NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Social Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Social Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions
Students of Class 10 studying Social Science are advised to carefully go through the NCERT questions and their detailed answers provided here for the chapter Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries. The questions in the NCERT textbook for Class 10 Social Science form an important part of school exams. These solutions for Class 10 follow a step-by-step approach and are highly beneficial for exam preparation. Scroll down to view detailed, chapter-wise solutions for Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries and explore more NCERT solutions and free study materials for Social Science and other subjects of Class 10.
Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography for chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Questions and Answers
Objective Questions
Question. Wastes from nuclear power plants, nuclear and weapon production facilities cause…………?
(a) Cancers, birth defects
(b) Skin diseases
(c) Viral diseases
(d) Bacterial diseases
Answer. A
Question. Study the given picture and answer the question that follow-

Identify the product produced in this factory.
(a) Cables
(b) Sewing Machines
(c) Cement
(d) Computers
Answer. A
Question. India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world yet, it is not able to perform to our full potential, why?
(a) High costs and limited availability of coking coal
(b) Lower productivity of labour
(c) Irregular supply of energy
(d) All of the above
Answer. D
Question. Name one function that occurs in the Blast Furnace in the steel manufacture process?
(a) Molten materials are poured into moulds
(b) Iron ore is melted
(c) Pressing and casting
(d) Pig iron is purified
Answer. B
Question. Observe the given image and answer the question that follows
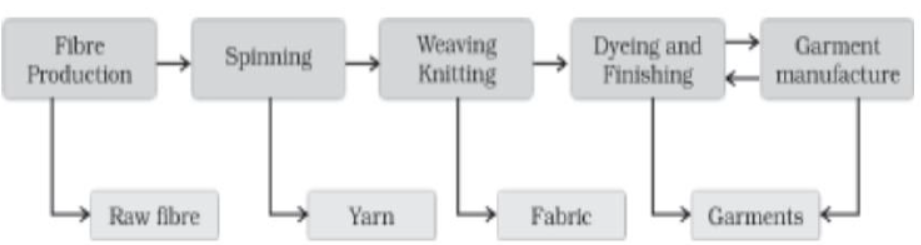
What is derived from spinning?
(a) Raw fibre
(b) Fabric
(c) Yarn
(d) Garments
Answer. C
Question. Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow
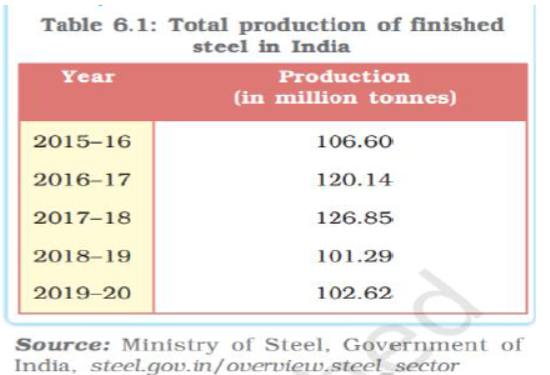
By how much did steel production decrease in 2019-20 as compared to the production in 2015-16?
(a) 3.02 million tonnes
(b) 3.56 million tonnes.
(c) 3.12 million tonnes
(d) 3.98 million tonnes
Answer. D
Question. Study the Picture and answer the question that follows-

Where is this Sewage Treatment Plant under Yamuna Action Plan situated?
(a) Faridabad
(b) Firozabad
(c) Ahmedabad
(d) Nasirabad
Answer. A
Question. Suppose you are working in a Steel Industry, what will be the proportion of Iron Ore, coking coal and limestone you would use to produce steel?
(a) 2: 1: 4
(b) 4: 1: 2
(c) 4: 2: 1
(d) 2: 4: 1
Answer. C
ASSERTION AND REASON
Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option.
Options
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Question. Assertion (A): Textile industry occupies a unique position in Indian economy.
Reason (R): It contributes significantly to industrial production employment generation directly
Answer. A
Question. Assertion (A): Air pollution is caused by the high proportion of presence of undesirable gases
Reason (R): Air pollution does not affect our health, and atmosphere as a whole.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion (A): There is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states, especially in Maharashtra.
Reason (R): Raw material is cheaper there.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion (A): Internal demand for jute has been on the increase.
Reason (R): This is because of the government policy of mandatory use of plastic packaging. It replaces the secondary and tertiary sector activities.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion (A): Rain water harvesting increases industrial pollution.
Reason (R): Rain water helps industry to meet water requirements.
Answer. A
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced?
Answer.
(1) To minimise use of water in industries
(2) To reuse and recycle water in two or successive stages
(3) To harvest rain water for meeting water requirements in industries
(1) To treat water and other industrial effluents before releasing them into rivers and ponds in three stages- Phase I- Primary treatment by mechanical means- screening, Grinding, Sedimentation Phase II- Secondary treatment by biological process Phase III- Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical
Question. Why is iron and steel industry called a basic industry?
