Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 12 Economics. Our expert-created answers for Class 12 Economics are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
For Class 12 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 12 Economics solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics NCERT Solutions PDF
Question. Discuss the central problems of an economy.
Answer: The allocation of scarce resources and the distribution of the final goods and services are the central problems of an economy. These are:
What to produce and in what quantities:
An economy has to decide what goods and services are to be produce and in what quantity as resource is available in limited quantity and also it have alternative uses. Whether to produce more of food, clothing, housing or to have more of luxury goods. Whether to use more resources in education and health or to use more resources in building military services.
How to Produce:
It is very important for an economy how to produce. Which of the resources to use in the production of each of the different goods and services. Whether to use more labour or more machines.
For whom to produce:
It generally means the distribution of the final goods. Who gets what and how much. Whether or not elementary education and basic health services should be available freely for everyone in the economy.
Question. What do you mean by the production possibilities of an economy?
Answer: The collection of all possible combinations of the goods and services that can be produced from a given amount of resources and a given stock of technological knowledge is called the production possibilities of the economy.
Question. What is a production possibility frontier?
Answer:A curve showing different possibilities of two goods that can be produced with efficient utilisation of the given resources and technology is called production possibility frontier.
In the above representation, a production possibility frontier between cotton and corn has been drawn. The points A,B,C, D and E which lie on PPC represent the situation when the resources of the economy are fully utilised. While any point lie under the curve, say F, shows inefficiency or underutilisation of available resources.
Question. Discuss the subject matter of economics.
Answer: The subject matter of economics has been studied under two broad branches:
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
In microeconomics, we study the behaviour of individual economic agents in the markets for different goods and services and try to figure out how prices and quantities of goods and services are determined through the interaction of individuals in these markets.
In macroeconomics, we try to get an understanding of the economy as a whole by focusing our attention on aggregate measures such as total output, employment and aggregate price level. We are interested in finding how the levels of these aggregate measures are determined and how the levels of these aggregate measures change over time.
Question. Distinguish between a centrally planned economy and a market economy.
Answer:
| Centrally Planned Economy | Market Economy |
| Means of production are owned by government. | Means of production are owned by private individuals. |
| The main motive of production is social welfare. | The main motive of production is profit making. |
| Prices of goods and services are generally high | Prices of goods and services are generally high |
| The production is governed by planning mechanism i.e., according to government plans. | The production is governed by price mechanism i.e., by demand and supply. |
| The inequality of income is low. | The inequality of income is high. |
Question. What do you understand by positive economic analysis?
Answer: Positive economic analysis is confined to cause and effect relationship. In other words, it states “what is.” It relates to what the facts are, were or will be about various economic phenomena in the economics. e.q., it deals with the analysis of questions like what are the causes of unemployment.
Question. What do you understand by normative economic analysis?
Answer: Normative economic analysis is concerned with what ‘ought to be’. It examines the real economic events from moral and ethical angles and judge whether certain economic events are desirable or undesirables. e.g., it deals with the analysis of questions like what should be the prices of food grains.
Question. Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Answer:
| Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
| It studies individual economic unit. | It studies entire economic unit |
| It deals with how prices and quantities of goods and services are determined in individual markets. | It deals with how general price level and quantities of goods and services are determined in entire economy. |
| It uses the method of partial equilibrium, i.e. equilibrium in one market. | It uses the method of general equilibrium, i.e. equilibrium in all markets of an economy. |
| The major microeconomic variables are price, individual consumer's demand, wages, rent, profit, revenues, etc. | The major macroeconomic variables are aggregate price, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, inflation, unemployment, etc. |
| Its central problems are price determination and allocation of resources. | Its central problem is determination of level of Income and employment in the economy. |
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is meant by economy?
Answer: Economy is a system which provides people with the means to work and earn living.
Question. What is economics?
Answer: Economics is about studying economic problems arising due to limited means (having alternative uses) in relation to unlimited wants.
Question. Why does an economic problem arise?
Or
what gives rise to an economic problem?
Or
why does the problem of choice arise?
Answer: If we are not able to satisfy unlimited wants out of limited resources then the economic problem arises.
Question. State two features of resources that give rise to an economic problem.
Answer: The two features of resources that give rise to an economic problem are:
1. Resources are limited.
2. They have alternative uses.
Question. Which type of science is economics?
Answer: Economics is a social science.
Question. What is the basic reason for economic problem in all economies?
Answer: It is scarcity of resources.
Question. What is meant by economising of resources?
Answer: Economising of resources means that resources are to be used in such a manner that maximum output is realised per unit of input. It also means optimum utilisation of resources.
Question. What is meant by central problem of an economy?
Answer: The problem of making a choice among alternative uses of resources is known as basic or central problem of an economy.
Question. What does a rightward shift of production possibility curve indicate?
Answer: It indicates growth of resources.
