ˆ The salt that is obtained when two or more salts having independent existence combine according to the laws of combination and which maintain the properties of original salts is called double salt e.g. Alum is a double salt.
ˆ Similarly, the compound that is obtained when two or more salts having independent existence combine according to laws of chemical combination and compound having new properties, formed is called complex compound. e.g. K3[Fe(CN)6] is a complex salt.
ˆ Most of the complex compounds are formed by elements of d-block (transition elements). In the electronic configuration of these elements, there is successive arrangement of electrons in d-orbitals. when the atom or ion of transition elements has vacant (n–1)d, ns and np or ns, np and nd orbitals, these transition elements accept negative ions or neutral molecules and they form the compounds which are called complex compounds. In this type of compounds, the bond that is formed between metal ions of elements and the negative ion or neutral molecules is called co-ordinate covalent bond. Around the centre of the metal ions of the molecules of these compounds, the negative ions or neutral molecules are combined with co-ordinate covalent bond.
ˆ Alfred Werner, first of all gave the theory for complex compounds which is known as Werner's coordination theory. Some metals have the secondary valency in addition to their primary valence. By this the ions of that metal combine strongly with the negative ion or neutral molecules in first attraction sphere [ ].
ˆ According to Werner's theory, the metal ion possesses two types of valencies : Primary valency and secondary valency.
ˆ The primary valency of the metal is equal to its oxidation number or equal to the positive electric charge of the positive ion, which forms ionic bond, so that it gets ionized. The negative ion combines with primary valency.
ˆ The secondary valency depends on the vacant orbitals in metal ion. The secondary valency is satisfied by negative ions or neutral molecules. It does not get ionized. The secondary valency mentions its coordination number. The secondary valency is fixed for the metal ion but now, it has been proved that the transition metal ions possess more than one co-ordination number. As the secondary valence being directional determines the geometrical shape of complex compound. From the magnetic properties also the shape of complex can be determined. e.g. In [Cr(NH3)6]Cl3, Cr is metal ion and six molecules of neutral molecule ammonia (NH3) are combined with it by secondary valency which do not get ionized. Hence, the co-ordination number is six. Three Cl– are combined by primary valency which gets ionized. Hence the primary valency of Cr is three.
ˆ Ligand is an ion having negative electric charge or neutral molecule. The classification of ligand is made on the basis of the number of electron pair donating atoms.
ˆ If the negative ion or neutral molecule in the ligand forms one co-ordinate covalent bond by giving one electron pair to metal ion, then it is called unidentate ligand. Neutral molecules like H2O, NH3, CO, NO and negative ions like Cl–, Br–, CN– act as unidentate ligands.
ˆ The ligand which donates two electron pairs to metal ion, and form two co-ordinate covalent bonds is called didentate ligand. e.g. ethane 1,2-diamine (en), neutral and SO2- 4 , CO2-3 negative ions act as didentate ligands.
ˆ The ligand in which three co-ordinate sites are indicated then it is called tridentate. In this type of ligand the atoms donate three pairs of electrons to metal ion and form three co-ordinate covalent bonds. e.g. Propane-1, 2, 3-triamine (ptn) neutral and PO3-4 , AsO3-4act as negative tridentate ligand.
ˆ Six atoms in EDTA, (ethylene diaminetetracetate) ion, the six atoms donate six electron pairs and form six co-ordinate covalent bonds, which act as hexadentate ligand.
ˆ Generally, the ligand in which two or more than two co-ordination sites are indicated, or the ligand in which two or more than two atoms form co-ordinate covalent bonds by donating electron pairs to metal ion is called polydenate ligand, which combines with metal ion and form complex compounds. They are called chelate compounds which are cyclic and possess higher stablity.
ˆ The basic requirements for formation of complex compounds are ligand which can easily donate electron pairs, there must be vacant d-orbitals in the metal ion to accept electron pairs and the metal ion should have the symmetry same as that of the ligand. The ion satisfying these basic requirements can easily form complex compounds.
ˆ The strength of formation of co-ordinate covalent bonds of different ligands being different, the stronger ligand possesses more attraction towards metal ion and form strong coordinate covalent bond. As a result, the stability of complex having strong ligand is more and the weak ligand containing complex compounds have less stability e.g. The strength of [Ni(CN)4]2– is more than that of [NiCl4]2.
