Read and download the CBSE Class 9 Physics Force And Laws Of Motion Worksheet Set C in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion
Students of Class 9 should use this Science practice paper to check their understanding of Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion Worksheet with Answers
Question: A passenger in a moving train tosses a coin which falls behind him. It means that motion of the train is
a) accelerated
b) uniform
c) retarded
d) along circular tracks
Answer: a
Question: Rocket works on the principle of conservation of
a) mass
b) energy
c) momentum
d) velocity
Answer: c
Question: Which of the following statement is not correct for an object moving along a straight path in an accelerated motion?
a) Its speed keeps changing
b) Its velocity always changes
c) It always goes away from the earth
d) A force is always acting on it
Answer: c
Question: A goalkeeper in a game of football pulls his hands backwards after holding the ball shot at the goal. This enables the goal keeper to
a) exert larger force on the ball
b) reduce the force exerted by the ball on hands
c) increase the rate of change of momentum
d) decrease the rate of change of momentum
Answer: b
Question: An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 ms–1 on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep the object moving with the same velocity is
a) 32 N
b) 0 N
c) 2 N
d) 8 N
Answer: b
Question: The inertia of an object tends to cause the object
a) to increase its speed
b) to decrease its speed
c) to resist any change in its state of motion
d) to decelerate due to friction
Answer: c
Question: According to the third law of motion, action and reaction
a) always act on the same body
b) always act on different bodies in opposite directions
c) have same magnitude and directions
d) act on either body at normal to each other
Answer: b
Question: Two identical bullets are fired one by a light rifle and another by a heavy rifle with the same force. Which rifle will hurt the shoulder more and why?
Answer: According to law of conservation of momentum; the momentum of bullet will be equal to the momentum of rifle. In case of light rifle; velocity will be more than the velocity of heavier rifle so that momentum (product of mass and velocity) for both shall be equal. Due to this, the lighter rifle will hurt the shoulder more.
Question: There are three solids made up of aluminium, steel and wood, of the same shape and same volume. Which of them would have highest inertia?
Answer: Steel- As the mass is a measure of inertia, the ball of same shape and size, having more mass than other balls will have highest inertia. Since steel has greatest density and greatest mass, therefore, it has highest inertia.
Question: Suppose a ball of mass m is thrown vertically upward with an initial speed v, its speed decreases continuously till it becomes zero. Thereafter, the ball begins to fall downward and attains the speed v again before striking the ground. It implies that the magnitude of initial and final momentums of the ball are same. Yet, it is not an example of conservation of momentum. Explain why?
Answer: Law of conservation of momentum is applicable to isolated system (no external force is applied). In this case, the change in velocity is due to the gravitational force of earth.
Question: A horse continues to apply a force in order to move a cart with a constant speed. Explain why?
Answer: When a cart is moving on the road, it has to encounter friction. To maintain a constant speed, some force need to be applied continuously to overcome the friction. Hence, the horse needs to continuously apply a force in order move the cart with a constant speed.
Question: Two balls of the same size but of different materials, rubber and iron are kept on the smooth floor of a moving train. The brakes are applied suddenly to stop the train. Will the balls start rolling? If so, in which direction? Will they move with the same speed? Give reasons for your Answer:
Answer: Yes. the balls will start rolling in the direction in which the train was moving. Due to the application of the brakes, the train comes to rest but due to inertia the balls try to remain in motion, therefore, they begin to roll. Since the masses of the balls are not the same, therefore, the inertial forces are not same on both the balls. Thus, the balls will move with different speeds.
Question: Water sprinkler used for grass lawns begins to rotate as soon as the water is supplied. Explain the principle on which it works.
Answer: The working of the rotation of sprinkler is based on third law of motion. As the water comes out of the nozzle of the sprinkler, an equal and opposite reaction force comes into play. So, the sprinkler starts rotating.
Question: Velocity versus time graph of a ball of mass 50 g rolling on a concrete floor is shown in Fig. 9.1. Calculate the acceleration and frictional force of the floor on the ball.
