Practice NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B provided below. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Chemical Kinetics Chemistry with answers and follow the latest NEET/ NCERT and KVS patterns. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NEET Full Syllabus Chemistry and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
Full Syllabus Chemistry students should review the 50 questions and answers to strengthen understanding of core concepts in Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Chemistry with Answers
Question: For a gaseous phase reaction 2A + B2→ 2AB, the following rate data was obtained at 300K
The rate constant for the reaction is
- a) 0.5 mol–1 min–1 litre
- b) 0.8 mol–1 min–1 litre
- c) 1.5 mole–1 min–1 litre
- d) 2 mol–1 min–1 litre
Answer: 0.8 mol–1 min–1 litre
Question: Inversion of a sugar follows first order rate equation which can be followed by noting the change in rotation of the plane of polarization of light in the polarimeter. If r∞, rt and r0 are the rotations at t = ∞, t = t and t = 0 then, first order reaction can be written as
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Which of the following is correct?
- a)
- b) For zero order t1/2 is inversely proportional to initial concentration
- c) Catalyst decreases the activation energy
- d) All of these
Answer: Catalyst decreases the activation energy
Question: The rate constant of a reaction is 1.5 × 107 s–1 at 50°C and 4.5 × 107 s–1 at 100°C. What is the value of activation energy?
- a) 2.2 × 103 J mol–1
- b) 2300 J mol–1
- c) 2.2 × 104 J mol–1
- d) 220 J mol–1
Answer: 2.2 × 104 J mol–1
Question: In Arrhenius equation,
A may not be termed as rate constant
- a) When 100% reactant will convert into the product
- b) When the temperature becomes infinite
- c) When the fraction of molecule crossing over the energy barrier becomes unity
- d) At very low temperature
Answer: At very low temperature
Question: The rate constant of the production of 2B(g) by the reaction,
A 1 : 1 molar ratio of A to B in the reaction mixture is attained after
- a) 26.25 minute
- b) 27.25 minute
- c) 28.25 minute
- d) 0 minute
Answer: 27.25 minute
Question: Two substances A and B are present such that [A]0= 4[B]0 and half life of A is 5 minute and that of B is 15 minute. If they start decaying at the same time following first order kinetics how much time will the concentration of both of them would be the same?
- a) 15 minute
- b) 10 minute
- c) 5 minute
- d) 12 minute
Answer: 15 minute
Question: If the rate of reaction increases by 27 times, when temperature is increased by 30 K, then temperature coefficient of the reaction is
- a) 3
- b) 2
- c) 1
- d) 2.5
Answer: 3
Question: The reaction A —→B follows first order kinetics. The time taken for 0.80 mole of A to produce 0.60 mole of B is 1 hour. What is the time taken for conversion of 0.90 mole of A to produce 0.675 mole of B?
- a) 1 hour
- b) 30 min
- c) 15 min
- d) 5 min
Answer: 1 hour
Question: If,
find B%
- a) 25%
- b) 50%
- c) 75%
- d) 80%
Answer: 25%
Question: The rate constant of the reaction A—→ B is 0.6 × 10–3 mole per second. If the concentration of A is 5 M, then concentration of B after 20 minutes is
- a) 0.36 M
- b) 0.72 M
- c) 1.08 M
- d) 3.60 M
Answer: 0.72 M
Question: The activation energy of a reaction can be determined from the slope of which of the following graphs?
- a)
- b) In K vs T
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: When initial concentration of a reactant is doubled in a reaction, its half-life period is not affected. The order of the reaction is
- a) More than zero but less than first
- b) Zero
- c) First
- d) Second
Answer: First
Question: A reaction having equal energies of activation for forward and reverse reactions has
- a) ΔG = 0
- b) ΔH = 0
- c) ΔH =ΔG =ΔS = 0
- d) ΔS = 0
Answer: ΔH = 0
Question: In a zero order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become
- a) 64 times
- b) 128 times
- c) 256 times
- d) 512 times
Answer: 512 times
Question: What is the activation energy for a reaction if its rate doubles when the temperature is raised from 20°C to 35°C? (R = 8.314 J mol–1K–1)
- a) 269 kJ mol–1
- b) 34.7 kJ mol–1
- c) 15.1 kJ mol–1
- d) 342 kJ mol–1
Answer: 34.7 kJ mol–1
Question: In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (A and B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as
- a) Rate = k[A] [B]
- b) Rate = k[A]2[B]
- c) Rate = k[A] [B]2
- d) Rate = k[A]2[B]2
Answer: Rate = k[A]2[B]
Question: Which one of the following statements for the order of a reaction is incorrect?