Question. Give two examples of growth of resources.
Answer:
1. Supply of skilled labour (like IT engineers) has increased in India causing a rightward shift in the production of IT software.
2. Discovery of oil reserves in the gulf countries has caused a substantial shift to the right in the PPC of these countries.
Question. Give two examples of underutilisation of resources.
Answer:
1. Related to less developed countries: Labour is underutilised as indicated by mass unemployment in countries like India.
2. Related to developed countries: Capital is underutilised during depression when production is decreased owing to lack of demand.
Question. Define Opportunity Cost.
Or
Give the meaning of ‘Opportunity Cost’.
Answer: Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative.
Question. Define Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT).
Answer: Marginal rate of transformation is the ratio of a number of units of a good sacrificed to produce an additional unit of another commodity.
Question. Why PPC is concave to the point of origin?
Answer: Because of increasing marginal opportunity cost.
Question. Define microeconomics.
Or
Give the meaning of microeconomics.
Answer: Microeconomics studies the behaviour of individual economic units of an economy, like households, firms, individual consumers and producers etc.
Question. Give one/two examples of microeconomics study.
Or
Name any three variables of micro-economics.
Answer:
1. Individual demand;
2. Individual supply; and
3. Individual income.
Question. Name any three variables of macroeconomics.
Answer:
1. Aggregate demand;
2. Aggregate supply; and
3. National income.
Question. State any two central problems under ‘problem of allocation of resources’.
Answer:
1. What to produce and in what quantity?
2. How to Produce?
II. Multiple Choice Questions
Question. The law of scarcity
(a) Does not apply to rich, developed countries.
(b) Applies only to the less developed countries.
(c) Implies that consumers’ wants will be satisfied in a socialistic system.
(d) Implies that consumers’ wants will never be completely satisfied.
Answer: (d)
Question. The central problem in economics is that of
(a) Comparing the success of command versus market economies.
(b) Guaranteeing that production occurs in the most efficient manner.
(c) Guaranteeing a minimum level of income for every citizen.
(d) Allocating scarce resources in such a manner that society’s unlimited needs or wants are satisfied in the best possible manner.
Answer: (d)
Use the given figure to answer question.
Question. Which one of the following bundles of goods cannot be produced with the resources the economy currently has?
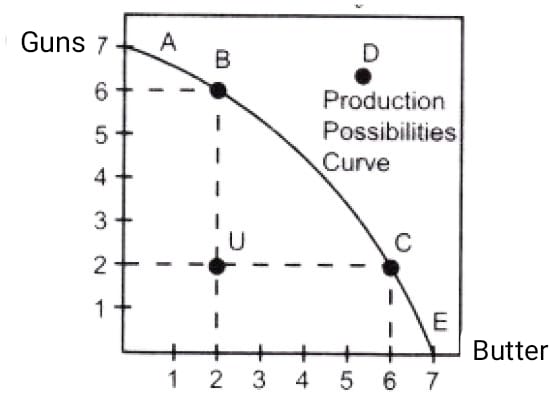
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer: (d)
Question. An economy achieves “productive efficiency” when:
(a) Resources are employed in their most highly valued uses.
(b) The best resources are employed.
(c) The total number of produced goods is the greatest.
(d) Goods and services are produced at least cost and no resources are wasted.
Using the figure gives below answer the following Question
Answer: (d)
Question. Which point on PPF shows a “productively efficient” level of output?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) All of the above.
Answer: (d)
Question. Which of the following clearly represents a movement toward greater productive efficiency?
(a) A movement from point A to point B.
(b) A movement from point C to point D.
(c) A movement from point F to point C.
(d) A movement from point E to point B.
Answer: (c)
Question. Which one of the following alternatives illustrate a decrease in unemployment using the PPF?
(a) A movement down along the PPF.
(b) A rightward shift of the PPF.
(c) A movement from a point on the PPF to a point inside the PPF.
(d) A movement from a point inside the PPF to a point on the PPF.
Answer: (d)
Question. If the PPF is linear, i.e., a straight line, which one of the following statements is true?
(a) As the production of a good increases, the opportunity cost of that good rises.
(b) As the production of a good increases, the opportunity cost of that good falls.
(c) Opportunity costs are constant.
(d) The economy is not at full employment when operating on the PPF.
Answer: (c)
Question. Which one of the following statements is a reason for the negative slope of PPF?
(a) The inverse relationship between the use of technology and the use of natural resources.
(b) Scarcity at any point of time due to limited amounts of productive resources.
(c) Resource specialisation.
(d) Increasing opportunity costs.
Answer: (b)
Question. Capital intensive technique is chosen in a
(a) Labour surplus economy.
(b) Capital surplus economy.
(c) Developed economy.
(d) Developing economy.
Answer: (b)
Question. Labour intensive technique is chosen in a
(a) Labour surplus economy.
