Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money And Credit here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 10 Social Science. Our expert-created answers for Class 10 Social Science are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 3 Money And Credit NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
For Class 10 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 10 Social Science solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 3 Money And Credit solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money And Credit NCERT Solutions PDF
Money: Money is something that can act as a medium of exchange in transaction. In day to day transactions, goods are being bought & sold with the use of money.
Barter System: When goods are directly exhanged for goods and there is no use of money. It is called barter system.
Double Coincidence of wants: When in the exchange, both parties agree to sell and byu each other commodities. It is called double coincidence of wants.
- In the barter system double coincidence of wants is an essential feature.
Reserve bank of India : R.B.I is the central bank of India which controls the monetary policy of the country.
R.B.I supervises the activities of formal sector and keep the track of their activities.
Credit : The activity of borrowing and lending money between the parties.
Collateral : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, live stocks, deposits with baks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Property such as land titles, deposite with banks. livestock are some common examples of collateral used for borrouring.
SELF HELP GROUP (SHG) : It’s basic idea is to provide financial resources for the poor through organizing the rural poor especially women into small help groups.
Modern forms of Money:
Functions of reserve bank
• Issue the currency
• Monitor the work culture of banks and SHG
• Provide Direction Regarding terms and Interest
• Provide Feedback Regarding Monetary Policies of India
• Hold a part of the cash reserve of the banks
Credit: It refern to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower money, good and services in return for the promise of future repayment.
MCQs :
Question. Which one of the following is not a formal source of credit?
(a) Commercial Banks
(b) State Bank of India
(c) Employers
(d) Co-operatives
Answer. C
Question. All the banks act as mediator between and ……........... .
a. rural people, urban people
b. literates, illiterates
c. people, government
d. depositors, borrowers
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following is the appropriate meaning of collateral?
(a) It is the sum total of money borrowed from banks.
(b) The amount borrowed from friends.
(c) It is an asset of the borrower used as guarantee to a lender.
(d) The amount invested in a business.
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is not an advantage of self-help group?
(a) Grant of timely loans
(b) Reasonable interests
(c) A platform to discuss various issues
(d) Does not help women to become self-reliant.
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following is a major reason that prevents the poor from getting loans from the banks?
(a) Lack of capital
(b) Not affordable due to high rate of interest
(c) Absence of collateral security
(d) Absence of mediators
Answer. C
Question. Which one of the following is the important characteristic of modern form of currency?
(a) It is made from precious metal
(b) It is made from thing of everyday use
(c) It is authorised by the commercial banks
(d) It is authorised by the Government of the country
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following is not included in the terms of credit?
(a) Rate of Interest
(b) Mode of payment
(c) Rate of saving
(d) Collateral
Answer. C
Question. Banks use the major portion of the deposit to:
(a) Keep reserve so that people may withdraw
(b) Meet their routine expenses
(c) Extend loans
(d) Meet renovation of the bank
Answer. C
Question. At present which form of money is increasingly used apart from paper money?
(a) Commodity money
(b) Metallic money
(c) Plastic money
(d) All the above
Answer. C
Question. What is the main source of income of a bank?
(a) Bank charges that the depositors pay for; keeping their money safe is the main ; source of the bank’s income.
(b) The difference between what is charged from the borrowers and paid to the depositors is the main source of bank’s income.
(c) Banks earn huge amounts of money by investing the money of the depositors in various company shares.
(d) The Government of India gives huge amounts of money to the banks to help their smooth functioning.
Answer. B
Fill in the Blanks:
Question. Majority of the credit needs of the ................. house holds are met from informal sources.
Answer. Poor
Question. .................... costs of brrowing increases the debt-burden.
Answer. High
Question. ...................... issues currency notes on behalf of the central government.
Answer. R.B.I
Question. Bank charge a higher interst rate on loans than what they offer on......................
Answer. Deposits
Question. ..................... is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the leader.
Answer. Collateral
Mark True and False:
Question. The banks use the major part of deposit in printing currency.
Answer. False
Question. Double coincidence of wants occurs when goods or commodities are exchanged without the use of money.
Answer. True
Question. Banks charge a less interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Answer. False
Question. In India currency is issued by RBI.
Answer. True
Question. SHG is school help groups.
Answer. False
Question. SHG provides loan to its membern.
Answer. True
Question. RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaing loan balance.
Answer. True
Question.The main source of Banks income is by interest.
Answer. True
CASE STUDY Questions:
Question. Ramu is a potter making pots, wants to exchange pots for wheat.
Luckily, he meets a farmer who has wheat and is willing to exchange it for the pots. What is this situation known as?
i. Incidence of wants
ii. Double coincidence of wants
iii. Barter system of wants
iv. None of the above
Answer. B
Question. Sam is a merchant. He has some surplus money, he opens a bank account and deposits in it. Whenever he needs money, he can go to his bank and withdraw from there. This kind of deposit with the banks are known as:
(a) demand deposit
(b) term deposit
(c) fixed deposit
(d) surplus deposit
Answer. A
Question. Thomas and Selvan are small farmers. Thomas has taken credit @ 1.5% per month on < 20000 from a trader while Selvan has taken credit at 8% per annum from bank on the same amount. Who is better off?
(a) Thomas is better because he has to do no paperwork.
(b) Selvan is better because his interest payment is less.
(c) Thomas is better because he has not paid any collateral.
(d) Both Thomas and Selvan are equal so no one is better off.
Answer. B
Question. Nakul is a trader. He provides farm inputs on credit on the condition that farmers will sell their crop products to him at prices so that he could sell them at------------- prices in the market.
