Read and download the CBSE Class 9 Biology Fundamental Unit Of Life Worksheet Set D in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Students of Class 9 should use this Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Worksheet with Answers
Question: Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time?
Answer: Soap solution is very concentrated – Hypertonic solution, so water moves out of your finger cells by osmosis.
Question: We eat food composed of all the nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. After digestion, these are absorbed in the form of glucose, aminoacids, fatty acids, glycerol etc. What mechanisms are involved in absorption of digested food and water?
Answer: Diffusion and osmosis respectively
Question: Why are lysosomes known as ‘suicide-bags’ of a cell?
Answer: Lysosomes are known as ‘suicide-bags’ because when cell gets damaged during the disturbance in cellular metabolism, lysosomes may burst and the digestive enzymes thus released digest their own cell.
Question: A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain.
Answer: Swallowing a concentration solution of salt results in exosmosis from cells of the alimentary canal. Due to this, dehydration occurs in the person. As a result, the person starts vomiting.
Question: If you are provided with some vegetables to cook. You generally add salt into the vegetables during cooking process. After adding salt, vegetables release water. What mechanism is responsible for this?
Answer: Exosmosis
Question: Why is endocytosis found in animals only?
Answer: Cell wall is absent in animals. Due to this, movement of substances inside the cells is easier in animals than in plants. Due to this, endocytosis is found in animals only.
Question: Do you agree that “A cell is a building unit of an organism”. If yes, explain why?
Answer: I agree with the statement that “A cell is a building block of an organism”. This is true because all living beings are made up of cells and cell is the smallest independent unit of living beings.
Question: Bacteria do not have chloroplast but some bacteria are photoautorophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of bacterial cell performs this?
Answer: Small vesicles which are associated with plasma membrane are present in such bacteria. These vesicles contain pigments which can trap solar energy to produce food.
Question: If cells of onion peel and RBC are separately kept in hypotonic solution, what among the following will take place? Explain the reason for your Answer:
(a) Both the cells will swell.
(b) RBC will burst easily while cells of onion peel will resist the bursting to some extent.
(c) a and b both are correct.
(d) RBC and onion peel cells will behave similarly.
Answer: (c) a and b both are correct. When surrounding medium is hypotonic, water moves into the cells. This will result in swelling of cells. RBCs do not have cell wall and hence they will easily burst. Presence of cell wall in the cells of onion peel will prevent their bursting.
Question: Match the following A and B
Answer: a—(iv); b—(v); c—(iii); d—(i); e—(ii).
Question: How is a bacterial cell different from an onion peel cell?
Answer:

Question: How do substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) move in and out of the cell?
Answer: Carbon dioxide moves through diffusion, while water moves through osmosis.
Question: Draw a plant cell and label the parts which
(a) determines the function and development of the cell
(b) packages materials coming from the endoplasmic reticulum
(c) provides resistance to microbes to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting
(d) is site for many biochemical reactions necessary to sustain life.
(e) is a fluid contained inside the nucleus
Answer: (a) Nucleus
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Cell wall
(d) Cytoplasm
(e) Nucleoplasm.

Question: Name the two organelles in a plant cell that contain their own genetic material and ribosomes.
Answer: Mitochondria and plastids
Question: Write the name of different plant parts in which chromoplast, chloroplast and leucoplast are present.
Answer: Flower and Fruit— Chromoplast
Leaves of the plant— Chloroplast
Root of the plant— Leucoplast
Question: How does amoeba obtain its food?
Answer: Amoeba makes pseudopodia to surround a food particle. It then ingest the food particles; along with a drop of water and then forms food vacuole. This process of obtaining food by Amoeba is called endocytosis.
Question: Why are lysosomes also known as “scavengers of the cells”?
Answer: Lysosomes contain enzymes which are used for destroying worn out parts of the cell. Lysosomes also destroys waste materials. Due to this, lysosomes are also known as ‘scavengers of the cells’.
Question: Why do plant cells possess large sized vacuole?
Answer: Vacuoles not only store many important substances, they also contain cell sap that give turgidity to cell.
Question: How are chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other?
Answer: Chromosomes are made up of chromatids and chromatids are made up of chromatin.
Question: Which cell organelle controls most of the activities of the cell?
Answer: Nucleus
Question: What are the consequences of the following conditions?