(b) Capital surplus economy.
(c) Developed economy.
(d) Developing economy.
Answer: (a)
Question. If the marginal (additional) opportunity cost is a constant, PPC would be
(a) Convex.
(b) A straight line.
(c) Backward bending.
(d) Concave.
Answer: (b)
Question. The branch of economic theory that deals with the problem of allocation of resources is
(a) Micro economic theory.
(b) Macroeconomic theory.
(c) Econometrics’.
(d) None of them.
Answer: (a)
Question. Which one of the following options is likely to cause an inward shift in a country’s PPC?
(a) Earthquake destroying resources of the country.
(b) Scientists discovering new machines.
(c) Workers getting jobs in a new metro- project.
(d) The country finds new reserves of crude oil.
Answer: (a)
Question. The various combinations of goods that can be produced in any economy when it uses its available resources and technology efficiently are depicted by
(a) Demand curve.
(b) Production curve.
(c) Supply curve.
(d) Production possibilities curve.
Answer: (d)
Question. Scarcity is a situation in which
(a) wants exceed the resources available to satisfy them
(b) something is being wasted
(c) people are poor
(d) none of them
Answer: (a)
Question. Production Possibilities Curve is also known as
(a) Demand curve
(b) Supply curve
(c) Indifference curve
(d) Transformation curve
Answer: (d)
Question. A lot of people die and many factories are destroyed due to floods in a country.
How will it affect the production possibility curve?
(a) PPC will shift towards right
(b) PPC will shift towards left.
(c) PPC will remain the same
(d) None of the above.
Answer: (b)
Question. Which of the following is not a subject matter of microeconomics?
(a) Consumer’s behaviour
(b) Market structure
(c) Monetary Policy
(d) Pricing of factor services
Answer: (c)
Question. Which of the following is an assumption of Production Possibility Frontier?
(a) Resources are not fully employed.
(b) Resources are not equally efficient for production of the two goods.
(c) Resources are not efficiently employed.
(d) Resources available are not fixed.
Answer: (b)
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why does an economic problem arise?
State any two causes of economic problem.
State two characteristics of the economic resources which give rise to economic problem.
Or
Why does problem of choice arise? Or
Explain three factors that lead to an economic problem.
Answer: Economic problem arises because of scarcity of resources in relation to demand for them.
1. Wants are unlimited:
(a) This is a basic fact of human life. Human wants are unlimited.
(b)They are not only unlimited but also grow and multiply very fast.
2. Resources are limited:
(a) The resources to produce goods and services to satisfy human wants are available in limited quantities. Land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship are the basic scarce resources.
(b)These resources are available in limited quantities in every economy, big or small, developed or underdeveloped, rich or poor. Some economies may have more of one or two resources but not all the resources.
(c) For example, Indian economy has relatively more labour but less capital and land.
The U.S. economy has relatively more land but less labour. No economy in the world is comfortable in all the resources.
3. Resources have alternative uses:
(a) Generally a resource has many alternative uses.
(b) A worker can be employed in a factory, in a school, in a government office, selfemployed and so on.
(c) Like this, nearly all resources have alternative uses. But the problem is that which resource should be put to which use.
Question. Give reasons for the following statements:
1. Every economy has to make the decision relating to what to produce.
2. Problem of choice arises because available resources have alternative uses.
Answer:
1. As, we know there is no economy in this world which possesses infinite resources to produce each and everything in infinite quantities. Therefore, if an economy decides to produce a quantity of one commodity, then they have to sacrifice the production of another commodity.
2. Resources in every economy are always scarce. But the available resources can be put to alternative uses. Therefore, an economy will always prefer to make use of its resources in production of those goods and services that are most required and sacrifice the production of less- required goods and services.
Question. Why do all economies have similar central problems?
Answer: All economies whether developed or developing, have similar central problem because one or more of their resources (land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship) are limited and these resources can be put to alternative uses. The wants of the economies are unlimited. Therefore all economies have to face the basic economic problem of choice (what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce).
Question. State the central problems of an economy.
Answer: The central problems of an economy are:
1. What to produce and in what quantity?
2. How to produce?
3. For whom to produce?
Question. Define Production Possibility Curve and state its properties.
Answer: Production possibility curve is a curve which depicts all possible combinations of two goods which can be produced with given resources and technology in an economy. Properties of Production Possibility Curve
1. PPC is downward sloping: The downward slope of PPC means if the country wants to produce more of one good, it has to produce less quantity of the other goods.
2. PPC is concave to the point of origin: Concave shape of PPC implies that the slope of PPC increases. Slope of PPC is defined as the quantity of goods Y given up in exchange for additional unit of goods X.[Slope of Production Possibility Curve]
ΔY/ ΔX = Amount of good Y lost / Amount of good X gained
Question. State any three assumptions on which a production possibilities curve is based.