(a) high, medium
(b) low, high
(c) medium, high
(d) high, low
Answer. B
Source Based Questions
The reserve bank of india monitors the functions of formal sources of credit. The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining the required 15% of the cash balance. It ensures that the banks give loans not just to profit-making business and trader but also to small cultivatorn, small scale industries to small borrowers etc. banks have to submit information to the RBI on their credit activities like how much they are landing, to whom, at what interest rates, etc.
Question. Name the organization which monitors the functioning of formal sources of credit.
Answer. Reserve bank of india
Question. Who ensures that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders.
Answer. Reserve bank of india
Credit is one of the major aspects that determine a countrys development.There is a huge demand for loans for various activities cheap and affordable loans give people an opportunity to develop their business. Credit plays a very crucial role in agricultural activities people can barrow money and use it to adopt modern farming methods to increase the crop production and grow crops which are more reliable than the traditional methods. By sanctioning loan to developing industries and trade, banks provide them with the necessary aid for improvement.
Question. By sanctioning loans to developing industries and trades .............. provide them with necessary aid for improvement.
Answer. Banks
Question. What is credit?
Answer. Credit: The activity of borrowing and landing money between two parties.
Question. Define role of credit in the development.
Answer. Credit is one of the major aspects that determine a countrys development.
Source A Currency
Modern forms of money include currency-paper notes and coins. Unlike the things that were used as money earlier, modern currency is not made of precious metal such as gold, silver and copper. And unlike grain and cattle, they are neither of everyday use. The modern currency is without any use of its own. Then, why is it accepted as a medium of exchange? It is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorised by the government as it legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India. No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange in the country. In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the central government. As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in selling transactions in India. No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
Question. Who issues the currency notes in India? Which is our currency used nowadays?
(i) The State Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the district government. Nowadays paper notes and coins are used as currency in our country.
(ii) The Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the state government. Nowadays paper notes and coins are used as currency in our country.
(iii) The Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central government. Nowadays paper notes and coins are used as currency in our country.
(iv) The Rural Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central government. Nowadays only coins are used as currency in our country.
Answer. C
Question. What is accepted as the medium of exchange in India?
(i) Dollar is accepted as the medium of exchange in India.
(ii) Rupee is accepted as the medium of exchange in India.
(iii) Euro is accepted as the medium of exchange in India.
(iv) Dinar is accepted as the medium of exchange in India.
Answer. B
Question. Fill in the blanks:
The Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the ---------------------.
(i) Central government
(ii) District government
(iii) State government
(iv) Village government
Answer. A
Question. What does the Indian Law say about the currency?
(i) As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue bills. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
(ii) As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalise the use of dollar as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
(iii) As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
(iv) As per Indian law, no other individual, except for two organisations, is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
Answer. C
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What is meaning of Barter system ? Why is double coincidence of wants is an essential feature of a Barter system ?
Answer.
Meaning of Barter system: A system in which goods are directly exchanged without the use of money is called barter system. Double coincidence of wants means when both the parties – seller and purchaser – agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities. It implies that what a person desires to sell is exactly what the other wishes to buy. No money is used in such an arrangement. Therefore it is an essential feature of barter system.
Question. Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own ? Point out the reasons.
Answer.
Modern currency is accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own due to reasons as :
• In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the central government.
• As per Indian law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency.
• The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in India.
• No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
• (Any other relevant point).
• (Any two points)
Question. Why should credit at reasonable rates from the banks and cooperatives be available for all ?
Answer. Credit at reasonable interest rates should be available for all so that they may increase their income and help in the over all development of the country.
1. High interest rate do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
2. It is necessary that the banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in rural areas, so that the dependence of the people on informal sources of credit reduces.
3. In addition to this more credit should be given to the poor to get maximum benefit from the cheaper loans.
4. This will help in increasing their income as well as standard of living.
5. Any other relevant point
Question. Why is it necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas?
Answer.
(i) Banks and cooperative societies can help people in obtaining cheap and affordable loans. (ii) This will empower people in a variety of ways. They could grow corps, do business, set up small- scale industries etc. They could set up new industries or trade in goods.
(iii) Loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers. Thus, it is necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending particularly in the rural areas, so that the dependence on informal sources of credit reduces. Cheap and affordable credit is also important for the country’s development.
Question. How do banks play an important role in the economy of India?
Answer. (i) Banks provide people the facility to deposit their surplus money by opening a bank account in their name. Banks also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest. Thus, banks add to the income of the family. (ii) Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans to the needy. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks, thus, mediate between those who have surplus money and those who are in need of this money. (iii) Banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, to small borrowers, etc. Thus, they empower these people and help indirectly in the country’s development. (iv) The rate of interest that banks demand from the borrowers is always cheap and affordable. This helps people to improve their condition. Banks also give loans to industrialists. These industrialists use these loans to expand their industries. In this way, they contribute in country’s development. (v) By employing a large number of people banks solve the problem of unemployment to a great extent.
SHORT ANSWER questions
Question. Why do banks ask for collateral while giving credit to a borrower?
Answer.
Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, land documents, deposits with banks etc. This stands as a security against the money borrowed from the bank. In case the borrower fails to repay the loan to the bank, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral.
