Read and download the CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set C in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter 11 Sound, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Sound
Students of Class 9 should use this Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 11 Sound as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Sound Worksheet with Answers
Question: Sound travels in air if
a) particles of medium travel from one place to another
b) there is no moisture in the atmosphere
c) disturbance moves
d) both particles as well as disturbance travel from one place to another
Answer: c
Question: In the curve (Fig.12.1) half the wavelength is
a) AB
b) BD
c) DE
d) AE
Answer: b
Question: Before playing the orchestra in a musical concert, a sitarist tries to adjust the tension and pluck the string suitably. By doing so, he is adjusting
a) intensity of sound only
b) amplitude of sound only
c) frequency of the sitar string with the frequency of other musical instruments
d) loudness of sound
Answer: c
Question: Note is a sound
a) of mixture of several frequencies
b) of mixture of two frequencies only
c) of a single frequency
d) always unpleasant to listen
Answer: a
Question: When we change feeble sound to loud sound we increase its
a) frequency
b) amplitude
c) velocity
d) wavelength
Answer: b
Question: Infrasound can be heard by
a) dog
b) bat
c) rhinoceros
d) human beings
Answer: c
Question: A key of a mechanical piano struck gently and then struck again but much harder this time. In the second case
a) sound will be louder but pitch will not be different
b) sound will be louder and pitch will also be higher
c) sound will be louder but pitch will be lower
d) both loudness and pitch will remain unaffected
Answer: a
Question: In SONAR, we use
a) ultrasonic waves
b) infrasonic waves
c) radio waves
d) audible sound waves
Answer: a
Question: Earthquake produces which kind of sound before the main shock wave begins
a) ultrasound
b) infrasound
c) audible sound
d) none of the above
Answer: b
Question: The given graph (Fig.12.2) shows the displacement versus time relation for a disturbance travelling with velocity of 1500 ms–1. Calculate the wavelength of the disturbance.
Answer: From the graph
Time period, T = 2 × 10-6 s.
Frequency, v = 1/T = 5 × 105 Hz.
Wavelength, λ =u / v = 5×10 m.
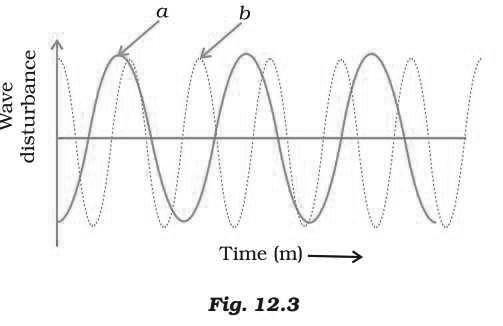
Question:Which of the two graphs (a) and (b) (Fig.12.3) representing the human voice is likely to be the male voice? Give reason for your Answer:
Answer: Graph (a) represents the male voice. Usually the male voice has less pitch (or frequency) as compared to female.
Question: Why do we hear the sound produced by the humming bees while the sound of vibrations of pendulum is not heard?
Answer: Humming bees produce sound by vibrating their wings which is in the audible range. In case of pendulum the frequency is below 20 Hz which does not come in the audible range.
Question: A girl is sitting in the middle of a park of dimension 12 m × 12 m. On the left side of it there is a building adjoining the park and on right side of the park, there is a road adjoining the park. A sound is produced on the road by a cracker. Is it possible for the girl to hear the echo of this sound? Explain your Answer:
Answer: If the time gap between the original sound and reflected sound received by the listener is around 0.1 s, only then the echo can be heard. The minimum distance travelled by the reflected sound wave for the distinctly listening the echo.
= velocity of sound × time interval
344× 0.1
34.4m
But in this case the distance travelled by the sound reflected from the building and then reaching to the girl will be (6 + 6) = 12 m, which is much smaller than the required distance. Therefore, no echo can be heard.
Question: Sound produced by a thunderstorm is heard 10 s after the lightning is seen. Calculate the approximate distance of the thunder cloud. (Given speed of sound = 340 ms–1.)
Answer: Speed of sound = 340 m/s and time = 10 s
Distance = speed × time = 340 × 10 = 3400 m
Question: For hearing the loudest ticking sound heard by the ear, find the angle x in the Fig.12.4.
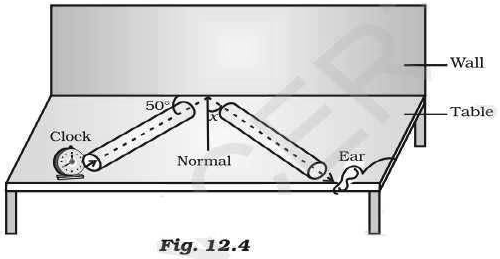
Answer: Incident line is making an angle of 50o with reflecting surface.
