
M.C.Q.
1. The temperature of the system decreases in an
(A) Adiabatic compression (B) Isothermal compression
(C) Isothermal expansion (D) Adiabatic expansion
2. If a refrigerator’s door is opened, then we get
(A) Room heated (B) Room cooled
(C) More amount of heat is passed out (D)No effect on room
3. The cooling in refrigerator is due to
(A) Reaction of the refrigerator gas (B) Expansion of ice
(C) The expansion of the gas in the refrigerator (D) The work of the compressor
4. The process, in which no heat enters or leaves the system, is termed as
(A) Isochoric (B) Isobaric (C) Isothermal (D) Adiabatic
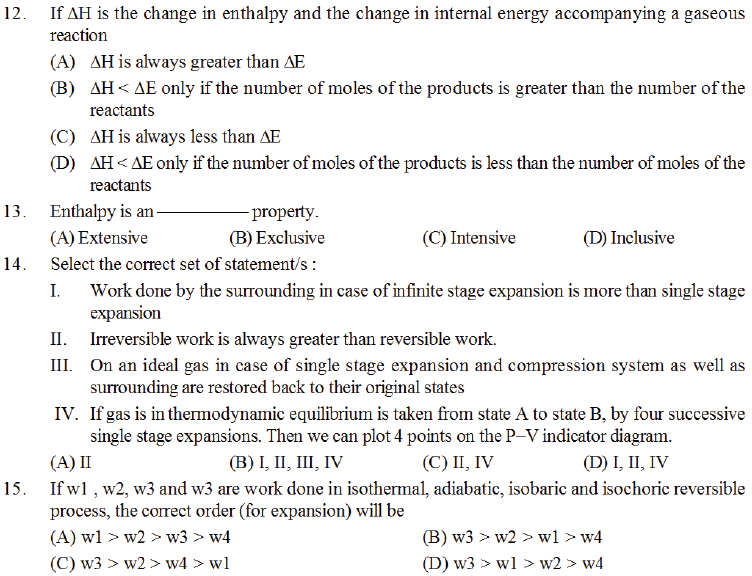
5. Warming ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide in a test tube is an example of :
(A) Closed system (B) Isolated system (C) Open system (D) None of these
6. Out of boiling point (I), entropy (II), pH (III) and e.m.f. of a cell (IV), intensive properties are –
(A) I, II (B) I, II, III (C) I, III, IV (D)All the above
7. A thermodynamic state function is
(A) one which obeys all the laws of thermodynamics
(B) a quantity which is used in measuring thermal changes
(C) one which is used in thermo chemistry
(D) a quantity whose value depends only on the state of the system.
8. In thermodynamics, a process is called reversible when
(A) surroundings and system change into each other
(B) there is no boundary between system and surroundings
(C) the surroundings are always in equilibrium with the system
(D) the system changes into the surroundings spontaneously
9. Which one of the following statement is false–
(A) work is a state function (B) temperature is a state function
(C) change in the state is completely defined when the initial and final states are specified
(D) work appears at the boundary of the system.
10. A mixture of two moles of carbon monoxide and one mole of oxygen, in a closed vessel is ignited to convert the carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. If ΔH is the enthalpy change and ΔE is the change in internal energy, then
(A) ΔH < ΔE (B) ΔH > ΔE (C) ΔH = ΔE
(D) The relationship depends on the capacity of the vessel
11. At constant T and P, which one of the following statements is correct for the reaction,
CO(g) + ½ O2 g → CO2 (g)
(A) ΔH is independent of the physical state of the reactants of that compound
(B) ΔH < ΔE (C) ΔH > ΔE (D) ΔH = ΔE

(A) The randomness of the universe decreases
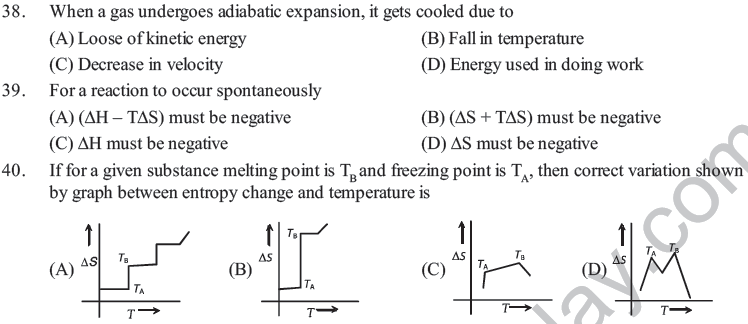
(B) The randomness of the surroundings decreases
(C) Increase is randomness of surroiundings equals the decrease in randomness of system
(D) The increase in randomness of the surroundings is greater as compared to the decrease in randomness of the system.
