Download the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B in PDF format. These Class 11 Biology revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 11 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
The process of exchange of O2 from the atmosphere with CO2 produced by the cell is called breathing. It occurs in two stages of inspiration and expiration. During inspiration air enters the lungs from atmosphere and during expiration air leaves the lungs.
Respiratory Organs – Mechanism of breathing varies in different organism according to their body structure and habitat.
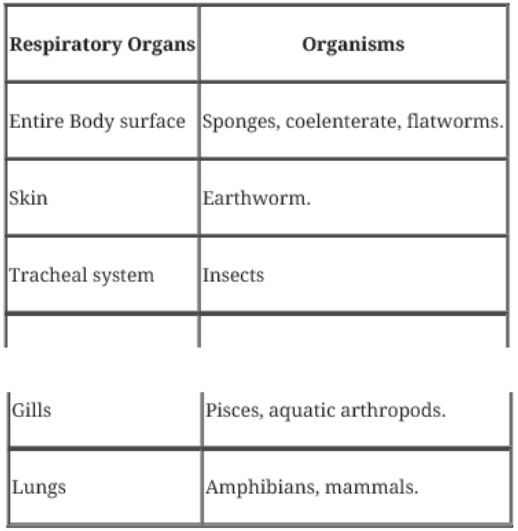
Human Respiratory System
- Human respiratory system consists of a pair of nostrils, pharynx, larynx, bronchi and bronchioles that finally terminates into alveoli.
- Nasal chamber open into pharynx that leads to larynx. Larynx contains voice box (sound box) that help in sound production.
- The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi and initial bronchioles are supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings to prevent collapsing in absence of air.
- Each bronchiole terminates into an irregular walled, vascularized bag like structure called alveoli.
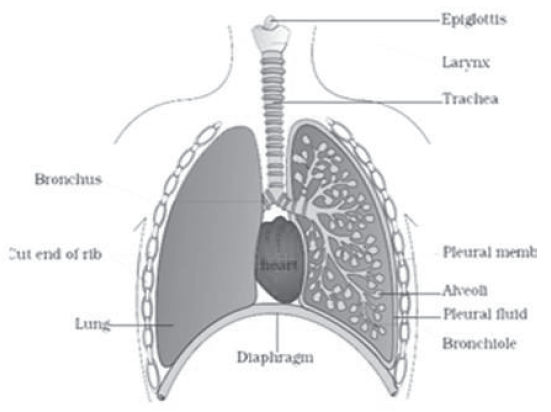
- The branching network of bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli collectively form the lungs.
- Two lungs are covered with double layered pleura having pleural fluid between them to reduce the friction on lung surface
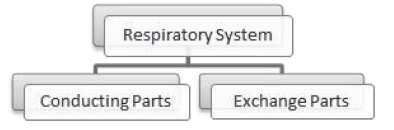
Conducting parts include nostrils, pharynx, larynx and trachea. Main functions include-
1. Transport of atmospheric air to alveoli.
2. Removing foreign particles from air, humidifying it and bringing it to body temperature.
The exchange parts are alveoli. It is the site of actual diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and atmospheric air.
Steps of Respiration
1. Breathing in which Oxygen rich atmospheric air is diffused in and CO2 rich alveolar air is diffused out.
2. Diffusion of gases across alveolar membrane.
3. Transport of gases by blood.
4. Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
5. Utilization O2 of by cells to obtain energy and release of CO2 (cellular respiration).
Mechanism of Breathing
- Breathing involves inspiration and expiration. During inspiration atmospheric air is drawn in and during expiration, alveolar air is released out.
- Movement of air in and out takes place due to difference in pressure gradient.
- Inspiration occurs when pressure inside the lung is less and expiration occurs when pressure is more in lungs than outside.
- The diaphragm and external and internal intercostal muscles between the ribs help in developing pressure gradient due to change in volume.
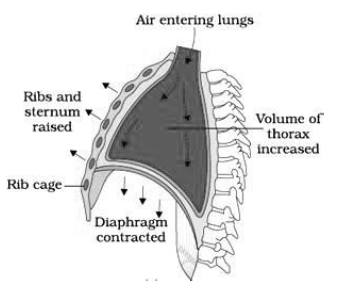
- The contraction of intercostal muscles lifts the ribs and sternum causing an increase in volume of thoracic cavity that results in decrease in pressure than the atmospheric pressure. This causes inspiration.
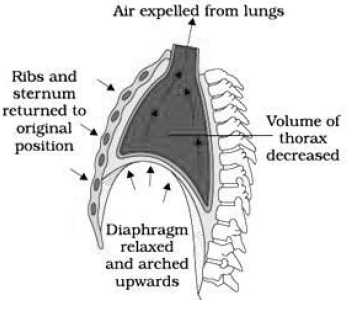
- Relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles reduce the thoracic volume and increase the pressure causing expiration.
- The volume of air involved in breathing movements is estimated by using spirometer for clinical assessment of pulmonary functions.
Respiratory Volume and Capacities
Tidal volume (TV) – volume of air inspired or expired during a normal respiration. It is about 500mL in healthy man.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) – additional volume of air a person can inspire by forceful inspiration. It is about 2500 mL to 3000mL.
Expiatory Reserve Volume (ERV) – additional volume of air a person can expire by forceful expiration. It is about 1000 mL to 1100mL.
Residual Volume (RV) – volume of air remaining in lungs even after a forcible expiration. It is about 1100mL to 1200mL.