Answer: The concept of PP curve is based on the following assumptions:
1. First, the amount of resources in the economy is fixed.
2. Second, the technology is given and unchanged.
3. Third, the resources are efficient and fully employed.
Using the figure given below answer the following Question
Question. Does production take place only on PPC?
Answer: Both Yes and No.
Yes, production will take place on PPC, if the given resources are fully and efficiently utilised. In such case, production will take place at any point on the curve AB, like point F. No, production will take place on PPC, if the resources are either underutilised or inefficiently utilised or both. In such case, production will take place on any point below the curve AB, like point H. Any point below the PP curve, thus highlights the problem of unemployment and inefficiency in the economy.
Question. “An economy always produces on but not inside PPC. Defend or refute.
Answer: The given statement is refuted. An economy operates on PPC, only when resources are fully and efficiently utilised. It means, if there is unemployment or inefficient use of resources, the economy may operate inside PPC. So, the economy may operate at point ‘H’ (Figure), in addition to the points on the curve AB on PPC.
Question. Why is Production Possibilities Curve concave? Explain.
Answer:
1. PPC is concave because of increasing marginal opportunity cost (MOC).
2. This behaviour of the MOC is based on the assumption that all resources are not equally efficient in production of all goods.
3. Rise in opportunity cost occurs when factors (resources) which are specialized or more adopted for production of a piece of particular good (say, tanks), is transferred to the production of another good (say, wheat) for which they are less productive or less specialized.
4. Thus, transfer of resources from more productive to less productive uses indirectly means fall in their productivity, with the result more of such resources are needed to produce an additional unit of the other commodity. Thus marginal opportunity cost goes on increasing making the PP curve concave in shape.
Question. Give reasons for the following statements:
1. A Production Possibility Frontier is always a downward sloping concave curve.
2. An efficient economy would always produce a combination of goods that lies on the given Production Possibility Frontier.
3. Growth of an economy is represented in the form of a rightward shift of a Production Possibility Frontier.
Answer:
1. A PPF slopes downward to indicate if an economy chooses to produce more of one commodity, then it would have to reduce the production of another commodity.
The concave shape of PPF is due to Increase in Marginal Opportunity Cost.
2. Any point on a given PPF presents a production possibility wherein all the available resources in an economy get fully utilized.Any combination located below the given PPF shows an underutilization of available resources. Likewise, any point to the right of the PPF is beyond the available resources.
3. By economic growth, we mean that an economy has developed greater capacity to produce larger quantity of goods by acquiring more resources. Graphically, this would be represented by a rightward shift of PPF.
Question. Explain the meaning of opportunity cost with the help of production possibility schedule.
Answer: Opportunity cost of any commodity is the amount of other good which has been given up in order to produce that commodity. Alternatively opportunity cost of a given activity is the value of the next best activity.
Production Possibilit Schedule
| Production Possibilities | Production of Commodity X | Production of Commodity Y |
| A | 0 | 15 |
| B | 1 | 14 |
| C | 2 | 12 |
| D | 3 | 9 |
| E | 4 | 5 |
| F | 5 | 0 |
Initially at combination B, in order to produce one unit of X, the economy has to sacrifice one unit of Y. So, at combination B, opportunity cost is 1 unit. At combination C, for producing additional unit of commodity X, the economy has to sacrifice 2 units of commodity Y. So, at combination C, opportunity cost is 2 units. Similarly, at combination D, for producing additional unit of commodity X, the economy has to sacrifice 3 units of commodity Y. So, at combination C, opportunity cost is 3 units and so on.
Question. Define Marginal Opportunity Cost. Explain the concept with a hypothetical numerical example.
Answer:
1. Marginal opportunity cost is an addition to a cost in terms of a number of units of a commodity sacrificed to produce one additional unit of another commodity.
2. Marginal opportunity cost can also be termed marginal rate of transformation,Marginal rate of transformation is the ratio of number of units of a good sacrificed to produce one additional unit of another commodity.
| Production Possibilities (Combination) | Rice (in lack tone) | Guns (in Thousand) | MOC of Rise (in Thousand Guns) | MRT |
| A | 0 | 15 | -- | - |
| B | 1 | 14 | 1 (= 15 - 14) | 1G : 1R |
| C | 2 | 12 | 2 (= 14 - 12) | 2G : 1R |
| D | 3 | 9 | 3 (= 12 - 9) | 3G : 1R |
| E | 4 | 5 | 4 (= 9 - 5) | 4G : 1R |
| F | 5 | 0 | 5 (= 5 - 0) | 5G : 1R |
IV. True or False
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false.
Question. An economy always manages to meet all the needs of the people living in the
country.
Answer: False: An economy always tries to provide means of living to all the people. It may be successful (as in most of the developed countries), or it may not be successful (as in many developing countries) to achieve its objective.