21. The enthalpy change for a given reaction at 298 K is – x J mol–1 (x being positive). If the reaction occurs spontaneously at 298 K, the entropy change at that temperature
(A) can be negative but numerically larger than x/298
(B) can be negative but numerically smaller than x/298
(C) cannot be negative (D) cannot be positive
22. Spontaneous adsorption of a gas on a solid surface is exothermic process because
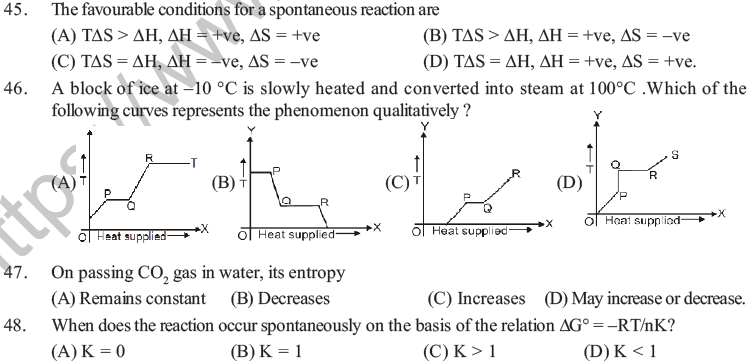
(A) enthalpy of the system increases. (B) entropy increases.
(C) entropy decreases. (D) free energy change increases.
23. Identify the correct statement regarding entropy :
(A) At absolute zero, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is +ve.
(B) At absolute zero, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is zero.
(C) At 0°C the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero.
(D) At absolute zero of temperature the entropy of all crystalline substances is taken to be zero.
24. Identify the correct statement regarding a spontaneous process :
(A) Exothermic processes are always spontaneous.
(B) Lowering of energy in the reaction process is the only criterion for spontaneity.
(C) For a spontaneous process in an isolated system, the change in entropy is positive.
(D) Endothermic processes are never spotaneous.

29. Identify the correct statement regarding entropy
(A) At 0°C, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
(B) At absolute zero of temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is +ve
(C) At absolute zero of temperature, the entropy of all crystalline substances is taken to be zero
(D) At absolute zero of temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
30. A container has hydrogen and oxygen mixture in ratio of 4 : 1 by weight, then
(A) Internal energy of the mixture decreases (B) Internal energy of the mixture increases