ˆ A complex compound, in which different types of ligands combine with metal ion and form complex compound, is called mixed ligand complex. If in any of the complex compounds only one metal ion is present, then it is called unicentred complex compound. If in any complex compound, more than one metal ions are present then it is called polycentred complex compound. In such unicentred or polycentred complex compounds, the three dimensional arrangement of ligand, the different geometrical structures are produced in co-ordination compounds, it is called polyhedra. Mostly the geometrical structures are of shapes-tetrahedral square planar, octahedral square pyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal. To understand these geometrical structures, the hybridization of orbitals of metal ion and magnetic properties are very useful. sp3 hybridisation, dsp2 hybridisation, d3s hybridization in metal ions of co-ordination number four is seen. In sp3d2 hybridization and d2sp3 hybridization, the metal ions of transition elements is seen in.






51. According to werner’s theory :
(A) Primary Valeccy can be ionized
(B) Secondary valency can be ionized
(C) Primary and secondary valencies cannot be ionized
(D) Only primary valency cannot be ionized
52. Ligand in a complex salt are :
(A) Anions linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion
(B) Cation linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion
(C) Moleculer linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion
(D) Ions or molecules linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion
53. According to Lewis the ligand are :
(A) Acidic in nature (B) Basic in nature
(C) Neither acidic nore basic (D) some are acidic and other are basic
54. Which of the following acts as a bidentate ligand in complex formation ?
(A) Acetate (B) oxalate (C) Thiocyanate (D) EDTA
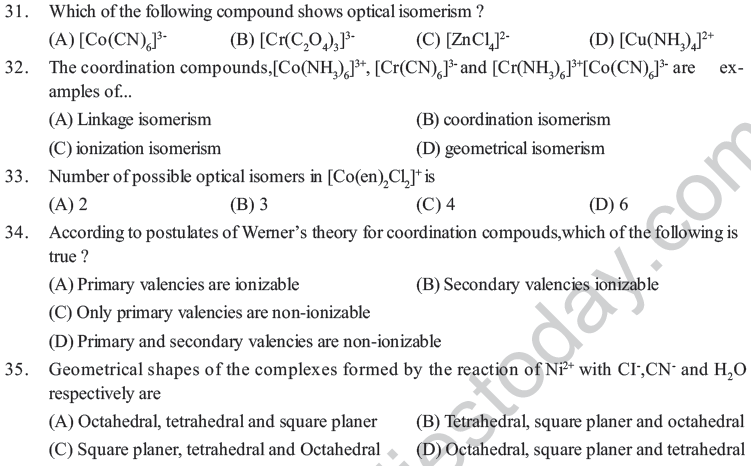
55. The coordination number of cobalt in the complex [Co(en)2Br2]cl2 ?
(A) 2 (B) 6 (C) 5 (D) 4
56. Which is the example of hexadentate ligand ?
(A) 2,2-dipyridyl (B) Dimethyl glyoxime
(C) Aminodiacetate ion (D) Ethylene diammine tetra actate ion
57. Which of the following is tridentate neutral Ligand ?
(A) Pn (B) Ptn (C) PO43 – (D) A and B both
58. The primary valency of the metal ion in the coordinateion compound K2[Ni(CN)4] is ___
(A) Four (B) Zero (C) Two (D) Six
59. The metal which forms polynuclear carbonyl is ?
(A) Mn (B) Co (C) Cr (D) Fe
60. Potasssium ferrocyanide is a _____
(A) Normal salt (B) Mixed salt (C) Double salt (D) Complex salt
61. Given the molecular formula of the hexa coordinated complexes.
(A) Co Cl3 6NH3
(B) Co Cl3 5NH3
(C) Co Cl3 4NH3
If the number of coordinated NH3 molecudes in A,B and C respectively are 6,5 and 4 the primary valency (A), (B) and (C) are:
(A) 6,5,4 (B) 3,2,1 (C) 0,1,2 (D) 3,3,3
62. In the compound lithium tetrahydroaluminate the ligand is:
(A) H+ (B) H– (C) H (D) None of these
63. Which of the folloiwing is the odd one out.
(A) Potassium ferrocyanide (B) Ferrous ammonium sulphate
(C) Potassium ferricyanide (D) Tetrammine copper (II) sulphate
64. Ligand in complex compounds
(A) Accept e– - pair (B) Donate e– - pair
(C) Neither accept e– - pair nor donate (D) All of these.
65. Which of the following is a common donor atom in ligands ?
(A) Arsenic (B) Nitrogen (C) Oxygen (D) Both B and C




Assertion and Reason
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the option given below :
(A) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) If both a ssertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(E) If the assertion is false but reason is true.