Question. In the context of an economy when we talk about ‘scarcity’, we refer to short supply of land.
Answer: False: Scarcity refers to limited availability of all types of goods and services in relation to their requirements. The concept of scarcity, thus, is not limited to land alone.
Question. Economic problem arises due to plenty of resources.
Answer: False: Economic problem arises due to scarcity of resources and alternative uses of various means.
Question. Because of destruction caused by war, a country’s PPF will shift to the left.
Answer: True: Country’s PPF will shift to the left; this will be due to the fact that the country’s capacity to produce will get reduced.
Question. A job guarantee scheme will lead to a rightward shift of PPF.
Answer: False: A job guarantee scheme does not add anything new to a country’s resources.
This will only ensure that available unutilised or unemployed resources are productively employed.
Question. If a PPF shifts to the right, the new PPF will be parallel to the original.
Answer: False: A new PPF need not be parallel to the old one. It can take any possible shape.
Question. A ‘Production Possibility Frontier’ (PPF) is always represented as a upward sloping curve.
Answer: False: A PPF represents different combinations of two commodities that can be produced with the help of available resources in an economy. If an economy decides to produce a larger quantity of one commodity, it would be left with lesser resources to produce another commodity. A downward sloping curve represents this relationship.
Question. If the economy operates inside PPC, it shows full utilisation of resources.
Answer: False: If economy operates inside PPC, it shows underutilisation of resources.
Question. Growth of resources shifts PPC towards left.
Answer: False: Growth of resources increases the capacity of economy to produce more. It shifts PPC towards right and not left.
Question. PPC is concave shaped as production of one good can be increased only by reducing quantity of another good.
Answer: False: PPC is concave shaped due to increasing marginal opportunity cost.
Question. Economy can never operate outside PPC with the given resources and technology.
Answer: True: Economy can never operate outside PPC with the given resources and technology as all points outside PPC are unattainable.
Question. Economy always operates on PPC.
Answer: False: Economy operates on PPC only when resources are fully and efficiently utilised. If resources are not fully and efficiently utilized, economy operates at any point inside PPC.
Note: As per CBSE guidelines, no marks will be given if reason to the answer is not explained.
V. Higher Order Thinking Skills Questions
Question. Define Marginal Opportunity Cost.
Answer: Marginal opportunity cost is an addition to the cost in terms of a number of units of a commodity sacrificed to produce an additional unit of another commodity.
Question. How does Maruti Udyog Ltd. fix the prices of its cars, is it studied in macroeconomics?
Answer: False: Macroeconomics is the study of aggregates e.g., determination of general price level in an economy. The principles underlying the pricing of a single good by a single firm or single industry are studied in microeconomics.
Question. Whether the cotton textile industry is an example of micro or macroeconomics?
Answer: Microeconomics.
Question. “Scarcity and choice go all together”. Defend or refute.
Answer:
1. We defend this statement because scarcity arises as resources are limited. The resources to produce goods and services to satisfy human wants are available in limited quantities. Land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship are the basic scarce resources.
2. These resources are available in limited quantities in every economy, big or small,developed or underdeveloped, rich or poor. Some economies may have more of one or two resources but not all resources.
3. For example, the Indian economy has relatively more labour but less capital and land.
The U.S. economy has relatively more land but less labour. No economy in the world is comfortable in all the resources.
4. Since resources are limited, then we have to make a choice because resources have an alternative use. Generally a resource has many alternative uses. A worker can be employed on a farm, in a factory, in a school, in a government office, self-employed and so on. Like this nearly all resources have alternative uses. But the problem is that which resource should be put to which use.
Question. “Only ‘Scarce Goods’ attract price.” Comment.
Answer:
1. The given statement is correct.
2. All resources are not scarce in the economy. For example, the water taken from river or air we breathe is abundant in relation to wants. Such goods are available free of cost. These goods are known as Non-Economic Goods.
3. On the other hand, some goods are scarce in relation to their wants. For example, diamonds, petrol, electricity, etc. are scarce in relation to wants. These goods command price and are known as Economic Goods.
Question. A lot of people died and many factories were destroyed in an earthquake.
How will it affect the PPC of the economy?
Answer: PPC of the economy will shift to the left from PP to P,Pr It happens because the number of possible combinations available with the economy has decreased due to destruction of resources in the economy.
Question. Massive unemployment will shift PPC to the left. Defend or refute.
Answer: The given statement is refuted. Massive unemployment does not decrease the capacity of economy to produce. So, there will be no shift of PPC. However, due to unutilisation of human resources, economy will operate at some point inside PPC as shown in the adjacent figure at point U.
VI. Value Based Questions
Question. A country’s resources are fully and p efficiently employed. The problem of scarcity exists. What advice would be given to raise the efficiency level of the human resource to fight scarcity?