So, angle of incidence = 90o – 50o = 40o
Angle of reflection = angle of incidence
Hence, ∠x = 40o
Question: Why is the ceiling and wall behind the stage of good conference halls or concert halls made curved?
Answer: Ceiling and walls are made curved so that sound after reflection reaches the target audience.
Question: If any explosion takes place at the bottom of a lake, what type of shock waves in water will take place?
Answer: Longitudinal waves; because sound waves are longitudinal waves.
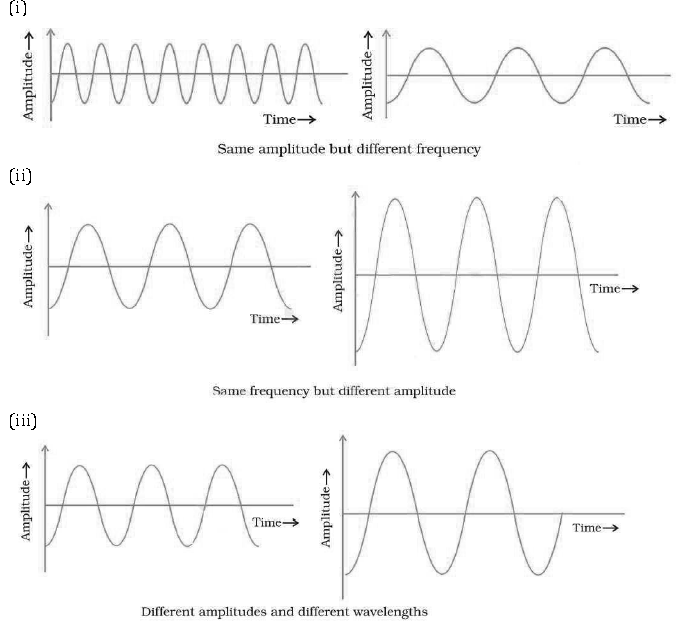
Question: Represent graphically by two separate diagrams in each case
(i) Two sound waves having the same amplitude but different frequencies?
(ii) Two sound waves having the same frequency but different amplitudes.
(iii) Two sound waves having different amplitudes and also different wavelengths.
Answer: (i)
Question: Draw a curve showing density or pressure variations with respect to distance for a disturbance produced by sound. Mark the position of compression and rarefaction on this curve. Also, define wavelengths and time-period using this curve.
Answer:
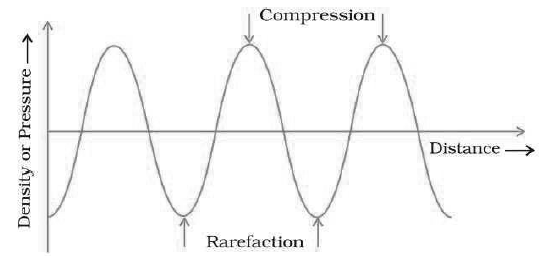
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive compressions or two consecutive rarefactions. Time period is the time taken to travel the distance between any two consecutive compressions or rarefactions from a fixed point.
Question: Establish the relationship between speed of sound, its wavelength and frequency. If velocity of sound in air is 340 ms–1, calculate
(i) wavelength when frequency is 256 Hz.
(ii) frequency when wavelength is 0.85 m.
Answer: Derivation of formula u = vλ.
(i) 340 = 256λ
λ= 1.33m.
(ii) 340 = v (0.85)
v = 400Hz
Please refer to below questions and answers for Sound Chapter 12 Class 9 Science Worksheets. Prepared by expert teachers for Standard 9 Science
Question. What do you understand by the term infrasonic vibrations?
Answer: The sounds of frequency lower than 20 Hz are called the infrasonics or subsonics.
Question. Which of the following sound waves we can hear : 10Hz, 500 Hz, 1500 Hz, 12000 Hz, 25000 Hz?
Answer: 500 Hz, 1500 Hz, 12000 Hz.
Question. Where is density of air higher at compression or at rarefaction?
Answer: At compression.
Question. Guess which sound has a higher pitch-guitar or car horn?
Answer: Guitar has a higher pitch because it has higher frequency.
Question. Do the particles of the medium move from one place to another in a medium?
Answer: No.
Question. What is intensity of sound?
Answer: The amount of sound energy passing through unit area each second is called the intensity of sound.
Question. What is relation between time period and frequency?
Answer: Frequency =1/Time period
Question. What is the range of frequencies associated with :
(a) Infrasound
(b) Ultrasound
Answer: (a) Infrasound : Sound waves between the frequencies 1 to 20 Hz.