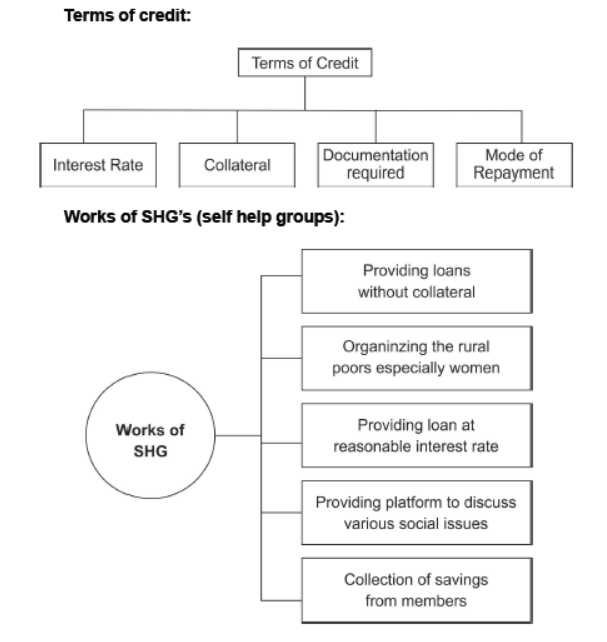
Question. What comprises ‘terms of credit’?
Answer. Rate of interest, collateral security, documentation requirements and mode of repayment together comprise terms of credit. This varies from bank to bank and borrower to borrower.
Question. “Supervision of the functioning of formal sources of loans is necessary”. Why?
Answer. Supervision of the functioning of formal sources of loans is necessary because banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom they are lending and at what interest rate etc.
Question. “There is a great need to expand formal sources of credit in rural India.” Examine the statement.
Answer. There is great need to expand formal sources of credit in rural India because: In the informal sector there is no organisation to supervises the credit activities of lenders. They lend at whatever interest rate they choose. No one can stop rural money-lenders from using unfair means to get their money back.
Question. Why are most of the poor households deprived from the formal sector of loans?
Answer. Most of the poor households are deprived from the formal sector loans because of lack of proper documents and absence of collateral.
Question. What do you understand by demand deposits?
Answer. Banks accept the surplus money from the people as deposits and pay interest for that. People have the provision to withdraw their money as and when they require. Since money can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are known as demand deposits. Its features are: Features:
• A demand deposit has the essential characteristic of money. It can be used as a medium of exchange.
• The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to make payments, without using cash.
• Since demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment along with currency, they constitute money in the modem economy.
Long Answer Questions
Question. How do SHG’s act to provide a platform for women to address their various social issues?
Answer.
SHGs act to provide a platform for women to address their various social issues in the following ways:
(1) A Self-Help Group is an organization of rural poor, particularly women who pool their savings.
(2) The SHG encourages its members for savings and enables them to take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. In this way, it addresses their economic issue that is the base of many social issues.
(3) SHGs are the building blocks of the organization of the rural poor. Not only does it help women to become financially self-reliant, but the regular meetings of the group also provide a platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
(4) The SHG provides self-employment opportunities to its members by providing them loans for meeting working capital needs, for housing materials, for acquiring assets like a sewing machine, handlooms, cattle, etc.
(5) The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the money-lenders charge
Question. Self-Help Groups enjoy a lot of freedom in their functioning. Explain.
Answer.
(1) In Self-Help Groups, there is no provision of a certain number of members or a certain amount to deposit. Members are free to their number and amount to deposit in the group.
(2) Most of the important decision regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members.
(3) The group decides as regards the loans to be granted—the purpose, amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule, etc.
(4) Also, it is the group which is responsible for the repayment of the loan. In any case of non-repayment of the loan by anyone, the member is followed up seriously by other members in the group.
(5) The SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral and documentation requirement. Besides, the regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
Question. Self-Help Groups can help in solving the problem of credit in rural areas. Explain. Or In what ways do Self-Help Groups help the rural sector of the economy?
Answer.
(1) The absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevent the poor from getting bank loans. Whereas, there is no need for collateral or difficult paperwork to take loans from SHGs.
(2) SHGs have a lower interest rate than that of moneylenders or traders. They can get timely loans for a variety of purposes.
(3) It creates employment opportunities for the members who are rural poor, particularly women.
(4) It encourages regular savings of the rural poor.
(5) SHGs help rural women not only to become financially self-reliant but also, the regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
Question. Describe the organization, working and importance of Self-Help Groups. Or What are the Self-Help Groups? How do they work? Explain. Or What is meant by Self Help Group? Explain its working.
Answer.
(1) SHGs are the groups created by the needy persons themselves, especially women to fulfil their credit and loan needs. A typical SHG has 15-20 members, who meet and save regularly.
(2) Saving of per member varies from 25 to Z 100 or more depending on the ability of the people to save.
(3) Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
(4) The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the money-lenders charge.
(5) If the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. The loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
Question. Why are informal sources of credit preferred in rural areas? Give five reasons.
Answer.
(1) There is no need for collateral such as land; building, vehicles, deposits with banks. The rural poor people are unable to provide collateral.
(2) Also, there is no need for complicated paperwork which the rural poor are not capable of providing.
(3) These moneylenders, traders and rich landlords continue to extend loans to defaulters even if the previous loan is unpaid.
(4) They are hesitant and unsure about the functioning of the banks.
(5) They may not have access to banks in their villages.
(6) The procedure for giving credit is often very simple.
Question. Why are credit arrangements not fair for all sections of society? Give three reasons. Suggest two remedies for the problem. Or Why is the share of formal sector credit higher for the richer households compared to the poorer households ? Give any three reasons responsible for this.
Answer.
(1) Undoubtedly, credit arrangements are not very fair for all sections of society The share of formal sector credit is higher for the richer households as compared to the poorer households. This has the following reasons:
(i) Poverty affects poor households’ capacity to borrow. Formal sector credit requires proper documents and collateral as security against loans. Collateral is an asset. So, poor people lack in providing such things which affect their capacity to borrow.