- a) Order of reaction is always whole number
- b) Order can be determined only experimentally
- c) Order is not influenced by stoichiometric coefficient of the reactants
- d) Order of reaction is sum of power to the concentration terms of reactants to express the rate of reaction
Answer: Order of reaction is always whole number
Question: The unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction is
- a) L2 mol–2 s–1
- b) s–1
- c) mol L–1 s–1
- d) L mol–1 s–1
Answer: mol L–1 s–1
Question: The half life of a substance in a certain enzyme- catalysed reaction is 138 s. The time required for the concentration of the substance to fall from 1.28 mg L–1 to 0.04 mg L–1 is
- a) 690 s
- b) 276 s
- c) 414 s
- d) 552 s
Answer: 690 s
Question: For the reaction, N2O5(g) → 2NO2 (g) + 1/2 O2(g), the value of rate of disappearance of N2O5 is given as 6.25×10–3 mol L–1s–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as
- a) 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1 & 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1
- b) 1.25 × 10–2 mol L–1s–1 & 3.125 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1
- c) 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1 & 3.125 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1
- d) 1.25 × 10–2 mol L–1s–1 & 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1
Answer: 1.25 × 10–2 mol L–1s–1 & 3.125 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1
Question: For an endothermic reaction, energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction is ΔH (both of these in kJ/mol). Minimum value of Ea will be
- a) Less than ΔH
- b) Equal to ΔH
- c) More than ΔH
- d) Equal to zero
Answer: More than ΔH
Question: During the kinetic study of the reaction, 2A+B→C+D, following results were obtained
Based on the above data which one of the following is correct ?
- a) Rate = K[A]2 [B]
- b) Rate = K[A][B]
- c) Rate = K[A]2 [B]2
- d) Rate = K[A][B]2
Answer: Rate = K[A][B]2
Question: The rate of the reaction, 2NO + Cl2—→2NOCl is given by the rate equation rate = k[NO]2[Cl2] The value of the rate constant can be increased by
- a) Increasing the temperature
- b) Increasing the concentration of the Cl2
- c) Increasing the concentration of NO
- d) Doing all of these
Answer: Increasing the temperature
Question: For the reaction, N2+ 3H2→2NH3,
- a) 4×10–4 mol L–1 s–1
- b) 6×10–4 mol L–1 s–1
- c) 1×10–4 mol L–1 s–1
- d) 3×10–4 mol L–1 s–1
Answer: 3×10–4 mol L–1 s–1
Question: In the reaction,
The rate of appearance of bromine (Br2) is related to rate of disappearance of bromide ions as following
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Half life period of a first-order reaction is 1386 seconds. The specific rate constant of the reaction is
- a) 0.5 × 10–2 s–1
- b) 0.5 × 10–3 s–1
- c) 5.0 × 10–2 s–1
- d) 5.0 × 10–3 s–1
Answer: 0.5 × 10–3 s–1
Question: For the reaction A + B —→ Products, it is observed that
(a) On doubling the initial concentration of A only, the rate of reaction is also doubled and
(b) On doubling the initial concentrations of both A and B, there is a change by a factor of 8 in the rate of the reaction.
The rate of this reaction is given by
- a) Rate = k [A] [B]2
- b) Rate = k [A]2[B]2
- c) Rate = k [A] [B]
- d) Rate = k[A]2[B]
Answer: Rate = k [A] [B]2
Question: The rate constants k1 and k2 for two different reactions are 1016 e–2000/T and 1015 e–1000/T respectively. The temperature at which k1= k2 is
- a)
- b) 1000 K
- c)
- d) 2000 K
Answer:
Question: The bromination of acetone that occurs in acid solution is represented by this equation
These kinetic data were obtained for given reaction concentrations
Based on these data, the rate equation is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
More Questions.............................
Question: In a first-order reaction A —→ B, if K is rate constant and initial concentration of the reactant A is 0.5M then the half-life is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The reaction of hydrogen and iodine monochloride is given as
H2(g)+ 2ICI(g)—→2HCl(g)+ I2(g)
This reaction is of first order with respect to H2(g)and ICI(g) , following mechanisms were proposed
Mechanism A:
H2(g)+ 2ICI(g)—→2HCl(g)+ I2(g)
Mechanism B:
H2(g)+ ICI(g)—→ HCl(g)+ HI(g); slow
HI(g)+ ICI(g)—→HCl(g)+ I2(g); fast
Which of the above mechanism(s) can be consistent with the given information about the reaction?