Answer: Spread of education and training. Value: Awareness about efficient utilization of resources
Question. In an underdeveloped economy why there is the need of efficient utilization of resources?
Answer: Developmental needs are more in underdeveloped economy and these are fulfilled with our limited resources. Value: Critical thinking
Question. India is a labour abundance and capital scarce economy. Which technique of production should be used to produce the commodity?
Answer: India should adopt labour intensive technique.
Value: Analytic
Question. As water resources are limited in our country, how can we economise the water resources so that it could not cause a future problem for us? Give any two suggestions.
Answer:
1. Rainwater should be conserved by rain water harvesting.
2. Water wastage should be avoided i.e., economical use of water.
Value: Awareness about efficient use of water.
Question. Scarcity of resources is a universal phenomenon and is not confined to poor and backward countries only. Comment.
Answer: All countries, rich and poor, face the problem of choice due to scarcity of resources to fulfil unlimited wants. Value: Critical thinking
Question. The problems of scarcity of resources and their alternate uses arise everywhere but particularly in backward countries. For their solution non-economic considerations can be stressed. How?
Answer: Central problems, what to produce?, How to produce? and for whom to produce?, can be solved in poor countries by laying more stress on the social aspects, e.g., public utility services may be developed, labour intensive techniques may be preferred and the distribution of national income may be made equitable.
Value: Analytic
Question. Although water is useful, yet it is cheap. On the contrary, diamond is not much of use, still it is very expensive. Give an economic reason for this paradox.
Answer: The economic reason for this paradox is scarcity. Although water is useful, yet it is cheap due to its abundance in the economy. Diamonds are very expensive because they are scarce and people are ready to pay a high price. Value: Analytic
Question. Why is it that on one hand coal is found in plenty, yet it is scarce while on the other, a rotten vegetable is rare but not scarce?
Answer: Coal is found in plenty yet it is scarce because its demand is also high. Scarcity means that availability is less than sufficient to satisfy all wants or desires. On the other hand, a rotten vegetable is rare but not scarce because there is no demand or want for a rotten vegetable. Value: Analytic
Question. A farmer is getting more profit by producing opium rather than that of wheat.
In situation of famine which crop should be produced?
Answer: Production of wheat. Because in situation of famine, food grain like wheat is required more than opium. Value: Social welfare
Question. Large number of technical training institutions have been started by the government. State its economic value in the context of production possibility frontier.
Answer: This would lead to technological innovations in the economy. When the level of technology improves production possibility frontier is expected to shift to the right. There
would be better utilization of the resources and the economy will move closer to the production possibility frontier.
Value: Economic Growth with technological innovation
Question. Unemployment is reduced due to the measures taken by the government.
State its economic value in the context of production possibilities frontier.
Answer: When unemployment is reduced due to the measures taken by the government, the economy will be able to realize its production potential (Full employment) level.
Value: Efficient utilization of resources
Question. The government has started promoting foreign capital. What is its economic value in the context of Production Possibilities Frontier?
Answer: The inflow of foreign capital is expected to increase the availability of the resources in an economy, which will thereby shift the production possibility frontier to the right. Value: Economic Growth with increase in resources
Question. Name the economic value achievable when attempts are made to increase resources in the country.
Answer: The economic value here is economic growth in the country, which will thereby shift the production possibility frontier to the right. Value: Economic Growth
Question. Production in an economy is below to its potentiality due to unemployment.
Government starts employment generation schemes. Explain its effects by using production possibility curve.
Answer: Production possibility curve is a curve which depicts all the possible combinations of goods which can be produced with given resources and technology in an economy i.e., producing goods at its full potentiality. Production below the potentiality means that total production in the economy is somewhere below the production possibility curve PPi; for example, point U in the diagram. We know production below the production possibility curve highlights unemployment. When government starts employment generation schemes, the economy moves towards the full employment, thereby removes unemployment. So, economy comes back to its potential level.
Value: Analytic
Question. there are various sources of income a teacher has; such as,
1. He can earn Rs 40000 from teaching in school.
2. He can earn Rs 50000 by tuition/ coaching
3. He earns Rs 60000 by writing the help book guides.
What is the opportunity cost of his teaching in school? Why should he choose teaching profession?
Answer: Opportunity cost of teaching is the writing of books. He should choose teaching
profession because it provides maximum social welfare. Value: Social welfare
Question. Economic slowdown in some parts of the world has adversely affected demand for Indian exports. What will be its effect on the production Possibilities frontier of India? Explain.
Answer: There will be no effect on Production Possibility Frontier (PPF). It is because PPF shows only what a country can potentially produce, and not what it actually produces. Slowdown by reducing demand for exports may ultimately bring down output. Assuming that the country’s actual production is somewhere on PPF, Slowdown may result in the country producing at a point somewhere below PPF as shown in the figure at point U.