(b) Ultrasound : Sound waves of the frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
Question. A Sitarist tries to adjust the tension and pluck the string suitably, before playing the orchestra in a musical concert. By doing so what is he adjusting?
Answer: He is adjusting frequency if the sitar string with the frequency of the other musical instrument.
Question. If the tension in the wire is increased four times, how will the velocity of wave in a string varies?
Answer: Velocity of the wave in string is directly proportional to the square root of the tension thus if tension is increased 4 times, the velocity will be doubled.
Question. Do waves transport matter?
Answer: No.
Question. Does the velocity of wave motion depend on the nature of the medium?
Answer: Yes.
Question. Does the velocity of wave motion depend on the nature or motion of the source?
Answer: No.
Question. What is the other name of a long flexible spring?
Answer: Slinky is the other name of a long flexible spring.
Question. Explain, how is the principle of echo used by the dolphin to locate small fish as its prey?
Answer: Dolphins are aquatic animals which send out ultrasonic sound to communicate with each other. They have a sound sensing system which enables them to find animals underwater with great accuracy due to the echo of the ultrasonic sound produced by them.
Question. Give two practical applications of the reflection of sound waves.
Answer: (i) In stethoscope the sound of patient’s heartbeat reaches the doctor’s ears by multiple reflections in the tubes.
(ii) Megaphones are designed to send sound waves in particular direction are based on the reflection of sound.
Question. Why are longitudinal waves called pressure waves?
Answer: Sound waves travels in the form of compression and rarefactions, which involve change in pressure, and volume of the air. Thus, they are called pressure waves.
Question. Sound travels faster on a rainy day than on a dry day. Why?
Answer: Sound travels faster on rainy day because the velocity of sound increases with increase in humidity. On rainy day, humidity is more thus, velocity of sound is also more.
Question. Define one hertz.
Answer: One hertz is one vibration per second.
Question. Define wavelength.
Answer: It is the distance between two nearest points in a wave which are in the same phase of vibration.
Question. What is the audible range of the average human ear?
Answer: An average human ear can hear sound waves between frequencies 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Question. What is sound and how is it produced?
Answer: Sound is mechanical energy which produces a sensation of hearing. When an object is set into vibrations, sound is produced.
Question. Why is sound wave called as longitudinal wave?
Answer: Sound wave is called longitudinal wave because the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction of the propagation of wave.
Question. Why do echoes produced in an empty auditorium usually decrease when it is full of audience?
Answer. When the hall is empty there are no obstacles in between to reflect the sound other than the walls.When the hall is full of audiences, the sound produced undergoes multiple reflections from the people and so it overlaps with the sound produced. Hence, the listener is not able to distinguish between the original sound and the echo.
Question. What are crests and troughs of a wave?
Answer. The elevation in a transverse wave is called crest. It is that part of transverse wave which s above the line of zero disturbance of the medium. The depression in a transverse wave is called trough. It is that part of the transverse wave which is below the line of zero disturbances.
Question. What is a stethoscope? Name the principle on which a stethoscope works.
Answer. Stethoscope is a medical instrument used for listening sounds produced within the body, chiefly in the heart or lungs. Stethoscope works on the principle of multiple reflection of sound.
Question. How moths of certain families are able to escape captures from bats? What is the range of frequencies associated with :
(a) infrasound?
(b) ultrasound?
Answer. They have very sensitive hearing equipment, that can hear the squeaks (ultrasound) of bat and know when a bat is flying nearby.
(a) Less than 20 Hz.
(b) More than 20,000 Hz.
Question. How does a stretched string on being set into vibration, produce the audible sound?
Answer. On being set into vibrations, the stretched string, forces the surrounding air to vibrate. This vibrating air, in turn, affects our eardrum and produces an audible sound.
Question. Will the sound be audible if the string is set into vibration on the surface of the Moon? Give reason for your answer.
Answer. No, we will not hear any audible sound on the surface of the Moon. This is because sound requires a medium to propagate, since there is no atmosphere on the surface of Moon, therefore, the sound will not be heard.
Question. What change, if any, would you expect in the characteristics of musical sound when we increase :
(i) its frequency, and
(ii) its amplitude?
Answer.
(i) Pitch of sound will increases,
(ii) Loudness of sound will increases.
Question. How do you account for the fact that two strings can be used to give notes of the same pitch and loudness but of different quality?
Answer. The ‘quality’ of a given note is determined by the overall effect of the harmonics present in it. The harmonics are multiples of the fundamental or basic frequency of the ‘note’. Depending on the conditions under which vibrations are taking place, sometimes we get one set of harmonics and sometimes another set.
