Download the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes Set B in PDF format. These Class 11 Biology revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 11 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology
PointsTo Remember
Autotroph: An organism that sythesize its required nutrients from simple and inorganic substance; Example-plants, blue green algae (cyanobacteria)
Heterotroph : An organism that cannot synthesise its own nutrients and depend on others. Example-Bacteria, protists, members of animalia.
Biological nitrogen fixation: Conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds by living organisms.
Chlorosis: Yellowing ofleaves due to loss of chlorophyll.
Nitrification : Conversion of ammonia (NH3) into nitrite and then to nitrate.
Denitrification : A process of conversion of nitrate into nitrous oxide and nitrogen gas (N2).
Leg-hemoglobin : Pinkish pigment found in the root nodules of legumes.
It acts as oxygen scavenger and protects the nitrogenase enzyme from oxidation.
Flux : The movement of ions is called flux. Influx is inward movement of ions into the cells and efflux is the outward movement of ions.
Inhibition of cell division : Deficiency ofN, K, S. and Mo.
Necrosis : Death of tissues particularly leaf tissue due to deficiency of Ca, Mg, Cu, K.
Delayed Flowering: due to deficiency ofN, S, Mo.
Mineral Nutrition : Plants require mineral elements for their growth and development. The utilization of various absorbed ions by a plant for growth and development is called mineral nutrition of the plant.
Hydroponics : Soil-less culture of plants, where roots are immersed in nutrient solution (without soil) is called hydroponics. The result obtained from hydroponics may be used to determine deficiency symptoms of essential elements.
Active Transport : Absorption occuring at the expense of metabolic energy.
Passive Transport : Absorption of minerals with concentration gradient by the process of diffusion without the expense of metabolic energy.
Essential Elements

In addition to the 17 essential elements, Na, Si, Co and Si are required by some higher plants.
Criteria for essentiality:
The element must be necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction.
Requirement must be specific and not replaceable by another element.
The element must be directly involved in the metabolism of the plant.
Role of Minerals Elements in Plants
MACRO NUTRIENTS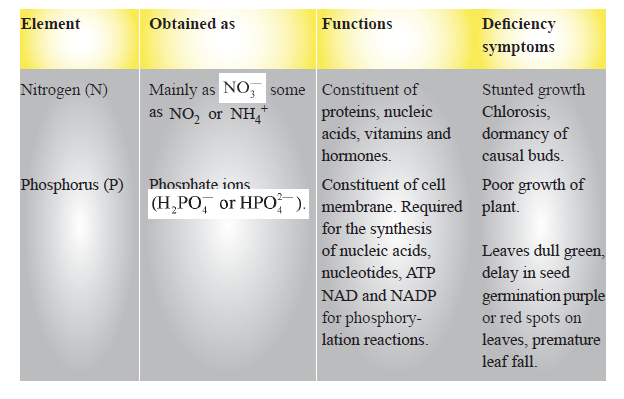
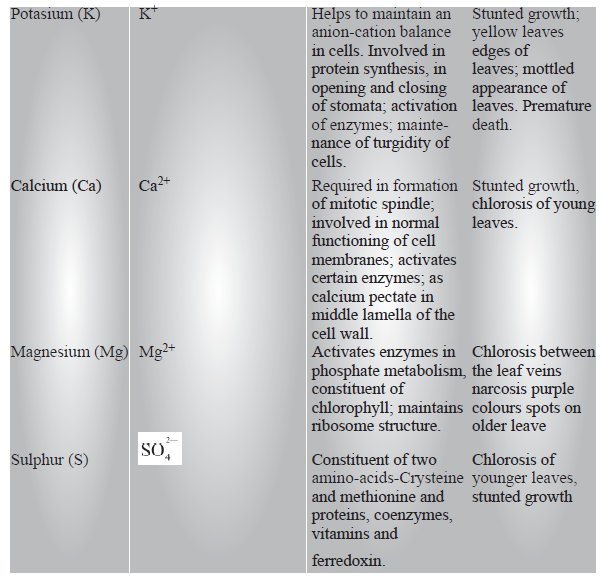
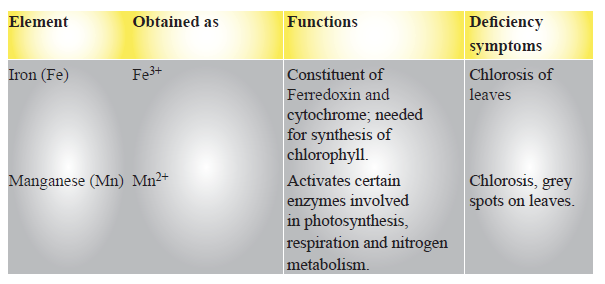
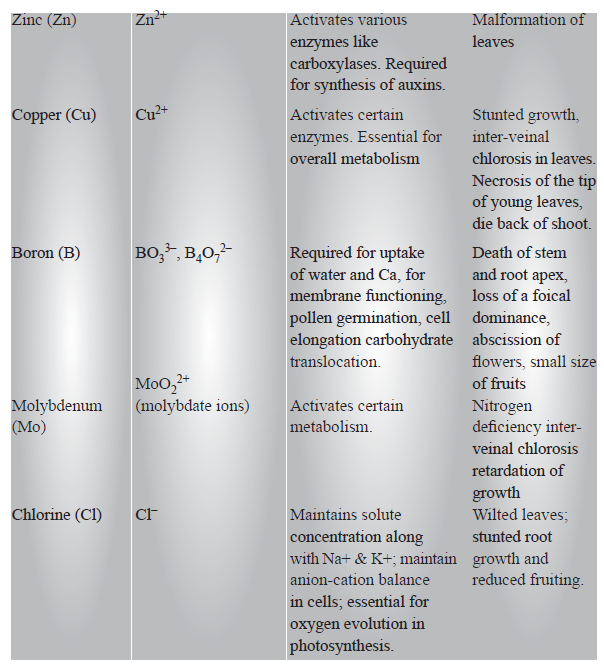
Critical Concentration : The concentration of the essential element below which plant growth is retarted. The element is said to be deficient when present below the critical concentration.