Value: Analytic
Question. Using a diagram explain what will happen to the PPC of Bihar if the river Kosi causes widespread floods?
Answer: If the river Kosi causes widespread floods in Bihar, it will lead to destruction of resources in Bihar. This will shift the PPC leftward. Initially PPC is PP. With floods, the PPC will shift to
VII. Applications Based Questions
Question. A teacher is getting Rs 6,000 per month as salary. If he leaves the job and starts tuition work, he is expected to earn Rs 5,000 per month. What would be his opportunity cost?
Answer: The opportunity cost of school job is Rs 5,000 p.m. that the teacher could have
earned in the alternative use, by doing tuition work.
Question. A doctor has a private clinic in New Delhi and his annual earnings are Rs 10 lakh. If he works in a government hospital in New Delhi, his annual earning will be Rs 8 lakh. What is the opportunity cost of having a clinic in New Delhi?
Answer: The opportunity cost of opening a clinic in New Delhi is Rs 8 lakh, that he could have earned in the next best alternative use, by working in a government hospital in New Delhi.
Question. With the same amount of resources a farmer can feed the following combination of goats and horses:
Goats Horses
Option I 168 44
Option II 150 50
Taking into consideration the options available with him, find out the opportunity cost of the farmer of feeding one horse.
Answer: The opportunity cost of the farmer ‘of feeding one horse is 3 goats i.e.,
(168-150)/50-44=18/6=3/1
Thus, the opportunity cost of feeding one horse is 3 goats.
Question. Why production possibility curve is also called opportunity cost curve?
Answer:
1. Production possibility curve is a curve which depicts all possible combinations of two goods which can be produced with given resources and technology in an economy.
2. PPC is also called opportunity cost curve because each and every point on PPC measures the opportunity cost of one commodity in terms of sacrificing other commodity.
3. The rate of this sacrificed commodity is called the Marginal Opportunity Cost of the expanding good.
Question. What will be the impact of recently launched ‘Clean India Mission’ (Swachh Bharat Mission) on the Production Possibilities curve of the economy and why?
Answer: Cleanliness reduces chances of people falling ill and, thus ensure better health. This in turn will reduce forced absenteeism from work, raise efficiency level and thus raise country’s production potential. Rise in potential shifts PP curve to the right.
Question. What will likely be the impact of large scale outflow of foreign capital on Production Possibility Curve of the economy and why?
Answer:
1. The Production Possibility Curve shifts to the left.
2. It is so because outflow of foreign capital decreases the capital resource in our country leads to fall in production capacity of our country.
3. It can be explained with the help of the diagram that PP is at full employment level and due to outflow of foreign capital it shifts leftwards P1P1.
Question. What is likely to be the impact of ‘Make in India’ appeal to the foreign investors by the Prime Minister of India, on the production possibilities frontiers of India?
Explain.
Answer: (i) The production possibility frontier of India shifts rightward because of ‘Make in India’ appeal.
(ii) It is so because it attracts foreign companies or investors to set up factories in India and invest in country’s infrastructure.
(iii) It leads to huge capital inflow shifting the production possibility curve rightward as shown in the figure.
Question. What is likely to be the impact of efforts towards reducing unemployment on the production potential of the economy? Explain.
Answer:
1. The economy moves towards the full employment, thereby removes unemployment.
2. This can be done when government starts employment generation schemes. By this,economy moves towards full employment and production potentiality of an economy increases.
3. It can be explained with the help of the following diagram. In the given figure,from unemployment (U), we are moving towards full employment (F).
