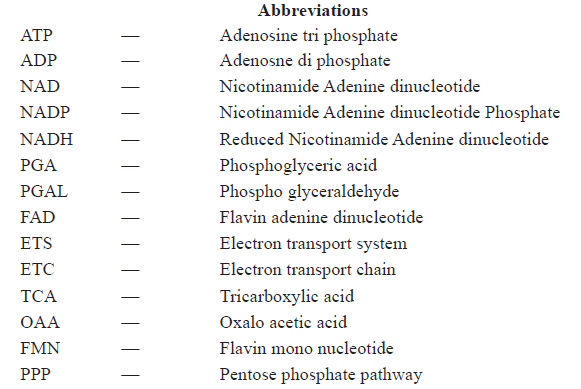
Download the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B in PDF format. These Class 11 Biology revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 11 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology
Points To Remember
Aerobic respiration : Complete oxidation of organic food in presence of oxygen thereby producing C02, water and energy.
Anaerobic respiration : Incomplete breakdown of organic food to liberate energy in the absence of oxygen.
ATP Synthetase : An enzyme complex that catalysis synthesis of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation
Biological oxidation : Oxidation in a series of reaction inside a cell.
Cytochromes : A group of iron containing compounds of electron transport system present in inner wall of mitochondria.
Dehydrogenase : Enzyme that catalyses removal of H atom from the substrate.
Electron acceptor : Organic compound which receive electrons produced during oxidation-reduction reactions.
Electron transport : Movement of electron from substrate to oxygen through respiratory chain during respiration.
Fermentation : Breakdown of organic substance that takes place in certain microbe like yeast under anaerobic condition with the production of C02 and ethanol.
Glycolysis: Enzymatic breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid that occurs in the cytoplasm.
Oxidative phosphorylation : Process of formation of ATP from ADP and Pi using the energy from proton gradient.
Respriation : Biochemical oxidation food to release energy.
Respiratory Quotient : The ratio of the volume of C02 produced to the volume of oxygen consumed.
Proton gradient : Difference in proton concentration across the tissue membrane.
Mitochondrial matrix : The ground material of mitochondria in which pyruvic acid undergoes aerobic oxidation through Kreb's cycle.
Electron Transport Chains (ETC)-A series of co-enzymes and electron/carriers where electrons can pass along increasing redox potential losing a bit of energy at every step of transfer.
Cellular Respiration-The process of oxidation/breakdown of food materials within the cell to release energy. Respiratory substarate to be oxidized during respiration is usually glucose, but these can also be proteins, fats or organic acids. In plants, respiratory gaseous exchange occurs through stomata and lenticels :
Overall cellular respiration is :
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (36ATPs)
Aerobic Respiration
Overall mechanism of aerobic respiration can be studied under the following steps:
(A) Glycolysis (EMP pathway) in cytoplasm
(B) Oxidative Decarboxylation-(Gateway Reaction)-in Mitochondrial matrix
(C) Kreb's cycle (TCA-cycle)-Matrix of mitochondria
(D) Oxidative phosphorylation
A. Glycolysis : The term has origianted from the Greek word, glycos = glucose, lysis = splitting, or breakdown means breakdown of glucose molecule to pyruvic acid. It was given by Embden Meyerhof and Parnas. It is a chain of 10 reactions to convert glucose into pyruvate. It is common for acerobic and anaerdomic respiration.
Steps for Glycolysis-(EMP Pathway)
1. Phosphorylation of Glucose into Glucose-6-phosphate
2. Isomerisation of Glucose-6-Phosphate into fractose-6-phosphate
3. Second phosphorylation in which Fructose-6-phosphate changes into Fructose-1, 6-biphosphate
4. Splitting ofFructiose-1, 6-biphosphate into DiHAP and PGAL
5. Isomerisation of DiHAP into PGAL
6. Oxidation ofPGAL into 1, 3-biphosphosphoglycerate
7. Synthesis ofATP and converssion of 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate into 3-phospholycerate
8. Isomerisation of 3-phosphoglycerate into 2-phospholycerate
9. Dehydration of2-phosphoglycerate into PEP
10. Substrate level ATP synthesis and formation of Pyruvic Acid.
- It is also called Embden- Meyerhof- Paranas pathway. (EMP pathway)
- It is common in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- It takes palce outside the mitochondria, in the cytoplasm.
- One molecule of glucose (Hexosesugar) ultimately produces two molecules of pyruvic acid through glycolysis.'
- During this process 4 molecules of ATP are produced while 2 molecules
ATP are utilised. Thus net gain of ATP is of 2 molecules.
Input and Output of glycolysis
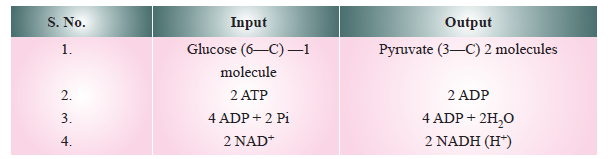
Net out put ...... 2 Pyruvate + 2ATP + 2NADH (+ H+) OR 2 Pyruvate + 8 ATP
The pyruvate, so produced, may under go (i) Lactic acid fermentation, Alcoholic fermentation of Aerobic Respiration (Krebs Cycle)
B. Oxidative decarboxylation : Pyruvic acid is converted into Acetyle CoA in presence of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
The Acetyle CoA enters in TCA cycle.
