Download the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes Set B in PDF format. These Class 11 Biology revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 11 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology
Points To Remember
Photosynthesis :Photosynthesis is an enzyme regulated anabolic process of manufacture of organic compounds inside the chlorophyll containing cells from carbon dioxide and water with the help of sunlight as a source of energy.
![]()
Historical Perspective
Josheph Pr·iestley (1770) : Showed that plants have the ability to take up C02 from atmosphere and release 02. (Candle with bell jar and mouse expt.)
Jan Ingenhousz (1779): Release of 02 by plants was possible only in sun light and only by the green parts of plants. (Expt. with aquatic plant in light & dark)
Theodore de Saussure (1804) : Water is an essential requirement for photosynthesis to occur.
Julius Von Sachs (1854) : Green parts in plant produce glucose which is stored as starch.
T.W. Engelmann (1888) : The effect of different wavelength of light on photosynthesis and plotted the first action spectrum of photosynthesis.
C.B. Van Niel (1931) : Photosynthesis is essentially a light dependent reaction in which hydrogen from an oxidisable compound reduces C02 to form sugar. He gave a simplified chemical equation of photosynthesis.
![]()
Hill (1937) : Evolution of oxygen occurs in light reaction.
Calvin (1954-55) : Traced the pathway of carbon fixation.
Site for photosynthesis : Photosynthesis takes place only in green parts of the plant, mostly in leaves. Within a leaf, photosynthesis occurs in mesophyll cells which contain the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are the actual sites for photosynthesis. The thylakoids in chloroplast contain most of pigments required for capturing solar energy to initiate photosynthesis: The membrane system (grana) is responsible for trapping the light energy and for the synthesis of ATP and NADPH. Biosynthetic phase (dark reaction) is carried in stroma.
Importance of Photosynthesis-
(1) Synthesis of organic compounds
(2) Change of radiant energy into chemical energy
(3) Useful products are obtained from plants gums, oils timber fire wood, resins rubber, fibers and drugs, etc.
(4) Balance the percentage of 02 and C02 in atmosphere
(5) Fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and petroleum have been formed inside the earth indirectly as a product of photosynthesis.
Pigments involved in photosynthesis :
Chlorophyll a : (Bright or blue green in chromatograph). Major pigment, act as reaction centre, involved in trapping and converting light into chemical energy. It is called universal photo-synthetic pigment.
Chlorophyll b : (Yellow green)
Xahthophylls : (Yellow)
Carotenoids : (Yellow to yellow-orange)
- In the blue and red regions of spectrum shows higher rate of photosynthesis.
Light Harvesting Complexes (LHC) :The light harvesting complexes are made up of hundreds of pigment molecules bound to protein within the photosystem I (PS-I) and photosystem II (PS-II). Each photosystem has all the pigments except one molecule of chlorophyll ‘a’ forming a light harvesting system (antennae). The reaction centre (chlorophyll a) is different in both the photosystems.
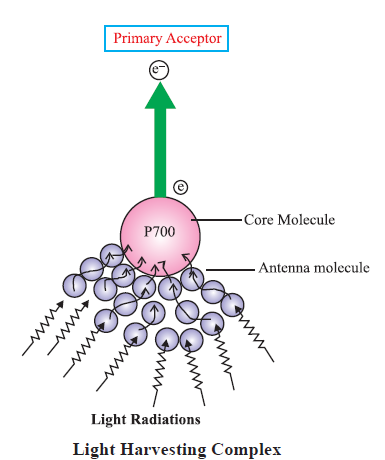
Photosystem I (PS-I) : Chlorophyll ‘a’ has an absorption peak at 700 nm (P700).
Photosystem II (PS-11) : Chlorophyll ‘a’ has absorption peak at 680 nm (P680),
Process of photosynthesis : It includes two phases-Photochemical phase and biosynthetic phase. (Formerly known as Light reaction and dark reaction)
(i) Photochemical phase (Light reaction) : This phase includes-light absorption, splitting of water, oxygen release and formation of ATP and NADPH. It occurs in grana region of chloroplast.
(ii) Biosynthetic phase (Dark reaction) : It is light independent phase, synthesis of food material (sugars). (Calvin cycle). It occurs in stroma region of chloroplast.
Photophosphor·ylation : The process offormation of high-energy chemicals (ATP and NADPH) in presence of light.
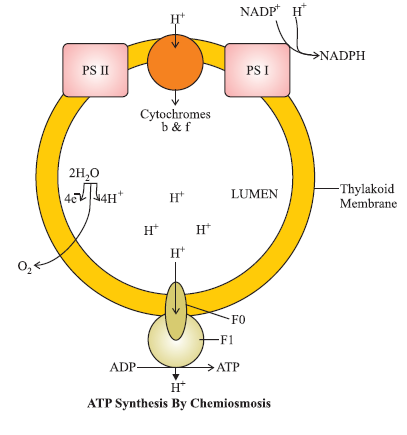
Non-Cyclic photophosphorylation :Two photosystems work in series-First PSII and then PSI. These two photosystems are connected through an electron transport chain (Z. Scheme). Both ATP and NADPH + H+ are synthesised by this process. PSI and PSII are found in lamellae of grana, hence this process is carried here.
Cyclic photophosphorylation : Only PS-I works, the electron circulates within the photosystem. It happens in the stroma lamellae (possible location) because in this region PSII and NADP reductase enzyme are absent. Hence only ATP molecules are synthesised. It occurs when only light of wavelengths beyond 680 nm are available for excitation.
