Read and download the CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set B in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Students of Class 9 should use this Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Worksheet with Answers
Question: In which of the following conditions, the distance between the molecules of hydrogen gas would increase?
(i) Increasing pressure on hydrogen contained in a closed container
(ii) Some hydrogen gas leaking out of the container
(iii) Increasing the volume of the container of hydrogen gas
(iv) Adding more hydrogen gas to the container without increasing the volume of the container
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer: c
Question: Which one of the following sets of phenomena would increase on raising the temperature?
a) Diffusion, evaporation, compression of gases
b) Evaporation, compression of gases, solubility
c) Evaporation, diffusion, expansion of gases
d) Evaporation, solubility, diffusion, compression of gases
Answer: c
Question: Choose the correct statement of the following
a) conversion of solid into vapours without passing through the liquid state is called vapourisation.
b) conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid state is called sublimation.
c) conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid state is called freezing.
d) conversion of solid into liquid is called sublimation.
Answer: b
Question: The boiling points of diethyl ether, acetone and n-butyl alcohol are 35°C, 56°C and 118°C respectively. Which one of the following correctly represents their boiling points in kelvin scale?
a) 306 K, 329 K, 391 K
b) 308 K, 329 K, 392 K
c) 308 K, 329 K, 391 K
d) 329 K, 392 K, 308 K
Answer: c
Question: Seema visited a Natural Gas Compressing Unit and found that the gas can be liquefied under specific conditions of temperature and pressure. Which is the correct set of conditions?
a) Low temperature, low pressure
b) High temperature, low pressure
c) Low temperature, high pressure
d) High temperature, high pressure
Answer: c
Question: On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperature will be
a) 298 K, 311 K and 339 K
b) 298 K, 300 K and 338 K
c) 273 K, 278 K and 543 K
d) 298 K, 310 K and 338 K
Answer: a
Question: The property to flow is unique to fluids. Which one of the following statements is correct?
a) Only gases behave like fluids
b) Gases and solids behave like fluids
c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
d) Only liquids are fluids
Answer: c
Question: Which condition out of the following will increase the evaporation of water?
a) Increase in temperature of water
b) Decrease in temperature of water
c) Less exposed surface area of water
d) Adding common salt to water
Answer: a
Question: During summer, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool because of the phenomenon of
a) diffusion
b) transpiration
c) osmosis
d) evaporation
Answer: d
Question: A few substances are arranged in the increasing order of ‘forces of attraction’ between their particles. Which one of the following represents a correct arrangement?
a) Water, air, wind
b) Air, sugar, oil
c) Oxygen, water, sugar
d) Salt, juice, air
Answer: c
Fill in the blanks:
Question: The arrangement of particles is less ordered in the __________ state. However, there is no order in the __________ state.
Answer: liquid, gaseous
Question: Evaporation of a liquid at room temperature leads to a __________ effect.
Answer: cooling
Question: The phenomenon of change of a liquid into the gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point is called __________.
Answer: evaporation
Question: __________ is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through the __________ state.
Answer: sublimation, liquid
Question: At room temperature, the forces of attraction between the particles of solid substances are __________ than those which exist in the gaseous state.
Answer: stronger
Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion
Question: Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water.
Answer: Osmosis
Question: Spreading of virus on sneezing.
Answer: Diffusion
Question: Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt.
Answer: Osmosis
Question: Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
Answer: Osmosis
Question: Preserving pickles in salt.
Answer: Osmosis
Question: Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration.
Answer: Diffusion
Question: A sample of water under study was found to boil at 102°C at normal temperature and pressure. Is the water pure? Will this water freeze at 0°C? Comment.
Answer: The boiling point of pure water is 100oC at 1 atm. Consequently, pure water freezes at 0oC. So, the sample of water which boils at 102oC at normal temperature and pressure is not pure water. It will freeze below 0oC.