(a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium
(b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium.
(c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium.
Answer: (A) Exosmosis
(B) (Endosmosis
(C) No effect
Question: Draw a neat diagram of plant cell and label any three parts which differentiate it from animal cell.
Answer:

Question: Illustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. How is it different from animal cell?Answer:

Question: Which kind of plastid is more common in
(a) roots of the plant
(b) leaves of the plant
(c) flowers and fruits
Answer: (A) Leucoplast
(B) Chloroplast
(C) Chromoplast
Question: Draw a well labelled diagram of an eukaryotic nucleus. How is it different from nucleoid?
Answer:

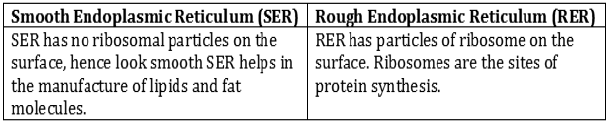
Question: Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biogenesis?
Answer: The ribosomes, which are present in all active cells, are the sites of protein synthesis. Endoplasmic reticulum helps in transporting these proteins to various places. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum help in manufacture of fat and lipids which along with proteins help in building the cell membrane.
Question: Draw a neat labelled diagram of an animal cell.
Answer:

Question. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer: Ribosomes are the site of protein is synthesis. Exercises
Question. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer. The plasma membrane selectively allows the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some other materials. Therefore, it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Question. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer. The Iysosomes contain very powerful hydrolytic enzymes which are capable of breaking down organic matter. For example, when a cell gets damaged, then Iysosomes burst and enzymes digest their own cell. Hence, the Iysosomes are known as ‘suicide bags’ of cells.
Question. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer. There are various components in the animal and plant cell known as cell organelles. Each kind of cell organelle performs a specific function, such as making new materials in the cells, release of waste, transportation, etc. Thus, a cell can perform all its functions with the help of these organelles. That is why the cells are called structural and functional unit of life.
Question. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer. Substances like CO2 accumulate in high concentration inside the cell. There is CO2 concentration difference in the internal and external environment of a cell. CO2moves out of the cell, from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration outside the cell by the process of diffusion.
Question. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer. Effect of absence of Golgi apparatus on life of a cell
(i) The packaging and dispatching of different types of proteins to various targets inside and outside the cell will be influenced.
(ii) The products of cell cannot be stored and modified later.
(iii) There will be effect on Iysosomes formation. This will cause accumulation of worn out and dead cell organelles within the cell which may cause cell death.
Question. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer. Comparison of plant cell and animal cell
Plant Cell
Cell wall is present outside the plasma membrane.
Generally regular in shape.
Larger in size than animal cells
Plastids are present.
A permanent and large vacuole is present.
Animal Cell
Cell wall is absent.
Generally irregular in shape.
Smaller in size than animal cells.
Plastids are absent except in Euglena.
Vacuoles are many, small and temporary.
Question. What are ribosomes? Where are ribosomes located in the cell? What is their function?
Answer: Ribosomes are spherical organelles present in the cell which are either freely distributed in the cytoplasm or may be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. It has ribosomal RNA (Ribonucleic acid) and proteins.It helps in protein synthesis.
Question. What is the energy currency of the cell?
Answer: ATP—Adenosine Triphosphate.
Question. What is the cell wall composed of ?
Answer: The cell wall is composed of cellulose.
Question. What is osmosis?
Answer: The movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. This takes place from higher water concentration to lower water concentration.
Question. What is the full form of DNA?
Answer: DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid).
Question. Name the cell organelle that helps in packaging?
Answer: Golgi apparatus.
Question. Why does mitochondria have largely folded inner membrane?
Answer: Mitochondria have largely folded inner membrane which provides the increased surface area for ATPgenerating chemical reactions. Mitochondria is the site for cellular respiration and provides energy to the cell.
Question. Which organelle makes the digestive enzyme of lysosome?
Answer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum makes the digestive enzyme of lysosomes.
Question. What are cisterns?
Answer: The Golgi bodies consist of a system of membranebound vesicles arranged in stacks called cisterns.
Question. Name the cell organelles that have their own DNA and ribosomes. Name the autonomous organelles in the cell.
Answer: The cell organelles with their own DNA and ribosomes are mitochondria and plastids. Chloroplast and mitochondria are the autonomous organelles in the cells.