Deficiency symptoms : Chlorosis, stunted growth, premature fall of leaves and buds and inhibition of cell division.
Toxicity of micronutrient : Any mineral ion concentration in tissues that reduces the dry weight of tissues by 10% is considered toxic. Toxicity of one element may lead to deficiency of other element since the former may inhibit the uptake of latter., e.g., Mn competes with Fe, Mg for uptake and also inhibits Ca translocation to shoot apex. Therefore Mn toxicity symptoms are actually same as deficiency symptoms ofFe, Mg and Ca.
Role of microbes in nitrogen cycle :
Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Rhodospirillum; Fix atmospheric nitrogen
Nitrosomonas and/or Nitrococcus :-Conversion of ammonia to nitrite
Nitrobacter : Conversion of nitrite into nitrate.
Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus : reduce nitrate into nitrogen.
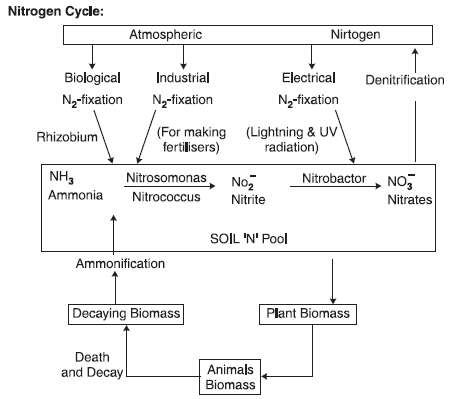
Nitrogen fixation-The process of conversiOn of Nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3).
Ammonification-The process of decomposition of organic nitrogen of plants and animals (proteins) into ammonia.
![]()
Nitrification-The ammonia so formed may volatilise and re-enter the atmosphere, or some of the ammonia may be converted first into nitrite and then into nitrate by soil bacteria

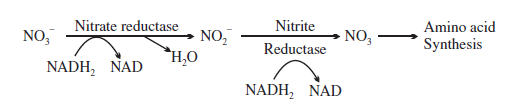
The Nitrate so formed can be easily absorbed by the plants and transported to leaves. In leaves, nitrate is reduced to ammonia to form amino-acids, because nitrate can not used by plants as such.
Denitrification-Process of reduction of the nitrate present in soil to nitrogen. It is carried out by bacteria like Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus.
Biological Nitrogen Fixation-Reduction of nitrogen to ammonia by living organisms. Certain prokaryotes are able to fix nitrogen because of presence of ‘nitrogenase’ enzyme in them.
Nitrogen fixing microbes may be
(a) Free living-(i) Aerobic-Azotobacter
(ii) Anaerobic-Rhodospirillum
(b) Cyanobacteria-Nostoc, Anabaena
(c) Symbiotic-(i) With leguminous plants-Rhizobium
(ii) With non-leguminous plants-Frankia
Enzyme nitrogenase-The enzyme nitrogenase is Mo-Fe protein and catalysis the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia (First stable product of nitrogen fixation)
Leg-hemoglobin-A pink colour pigment, similar to hemoglobin of vertebrates and functions as an oxygen scavenger and protects nitrogenase from oxygen.
![]()
Mineral Nutrition
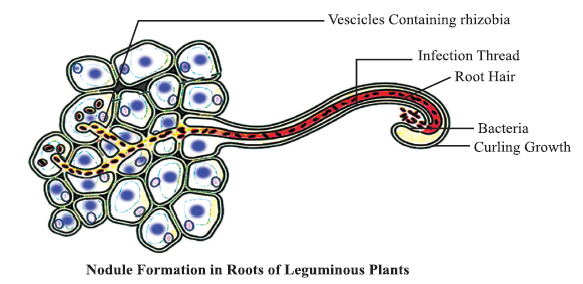
Steps of nodule formation :
(a) Rhizobium bacteria present in soil contact a susceptible root hair.
(b) Infection of the root hair cause it to curve and deformed due to chemical secretion.
(c) An infection thread is produced carrying the bacteria into the cortex of the root.
(d) The bacteria get modified into rod-shaped bacteria and cause inner cortical and pericycle cells to divide plant produce cytokinin and auxin to stimulate cell division and enlarge to form nodules.
(e) Division and growth of cortical and pericycle cells lead to nodule formation.
Mechanisms ofN2 fixation
It require 3 components-
(a) A strong reducing agent like FADH2, NADPH2
(b) Nitrogenase enzyme
(c) ATP (as energy service)
Steps
(a) Formation ofDiamide
(b) Formation ofHydrazine (N2H4)
(c) Formation of Ammonia
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Biology
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 11. Our teachers always suggest that Class 11 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Biology.
Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Biology exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes Set B from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 11 students get the best study material for Biology.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes Set B include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Biology principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes Set B provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 11 is covered.
These notes for Biology are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes Set B, Class 11 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes Set B, are available for immediate free download. Class 11 Biology study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