The quality of the two notes will, therefore, different even though their fundamental frequencies may be the same.
Question. State any two characteristics of a wave motion.
Answer. The characteristics of wave motion are :
(i) It is a periodic disturbance.
(ii) Energy transfer takes place at a constant speed.
Question. A person fires a gun standing at a distance of 55 m from a wall. If the speed of sound is 330 ms–1, find the time for an echo to be heard.
Answer.
Given d = 55 m, v = 330 ms–1, t = ?
2d = v × t
t=2d/v=(2×55)/330=0.3s
Question. Give one example each of natural vibration, forced vibration and resonance.
Answer.
(i) Natural vibration : The vibrations of a simple pendulum about its mean position.
(ii) Forced vibration : A sonometer wire, under tension, vibrating under the influence of a vibrating tuning fork.
(iii) Resonance : A correctly adjusted length of a sonometer wire under proper tension, vibrating under the influence of a vibrating tuning fork.
Question. The pulse rate of a man is 80 beats in one minute. Calculate its frequency.
Answer.
No. of beats per minute = 80
No. of beats per second = 80/60 = 1.3
So, frequency = 1.3 Hz
Question. What is echo? Explain the conditions that have to be satisfied to hear an echo?
Answer. Reflection of sound wave from a large obstacle is called an echo. The most important condition for hearing an echo is that the reflected sound should reach the ear only after a lapse of at least 0.1 second after the original sound is off and the obstacle is at least at a distance of 17 m.
Question. Which wave property determines :
(i) loudness (ii) pitch
Answer.
(i) The amplitude of the wave determines the loudness. More the amplitude of a wave, more is the loudness produced.
(ii) The pitch is determined by the frequency of the wave. Higher the frequency of a wave, more is its pitch and shriller is the sound.
Question. Explain, why can echoes not be heard in a small room?
Answer. For hearing echo, there should be at least a distance of 17 m between the source of sound and the body from which sound is reflected. In small rooms this is not the case, hence, echoes are not heard.
Question. The stem of a tuning fork is pressed against a table top. Answer the following questions :
(i) Would the above action produce any audible sound?
(ii) Does the above action cause the table to set into vibrations?
(iii) If the answer above is yes, what type of vibrations are they?
(iv) Under what conditions does the above action lead to resonance?
Answer.
(i) Yes, there is an audible sound produced.
(ii) Yes, the table top is set into ‘forced vibrations’ by this.
(iii) The vibrations are forced vibrations.
(iv) Pressing the stem of a vibrating tuning fork against a table top, would lead to resonance if the frequency of the tuning fork equals the natural frequency of oscillations of the table top.
Question. Give application of ultrasound (ultrasonic waves).
Answer. Ultrasonic waves have number of uses :
(1) Ultrasonic vibrations are used for homogenising milk. These vibrations break down the larger particles of the fat present in milk to smaller particles.
(2) Ultrasonic vibrations are used in dish washing machines. The vibrating detergent particles rub against the dirty utensils and thus, clean them.
(3) Ultrasonic vibrations produce a sort of depression in rats and cockroaches.
(4) Ultrasonic vibrations are used to study the growth of foetus in mother’s womb.
(5) Ultrasonic vibrations are used in relieving pain in joints and muscles.
(6) Ultrasonic vibrations are used in detecting flaws in articles made from metals. They are also used in finding the thickness of various parts of a metallic component.
Question. Write conditions for the production of an echo.
Answer. Conditions for the production of an echo are :
(i) Time gap between the original sound and the reflected sound.
The echo will be heard if the original sound reflected by an obstacle reaches our ears after 0.1 s.
(ii) Distance between the source of sound and obstacle.
Thus, the minimum distance (in air at 25°C) between the observer and the obstacle for the echo to be heard clearly should be 17.2 m.
(iii) Nature of the obstacle : For the formation of an echo, the reflecting surface or the obstacle must be rigid such as a building, hill or a cliff.
(iv) Size of the obstacle : Echoes can be produced if the size of the obstacle reflecting the sound is quite large.
Numerical Questions
Question. (a) A sound wave of wave length 0.33 m has a time period of 10–3 s. If the time period is decreased to 10–4 s, calculate the wave length and frequency of the new wave.
(b) Name the subjective property of sound related to its frequency and of light related to its wavelength.
Answer.
(a) λ = 0.33 m
Time taken to travel λ , t = 10–3
velocity= λ/t=0.33/10–3
= 300 m s–1
Time period of 2nd wave = 10–4 s
Therefore, wavelength λ = v × t
= 330 × 10–4 = 0.033 m
Frequency 1/t =1/10–3
= 103 Hz
(b) Pitch is related to the frequency of sound and colour is related to the wavelength of light.