(ii) The poor people do not repay
(iii) The people in villages may not have access to banks in their village. Also, they are R. loan on time because of the various day-to-day needs. - hesitant and unsure about the functioning of the banks.
(2) (i) More credit facilities should be made available in rural areas by opening more banks there.
(ii) The procedure of giving loans should be made easier and simpler.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics for Chapter 3 Money And Credit
Question. In situation of high risk, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
Answer.
In situation of high risk, the problem of collateral and debt trap arises for the borrower. Collateral is the guarantee given by the borrower to the bank, against the amount of loan provided by the bank. If the borrower is not able to repay the credit taken, bank can sell the collateral to obtain payment. This makes the situation worse for the borrower as compared to situation before taking the credit.
For Example: A trader (borrower) takes a loan from bank to buy a raw material for his plant. He keeps a machine in plant as collateral. In a high risk situation; if he defaults, then this would lead the bank to confiscate his machine. In this situation trader would be worse off than before taking credit; as in future he wouldn’t have a machine to produce. In case he again takes up credit and if not able to repay again, he might end up in a situation of debt trap.
Question. How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with an example of your own.
Answer.
Suppose there is a baker and a shoe seller in the town. Shoe seller wants to have a loaf of bread from the baker’s shop. In barter system, shoe seller has to wait until the time baker agrees to exchange loafs of bread for shoes. As the shoe seller has to wait for the baker to agree for the exchange, this gives a rise to problem of double coincidence of wants. If they use money as the medium of exchange they can solve the problem of double coincidence of wants; Shoe seller can have a loaf of bread anytime he desires, he doesn’t need to wait for the baker to agree for the exchange.
Question. How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Answer:
Banks act as intermediaries between those who have surplus money and who need money. Banks accept money in form of deposits from people who have surplus and provide interest on deposit. Simultaneously, they provide loan to those who need money and charge interest from them. Interest rate charged on loan is higher than the interest provided on deposits.
Question. Look at a 10 rupee note. What is written on top? Can you explain this statement?
Answer:
On a 10 rupee note, “Reserve Bank of India” and “Guaranteed by Central Government” are written on the top. This means that RBI has issued these notes on behalf of the Indian Government. And law legalizes the use of this note as a medium of payment which cannot be denied by any one in settlement of a transaction within India.
Question. Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
Answer:
There is a need to expand the formal sources of credit in India, to curb exploitation & harassment done by the informal sector.
• Informal sector charges higher interests on loans then the formal sector.
• Large part of earnings is used for repayment of loan.
• There is no supervision on informal lending.
• High rate of interests discourages small enterprises to take credit.
• Sometimes this leads to debt trap, when income of the borrower is lower than the amount to be repaid.
Question. What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
Answer:
Self Help Groups (SHGs) for poor are organised to overcome the hurdle of exploitative money lenders, lack of collateral and to avail cheap credit timely in rural areas. SHGs are a group of 15-20 members, (especially women) belonging to a particular area. They pool up their savings depending upon the ability to save of each member. Members can avail a timely loan from the group itself to meet their requirements at a reasonable or lower interest than what the money lenders offer. SHGs are building block of the rural economy as from these groups; members can avail loan very easily without any collateral. If the group is regular in their activities for more than a year, they are eligible to avail small loan from bank for creating self employment activities. All the important decisions regarding the saving and lending activities are taken by members of the group. In case a member is not able to repay, it is very seriously followed by other members. SHGs also help rural poor by providing them a platform to discuss the social issues such as health, nutrition, etc.
Question. What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers?
Answer:
The banks might not be willing to lend certain borrowers, due to:
• Lack of collateral
Borrower might have no collateral, against which he can avail a loan from the bank. Banks are not willing to grant any loan to a borrower who has no collateral, as they’ll run into debt if borrower is not able to repay the loan.
• Bad credit history
Borrower might have a bad credit history, i.e. he might have not been able to repay his earlier loans.
• Risky interest of the borrower
Borrower might be interested in investing in high risk project.
Question. In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of banks? Why is this necessary?
Answer:
-Reserve bank being the central bank decides the guidelines for functioning of all the banks.
-Banks need to have minimal cash reserve balances which are monitored & decided by RBI.
-RBI makes sure that credit is equally rationed between big businesses and farmers, small scale industries, small scale borrowers, etc.
-Banks needs to submit information to RBI; periodically, regarding whom they are lending, how much and at what interest rate, etc.
-It is necessary to have a central bank supervise functioning of banks so as to keep:
• Uniformity in the banking system.
• Ensure equality & quality in system of providing credit to everyone, irrespective of being a small or big borrower.
• Setting a reasonable & uniform rate of interest on borrowings.
• Avoid malpractices in the financial system.
Question. Analyse the role of credit for development.
Answer:
Credit plays a very important factor in the development of a country. Credit helps in expanding the scope of economic activities in an economy. Credit is required for all the different purposes. Credit helps in expanding the production process of the economy, if the credit is provided to the farmers, small scale enterprises, profit making businesses, etc. If the credit is provided for consumption purposes like home loan, car loan, etc. It leads to increase in the demand in the economy. On a broader scale, credit is expanding the scope of economic activities in all the sectors.
Question. Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender? Discuss.
Answer:
Manav has to compare the terms of credit of both lenders (Bank & Moneylender). He needs to compare the
• Interest rate charged by both them
• Collateral required
• Documentation requirement
• Mode of repayment for both
To borrow from banks Manav must have proper documentation and collateral, or else he won’t be eligible for loan.
Question. In India, about 80% of farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a) Why might banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b) What are the other sources from which small farmers can borrow?
(c) Explain with an example how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer.
