
Answer: c
Question: Everytime copulation does not lead to fertilisation and pregnancy because of failure of sperm to reach the
a) ampulla
b) cervix
c) endometrium
d) myometrium
Answer: a
Question: Sperms of mammals depend for movement on
a) only tail
b) tail and middle piece
c) middle piece
d) Only head
Answer: b
Question: The first menstruation that begins at puberty is called
a) menopause
b) ovulation
c) gametogenesis
d) menarch
Answer: d
Question: A regular cycling woman is not menstruating, which one of the following is the most likely to be the root cause?
a) Maintenance of the hypertrophical endometrial lining
b) Maintenance of high concentration of sex-hormones in the bloodstream
c) Regression of well-developed corpus luteum
d) Fertilisation of the ovum
Answer: d
Question: During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zonapellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of …A… . The secretions of the …B… help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the
ovum.
A B
a) eggs zona pellucida
b) eggs acrosome
c) additional sperms acrosome
d) additional sperms zona pellucida
Answer: c
Question: What happens during the follicular phase of menstrual cycle?
a) Proliferation of endometrium
b) Reduction in blood supply to endometrium
c) Regression of endometrium
d) No effect on endometrium
Answer: a
31. When does ovulation occur in a healthy menstruating female?
a) 9-14 days
b) 14-16 days
c) 16-28 days
d) 20-26 days
Answer: b
Question: The reproductive cycle in the female primates such as monkeys, apes and human beings is called
a) menstrual cycle
b) oestrus cycle
c) circadian cycle
d) ovulatory cycle
Answer: a
Question: Rapid secretion of LH in ovulatory phase causes
a) rupturing of Graafian follicle
b) release of ova
c) ovulation
d) All of the above
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following cells present in the mammalian testes forms the sperms?
a) Leydig cells
b) Spermatogonia
c) Interstitial cells
d) Sertoli cells
Answer: b
Question: Inner cell mass or embryoblast gives rise to
a) foetal part
b) embryo
c) notochord
d) nourishment cell
Answer: b
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet Set C
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology And Its Application Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Question Bank |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
More free study material for Biology
Chapter 2 Human Reproduction CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheet
Students can use the Chapter 2 Human Reproduction practice sheet provided above to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This solved questions and answers follow the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12 Biology. You can easily download the PDF format and solve these questions every day to improve your marks. Our expert teachers have made these from the most important topics that are always asked in your exams to help you get more marks in exams.
NCERT Based Questions and Solutions for Chapter 2 Human Reproduction
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create this practice material for students. After solving the questions our teachers have also suggested to study the NCERT solutions which will help you to understand the best way to solve problems in Biology. You can get all this study material for free on studiestoday.com.
Extra Practice for Biology
To get the best results in Class 12, students should try the Biology MCQ Test for this chapter. We have also provided printable assignments for Class 12 Biology on our website. Regular practice will help you feel more confident and get higher marks in CBSE examinations.
You can download the teacher-verified PDF for CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet Set C from StudiesToday.com. These practice sheets for Class 12 Biology are designed as per the latest CBSE academic session.
Yes, our CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet Set C includes a variety of questions like Case-based studies, Assertion-Reasoning, and MCQs as per the 50% competency-based weightage in the latest curriculum for Class 12.
Yes, we have provided detailed solutions for CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet Set C to help Class 12 and follow the official CBSE marking scheme.
Daily practice with these Biology worksheets helps in identifying understanding gaps. It also improves question solving speed and ensures that Class 12 students get more marks in CBSE exams.
All our Class 12 Biology practice test papers and worksheets are available for free download in mobile-friendly PDF format. You can access CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet Set C without any registration.