Question. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell?
Answer: The substances like CO2 move in and out of a cell by diffusion from the region of high concentration to low concentration. Water also obey the law of diffusion.
The movement of water molecule through such a selective permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Question. What is the role of cell organelles in the cell?
Answer: Each kind of cell organelles performs a specific function such as making new material, clearing of the waste, transporting material, etc.
Question. What is the function of ribosome?
Answer: Ribosome helps in protein synthesis.
Question. Where are genes located in the cell?
Answer: Genes are located in the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell.
Question. Name the cell organelle which helps in the transportation of material.
Answer: Endoplasmic reticulum.
Question. Name the cell organelle due to which leaves, flowers and fruits get their colour.
Answer: Chromoplast.
Question. Name the cell organelle which helps in the formation of lysosome.
Answer: Golgi apparatus.
Question. Name the cleaning organelle in the cell.
Answer: Lysosomes.
Question. List two similarities between mitochondria and plastids.
Answer: Plastids are similar to mitochondria in external structure. Like the mitochondria, plastids also have their own DNA and ribosome.
Question. (i) Name the largest animal cell.
(ii) Name the smallest cell.
Answer: (i) An ostrich egg.
(ii) Pleuro pneumonia bacterium.
Question. What is cell wall?
Answer: Cell wall is the rigid outer covering of plasma membrane in plant cells.
Question. Name the autonomous organelles in the cell.
Answer: Chloroplast and mitochondria are the autonomous organelles in the cells.
Question. Name the type of organism in which a single cell constitutes the whole organism.
Answer: Organism in which a single cell constitutes the whole organism is unicellular organism.
Question. Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Answer: The proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes, known as protein factories too.
Question. What could happen if nucleus is removed from the cell?
Answer: If nucleus is removed from a cell, the protoplasm will ultimately dry up and the cell will die because the nucleus controls all the metabolic activities of a cell.
Question. Give example of working of chromoplasts.
Answer: Spinach looks green due to the presence of chloroplasts,papaya is yellow and edible part of watermelon is red due to the presence of chromoplasts.
Question. What is the function of cell wall and plasma membrane?
Answer: Cell Wall : Gives rigidity, shape and protection to plant cell.
Cell Membrane : Allows only selected materials to move in and out of the cell.
Question. Name the smallest cell and the longest cell in human body.
Answer: The smallest cell is the red blood cell or sperm cell in male. The longest cell is the nerve cell.
Question. Give brief introduction of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell.
Answer. Prokaryotic cell :
1. Cell size is generally small.
2. Only a single chromosome is present.
3. Nucleolus is absent.
4. Cell division takes place by fission or budding.
Eukaryotic cell :
1. Cell is generally large.
2. More than one chromosome is present.
3. Nucleolus is present.
4. Cell division takes place by mitotic or meiotic.
Question. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Justify?
Answer. All organisms around are made up of one or more cells. There are single cells organism called unicellular like amoeba whereas some single body are made up of many cells called multicellular organism. Cells divide to produce cells of their own kind. Hence, all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Question. What is the function of nucleus in a cell?
Answer.The nucleus plays a very important role in the reproduction of cells. It also helps the single cell to divide and form two new daughter cells. It also helps in an important role in determining how cell will develop.
Question. What is endoplasmic reticulum? Write its main functions.
Answer. Endoplasmic reticulum is a network, enclosing a fluidfilled lumen. Its main functions are :
(i) Synthesis of proteins (rough ER).
(ii) Synthesis of lipids and other metabolic products and their secretion (SER).
(iii) Helps in formation of cell plate and nuclear membrane during cell division.
(iv) ER also produces substance for new cellular parts (especially cell membrane).
(v) ER provides internal support to the colloidal cytoplasmic matrix of the cell.
Question. What is the function of plastids?
Answer. Plastids are present only in plant cells. There are two types of plastids chromoplasts (coloured plastids) and leucoplasts (white or colourless).
Chromoplast : Consists of coloured pigments and given different colours to flowers, fruits and leaves.
The green colour pigment present in leaf is called chlorophyll which helps in the photosynthesis and a plastid with chlorophyll is called chloroplast.
Leucoplast : It stores starch, oil and protein granules in it.
Question. List any six functions of nucleus of a cell.