Question: Match the physical quantities given in column A to their SI units given in column B
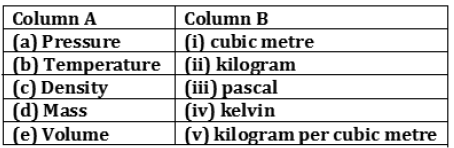
Answer: a) — (iii)
(b) — (iv)
(c) — (v)
(d) — (ii)
(e) — (i)
Question: The non-SI and SI units of some physical quantities are given in column A and column B respectively. Match the units belonging to the same physical quantity:
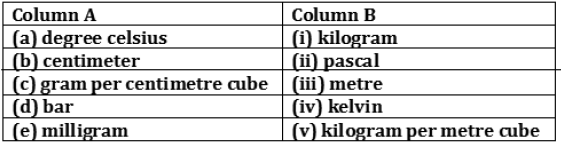
Answer: (a) — (iv)
(b) — (iii)
(c) — (v)
(d) — (ii)
(e) — (i)
Question: A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the content of the beaker as a function of time. Which of the following (Fig. 1.1) would correctly represent the result? Justify your choice.
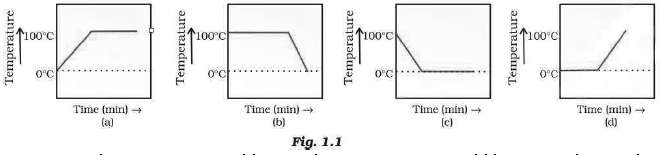
Answer: Since ice and water are in equilibrium, the temperature would be zero. When we heat the mixture, energy supplied is utilized in melting the ice and the temperature does not change till all the ice melts because of latent heat of fusion. On further heating, the temperature of the water would increase. Therefore, the correct option is (d).
Question: Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations.
Answer: In case of ice the water, molecules have low energy while in the case of steam the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of water molecules in steam is transformed as heat and may cause burns. On the other hand, in case of ice, the water molecules take energy from the body and thus give a cooling effect.
Question: Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion’. Comment.
Answer: Yes, this is true. In both the phenomena, there is movement of particles from region of higher concentration to that of lower concentration. However, in the case of osmosis the movement of solvent is through a semi permeable membrane which is permeable only to water molecules.
Question: It is a hot summer day, Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes respectively. Who do you think would be more comfortable and why?
Answer: Cotton being a better absorber of water than nylon helps in absorption of sweat followed by evaporation which leads to cooling. So Priyanshi is more comfortable, whereas Ali is not so comfortable.
Question: A glass tumbler containing hot water is kept in the freezer compartment of a refrigerator (temperature < 0°C). If you could measure the temperature of the content of the tumbler, which of the following graphs (Fig.1.2) would correctly represent the change in its temperature as a function of time.
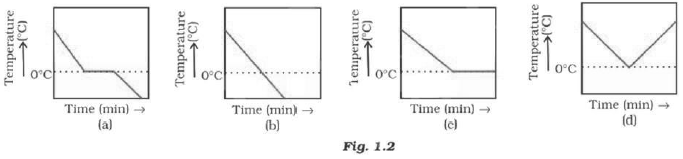
Answer: (a) The water will cool initially till it reaches 0°C, the freezing point. At this stage the temperature will remain constant till all the water will freeze. After this temperature, would fall again.
Question: Look at Fig. 1.3 and suggest in which of the vessels A, B, C or D the rate of evaporation will be the highest? Explain.
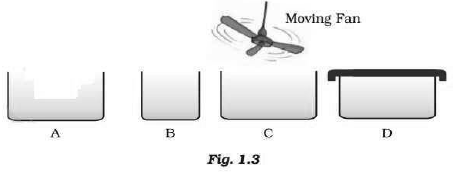
Answer: (c) The rate of evaporation increases with an increase of surface area because evaporation is a surface phenomenon. Also, with the increase in air speed, the particles of water vapour will move away with the air, which will increase the rate of evaporation.
Question: Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment.
Answer: The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C, but steam has more energy because of latent heat of vapourisation.
Question: (a) Conversion of solid to vapour is called sublimation. Name the term used to denote the conversion of vapour to solid.
