Download the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes Set B in PDF format. These Class 11 Biology revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 11 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology
Cell cycle : The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesises the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells.
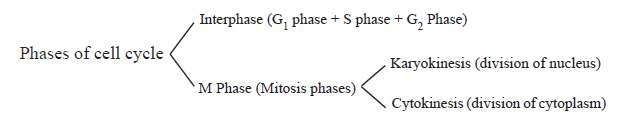
Interphase : (Resting Phase)
- G1 Phase : Cell metabolically active and grows continuously but does not replicate DNA
- S Phase : DNA synthesis occurs, DNA content increases from 2C to 4C, but the number of chromosomes remains same i.e.,2n.
- G2 Phase : Proteins are synthesised in preparation for mitosis while cell growth continues.
M Phase (Mitosis Phase) : Starts with nuclear division, corresponding to separation of daughter chromosomes (karyokinesis) and usually ends with division of cytoplasm, (cytokinesis).
Quiescent stage (G0) In adult animals cells that do not divide and exit G1 phase to enter an inactive stage called G0. Cells at this stage remain metabolically active but do not proliferate.
e.g., Heart cells
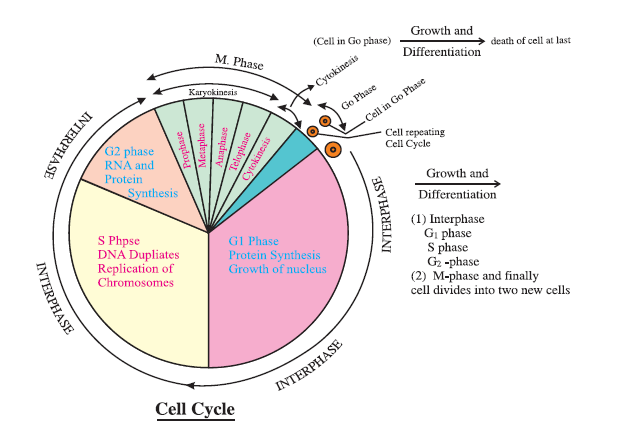
Mitosis
Since the number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny cells is the same, it is called as equational division. Mitosis is divided into four sub stages.
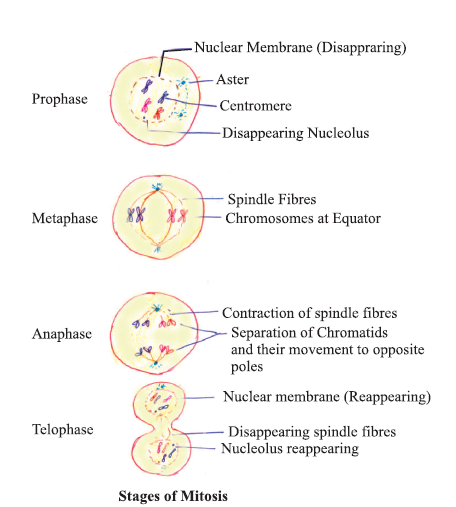
1. Prophase : (i) Replicated chromosomes, each consisting of 2 chromatids, condense and become visible.
(ii) Microtubules are assembled into mitotic spindle.
(iii) Nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear.
(iv) Centriole moves to opposite poles.
2. Metaphase : (i) Spindle fibres attached to kinetochores (small disc-shaped structures at the surface of centromere) of chromosomes.
(ii) Chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle to form metaphase plate.
3. Anaphase : (i) Centromeres split and chromatids separate.
(ii) Chromatids move to opposite poles due to shortening of spindle fibres.
4. Telophase : (i) Chromosomes cluster at opposite poles.
(ii) Nuclear envelope assembles around chromosomes clusters’.
(iii) Nucleolus, Golgi Complex, E.R. reforms.
Cytokinesis : Is the division of protoplast of a cell into two daughter cells after karyokinesis (nuclear division)
Animal Cytokinesis: Appearance of furrow in plasma membrane which deepens and joins in the centre, dividing cell cytoplasm into two.
Plant cytokinesis : Formation of new cell wall begins with the formation of a simple precursor-cell plate which represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacent cells.
When karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis, a multinucleated condition arises. This is called syncytium.
Significance of Mitosis :
- Growth-addition of cells.
- Maintenance of surface/volume ratio. Maintain Nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio.
- Maintenance of chromosomes number.
- Regeneration.
- Reproduction in unicellular organisms, lower plants and some insects.
- Repair and wound healing.
- Vegetative reproduction in plants takes place by mitosis.
Meiosis:
- Specialised kind of cell division that reduces the chromosomes number by half. hence it is called reductional division.
- Occurs during gametogenesis in plants and animals.
- Involves two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell division called Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
- It results in 4 haploid daughter cells.
- Interphase occurs prior to meiosis which is similar to interphase of mitosis except the S phase is prolonged.
Meiosis I
Prophase I: Subdivided into 5 phases.
(i) Leptotene :
Chromosomes make their appearance as single stranded structures.
Compaction of chromosomes continues.
(ii) Zygotene :
Homologous chromosomes start pairing and this process of association is called synapsis.
Chromosomal synapsis is accompanied by formation of Synaptonemal complex.
Complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes is called bivalent or tetrad.
(iii) Pachytene : Crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. The enzymes involved in the process is ‘recombinase’. Recombination between homologous chromosomes is completed. Exchange of genetic material.
(iv) Diplotene : Dissolution of synaptonemal complex occurs and the recombined chromosomes separate separate from each other except at the sites of crossing over. These X-shaped structures are called chaismata. In oocytes of some vertebrates diplotene can last for month or years.
(v) Diakinesis : Terminalisation of chaismata.
Chromosomes are fully condensed and meiotic spindles assembled.
Nucleolus disappear and nuclear envelope breaks down.
Metaphase : Bivalent chromosomes align on the equatorial plate.
Microtubules from opposite poles of the spindle attach to the pair of homologous chromosomes.
Anaphase I : Homologous chromosomes, separate while chromatids remain associated at their centromeres.
Telophase I :
Nuclear membrane and nucleus reappear.
Cytokinesis follows (diad of cells).
Interkinesis : Stage between two meiotic divisions, (meiosis I and meiosis II) generally short lived.
Meiosis II: (It resembles the normal mitosis).
Prophase II
Nuclear membrane disappears.
Chromosomes again become compact.
Metapahse II
Chromosomes align at the equator.
Microtubules from opposite poles of spindle get attached to kinetochores of sister chromatids.
Anaphase II
Simultaneous splitting of the centromere of each chromosome, allowing them to move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II
Two groups of chromosomes get enclosed by a nuclear envelope.
Cytokinesis follows resulting in the formation of tetrad of cells i.e., 4 haploid cells.
Significance of Meiosis
Formation of gametes : In sexually reproducing organisms.
Genetic variability : Variations are very important for evolution.
Maintenance of chromosomal number : By reducing the chromosome number in gametes. Chromosomal number is restored by fertilisation of gametes.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Biology
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 11. Our teachers always suggest that Class 11 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Biology.
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Biology exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes Set B from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 11 students get the best study material for Biology.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes Set B include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Biology principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes Set B provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 11 is covered.
These notes for Biology are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes Set B, Class 11 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes Set B, are available for immediate free download. Class 11 Biology study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