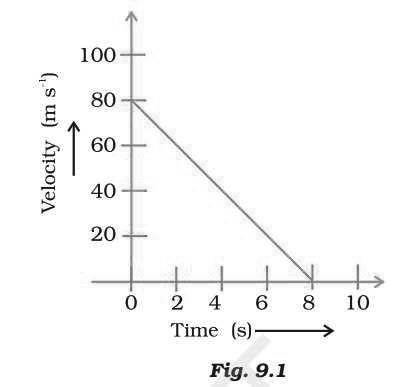
Answer: Acceleration = a = u – u / t = – 80/8 ms-2 = – 10ms-2
Force = ma = 50 / 1000 x 10 = 0.5N
Question: A truck of mass M is moved under a force F. If the truck is then loaded with an object equal to the mass of the truck and the driving force is halved, then how does the acceleration change?
Answer: Acceleration can be given as follow:
F = ma or a = F/m or a1 = F/M
When mass is doubled and force is halved;
a2 = F/4M or a2/a1 = F/4M ÷ F/M = 1/4
So, acceleration becomes one-fourth.
Question: Derive the unit of force using the second law of motion. A force of 5 N produces an acceleration of 8 ms–2 on a mass m1 and an acceleration of 24 ms–2 on a mass m2. What acceleration would the same force provide if both the masses are tied together?
Answer: F = m a = kg ms-2
This unit is also called newton. Its symbol is N.
m1 = F/a1 = (5/8) kg
m2 = F/a2 = (5/24) kg
M = (5/8 + 5/24) kg = (5/6) kg
Acceleration produced in M,
![]()
Question: Using second law of motion, derive the relation between force and acceleration. A bullet of 10 g strikes a sand-bag at a speed of 103 ms-1 and gets embedded after travelling 5 cm. Calculate
(i) the resistive force exerted by the sand on the bullet
(ii) the time taken by the bullet to come to rest.
Answer: (i) m = 10g g = (10/1000) kg
u =10 m/ s
u = 0
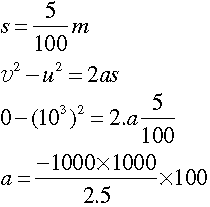
= − 107 ms-2
F = m.a =105 N
(ii) u = u + at
0 = 103 – 107 t
107 t = 103
t = 103/107
= 10-4s
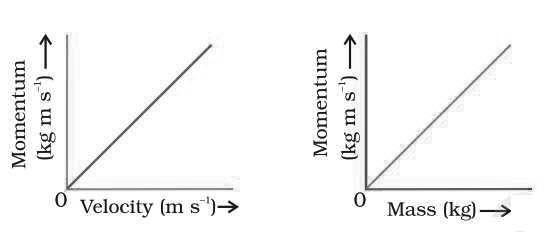
Question: What is momentum? Write its SI unit. Interpret force in terms of momentum. Represent the following graphically.
(a) momentum versus velocity when mass is fixed.
(b) momentum versus mass when velocity is constant
Answer: Momentum = mass × velocity
SI unit of momentum is kg ms-1
Force = Rate of change in momentum
Question: Two friends on roller-skates are standing 5 m apart facing each other. One of them throws a ball of 2 kg towards the other, who catches it, How will this activity affect the position of the two? Explain your Answer:
Answer: Separation between them will increase. Initially the momentum of both of them are zero as they are at rest. In order to conserve the momentum, the one who throws the ball would move backward. The second will experience a net force after catching the ball and therefore will move backwards that is in the direction of the force
Question. How is inertia measured quantitatively?
Answer: Quantitatively the inertia of an object is measured by its mass.
Question. The fruits fall off the branches when a strong wind blows. Give reason.
Answer: Fruits tend to continue in the state of rest on account of inertia while branches suddenly come into motion.
Question. Why do athletes run some distance before jumping?