The electron transport (Z-Scheme): In PS II, reaction centre (chlorophyll a) absorbs 680 nm wavelength of red light which make the electrons to become excited. These electrons are taken up by the electron acceptor that passes them to an electron transport system (ETS) consisting of cytochromes. The movement of electron is down hill. Then, the electron pass to PS I and move down hill further.
The splitting of water : It is linked toPS II. Water splits into H+, [0] and electrons.
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e–
Chemiosmotic Hypothesis : Chemiosmotic hypothesis explain the mechanism of ATP synthesis in chloroplast. In photosynthesis, ATP synthesis is linked to development of a proton gradient across a membrane. The protons are accumulated inside of membrane of thylakoids (in lumen). ATPase enzyme has a channel of that allow diffusion of protons back across the membrane. This release energy to activate ATPase enzyme that catalyses the formation of ATP.
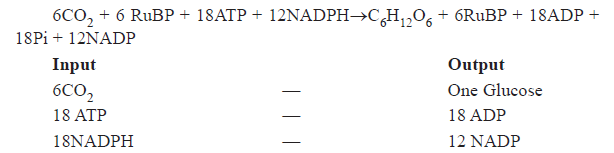
Biosynthesis phase in C3 plants:
ATP and NADPH, the products of light reaction are used in synthesis offood. The first C02 fixation product in C3 plant is 3-phosphoglyceric acid or PGA. The C02 acceptor molecule is RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate). The cyclic path of sugar formation is called Calvin cycle on the name of Melvin Calvin, the discover of this pathway. Calvin cycle proceeds in three stages.
(1) Carboxylation: C02 combines with ribulose 1, 5 bisphosphate to form 3 PGA in the presence ofRuBisCo enzyme (present in stroma)
(2) Reduction : Carbohydrate is formed at the expense of ATP and NADPH.
It involves 2ATP for phsophorylation and 2NADH2 for reduction per C02 molecule fixed.
(3) Regeneration: The C02 acceptor ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate is formed agam.
6 turns of Calvin cycles and 18 ATP molecules are required to synthesize one molecule of glucose
The C4 pathway C4 plants such as maize, sorghum, sugarcane have special type, of leaf anatomy, they tolerate higher temperatures. In this pathway, oxaloacetic acid (OAA) is the first stable product formed. It is 4 carbon atoms compound, hence called C4 pathway (Hatch and Slack Cycle). The leaf has two types of cells: mesophyll cells and Bundle sheath cells (Kranz anatomy). Initially C02 is’ taken up by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in mesophyll cell and changed to oxaloacetic acid (OAA) in the presence of PEP carboxylase. Oxaloacetate is reduced to maltate/asparate that reach into bundle sheath cells.
The decarboxylation ofmaltate/asparate occurs with the release of C02 and formation of pyruvate (3C). In high C02 concentration RuBisCO carboxylase and not as oxygenase, hence the photosynthetic losses are prevented. RuBP operates now under Calvin cycle and pyruvate transported back to mesophyll cells and changed into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to keep the cycle continue.
![]()
Photorespiration : The light induced respiration in green plants is called photorespiration. In C3 plants some 02 binds with RuBisCO and hence C02 fixation is decreased. In this process RuBP instead of being converted to 2 molecules of PGA binds with 02 to form one molecule of PGA and phosphoglycerate.
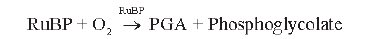
There is neither synthesis of ATP nor NADPor sugar. There is 25% loss of fixed C02 so it is wasteful process.
C4 Plants:
(1) Lack Photorespiration
(2) Show response to high light intensities
(3) Have greater productivity of biomass.
Adaptations in C4 Plants :
(i) Kranz Anatomy
(ii) Occurrence of two types of cells
(iii) Dimorphic chloroplast
(iv) Presence ofRuBisCO in Bundle Sheath cells and PEPase in mesophyll cells.
(v) Mechanism to increase C02 concentration near RuBisCO in Bundle Sheath cells.
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) Plants-Stomata open at night. e.g., Cacti, Bryophyllum, Pineapple.
Law of Limiting Factors :If a chemical process is affected by more than one factor, then its rate will be determined by the factor which is nearest to its minimal value. It is the factor which directly affects the process if its quantity is changed Factors affecting photosynthesis:
Light : Rate of photo-synthesis increases at low light At high intensities of light beyond a point the rate of C02 fixation decreases. Longer hours of light duration favour more photosynthesis rate.
Car·bon dioxide : Increase in C02 concentration causes increases in C02 fixation. It is the major limiting factor for photosynthesis.
Temper·ature: The rate of photosynthesis at optimum temperature is, high. It is 20°C-25°C For C3 plants and 30-45°C for C4 plants.
Water: Water is one of the reactant in photosynthesis, but it effects the rate of C02 fixation. Low water content causes the stomata to close and reduces the C02 availability.
Regardless of whether you wish to have an overview of a chapter, revision notes are here to do it for you. These notes will surely save your time during stressful exam times.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 11. Our teachers always suggest that Class 11 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Biology.
Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Biology exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes Set B from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 11 students get the best study material for Biology.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes Set B include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Biology principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes Set B provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 11 is covered.
These notes for Biology are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes Set B, Class 11 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes Set B, are available for immediate free download. Class 11 Biology study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