(d) Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
Answer:
-Banks are unwilling to lend to small farmers because most of the small farmers do not have proper documentation and collateral to provide which are necessary requirement to avail a loan from banks.
-Small farmers can borrow from local money lenders, cooperative societies and SHGs.
-Suppose Perumal is a small farmer; he takes up a loan to meet the expenses of cultivation. Though he used expensive and high quality pesticide sprays on the crops, his field got infected by pest and crop failed. To pay the loan he had to sell a major part of his land. As we can see he is worse off than earlier. Now, he has a small piece of land to work upon and has to take new loan to meet expenses or he has to work as a landless labourer.
-Small farmer can avail cheap loans from cooperative societies, agricultural banks or they can also form Self Help Groups
Question. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Majority of the credit needs of the households are met from informal sources.
(ii) debt-burden. costs of borrowing increase the
(iii) issues currency noted on the behalf of the central government.
(iv) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on .
(v) is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender.
Answer:
(i) Majority of the credit needs of the _rural households are met from informal sources.
(ii) High burden. costs of borrowing increase the debt-
(iii) Reservebank of India_ issues currency noted on the behalf of the central government.
(iv) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on _deposits_.
(v) Collateral_ is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender.
Question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) In a SHG most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by (a) Bank.
(b) Members.
(c) Non-government organization.
(ii) Formal sources of credit does not include
(a) Banks.
(b) Cooperatives.
(c) Employers.
Answers:
(i) Correct choice: Members
Explanation: SHGs comprises of 15-20 members, (especially women) belonging to a particular area and all the decisions regarding the savings & loan activities are taken by group members on collective basis.
(ii) Correct choice: Employers
Explanation: Formal sources of credit include banks and cooperatives only, while informal sources of credit include moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends,etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Objective Questions
Question. Raghav has surplus money so he open a bank account and deposits in it. Whenever, he needs money, he can go to his bank and withdraw from there. This kind of deposit' with the banks is known as
(a) Fixed Deposit
(b) Term Deposit
(c) Demand Deposit
(d) Surplus Deposit
Answer: C
Question. Which among the following option will be the cheapest source of credit in rural areas?
(a) Bank
(b) Cooperative Society
(c) Moneylender
(d) Finance Company
Answer: B
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair from the given options.
(a) Formal Sector — Provides loans at lower rate of interest
(b) Informal Sector — Includes bank and cooperatives
(c) RBI — Didn’t monitor the banks
(d) Moneylenders — Provides loans to industry owners
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is not included in the terms of credit in a bank loan?
(a) The rate of interest
(b) The lender’s land
(c) The borrower’s land
(d) The time period of the loan
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following are not modern forms of money?
(a) Currency notes
(b) Deposits with banks
(c) Coins
(d) None of these
Answer: D
Question. Which among the following is not a feature of informal sources of credit?
(a) It is supervised by the Reserve Bank of India
(b) Rate of interest is not fixed
(c) Terms of credit are very flexible
(d) Traders, employers, friends, etc provides informal credit source.
Answer: A
Question. Ram and Shyam are small-farmers who have taken loans of ₹ 20,000 from different parties. Ram has taken credit at 1.5% per month interest from a trader while Shyam has taken credit at 8% per annum from a cooperative. Analyse the loan information given above, consider the correct option from the following.
(a) Shyam is better because he receives more interest.
(b) Ram is better as he does no paper work.
(c) Shyam is worse off as he pays more interest.
(d) Ram is worse off as he pays more interest.
Answer: D
Question. Sunil works in a private company, Anil works as a daily wage earner. Both want a credit of ₹ 30,000.
The Bank is more likely to give credit to whom?
(a) Anil as he is more needy.
(b) Sunil as he has regular employment.
(c) Neither Sunil nor Anil will be provided credit from bank.
(d) Both Anil and Sunil will be provided credit from bank.
Answer: B
Question. Match the following:
| List I (Terms) | List II (Description) |
| A. Double Coincidence of Wants |
1. An individual or organisation taking funds on credit. |
| B. Cheque | 2. Proportion of amount charged on the principal amount taken by the borrower. |
| C. Rate of Interest | 3. A paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from one account to another account. |
| D. Borrower | 4. A situation where the supplier of goods A wants goods B and the supplier of goods B wants goods A. |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 3 4 1
(b) 4 3 2 1
(c) 3 4 1 2
(d) 1 2 4 3
Answer: B
Question. Modern currency is not made up of any precious metals and does not have any use of its own. Still, it is accepted as money because
(a) it is made up of some metal or paper.
(b) it is authorised by the government of the country.
(c) it can be issued by any legal authority.
(d) All of the above
Answer: B
Question. Which one of the following options describes ‘Collateral’?
(a) Double coincidence of wants
(b) Certain products for barter
(c) Trade in barter
(d) Asset as guarantee for loan
Answer: D
Question. In which of the following situations debt trap occurs? Identify from the given options.
(a) Inability of the poor to repay back the loans at higher rate of interest to money lenders.
(b) In case of crop failure, when the farmer get no return for the capital invested in buying agricultural inputs.
(c) Farmer has to sell a part of his land to repay his loan and has no resources to generate income in the next year.
(d) All of the above
Answer: D
Question. Sunita owns a small flower shop near a temple. She wants to expand her shop by keeping exotic flowers and flower bouquets.
To whom she should approach for a very short term credit?
(a) Moneylenders as they provide short term credit.
(b) Banks as they charge low interest.
(c) Cooperatives as they do not require collateral.
(d) Any of the above
Answer: C
Question. Why money is called a ‘medium of exchange’ ?
Choose the best suitable option:
(a) Because money act as an intermediate in the process of exchange.