Answer: Athlete has the inertia of motion and thus continues to move past the line.
Question. Name the physical quantity which is determined by the rate of change of linear momentum.
Answer: Force.
Question. What is frictional force?
Answer: The force that always opposes the motion of object is called force of friction.
Question. What is inertia?
Answer: The natural tendency of an object to resist a change in their state of rest or of uniform motion is called inertia.
Question. If a ball is thrown up in a moving train, it comes back to the person’s hands. Why?
Answer: This is because no horizontal force acts on it. It moves with the same horizontal speed.
Question. Which type of force brings an object in motion?
Answer: Unbalanced force.
Question. State Newton’s first law of motion.
Answer: An object remains in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Question. State Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction and they act on two different bodies.
Question. Why are road accidents at high speeds very much worse than accidents at low speeds?
Answer: The time of impact of vehicles is very small at high speed. So, they exert very large forces on each other.Hence, road accidents at high speeds are highly fatal.
Question. Name the factor on which the inertia of the body depends.
Answer: Inertia of a body depends upon the mass of the body.
Question. Name two factors which determine the momentum of a body.
Answer: Two factors on which momentum of a body depend is mass and velocity. Momentum is directly proportional to the mass and velocity of the body.
Question. What decides the rate of change of momentum of an object?
Answer: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of force.
Question. What is momentum?
Answer: The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity and has the same direction as that of the velocity. The SI unit is kg m/s. (p = mv)
Question. If a person jumps from a height on a concrete surface he gets hurt. Explain.
Answer. When a person jumps from a height he is in state of inertia of motion. When he suddenly touches the ground he comes to rest in a very short time and hence the force exerted by the hard concrete surface on his body is very high, and the person gets hurt.
Question. What is the relation between Newton’s three laws of motion?
Answer.
(i) Newton’s first law explains about the unbalanced force required to bring change in the position of the body.
(ii) Second law explains about the amount of force required to produce a given acceleration.
(iii) While Newton’s third law explains how these forces acting on a body are interrelated.
Question. Why we tend to get thrown to one side when a motorcar makes a sharp turn at a high speed?
Answer. We tend to get thrown to one side when a motorcar makes a sharp turn at a high speed due to law of inertia. When we are sitting in moving car on a /straight road, we tend to continue in our straight-line motion. But when an unbalanced force is applied on car to change the direction of motion, we slip to one side of the seat due to the inertia of our body.
Question. Why do fielders pull their hand gradually with the moving ball while holding a catch?
Answer.While catching a fast moving cricket ball, a fielder on the ground pulls his hands backwards with the moving ball. This is done so that the fielder increases the time during which the high velocity of the moving ball decreases to zero. Thus, the acceleration of the ball is decreased and therefore, the impact of catching the fast moving ball is reduced.
Question. Why are athletes made to fall either on a cushioned bed or on a sand bed in a high jump athletic event?
Answer. In a high jump athletic event, athletes are made to fall either on a cushioned bed or on a sand bed so as to increase the time of the athlete’s fall to stop after making the jump. This decreases the rate of change of momentum and hence the force.
Question.Why are roads on mountains inclined inwards at turns?
Answer. A vehicle moving on mountains is in the inertia of motion. At a sudden turn there is a tendency of vehicle to fall off the road due to sudden change in the line of motion hence the roads are inclined inwards so that the vehicle does not fall down the mountain.
Question. Why do athletes have a special posture with their right foot resting on a solid supporter for athletic races?
Answer. Athletes have to run the heats and they rest their foot on a solid supports before start so that during the start of the race the athlete pushes the support with lot of force and this support gives him equal and opposite push to start the race.
Question. Why you get hurt by hitting a stone while when you kick a football it flies away?
Answer. This is because stone is heavier than football and heavier objects offer larger inertia. When we kick a football its mass is less and inertia is also less so force applied by our kick acts on it and hence it shows larger displacement but in case of stone, it has more mass and offers larger inertia. When we kick (action) the stone it exerts an equal and opposite force (reaction) and hence it hurts the foot.