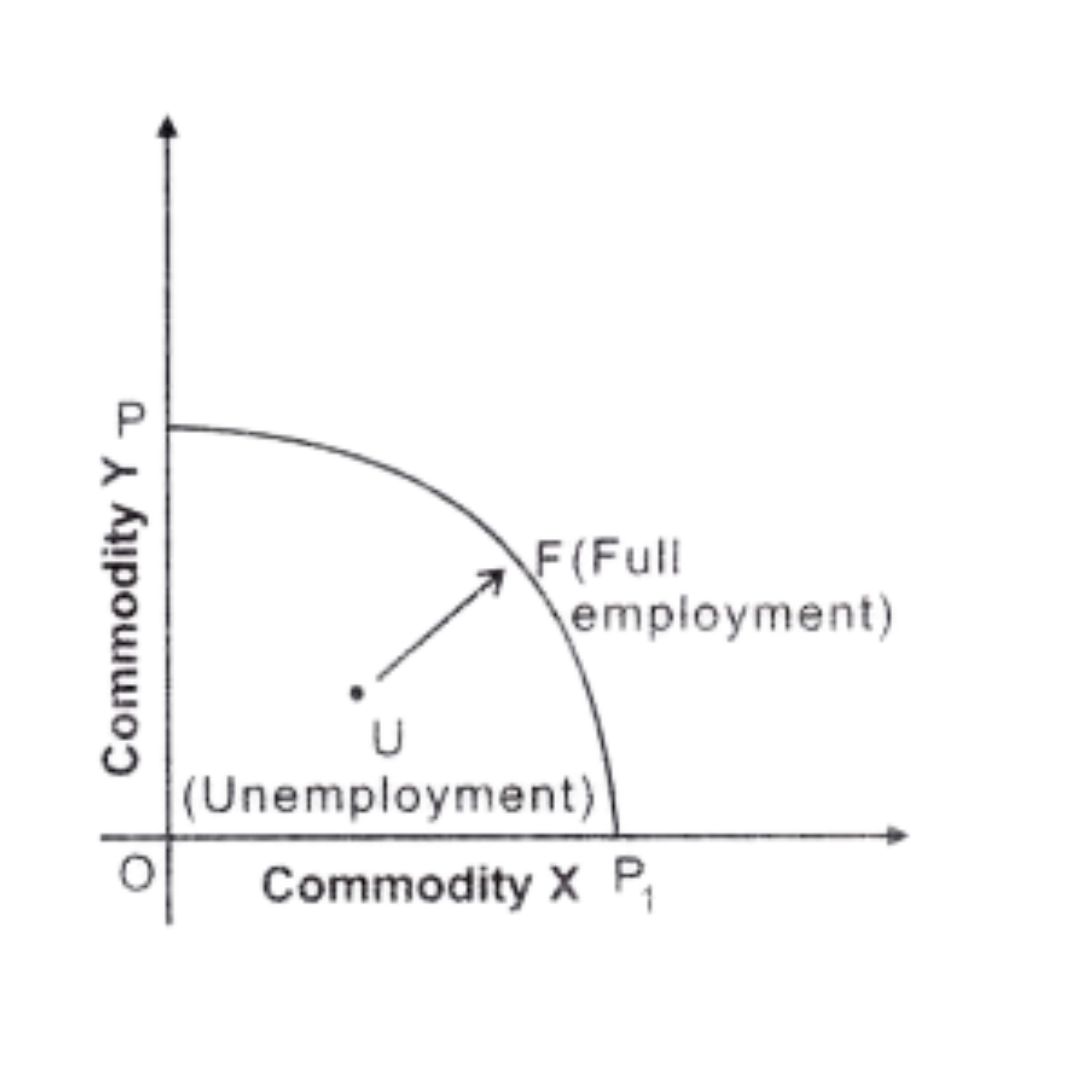
Question. Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule.
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) |
| 0 | 10 |
| 1 | 9 |
| 2 | 7 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 0 |
Answer:
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) | Marginal opportunity Cost of X (in term of Y) ΔY/ΔX |
| 0 | 10 | ------- |
| 1 | 9 | 1 |
| 2 | 7 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 4 | 0 | 4 |
The Production Possibility Curve is downward sloping concave because of increasing marginal opportunity cost.
Question. Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule.
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) |
| 0 | 8 |
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 0 |
Answer:
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) | Marginal opportunity Cost of X (in term of Y) ΔY/ΔX |
| 0 | 8 | ------- |
| 1 | 6 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 0 | 2 |
The Production Possibility Curve is downward sloping straight line because of constant marginal opportunity cost.
Question. Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities curve based on the following schedule.
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) |
| 0 | 30 |
| 1 | 27 |
| 2 | 21 |
| 3 | 12 |
| 4 | 0 |
Answer:
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) | Marginal opportunity Cost of X (in term of Y) ΔY/ΔX |
| 0 | 30 | ------- |
| 1 | 27 | 3 |
| 2 | 21 | 6 |
| 3 | 12 | 9 |
| 4 | 0 | 12 |
The Production Possibility Curve is downward sloping straight line because of constant marginal opportunity cost.
Question. Giving reason comment on the shape of Production Possibilities Curve based on the following schedule.
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) |
| 0 | 16 |
| 1 | 12 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 0 |
Answer:
| Good X (Units) | Good Y (Units) | Marginal opportunity Cost of X (in term of Y) ΔY/ΔX |
| 0 | 16 | ------- |
| 1 | 12 | 4 |
| 2 | 8 | 4 |
| 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 0 | 4 |
The Production Possibility Curve is downward sloping straight line because of constant marginal opportunity cost.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 Demand |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 Elasticity of Demand |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Cost |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Perfect Competition |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Producer Equilibrium |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Revenue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Supply |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Macroand its Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 National Income and Related Aggregates |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Banking |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Money |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Aggregate Demand and Its Related Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 National Income Determination and Multiplier |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Government Budget and the Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Balance of Payment |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Foreign Exchange Rate |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Economics
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 12 Economics textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 12 Economics chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 12 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Economics Class 12 Solved Papers
Using our Economics solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 12 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 12 Economics are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Economics concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 12 Economics. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