Answer.(i) Nucleus plays a central role in cellular reproduction.
(ii) It plays an important role in determining the way the cell will develop.
(iii) It also determines what form the cell will exhibit at maturity.
(iv) It contains chromosome thus inherits characters.
(v) It is the control centre of the cell.
(vi) It directs chemical activities of the cell.
Question. Explain the structure and function of Golgi bodies.
Answer. Structures : Golgi bodies consist of a system of membrane-bound vesicles arranged in stacks parallel to each other called cisterns. These membranes have connections with the membrane of endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Functions :
(i) The material synthesized near the ER is packaged and dispatched to various targets inside and outside the cell through Golgi apparatus.
(ii) It also stores, modifies and helps in the packaging of products in vesicles.
(iii) In some cases, complex sugars may be made from simple sugars in it.
(iv) It also helps in the formation of lysosomes.
Question. Name some organelles which are found only in animal cells and those which occur only in plant cells.
Answer.
(i) Structures found only in animal cells : centrosomes, lysosome.
(ii) Structures found only in plant cells : cell wall,plastids and big vacuoles.
Question. What is lacking in a virus which makes it dependant on a living cell to multiply?
Answer. Viruses look selectively permeable process membrane and cell organelles. Thus, they lack a basic structural organization to perform various life processes effectively and in their own way. After entering in a living cell, a virus utilizes its own genetic material and machinery of host cell to multiply.
Question. Give difference between organs and organelles.
Answer. Organs :
They are found in multicellular organisms.
They are large sized.
They may be external or internal to the body of organisms.
Organelles :
1. They are found in all eukaryotic cells.
2. They are very small sized.
3. They are mostly internal.
Question. Give difference between diffusion and osmosis.
Answer. Diffusion :
1. Diffusion can occur in any medium.
2. The diffusing molecules may be solids, liquids or gases.
3. Semipermeable membrane is not required.
4. An equilibrium in the free energy of diffusion molecules is achieved in the system.
Osmosis :
1. It occurs only in liquid medium.
2. It involves movement of solvent molecules only.
3. Semipermeable membrane is required.
4. Equilibrium in the free energy of solvent molecules is never achieved.
Question. Explain endocytosis.
Answer. Endocytosis is the ingestion of material by the cells through the plasma membrane. It is a collective term that describes three similar processes : phagocytosis (cell eating), potocytosis (cell drinking) and receptormediated endocytosis. These processes are pathways to specifically internalize solid particles, small molecules and macromolecules, respectively.
Question. Why do plant cells have more in number and big-sized vacuoles as compared to the animal cells?
Answer. Plants cells attain turgidity and rigidity due to the more number of vacuoles as well as large-sized vacuoles help the plant cells to withstand the wear and tear, external environmental conditions. They also help in the storage of essential material required by plants for their growth like amino acids, sugar and various organic substances.
Question. (a) Name the organelle which provides turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell. Name any two substances which are present in it.
(b) How are they useful in unicellular organisms?
Answer.
(a) Plant cells have big vacuoles that provide them turgidity and rigidity. Plant vacuoles store amino acids, sugars, various organic acids and some proteins.
(b) In unicellular organism they can serve the following works :
(i) Forming food vacuoles : In single celled organisms like amoeba, the food vacuole contains the food items that the amoeba has engulfed. After that the food items are digested by the enzymes.
(ii) Removal of excess water and wastes : In some unicellular organisms, vacuoles play important roles in egesting excess water and some wastes from the cell.
Question. Explain the functions of various cell organelles.
Answer. Functions of cell organelles :
(i) Endoplasmic Reticulum : It forms the supporting skeletal framework of the cell.
(ii) Ribosomes : It synthesises proteins.
(iii) Golgi Apparatus : It produces vacuoles which contain cellular secretion.
(iv) Lysosomes : It serves as intracellular digestive system as it digest the foreign materials which enter the cell.
(v) Mitochondria : These are the sites of cellular respirations.
(vi) Plastids : These are present only in plants and trap solar energy to manufacture food for plants.
(vii) Vacuoles : They help to maintain the osmotic pressure in a cell.
(viii) Peroxisomes : They carry-out some oxidative reactions.
(ix) Centrosome : It helps in cell division in the animal cell.
Question. Write a note on the structure of cell.
Answer.