(b) Because money adds to the value of a commodity.
(c) Because money is portable.
(d) Because money is used fo several transactions.
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is not a formal source of credit from the given options?
(a) Banks
(b) Cooperative
(c) Employer
(d) All of these
Answer: C
Question. Read the given information carefully and select the most appropriate answer from the given options.
A shoemanufacturer,M.Salimhas to make a payment to the leather supplier and writes a cheque for a specific amount. This means that the shoe manufacturer instructs the bank to pay this amount to the leather supplier. The leather supplier takes this cheque and deposits it in his own bank account in the bank. The money is transferred from one bank to another account in a couple of days. The transaction is complete without any payment of cash. After the transaction between Salim and Prem .......... .
(a) Salim’s balance in his bank, account increases and Prem’s balance also increases
(b) Salim’s balance in his bank account decreases and Prem’s balance increases
(c) Salim’s balance in his bank account increases and Prem’s balance decreases
(d) Salim’s balance in his bank account decreases and Prem’s balance also decreases
Answer: B
Question. Identify the system where goods were exchanged without using money from the given options.
(a) Goods system
(b) Exchange system
(c) Barter system
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: C
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Assertion-Reason MCQs
Directions Each of these questions contains two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) Credit would be useful or notdepends on the risk involved in a situation.
Reason (R) The chance of benefitting from credit is highest in agricultural sector.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion (A) Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and use this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Reason (R) Collateral is given as the lender can sell the collateral to recover the loan amount if the borrower fails to repay the loan.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
Reason (R) Banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion (A) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Reason (R) The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Modern currency is used as a medium of exchange, however, it does not have a use of its own.
Reason (R) Modern currency is easy to carry.
Answer: B
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Case Based MCQs
Read the case given and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option.
In recent years, people have tried out some newer ways of providing loans to the poor. The idea is to organise rural poor, in particular women, into small Self Help Groups (SHGs) and pool (collect) their savings. A typical SHG has 15-20 members, usually belonging to one neighbourhood, who meet and save regularly.
Saving per member varies from ₹ 25 to ₹ 100 or more depending on the ability of the people to save. Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the moneylender charges. After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank.
Loan is sanctioned in the name; of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members. For instance, small loans are provided to the members for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs (e.g. buying seeds, fertilisers, raw materials like bamboo and cloth), for housing materials, for acquiring assets like sewing machine, handlooms, cattle, etc.
Question. Which of the following aspect is correct regarding the Self Help Groups? Identify the correct option.
(a) They have mainly encouraged rural women to obtain credit.
(b) They have helped women to become self-reliant.
(c) They have helped women to discuss on relevant issues like health.
(d) All of the above
Answer: D
Question. Assertion (A) Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs through Self-Help Groups.
Reason (R) SHGs are the building blocks of organisation of the rural poor.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false (d) A is false, but R is true
Answer: B
Question. Which is one of the major reasons that prevent the poor from getting bank loans? Choose the best suitable option:
(a) Absence of collateral
(b) Lack of availability of banks in rural areas
(c) Lack of approach towards formal organisations.
(d) All of the above
Answer: A
Question. Why Self Help Groups (SHG) are growing in popularity? With reference to the above context, infer the appropriate option.
(a) As they provide loans at a nominal rate of interest.
(b) They create self-employment opportunities for its members.
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) As members of SHG's require collateral to get loans.
Answer: C
Question. Fill in the blanks from the given options:
In Self Help Groups, ........ decide the savings and loan activity option.
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) Members
(c) Co-operatives
(d) Rural Banks
Answer: B
Question. 85% of the loans taken by the poor households in the rural areas are from which of the following sources?
Identify the source from the given options.
(a) Cooperatives
(b) Government Bank
(c) Informal Sources
(d) Local bank
Answer: C
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain any three reasons for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas.
Answer: Banks and cooperatives are needed to increase their lending facilities in rural areas because
(i) People in rural areas take credit from moneylenders and traders who charge very high rate of interest.
These people must be aware about the role of banks and cooperatives so that they can be provided by cheap credit facilities.
(ii) Rural people are exploited by using unfair means thus, leading them to debt traps. To reduce the dependence of informal sector in rural areas, there is need for setting up of more banks.
• (iii)Formal sources of credit provide cheap and affordable credit in rural areas without any undue exploitation. These formal sources will serve as a building block for rural households. This will help the people to start up their small business or trade in certain goods.
Question. How do demand deposits have the essential features of money? Explain.
Answer: Demand deposits have the essential features of money in the following ways
• Demand deposits can be withdrawn from the bank whenever it is required.
• Demand deposits are widely accepted as a means of payment, along with the currency, thus they are considered as money.
• Demand deposits are also accepted widely as means of payment by way of a cheque instead of cash.
Question. Examine any three situations in which credit pushes the borrower into a debt-trap.
Answer: Three situations in which credit pushes the borrower into a debt-trap are
(i) When a borrower sells the agricultural produce to repay a loan but it may not be enough. Then more credit is taken to repay the entire amount which pushes the borrower into debt-trap.
(ii) When borrowers depend on informal sources of credit who charge a high rate of interest. This increases the repayment amount and new loans have to be taken to repay the earlier ones.
(iii) In high risk situations, for example, farmers taking credit before sowing of crops. If harvest fails then fresh loans are taken to repay the existing loans leading to debt-trap.
Question. Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending? Explain.
Answer: The lenders ask for collateral before lending because it is an asset that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to the lender, until the loan is repaid. A collateral is an asset such as land, building, livestock, vehicle or deposits with banks that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to the lender until the loan is repaid.