Question. A human heart, on an average, is found to beat 75 times a minute. Calculate its frequency.
Answer. No. of beats of human heart = 75 min–1
= 75/1 min
= 75/60s = 1.25 s–1
So, average frequency of human heart beating
= 1.25 s–1.
Question. A boat at anchor is rocked by waves whose consecutive crests are 100 m apart. The wave velocity of the moving crests is 20 m/s. What is the frequency of rocking of the boat?
Answer. Distance between two consecutive crests = 100 m
Wave velocity v = 20 m/s
The distance between two consecutive crests is equal
to the wavelength of the wave. So,
Frequency = Wave velocity/Wave length
20 m s–1/100 m
= 0.2 s–1
So, the frequency of rocking of the boat is 0.2 s–1.
Question. A bat can hear sound at frequencies up to 120 kHz.Determine the wavelength of sound in the air at this frequency. Take the speed of sound in the air as 344
m/s.
Answer. Frequency, n = 120 kHz = 120 × 103 Hz
= 120 × 103 s–1 Velocity of sound in the air, v = 344 m/s
Wavelength of the sound wave = λ
We know,
Wavelength, λ = wave velocity/frequency
344 ms–1/120 × 103 s–1
= 2.87 × 103 m = 0.29 cm
Question. A gun is fired in the air at a distance of 660 m, from a person. He hears the sound of the gun after 2 s. What is the speed of sound?
Answer. Distance travelled by sound = 660 m,
Time taken by the sound = 2 s,
Speed of sound in air = ?
So, Speed of sound = Distance/Time
= 660 m/2 s = 330 m/s
Thus, the speed of sound in the air is 330 m/s.
Question. A child hears an echo from a cliff 4 seconds after the sound from a powerful cracker is produced. How far away is the cliff from the child? Velocity of sound in air at 20°C is 344 m/s.
Answer. Let the distance between the child and the cliff be d.
Then,
Total distance travelled by the sound = 2d
Total time taken by the sound = 4 s
Then, Velocity of sound = 344 m/s = d/2s
This gives, d = 344 m/s × 2 s
= 688 m
Thus, the cliff is at a distance of 688 m from the child.
Question. A ship sends on a high frequency sound wave and receives an echo after 1 second. What is the depth of the sea? Speed of sound in water is 1500 m/s.
Answer.
Let, Depth of the sea = d
So, total distance travelled by the sound wave = 2d
Time taken by sound to travel both ways = 1s
As per definition,
Speed of the sound = 1500 ms–1 = 2d/1s
or d = 1500 ms–1 × 1s/2
1 = 750 m
Thus, the depth of the sea is 750 metres.
Question. A sonar echo takes 2.2 s to return from a whale. How far away is the whale?
Answer.
Total time taken by the signal = 2.2 s
So, time taken the signal to reach the whale = 1.1 s
Distance of the whale = d (assume)
Speed of sound in sea water at 25°C = 1533 ms–1
So, distance of the whale,
d = Speed of the signal × Time taken
or d = 1533 m s–1 × 1.1 s = 1686.3 m
Question. A tuning fork produces 1024 waves in 4 seconds. Calculate the frequency to the tuning fork.
Answer. As the tuning fork produces 1024 waves in 4 seconds,hence
Frequency of tuning fork,
n = Number of vibration per second
= 1024/4 = 256 Hz
Question. Using the SONAR, sound pulses are emitted at the surface of water. These pulses after being reflected from the bottom are detected. If the time interval from the emission to the detection of the sound pulses is 2 seconds, find the depth of the water. Velocity of sound in water = 1498 m/s.
Answer. Let, depth of the water from the Earth’s surface be d. Then,
Total distance travelled by the pulse = 2d
Total time taken by the pulse = 2s
As per definition,
Velocity = Distance travelled/Time taken
So, Velocity of the sound =2d/2s =d/s
1498 m/s =d/s
This gives, d = 1498 m/s × 1s
= 1498 m
Thus, the depth of water is 1498 m.
Question. A wave moves a distance of 8 m in 0.05 s :
(a) Find the velocity of the wave.
(b) What is the wavelength of the wave if its frequency is 200 Hz?
Answer.
(a) Velocity 8/ 0.05= 160 ms–1
(b) λ= 160/200 = 0.8 m
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Science Class 9 Chapter 11 Sound Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 11 Sound to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 9. We suggest that Class 9 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Science.
Chapter 11 Sound Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 9 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 9 Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 11 Sound difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 11 Sound for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 11 Sound focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 11 Sound to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 9 Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 11 Sound, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

