Read and download the CBSE Class 9 Biology Tissues Worksheet Set C in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter 6 Tissues, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Students of Class 9 should use this Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 6 Tissues as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Worksheet with Answers
Fill in the blanks
Question: Cork cells possess __________ on their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water.
Answer: Suberin
Question: __________ have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature.
Answer: Sieve tubes
Question: Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of __________ and __________.
Answer: Calcium and phosphorus
Question: Lining of blood vessels is made up of __________.
Answer: Squamous epithelium
Question: Lining of small intestine is made up of __________.
Answer: Columnar epithelium
Question: Lining of kidney tubules is made up of __________.
Answer: Cuboidal epithelium
Question: Epithelial cells with cilia are found in __________ of our body.
Answer: Respiratory tract
Question: __________ are forms of complex tissue.
Answer: Xylem and phloem
Question: __________ have guard cells.
Answer: Stomata
Question: Cells of cork contain a chemical called __________.
Answer: Suberin
Question: Husk of coconut is made of __________ tissue.
Answer: Sclerenchyma
Question: __________ gives flexibility in plants.
Answer: Collenchyma
Question: __________ and __________ are both conducting tissues.
Answer: Xylem; phloem
Question: Xylem transports __________ and __________ from soil.
Answer: Water; minerals
Question: Phloem transports __________ from __________ to other parts of the plant.
Answer: Food; leaf
Question: Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of subcutaneous fat. Describe why?
Answer: Fat acts as subcutaneous insulation of body for thermoregulation.
Question: Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary (V) or involuntary (IV) muscles.
(a) Jumping of frog
(b) Pumping of the heart
(c) Writing with hand
(d) Movement of chocolate in your intestine
Answer: (a)—V, (b)—IV, (c)—V, (d) —IV
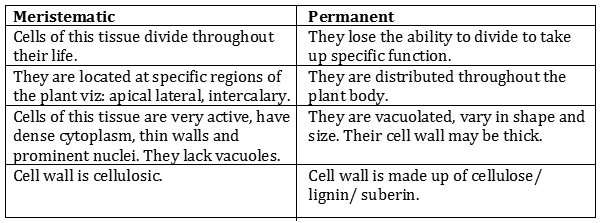
Question: (a) Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
Question: Define the process of differentiation.
Answer: The loss of ability to divide by taking up a permanent shape, size and function is called differentiation.
Question: Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Answer: Simple: Parenchyma/collenchyma/sclerenchyma Complex: Phloem/xylem.
Question: Match the column (A) with the column (B)

Answer: —(v); b—(iv); c—(iii); d—(i); e—(ii); f—(vi);
Question: Match the column (A) with the column (B)
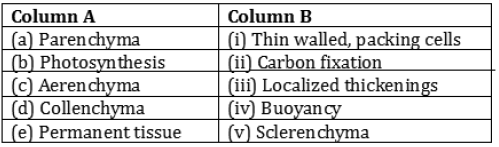
Answer: a—(i); b—(ii); c—(iv); d—(iii); e—(v);
Question: Write true (T) or false (F)
(a) Epithelial tissue is protective tissue in animal body.
(b) The lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made up of epithelial tissue.
(c) Epithelial cells have a lot of intercellular spaces.
(d) Epithelial layer is permeable layer.
(e) Epithelial layer does not allow regulation of materials between body and external environment.
Answer: (a)—T, (b)—T, (c)—F, (d) —T, (e)—F
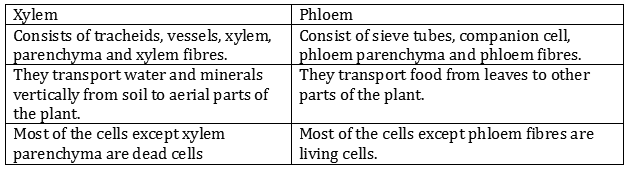
Question: Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component?
Answer: Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.

Question: Draw and identify different elements of phloem.
Answer: Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma.