(a) Cell is the basic unit of all living organisms. It is surrounded by an outer selectively permeable Plasma Membrane. Plant cells have an additional covering called “cell wall” outer to the Plasma Membrane.
(b) Inside the plasma membrane there is a translucent viscous substance the cytoplasm in which the organelles are embedded. The control centre of the cell is the nucleus; it contains all the information necessary for the cell to function and to reproduce. Surrounding the nucleus is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) on which ribosomes may be embedded. Ribosomes are granular structures which are the site of protein synthesis.
(c) The powerhouse of cell is the mitochondria. It helps in releasing energy by the oxidation of food in cell. There are flat membranous secretory structures in the cell called the Golgi bodies. In plant cells, an additional structure located near the nucleus called the chloroplast, is also present.They are the site of photosynthesis.
(d) Cells also contain lysosomes which are also called suicide bags. They digest and remove the unwanted debris of the cell. Centriole located near the nucleus helps in cell division. Cytoplasm also contains vacuoles filled with the cell sap. In plant cells, vacuole is large and centrally placed.
Question. Give brief information about the mitochondria.Describe the structure of mitochondria.
Answer. The mitochondria are tiny bodies of varying shapes and size. Each mitochondria is bounded by a double membrane envelope. Outer membrane is porous. The inner membrane is thrown into folds. These folds are called cristae and are studded with small rounded bodies known as oxysomes. The interior cavity of the mitochondria is filled with a protein matrix which contains a few small-sized ribosomes, a circular DNA molecule and phosphate granules. Mitochondria are sites of cellular respiration.Mitochondria are membrane bound cell organelle found in the cytoplasm. Each mitochondria is a double membrane bounded structure. The outer membrane of mitochondrion is smooth. But, the inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded inwardly, into the matrix of mitochondrion forming finger like projections. The inward finger like projections of inner membrane is called cristae. Cristae greatly increase the surface area of inner membrane. Mitochondria contain extra nuclear DNA.
Question. (i) Name the organelle which provides turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell. Name any two substances which are present in it.
(ii) How are they useful in unicellular organisms?
Answer.
(i) Plant cells have big vacuoles full of cell sap that provide them turgidity and rigidity. Plant vacuoles store amino acids, sugars, various organic acids and some proteins.
(ii) In unicellular organism they may serve the following purposes :
1. Forming food vacuoles : In single celled organisms like amoeba, the food vacuole contains the food items that the amoeba has ingested. The food items are digested by the enzymes later on.
2. Removal of excess water and wastes : In some unicellular organisms, specialized vacuoles play important roles in expelling excess water and some wastes from the cell.
Question. Describe the role played by the lysosomes. Why are these termed as suicidal bags? How do they perform their functions?
Answer. Functions of lysosomes :
1. Extracellular digestion. Sometimes lysosome enzymes are released outside the cell to break down extracellular material.
2. Digestion of foreign material. Lysosome also destroys any foreign material which enters inside the cell such as bacteria.
3. Cellular digestion. In damaged cells, ageing cells or dead cells lysosomes get ruptured and enzymes are released. These enzymes digest their own cell. Lysosomes contain about 40 hydrolytic enzymes.When the cell gets damaged, lysosomes burst and their enzymes digest their own cell. So, lysosomes are called ‘suicide bags’.
Question. Describe an activity to demonstrate endosmosis and exosmosis. Draw a diagram also.
Answer.
1. Endosmosis : The movement of water in the cell or a body through a semipermeable membrane is called endosmosis. It can be demonstrated as follows :
(i) Take some raisins with stalks and put them in plain water in a beaker.
(ii) Observation : Raisins absorb water and swell.Raisins have high concentration of sugar than surrounding plain water. Because of this, water from the outside passing through semipermeable membrane enters into the cell.
This is endosmosis.
2. Exosmosis : The movement of water out from a cell or a body through a semipermeable membrane is called exosmosis. This can be demonstrated as follows :
(i) We place the swollen raisins (from above activity) into a beaker containing a concentrated solution of sugar or salt.
(ii) Observation : When swollen raisins are placed in concentrated sugar or salt solution, they shrink because the solution surrounding the raisins is having low water concentration. Thus, raisins loose water by osmosis, this process is called exosmosis.
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Science Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 9. We suggest that Class 9 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Science.
Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 9 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 9 Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 9 Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