(C) Entropy of the mixture increases (D) Entropy of the mixture decreases
31. The second law of thermodynamics says that in cyclic process.
(A) Work cannot be converted into heat (B) Heat cannot be converted into work
(C) work cannot be completely converted into heat
(D) Heat cannot be completely converted into work
32. A heat engine absorbs heat Q1 at temperature T1 and heat Q2 at temperature T2. Work done by
the engine is (Q1 + Q2). This data
(A) Violates Ist law of thermodynamics
(B) Violates Ist law of thermodynamics if Q1 is –ve
(C) Violates Ist law of thermodynamics if Q2 is –ve
(D) Does not violate Ist law of thermodynamics
33. The molar neutralization heat for and as compared to molar neutralization heat of NaOH and HCl
(A) Less (B) More (C) Equal (D) Depends on pressure
34. If the enthalpy of B is greater than of A, the reaction A→B is
(A) Endothermic (B) Exothermic (C) Instantaneous (D) Spontaneous
35. Which of the following fuels will have the highest calorific value (kJ/kg)
(A) Charcoal (B) Kerosene (C)Wood (D) Dung
36. Which is the best definition of “heat of neutralization”
(A) The heat set free when one gram molecule of a base is neutralized by one gram molecule of an acid in dilute solution at a stated temperature
(B) The heat absorbed when one gram molecule of an acid is neutralized by one gram molecule of a base in dilute solution at a stated temperature
(C) The heat set free or absorbed when one gram atom of an acid is neutralized by one gram atom of a base at a stated temperature
(D) The heat set free when one gram equivalent of an acid is neutralized by one gram equivalent of a base in dilute solution at a stated temperature
37. Compounds with high heat of formation are less stable because
(A) High temperature is required to synthesise them
(B) Molecules of such compounds are distorted
(C) It is difficult to synthesis them (D) Energy rich state leads to instability
41. A Beckmann thermometer is used to measure
(A) High temperature (B) Low temperature (C) Normal temperature (D) All temperature
42. The calorific value of fat is _____
(A) less than carbohydrates and protein
(B) less than that of protein but more than carbohydrates
(C) less than that of carbohydrates and more than that of protein
(D) more than thant of carbohydrates and protein
43. Which of the following processes is accompanied by an increase in entropy ?
(A) Normal rubber band to stretched rubber band (B) Normal egg to hard boiled egg
(C) Decomposition of N2O5 to N2O to O2 (D) Formation of NH3 for N2H2.
44. Which of the following does not exhibit zero entropy at absolute zero
(A) Benzene (B) Glass (C) Pyridine (D) CCl4
49. In thermodynamics, a process is called reversible when,
(A) Surroundings and system change into each other
(B) The surroundings are always in equilibrium with the system
(C) The system changes into the surroundings spontaneously.
(D) There is no boundary between system and surroundings.
50. Under certain conditions, the value of ΔG for a hypothetical reaction, X + Y → Z is greater than zero, then –
(A) The reaction has tendency to proceed towards Z
(B) The reaction has attained equilibrium
(C) increase in temperature increases the yield of product Z
(D) X and Y predominate in the final mixture
51. For which of the following processes will energy be absorbed –
(A) Separating an electron from an electron (B) Separating proton from a proton
(C) Separating a neutron from neutron (D) Separating an electron from neutral atom






83. The latent heat of vaporisation of a liquid at 500 K and 1 atm pressure is 10 kcal/mol. What will be the change in internal energy (ΔE) of 3 moles of liquid at the same temperature?
(A) 13.0 kcal (B) – 13.0 kcal (C) 27.0 kcal (D) – 27.0 kcal
84. The work done in ergs for a reversible expansion of one mole of an ideal gas from a volume of 10 litres at 25°C is :
(A) 3.43 KJ (B) 3.43 Kcal (C) 3.43 J (D) 3.43 cal
85. Reaction, H2(g) + I2 (g) → 2HI; ΔH = 12.40 kcal.
According to this, heat of formation of HI will be
(A) 12.40 kcal (B) – 12.4 kcal (C) – 6.20 kcal (D) 6.20 kcal
86. The heat of combustions of yellow phosphorus and red phosphorus are – 9.91 kJ and – 8.78 kJ respectively. The heat of transition of yellow phosphorus to red phosphorus is :
(A) – 18.69 kJ (B) +1.13 kJ (B) +18.69 kJ (D) – 1.13 kJ
87. The heat of formation of CO(g) and CO2 (g) are – 26.4 kcal and – 94.0 kcal respectively. The heat of combustion of carbon monoxide will be :
(A) + 26.4 kcal (B) – 67.6 kcal (C) – 120.6 kcal (D) +52.8 kcal
88. The heats of combustion of rhombic and monoclinic sulphur are – 70960 and – 71030 calorie respectively. What will be the heat of conversion of rhombic sulphur to monoclinic sulphur?
(A) – 70960 cal (B) – 71030 cal (C) 70 cal (D) – 70 cal