Question. Give any three examples in daily life which are based on Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer. Three examples based on Newton’s third law are :
Swimming : We push the water backward to move forward.
(i) Action - water is pushed behind
(ii) Reaction - water pushes the swimmer ahead
Firing gun : A bullet fired from a gun and the gun recoils.
(i) Action - gun exerts force on the bullet
(ii) Reaction - bullet exerts an equal and opposite force on the gun Launching of rocket :
(i) Action - hot gases from the rocket are released
(ii) Reaction - the gases exert upward push to the rocket
Question. Why does a ball rebound after striking against a floor?
Answer. When a ball strikes against a floor, it exerts a force on the floor. According to Newton’s third law of motion, the floor exerts an equal and opposite force on the ball. Due to this reaction, the ball rebounds.
Question. How do we swim?
Answer. While swimming, a swimmer pushes the water backward with his hands. The reaction offered by the water to the swimmer pushes him forward.
Question. Which concept is behind the phenomenon-boatman pushes the river bank with a bamboo pole to take his boat into the river”.
Ans : When the boatman pushes the river bank with a bamboo pole, the river bank offers an equal and opposite reaction. This reaction helps the boat to move into the river.
Question. Why does a fireman struggle to hold a hose-pipe?
Answer. A fireman has to make a great effort to hold a hosepipe to throw a stream of water on fire to extinguish it. This is because the stream of water rushing through the hose-pipe in the forward direction with a large speed exerts a large force on the hose-pipe in the backward direction.
Question. Why is the movement of a rocket in the upward direction?
Answer.
(i) The movement of a rocket in the upward direction can also be explained with the help of the law of conservation of momentum.
(ii) The momentum of a rocket before it is fired is zero. When the rocket is fired, gases are produced in the combustion chamber of the rocket due to the burning of fuel. These gases come out of the rear of the rocket with high speed. The direction of the Momentum of the gases coming out of the rocket is in the downward direction. To conserve the momentum of the system (rocket gases), the rocket moves upward with a momentum equal to the momentum of the gases. The rocket continues to move upward as long as the gases are ejected out of the rocket.
Question. What happens when a quick jerk is given to a smooth thick cardboard placed on a tumbler with a small coin placed on the cardboard? The coin will fall in the tumbler. Why?
Answer. The coin was initially at rest. When the cardboard moves because of the jerk, the coin tends to remain at rest due to inertia of rest. When the cardboard leaves contact with the coin, the coin falls in the tumbler on account of gravity.
Question.Explain why- An inflated balloon lying on the surface of a floor moves forward when pierced with a pin.
Answer. The momentum of the inflated balloon is zero before it is pierced with a pin. Air comes out with a speed in the backward direction from balloon after it is pierced with a pin. The balloon moves in the forward direction to conserve the momentum.
Question. State Newton’s three laws of motion.
Answer. Sir Isssac Newton further studied the idea of Galileo’s on force and motion and presented three laws of motion. These laws are as follows :
(i) First Law : A body remains in resting position unless it is not introduced with an unbalanced external force.
(ii) Second Law : The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied unbalanced force and change takes place in the direction of the force.
(iii) Third law : Action and reaction are equal and opposite and they act on different bodies.
Question. What are the disadvantages of friction?
or
Why friction is considered wasteful?
Answer. Friction is considered wasteful because :
(1) Friction leads to a loss of energy. Therefore, it reduces the efficiency of machines.
(2) Friction cause wear and tear of machine’s parts.
Question. Why all cars are provided with seat belts?
Answer. Sudden movement of the vehicle results in the sudden change in the state of motion of the vehicle when our feet are in contact with it. But the rest of our body opposes this change due to its inertia and tends to remain where it was. Seat belts are provided to protect the passengers from falling backward or forward during such situation.
Question. State all 3 Newton’s law of motion.