Answer: Sublimation
(b) Conversion of solid state to liquid state is called fusion; what is meant by latent heat of fusion?
Answer: The amount of heat required to convert 1 kg of solid into liquid at one atmosphere pressure at its melting point is known as its latent heat of fusion.
Question: You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster?
Answer: Conditions that can increase the rate of evaporation of water are
(a) an increase of surface area by spreading the shirt
(b) an increase in temperature by putting the shirt under the sun
(c) increase the wind speed by spreading it under the fan.
Question: You are provided with a mixture of naphthalene and ammonium chloride by your teacher. Suggest an activity to separate them with well labelled diagram.
Answer: Naphthalene is insoluble in water but soluble in ether an organic solvent. It is volatile at room temperature. Ammonium chloride is soluble in water and volatile at higher temperature. It decomposes on heating to dryness.

Question: Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during its melting point or boiling point?
Answer: The temperature of a substance remains constant at its melting and boiling points untill all the substance melts or boils because, the heat supplied is continuously used up in changing the state of the substance by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. This heat energy absorbed without showing any rise in temperature is given the name latent heat of fusion/latent heat of vapourisation.
Comment on the following statements:
(a) Evaporation produces cooling.
Answer: Evaporation produces cooling as the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings and change into vapour thereby producing a cooling effect.
(b) Rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with increase in humidity.
Answer: Air around us cannot hold more than a definite amount of water vapour at a given temperature which is known as humidity. So, if the air is already rich in water vapour, it will not take up more water therefore, rate of evaporation of water will decrease.
(c) Sponge though compressible is a solid.
Answer: A sponge has minute holes in which air is trapped. Also, the material is not rigid.
When we press it, the air is expelled out and we are able to compress it.
Question. An atom is
(a) the smallest particle of matter known
(b) the smallest particle of a gas
(c) thesmallest indivisible particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction
(d) radioactive emission
Answer: A
Question. Air is regarded as a mixture because
(a) it pressure may vary
(b) its temperature may change
(c) its volume changes under different conditions
(d) its composition may vary
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following properties is different for solids, liquids and gases ?
(a) movement of molecules
(b) particle size of the substance
(c) mass of the substance
(d) energy exchange
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is an example of a mixture ?
(a) Sugar
(b) Brass
(c) \( \text{CO}_2 \)
(d) \( \text{NO}_3 \)
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is not a chemical change ?
(a) rusting of iron
(b) converting water into steam
(c) making curd from milk
(d) heating coal
Answer: B
Question. A chemical equation is a means
(a) of representing chemical and physical properties of reactant molecules
(b) of acquiring instructions for the preparation of a compound
(c) or representing a chemical change by means of symbol and formulas
(d) of showing the kind of elements present in a mixture
Answer: C
Question. In a balanced chemical equation, the reactant side and the product side have the same number of
(a) atoms
(b) molecules
(c) ions
(d) electrons
Answer: A
Question. In the chemical equation, \( \text{Mg} + \text{O}_2 \longrightarrow 2\text{MgO} \), \( \text{O}_2 \) represents
(a) atoms of oxygen joined together in a molecule
(b) molecules of oxygen
(c) grams of oxygen
(d) mole of oxygen
Answer: A
Question. The chemical formula of a compound does not represent
(a) the total number of atoms in one molecule of the compound
(b) the number of the molecules of the compound
(c) the state of the molecules of the compound
(d) the composition of a molecule of the compound
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following statements about a balanced chemical equation is true ?
(a) mass is conserved
(b) atoms are conserved
(c) mass as well as atoms are conserved
(d) molecules are conserved
Answer: C
Question. Boiling point of 10% aqueous solution of common salt at atmospheric pressure is
(a) 100°C
(b) > 100°C
(c) < 100°C
(d) not possible to predict
Answer: B
Question. The change of state of substance from gas to liquid is called-
(a) melting
(b) boiling
(c) condensation
(d) vaporization
Answer: C
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Science Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 9. We suggest that Class 9 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Science.
Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 9 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 9 Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 9 Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