Collateral with the lender acts as a proof that the borrower will return the money. By keeping a collateral with the lender the borrower is bound to be regular in paying the interest because the borrower does not want to lose the collateral. In case of default i.e. borrower is unable to pay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the collateral or use it.
Question. Examine any three situations in which credit helps in the development of agriculturists.
Answer: Three situations in which credit helps in the development of agriculturists are
(i) Farmers can buy farm machinery and equipments along with fertilisers for better crop production by taking cheap loans.
(ii) Farmers can buy other agricultural inputs like hybrid seeds, raw materials or undertake irrigational activities in their farms to get better crop yields.
(iii) Farmers can buy farm animals and other livestock to raise their secondary income with the help of credit facilities.
Question. The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer: The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged because
• It is seen that around 85% of the loans taken by the poor households in the urban areas are from informal sources. There is no monitoring system that supervises the credit activities of the lenders in the informal sector.
• High cost of borrowing leads to a major share of earnings going into payment of interest on the loan so formal source of credit is needed.
• Sometimes the higher interest rate leads to the requirement to pay more than the earnings, thus falling into a debt trap. To eliminate this, formal sources are needed.
• Borrowers falling into debt-traps discourage more people from borrowing, which ultimately reduces development of the country.
Question. Explain the role of credit for economic development.
Answer: The role of credit for economic development is
• A country’s growth and economic development is greatly dependent on cheap and affordable credit system. Different kinds of economic activities need credit like to set up business for investment purpose, and also buying new house, cars and so on.
• Mostly manufacturing units need a huge amount of money to buy raw materials for their production process. Thus, credit here helps to make such manufacturing works easy.
• Cheap, affordable and fast credit system helps farmers to buy new and advanced technology for agricultural practices, e.g. tractors, threshers, fertilisers, new and advanced seeds (HYVs) and so on.
Question. Explain the three important terms of credit.
Answer: Terms of credit is a set of conditions under which a loan is given. Three important terms of credit are
(i) Collateral A borrower has to offer a collateral to the lender. It is a security to use as a guarantee till the loan is paid such as land title, bank deposits, livestock, house, factory etc.
(ii) Rate of Interest It is the proportion of amount at which the lender lends money to the borrower. The rate at which loan is given is decided by the RBI.
(iii) Time Period It is duration of the loan till which the amount will be repayed along with interest.
Question. ‘‘Credit can play a negative role.’’ Justify the statement with arguments.
Answer: Credit can play a negative role in the following ways
• In situations where credit is taken to repay the earlier loans then it will increase the burden of repayment.
• In high risk situations when the future is uncertain, there credit plays a negative role. For example, farmers taking credit before sowing but their harvest may not be good and they may not be able to repay their loans.
• Rural borrowers normally depend on informal sources of credit who charge a high rate of interest. This repayment of larger amounts may sometimes be larger then their income. In that case, credit plays a negative role.
Question. How is money used as a medium of exchange? Explain with examples.
Answer: Money is used as a medium of exchange in the following ways
• In day-to-day transactions, goods are being bought and sold with the use of money.
• The transactions are made in money as a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or services.
• Use of money has made it easier to exchange services such as the service of a doctor, teacher etc.
Question. Why is cheap and affordable credit important for the country’s development ? Explain any three reasons.
Answer: Cheap and affordable credit is important for the country’s development because
(i) More lending would lead to higher income and encourage people to invest in agriculture, engage in business and set up small scale industries.
(ii) Cheap credit will allow weaker sections of society to get rid of the exploitation at the hands of money lenders and come out of debt trap.
(iii) Affordable credit would lead to sustainable economic activity that would allow borrowers to invest in better technology to make their business more competitive.
Question. Compare and contrast the role of formal and informal source of credit.
Answer: The comparison between the role of formal and informal source of credit is
| Formal sector | Informal sector |
| It consists of banks and cooperatives, which are supervised by the Reserve Bank of India. |
It consists of moneylenders, traders, employers, landowners etc. which are not supervised by any organisation. |
| They give loans on low interest rates. |
They usually give loans at a high interest rate, which means that the cost of the loan is very high to the borrower. |
| Usually the loans require extensive documentation and some property to be kept as collateral or security against any default in payment. |
Usually the informal sources do not require extensive documentation for giving the loan. |
Question. Explain the features of Self Help Groups.
Answer: The features of the Self Help Groups (SHGs) are
• SHGs typically consist of 15-20 members and each member is required to save and pool (collect) in their resources.
• The SHGs are constituted to provide loans to its members at a reasonable rate.
• After a year or two and with regular savings, the group is eligible to take loans from banks.
• SHGs seek loans from banks for its member collectively and meet the needs of buying assets, machinery, raw materials, construction or repair.
• SHGs also meet regularly to discuss and act on various social issues like dowry, domestic violence, child marriage, health, nutrition, etc.
Question. Why are service conditions of formal sector loans better than informal sector ? Explain.
Answer: Service conditions provided by formal sector loans are better than informal sector loans because
• Formal sources of credit provide cheap and affordable credit without any undue exploitation.
• People in rural areas take credit from moneylenders and traders (informal sector) who charge very high rate of interest.
• Informal sector exploit the borrowers leading to debt traps.
• Formal sector is mainly supervised by the Reserve Bank of India. So, every clause is in writing and clear to comprehend. Whereas, no external organisation supervises informal sector. So, there is no such written clause.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Long Answer type Questions
Question. Which government body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India? Explain its functioning.
Or Describe the functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
Or Describe the significiance of the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India.
Functions or significance of Reserve Bank of India are
• The RBI monitors that the banks actually maintain the cash balance and do not give all the deposits as loans.