Answer. Newton’s I law of motion : An object remains in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Newton’s II law of motion : The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force. Newton’s III law of motion : To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction and they act on two different bodies.
Question. Explain inertia and momentum.
Answer.Inertia : The natural tendency of an object to resist a change in their state of rest or of uniform motion is called inertia. For example : A book lying on a table will remain there until an external force is applied on it to remove or displace it from that position. Momentum : Momentum of body is the quantity of motion possessed by the body. It is equal to the product of the mass and velocity of the body and is denoted by p. p = mv
Momentum is a vector quantity and its direction is same as the direction of velocity of the object. Its SI
unit is kilogram metre per second (kg ms–1).
Question. Define force. What are different types forces?
Answer. Force : It is a push or pull on an object that produces acceleration in the body on which it acts. The S.I. unit of force is Newton.
Types of forces :
Balanced force : When the forces acting on a body from the opposite direction do not change the state of rest or of motion of an object, such forces are called balanced forces.
Unbalanced force : When two opposite forces acting on a body move a body in the direction of the greater force or change the state of rest, such forces are called as unbalanced forces.
Frictional force : Force of friction is the force that always opposes the motion of object.
Question. What is inertia? Explain different types of inertia.
Answer. Inertia : The natural tendency of an object to resist change in their state of rest or of motion is called inertia. The mass of an object is a measure of its inertia. Its S.I. unit is kg.
Types of inertia :
Inertia of rest : The object remain in rest unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Inertia of motion : The object in the state of uniform motion will continue to remain in motion with same speed and direction unless external force is not applied on it.
Numerical Questions
Question. When a force of 40 N is applied on a body it moves with an acceleration of 5 ms2. Calculate the mass of the body.
Answer. Let m be the mass of the body.
Given : F = 40 N, a = 5 ms2
From the relation F = m a, we have
40 = m × 5
m =40/5 = 8 kg
Question. An object undergoes an acceleration of 8 ms–2 starting from rest. Find the distance travelled in 1 second.
Answer.
Given,
Acceleration, a = 8 ms–2
Initial velocity, u = 0
Time interval, t = 1 s
Distance travelled, s = ?
Using the equation of motion, s = ut +1/2 at2, one gets
s = 0 × 1 + 1/2 × 8 × 12 = 4 m
The object travels a distance of 4 m.
Question. Calculate the force required to impact to a car, a velocity of 30 ms–1 in 10 seconds. The mass of the car is 1,500 kg.
Answer.
Here u = 0 ms–1; v = 30 ms–1; t = 10 s; a = ?
Using v = u + at, we have
30 = 0 + a (10)
a = 3 ms–2
Now F = ma = 1,500 × 3
or F = 4,500 N
Question. A bullet of mass 10 g is fired from a rifle. The bullet takes 0.003 s to move through its barrel and leaves with a velocity of 300 ms–1. What is the force exerted on the bullet by the rifle?
Answer.
Here m = 10 g = 0.010 kg; u = 0; v = 300 ms–1
t = 0.003 s, F = ?
F =m (v - u)/t
F =0.010(300 - 0)/ 0.003
or F = 1,000 N
Question. What force would be needed to produce an acceleration of 1 ms–2 on a ball of mass 1 kg?
Answer.
Here m = 1 kg; a = 1 ms– 2; F = ?
Now F = ma
= 1 × 1
or F = 1 Newton
Question. What is the acceleration produced by a force of 5 N exerted on an object of mass 10 kg?
Answer.
Here F = 5 N; m = 10 kg; a = ?
Now F = ma or a = F/m
a = 0.5 ms–2
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Matter In Our Surrounding Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Is Matter Around Us Pure Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Motion Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Gravitation Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Work And Energy Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Physics Sound Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 9 Biology Natural Resources Worksheet Set C |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Science Class 9 Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 9. We suggest that Class 9 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Science.
Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 9 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 9 Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 9 Science worksheets for Chapter Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 9 Science Chapter Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 9 Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