Inspiratory Capacity (IC) – TV + IRV
Expiratory Capacity (EC) – TV + ERV
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) – ERV + RV
Vital Capacity (VC) – maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forceful expiration. ERV+ TV+ IRV
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) – total volume of air accommodated in lung at the end of forced inspiration. RV+ ERV+ TV+ IRV or Vital capacity + Residual Volume.
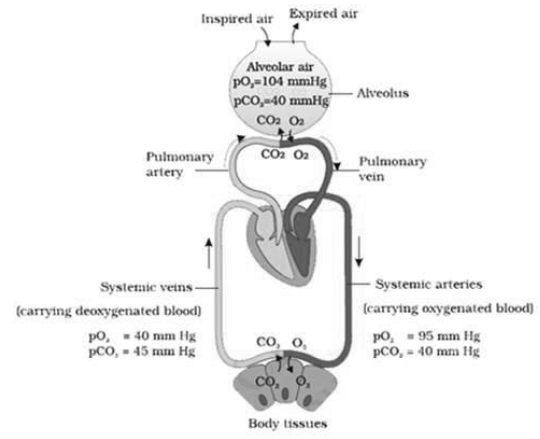
Exchange of Gases
- Exchange of gases takes place at two sites
1. Alveoli to blood
2. Between blood and tissues.
- Exchanges of gases occur by simple diffusion due to pressure/ concentration gradient,solubility of the gases and thickness of membrane.
Pressure contributed by individual gas in a mixture of gas is called partial pressure represented by pCO2 and pO2 .
Partial pressure of Oxygen and carbon dioxide at different part involved in diffusion varies from one part to another and moves from higher partial pressure to lower partial pressure.
Solubility of CO2 is 20-25 times more than solubility ofO2 , so CO2 diffuse much faster through membrane.
Diffusion membrane is three layered thick, that is alveolar squamous epithelium,endothelium of alveolar capillaries and basement substance between them.
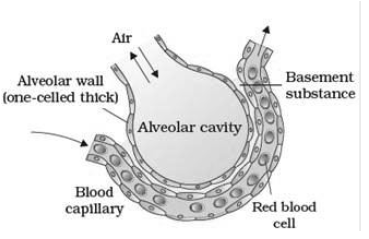
Transport of Gases
- Blood is the medium of transport for CO2 and O2. Most of oxygen (97%) is transported through RBC and remaining 3% by blood plasma.
- 20-25% of CO2 is transported by RBC, 70% as bicarbonate and rest 7% in dissolved state by blood plasma.
Transport of Oxygen
- Haemoglobin in RBC combines with O2 to form Oxyhaemoglobin. Each haemoglobin combine with four oxygen molecules.
- Binding of O2 is related with partial pressure of O2 and CO2, hydrogen ion concentration and temperature.
- Percentage saturation of haemoglobin and partial pressure of oxygen forms sigmoid curve (oxygen dissociation curve).
- In the alveoli, pO2 is more and pCO2 is less, less H+ ions concentration and lower temperature favour the binding ofO2 with hemoglobin. Where opposite condition in tissues favour the dissociation of Oxyhaemoglobin.
Transport of Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is transported by haemoglobin as carbamino-haemoglobin. In tissues pCO2 is high and pO2 is less that favour the binding of carbon dioxide with haemoglobin. Opposite condition help in dissociation of carbamino- haemoglobin in alveoli.
Enzyme carbonic anhydrase help in formation of carbonate ions to transport carbon dioxide.
Regulation of Respiration
Human beings have ability to maintain and moderate the rate of respiration to fulfill the demand of body tissues by neural system.
Respiratory rhythm centre is located in medulla region of hind brain. Pneumotaxic
centre in pons moderate the function of respiratory rhythm centre.
Chemo-sensitive area near rhythm centre is highly sensitive to C and H+ ions that ultimately control the respiratory rate. Oxygen do not play major role in controlling rate of respiration.
Functions of Respiration-
1. Energy production
2. Maintenance of acid-base balance.
3. Maintenance of temperature
4. Return of blood and lymph.
Mountain Sickness is the condition characterised by the ill effect of hypoxia (shortage of oxygen) in the tissues at high altitude commonly to person going to high altitude for the first time.
Symptoms-
- Loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting occurs due to expansion of gases in digestive system.
- Breathlessness occurs because of pulmonary oedema.
- Headache, depression, disorientation, lack of sleep, weakness and fatigue.
Disorder of Respiratory System
1. Asthma- it is due to allergic reaction to foreign particles that affect the respiratory tract.
The symptoms include coughing, wheezing and difficulty in breathing. This is due to excess of mucus in wall of respiratory tract.
2. Emphysema- is the inflation or abnormal distension of the bronchioles or alveolar sacs of lungs. This occurs due to destroying of septa between alveoli because of smoking and inhalation of other smokes. The exhalation becomes difficult and lung remains inflated.
3. Occupational Respiratory Disorders- occurs due to occupation of individual. This is caused by inhalation of gas, fumes or dust present in surrounding of work place. This includes Silicosis, Asbestoses due to exposer of silica and asbestos. The symptom includes proliferation of fibrous connective tissue of upper part of lung causing inflammation.
4. Pneumonia- it is acute infection or inflammation of the alveoli of the lungs due to bacterium streptococcus pneumoniae. Alveoli become acutely inflamed and most of air space of the alveoli is filled with fluid and dead white blood corpuscles limiting gaseous exchange.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 11. Our teachers always suggest that Class 11 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Biology.
Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Biology exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 11 students get the best study material for Biology.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Biology principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 11 is covered.
These notes for Biology are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B , Class 11 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B , are available for immediate free download. Class 11 Biology study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