- a) A only
- b) B only
- c) Both (1) and (2)
- d) Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer: B only
Question: If 60% of a first order reaction was completed in 60 minutes, 50% of the same reaction would be completed in approximately (log 4 = 0.60, log 5 = 0.69)
- a) 40 minutes
- b) 50 minutes
- c) 45 minutes
- d) 60 minutes
Answer: 45 minutes
Question: For the reaction, 2A + B —→3C + D. Which of the following does not express the reaction rate?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Consider the reaction, N2(g) + 3H2(g) —→2NH3(g). The equality relationship between 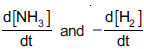 is
is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: For a first order reaction A—→ B, the reaction rate at reactant concentration of 0.01 M is found to be 2.0 ×10–5 mol L–1 s–1. The half life period of the reaction is
- a) 220 s
- b) 30 s
- c) 300 s
- d) 347 s
Answer: 347 s
Question: A nuclide of an alkaline earth metal undergoes radioactive decay by emission of three α-particles in succession. The group of the periodic table to which the resulting daughter element would belong is
- a) Group 14
- b) Group 16
- c) Group 4
- d) Group 6
Answer: Group 14
Question: The rate of reaction between two reactants A and B decreases by a factor of 4, if the concentration of reactant B is doubled. The order of this reaction with respect to reactant B is
- a) –1
- b) –2
- c) 1
- d) 2
Answer: –2
Question: A reaction is 50% complete in 2 hours and 75% complete in 4 hours. The order of reaction is
- a) 0
- b) 1
- c) 2
- d) 3
Answer: 1
Question: The half life time of 2g sample of radioactive nuclide ‘X’ is 15 min. The half life time of 1g sample of X is
- a) 7.5 min
- b) 15 min
- c) 22.5 min
- d) 30 min
Answer: 15 min
Question: The rate of the reaction : 2N2O5 —→ 4NO2+ O2 can be written in three ways :
The relationship between k and k’ and between k and k” are
- a) k’ = 2k; k” = 2k
- b) k’= k; k” = k
- c) k’ = 2k; k” = k
- d)
Answer:
Question: For the following reaction
Which one of the following is not affected by the addition of catalyst?
- a) Rate of forward reaction
- b) Rate of backward reaction
- c) Time required to reach the equilibrium
- d) Spontaneity
Answer: Spontaneity
Question: A chemical reaction proceeds into the following steps
The rate law for the overall reaction is
- a) Rate = k[A]2
- b) Rate = k[B]2
- c) Rate = k[A][B]
- d) Rate = k[A]2[B]
Answer: Rate = k[A]2[B]
Question: The data for the reaction A + B —→ C, is
The rate law corresponds to the above data is
- a) Rate = k[A][B]3
- b) Rate = k[A]2[B]2
- c) Rate = k[B]3
- d) Rate = k[B]4
Answer: Rate = k[B]3
Question: Half-life for radioactive 14C is 5760 years. In how many years 200 mg of 14C will be reduced to 25 mg?
- a) 17280 years
- b) 23040 years
- c) 5760 years
- d) 11520 years
Answer: 17280 years
Question: A chemical reaction is catalyzed by a catalyst X. Hence X
- a) Reduces enthalpy of the reaction
- b) Does not affect equilibrium constant of reaction
- c) Decreases rate constant of the reaction
- d) Increases activation energy of the reaction
Answer: Does not affect equilibrium constant of reaction
Question: The given reaction 2 FeCl3+ SnCl2—→ 2 FeCl2+ SnCl4 is an example of
- a) Third order reaction
- b) First order reaction
- c) Second order reaction
- d) None of these
Answer: Third order reaction
Question: The experimental data for the reaction
2A + B2→ 2AB is
The rate equation for the above data is
- a) rate = k [A]2 [B]2
- b) rate = k [A]2 [B]
- c) rate = k [B2]
- d) rate = k [B2]2
Answer: rate = k [B2]
Question: Carbon-14 dating method is based on the fact that
- a) Ratio of carbon-14 and carbon-12 is constant
- b) Carbon-14 is the same in all objects
- c) Carbon-14 is highly insoluble
- d) All of these
Answer: Ratio of carbon-14 and carbon-12 is constant
Question: Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by
- a) Evaluating rate constants at two different temperatures
- b) Evaluating velocities of reaction at two different temperatures
- c) Evaluating rate constant at standard temperature
- d) Changing concentration of reactants
Answer: Evaluating rate constants at two different temperatures
Question: For a first-order reaction, the half-life period is independent of
- a) First power of final concentration
- b) Cube root of initial concentration
- c) Initial concentration
- d) Square root of final concentration
Answer: Initial concentration
Question: The half-life of 6C14, if its λ is 2.31 × 10–4 year–1, is
- a) 3.5 × 104 years
- b) 3 × 103 years
- c) 2 × 102 years
- d) 4 × 103 years
Answer: 3 × 103 years
Question: A 300 gram radioactive sample has a half life 3 hours. After 18 hours remaining quantity
- a) 4.68 gram
- b) 2.34 gram
- c) 3.34 gram
- d) 9.37 gram
Answer: 4.68 gram
Question: How enzymes increases the rate of reactions?