C. Tri Carboxylic Acid Cycle (Kereb's cycle) or Citric acid Cycle : This cycle starts with condensation of acetyle group with oxaloacitic acid and water t o yield citric acid which under goes a series of reactions.
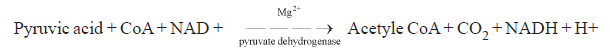
- It is aerobic and takes a place in mitochondrial matrix.
- Each pyruvic acid molecule produces 4 NADH + H+, one FADH2 , one ATP.
- One glucose molecule has been broken down t o release C02 and eight molecules of NADH + H+, two molecules of FADH2 and 2 molecules of ATP.
Compensation Point : It is the value of a factor at which the rate of photosynthesis controlled by it is just equal to the rate of respiration and photorespiration so that there is not net exchcange of gases between the phtosynthetic organ and the environment.
At compensation point the photosynthetic tissue manufacture only such amount of food which of sufficient for it to remain alive. No food is supplied to rest of the plant. Therefore, net photosynthesis is zero.
(D) Oxidative Phosphorylation
The synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate using energy from proton gradient is called oxidative phosphorylation. This takes place in elementry particles present on the inner membrane of cristae of mitochondria. This process in mitochondria is catalysed by ATP synthestase (complex V). This compmlex has two major components F0 and and F1' F0 acts a channel for proton and F1 acts as an ATP synthetase.
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation
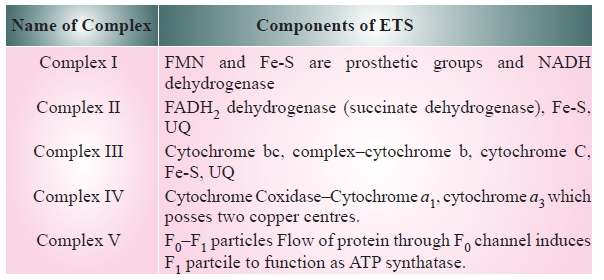
Respiratory Balance Sheet :
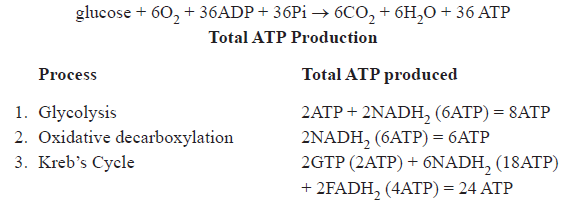
Energy production in prokaryotes during aerobic respiration = 38 ATP
Energy poroduction in eukaryotes during aerobic respiration= 38 -2 = 36 ATP
In eukaryotes 2 ATP are used in transporting 2 molucules of NADH + H+ formed in glycolysis from cytoplasm to mitochandria for oxidation through ETS shuttle.
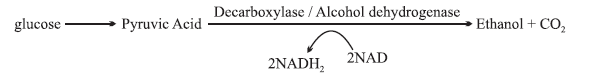
(2) Anaerobic Respiration-In anaerobic respiration, Glycolysis is followed by formation of ethanol or lactic acid in the cytoplasm.
Fermentation :It is the process of anaerobic respiration which occurs in yeast and some bacteria. Fermentation involves incomplete oxidation of food into enthanol and carbon-dio-oxide. It results in the production of 2 ATP molcules.
(i) Conversion of Acetyl CoA into fatty acid and PGA.
(ii) Synthesis of chlorophyll and cytochromes from Succinyl CoA
(iii) Synthesis of Amino acids from OAA and α-ketoglutaric acid
(iv) Synthesis of Alkaloid from OAA.
Enzymes involved-Pyruvic acid decarboxylase, Alcohol dehydrogenase
Anaerobic respiration in muslces : During vigrous exercise a person feels pain and fatigue in his muscles. This is due to accumulation of lactic acid in muscles. When oxygen is inadequate pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid in presence of enzyne-lactic dehydrogenase.
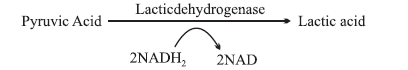
During rest lactic acid is reconverted to pyruvic acid.
Amphibolic Pathway :
During the process of cellular respiration Carbohydrates, fats and protiens are broken down to release energy and hence respiration is a catabolic process/ catabolic pathway. From this pathway many compound are withdrawn for synthesis of substrates. Some anabolic processes are formation of pyruvic acid from amino acids, and formation of Acetyl CoAfrom Fatty acid. So-Respiratory pathway is involved in both catabolism and anabolism, it is better to consider the respiratory pathway as an amphibalic pathway.
RQ (Respiratory quotient)
(a) RQ = 1 (When carbohydrate is used as substrate)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
(b) RQ is less than 1 (i.e., < 1) for fats.
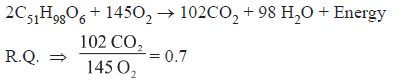
(c) RQ is 0.9 for proteins.
(d) RQ is more than 1 (i.e., > 1) for organic acids.
(e) RQ is inifinite in case of anerobic respiration, because C02 is evolved but 02 is not consumed.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 11. Our teachers always suggest that Class 11 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Biology.
Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 12 Respiration in Plants. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Biology exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 11 students get the best study material for Biology.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Biology principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 11 is covered.
These notes for Biology are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B, Class 11 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B, are available for immediate free download. Class 11 Biology study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