• The RBI ensures that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and rich traders, but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, small borrowers, etc.
• Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, etc.
• The rate of interest charged on loans given by the banks is decided by the Reserve bank.
• In this way, the RBI keeps a check on all the activities of banks and checks the flow of credit also.
Question. How can the formal sector loans be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers? Suggest any five measures.
Answer: The measures to make formal sector loan beneficial for poor farmers and workers are
(i) The formal sector like banks and cooperatives should lend more to poor people and workers, particularly in rural areas.
(ii) The formal sector should provide cheap and affordable credit to the poor people so that repayment is easy.
(iii) Formal sector should work out other ways of arranging collateral from the poor people.
(iv) By providing linkage between Self Help Groups and banks, formal sector of credit can be increased.
(v) There should be more number of cooperatives and banks in rural areas and people should be made aware of their presence.
Question. ‘‘Bank plays an important role in the economic development of the country.’’ Support the statement with examples.
Answer: Bank plays an important role in the economic development of the country in the following ways
(i) Bank Accepts the Deposits Bank accepts the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest.
People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank account can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
(ii) Bank Provides Loans Bank keep only a small portion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
Banks use the major portion of the deposits to give loans. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
(iii) Bank Provides Credit A large number of transactions in our day-to-day activities involve credits in some form or the other. Many industries are provided credit by the Banks which further helps in the economic development of the country. This generates more employment and raises income the people.
Question. Name two formal and two informal sources of credit in India. State advantages of formal and informal sources of credit.
Answer: Two formal sources of credit are bank and cooperatives and two informal sources of credit are moneylenders and traders. The advantages of formal sources of credit are
• It provides loans at a fixed rate and terms.
• It gives loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries and small borrowers etc.
• Cost of borrowing is less and hence promote borrowing and more economic growth.
• There is no exploitation as in the case with the informal sectors.
The advantages of informal sources of credit are
• There is no external control over the lending practices.
• It is suitable for poor households as they didn’t have to follow a certain kind of procedure which is required in formal sources of credit.
Question. Mohan works at a construction site in a sub-urban area while Sudhir is a marketing manager in a company. Both want credit to buy a home. Create a list of arguments explaining who has more possibility of getting a home loan from formal sector.
Answer: Sudhir has more possibility of getting a home loan from the formal sector due to the following arguments
• Formal sector consists of banks and cooperatives. Banks require proper documentation and collateral. In the above case, Sudhir will be able to provide the necessary
documents like salary slip, employment record and other documents that are needed by the banks.
• Banks also require collateral security which can be provided by Sudhir since his economic condition is better. Even if he is not able to provide collateral security then bank can retain the ownership papers of the house as collateral security.
• Since Sudhir has a regular source of income, he is in a better position to repay the loan amount in future. But Mohan will not be able to provide proper documents or collateral security so he has to depend on informal sector for credit needs.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money and Credit Case Based Questions
1. Read the following case and answer the questions that follow
Source A Informal Credit
Compared to the formal lenders, most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans Thus, the cost to the borrower of informal loans is much higher. Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
Question. In the above lines, which function of the bank is highlighted?
Answer: The function of giving loans is highlighted here. Banks after keeping 15% of their deposits as cash, extend the rest of the deposits to people as loans.
Question. To what extent, do you agree that credit from informal sector is not good for borrowers?
Answer: Yes, credit from informal sector is not good for the borrowers as the rate of interest charged by the informal lenders is so high that a larger part of income of the borrowers goes to interest payment which results in debt-trap or more poverty.
Source B Currency Unlike the things that were used as money earlier, modern currency is not made of precious metal such as gold, silver and copper. And unlike grain and cattle, they are neither of everyday use.
The modern currency is without any use of its own.
Question. Why modern currency is not like the earlier forms of currency like grain or cattle?
Answer: Modern form of currency is unlike earlier forms of currency as Grain and cattle even when they were not used as currency had value of its own. On the other hand, modern currency if not authorised by Reserve Bank of India, becomes an ordinary piece of paper as it has no value of its own.
Source C Loan Activities of Bank
There is an interesting mechanism at work here.
Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. For example, banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash.
2. Read the case given below and answer the questions that follow.
In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government. As per Indian Law, no other individual or organisation is allowed to issue currency. Moreover, the law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in setting transactions in India.
No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
The other form in which people hold money is as deposits with banks. At a point of time, people need only some currency for their day-to-day needs. For instance, workers who receive their salaries at the end of each month have extra cash at the beginning of the month.
What do people do with this extra cash? They deposit it with the banks by opening a bank account in their name. Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an amount as interest. People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question. Mention two uses of opening a bank account by the people.
Answer: Two uses of opening a bank account are
(a) To deposit surplus cash into the bank account.
(b) To earn interest given by the banks on deposits.
Question. How demand deposits are useful for the banks as well as for the people?
Answer: Demand deposits are useful for the banks as well as for the people in the following ways
• For the banks, demand deposits provide an opportunity to extend them as loans.
• For the people, demand deposits are like near money that can be easily withdrawn from the bank.
Question. Why is there a need to legalise rupee as a medium of exchange? What monentary system does India follows?
Answer: There is a need to legalise rupee as a medium of exchange so that all payments can be made and no one can refuse rupee in settling of transactions.
India has adopted a representative paper currency or we can say that managed currency standard.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Social Science
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Money And Credit
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 Money And Credit prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 10 Social Science textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 3 Money And Credit
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 10 Social Science chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 10 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Social Science Class 10 Solved Papers
Using our Social Science solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 10 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 3 Money And Credit to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 10 Social Science are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Social Science concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 10 Social Science. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