- a) By lowering activation energy
- b) By increasing activation energy
- c) By changing equilibrium constant
- d) By forming enzyme substrate complex
Answer: By lowering activation energy
Question: For the reaction; 2N2O5→ 4NO2+ O2 rate and rate constant are 1.02 × 10–4 Ms–1 and 3.4 × 10–5 s–1 respectively, then concentration of N2O5 at that time will be (in molarity)
- a) 1.732
- b) 3
- c) 1.02 × 10–4
- d) 3.4 × 105
Answer: 3
Question: A human body required 0.01 m activity of radioactive substance after 24 hours. Half life of radioactive substance is 6 hours. Then injection of maximum activity of radioactive substance that can be injected
- a) 0.08
- b) 0.04
- c) 0.16
- d) 0.32
Answer: 0.16
Question: When a biochemical reaction is carried out in laboratory, outside the human body in absence of enzyme, then rate of reaction obtained is 10–6 times, the activation energy of reaction in the presence of enzyme is
- a) 6/RT
- b) P is required
- c) Different from Ea obtained in laboratory
- d) Can’t say anything
Answer: Different from Ea obtained in laboratory
Question: 3A → 2B, rate of reaction
is equal to
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: 2A → B + C
It would be a zero order reaction when
- a) The rate of reaction is proportional to square of conc. of A
- b) The rate of reaction remains same at any conc. of A
- c) The rate remains unchanged at any conc. of B and C
- d) The rate of reaction doubles if conc. of B is increased to double
Answer: The rate of reaction remains same at any conc. of A
Question: The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A →B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction
- a) Is negative of Ea
- b) Is always less than Ea
- c) Can be less than or more than Ea
- d) Is always double of Ea
Answer: Can be less than or more than Ea
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Biomolecule MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Bonding MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Chemical Thermodynamics MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Chemistry In Everyday Life MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry in Everyday Life MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Classification of Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Classification Of Elements and Periodicity In Properties MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry D and F Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQs Set C |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Environmental Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry General Principles and Processes Of Isolation Of Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs Set C |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrocarbons MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Isolation of Metals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Halogens MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compound Containing Nitrogen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry P Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Practicals MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry MCQs |
| NEET UG Chemistry S Block Elements MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Solutions MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Solutions MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Some Basic Concepts MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry States Of Matter MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry States of Matter MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry Structure Of Atom MCQs Set B |
| NEET UG Chemistry Structure of Atom MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs Set A |
| NEET UG Chemistry Surface Chemistry MCQs |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The D and F Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set A |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set B |
| NEET Chemistry The P Block Elements MCQs Set C |
Important Practice Resources for NEET Chemistry Advanced Study Material
MCQs for Chemical Kinetics Chemistry Full Syllabus
Students can use these MCQs for Chemical Kinetics to quickly test their knowledge of the chapter. These multiple-choice questions have been designed as per the latest syllabus for Full Syllabus Chemistry released by NEET. Our expert teachers suggest that you should practice daily and solving these objective questions of Chemical Kinetics to understand the important concepts and better marks in your school tests.
Chemical Kinetics NCERT Based Objective Questions
Our expert teachers have designed these Chemistry MCQs based on the official NCERT book for Full Syllabus. We have identified all questions from the most important topics that are always asked in exams. After solving these, please compare your choices with our provided answers. For better understanding of Chemical Kinetics, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Chemistry created by our team.
Online Practice and Revision for Chemical Kinetics Chemistry
To prepare for your exams you should also take the Full Syllabus Chemistry MCQ Test for this chapter on our website. This will help you improve your speed and accuracy and its also free for you. Regular revision of these Chemistry topics will make you an expert in all important chapters of your course.
You can get most exhaustive NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B for free on StudiesToday.com. These MCQs for Full Syllabus Chemistry are updated for the 2025-26 academic session as per NEET examination standards.
Yes, our NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B include the latest type of questions, such as Assertion-Reasoning and Case-based MCQs. 50% of the NEET paper is now competency-based.
By solving our NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B, Full Syllabus students can improve their accuracy and speed which is important as objective questions provide a chance to secure 100% marks in the Chemistry.
Yes, Chemistry MCQs for Full Syllabus have answer key and brief explanations to help students understand logic behind the correct option as its important for 2026 competency-focused NEET exams.
Yes, you can also access online interactive tests for NEET Chemistry Chemical Kinetics MCQs Set B on StudiesToday.com as they provide instant answers and score to help you track your progress in Chemistry.