Question: Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Answer: Epidermis is important for plants due to the following reasons
(i) it gives protection
(ii) helps in gaseous exchange
(iii) checks water loss
(iv) root hairs arising from epidermis helps in absorption of water and minerals.
Question: Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each type.
Answer:

Question: List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role.
Answer: Characteristics
a) – Cells of cork are dead at maturity
– These cells are compactly arranged
– Cells do not possess intercellular spaces.
– Cells possess a chemical substances suberin in their walls
– They are several layers thick.
b) As plants grow older, a strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of the stem.
Cells cut on the outer side by this meristem are called cork.
c) They are protective in function for older stem/twigs/branches. They are impervious to gases and water.
Question: Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
Answer: Epidermis having thick cuticle and waxy substances to prevent the invasion of parasites.
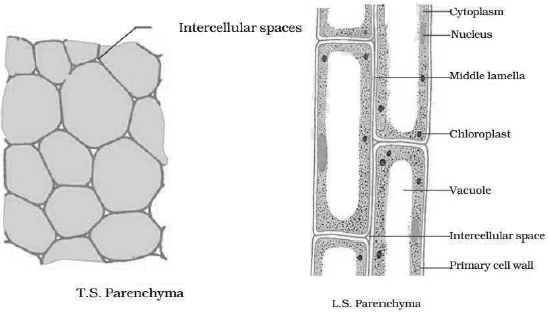
Question: Differentiate between sclerenchyma and parenchyma tissues. Draw well labelled diagram.
Answer:


Question: If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of glass jar. Explain why?
Answer: Transpiration takes place through stomata. Water vapour comes out of leaves during transpiration. When a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapour (coming out becomes of transpiration) condenses on the wall of glass jar and hence it appears as fine droplets.
Question: Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues. Draw diagram of each type of epithelial tissue.
Answer: Epithelial tissues are the covering or protective tissues in the animal body. Epithelium covers most organs and cavities within the body and keep different body systems separate. The skin, the lining of the mouth, the lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made of epithelial tissue. Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. They have only a small amount of cementing material.
between them and almost no intercellular spaces. The permeability of the cells of various epithelia play an important role in regulating the exchange of materials between the body and the external environment and also between different parts of the body. Regardless of the type, all epithelia are usually separated from the underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane.
Epithelial tissues are of following types— (1) Simple squamous epithelium (2) Stratified squamous epithelium (3) Columnar epithelium, and (4) Cubodial epithelium. These tissues differ in structure that correlate with their unique functions. For example, in cells lining blood vessels or lung alveoli, where transportation of substances occurs through a selectively permeable surface, there is a simple flat kind of epithelium. This is called the simple squamous epithelium. Simple squamous epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining. The skin, oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are also covered with squamous epithelium.
Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. Since, they are arranged in a pattern of layers, the epithelium is called stratified squamous epithelium. Where absorption and secretion occur, as in the inner lining of the intestine, tall epithelial cells are present. This columnar epithelium facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier. In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which are hairlike projections on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells. These cilia can move, and their movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it. This type of epithelium is thus ciliated columnar epithelium.
Cuboidal epithelium forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, where it provides mechanical support. Epithelial cells often acquire additional specialisation as gland cells, which can secrete substances at the epithelial surface. Sometimes a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular gland is formed. This is glandular epithelium.

Question: Draw well labelled diagrams of various types of muscles found in human body.
Answer:


Question: Water hyacinth float on water surface. Explain.
Answer: A special type of parenchyma; called aernchyma is present in water hyacinth. This tissue
has air-filled spaces inside. Due to this, water hyacinth floats on water surface.
Question: Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues? How are they different from one other?
Answer: Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells, which coordinate to perform a common function.
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Science Class 9 Chapter 6 Tissues Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 6 Tissues to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 9. We suggest that Class 9 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Science.
Chapter 6 Tissues Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 9 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 9 Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 6 Tissues difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 6 Tissues for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 6 Tissues focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 6 Tissues to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 9 Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 6 Tissues, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