Answer. (1) It is the industry which lays foundation of rapid development of other industries such as heavy engineering, defence equipment automobiles, aeroplanes etc.
(2) Generates employments
(3) Helps development in agriculture.
Question. Why did Mahatma Gandhi lay emphasis on spinning yarn and weaving khadi?
Answer. Weaving is done by handloom, power loom and in mills. The handspun khadi provides large-scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry. Mahatma Gandhi also wanted to propagate the use of the indigenous khadi material to revive the jobs of jobless weavers during the British period
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question. Which factors are responsible for the decentralization of cotton textile mills in India?
Answer. (i) Cotton textile have a very high demand throughout the country.
(ii) Major inputs like banking, electricity, transportation is available in almost every part of the country
(iii) Textile industry is labour intensive industry and labour is easily available in India.
(iv) Textile industry requires less technological inputs and can be carried out using simple tools and machines.
(v) Generates employment in rural and urban sector.
Question. The sugar industry is now shifting from north to south.
Mention main reasons.
Answer. (i) The sugar contents in the cane are higher i.e. 10.5% in Maharashtra and other southern states.
(ii) Climate is suitable for the cultivation of sugarcane.
(iii) South has better export facilities as compared to North.
(iv) Cooperative sugar mills are more successful in management in south India.
(v) The Peninsular climate helps to extend the crushing season by two months in the south India than north India.
Question. Name the factor which plays the most dominant role in the ideal Location of an industry. Explain any four reasons in support of this factor.
Answer.
(1) Availability of raw material: The factory needs to be close to the location of raw materials if they are heavy and bulky to transport. For example, iron and steel and cement industries are located near the source of raw materials. It cuts down the cost of transportation. ‘
(2) Labour: A large and cheap labour force is required for labour-intensive manufacturing industries. High-tech industries have to locate where suitable skilled workers are available. (3) Power: Power supply is needed for working of the machines in a factory. Earlier industries were near to coalfields.
(4) Capital: Money that is invested to start the business. The amount of capital will determine the size and location of the factory
(5) Transport: A good transport network helps to reduce costs and made the movement of raw materials and finished goods easier.
(6) Market: An accessible place to sell the products is essential.
(7) Government policies: Industrial development is encouraged receive financial incentives and assistance from the government in the form of low rent and tax rebates.
1. Multiple choice questions
Question. Which one of the following industries uses limestone as a raw material?
(a) Aluminum
(b) Cement
(c) Sugar
(d) Jute
Answer: (b) Cement
Question. Which one of the following agencies markets steel for the public sector plants?
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC
Answer: (b) SAIL
Question. Which one of the following industries uses bauxite as a raw material?
(a) Aluminum
(b) Cement
(c) Jute
(d) Steel
Answer: (a) Aluminum
Question. Which one of the following industries manufactures telephones, computer, etc?
(a) Steel
(b) Electronic
(c) Aluminum
(d) Information Technology
Answer: (b) Electronic
2. Answer the following briefly in not more than 30 words.
Question. What is manufacturing?
Answer: Manufacturing is the process in which goods are produced after processing the various raw materials.
Question. Name any three physical factors for the location of the industry.
Answer: Three physical factors for the location of the industry are:
- Availability of raw material
- Availability of water and power supply and
- Suitable climate
Question. Name any three human factors for the location of an industry.
Answer: Three human factors for the location of an industry are
- Availability of cheap and skilled labour
- Availability of Market
- Consultants and financial advice
Question. What are basic industries? Give an example.
Answer: Basic or key industries are those which supply their raw materials to industries that manufacture other goods. An example is the iron and steel industry that supplies steel to the automobile industry.
Question. Name the important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement?
Answer: The important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement are limestone, silica, alumina, and gypsum.
3. Write the answers of the following questions in 120 words.
Question. How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants? What problems does the industry face? What recent developments have led to a rise in the production capacity?
Answer: Integrated Steel Plants are large plants, which handle everything in one complex – from putting together raw material to steel making, rolling, and shaping. Mini Steel Plants are smaller, have electric arc furnaces, use mainly steel scrap and sponge iron as inputs. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots as well. They produce mild and alloy steel of given specifications.
Problems of Steel Industry
- High costs and limited availability of coking coal
- Irregular supply of energy
- Lower productivity of labour
- Poor infrastructures like roads, transport and communication
Following are some recent developments that have led to a rise in the production capacity:
- Liberalization
- Foreign direct investments (FDI) with the efforts of private entrepreneurs
- Improvement in production process by the use of newer technologies
- Allocation of fund and other resources for research and development
Question. How do industries pollute the environment?
Answer: Industries are responsible for four types of pollution – air, water, land, and noise pollution. Following are the various reasons:
- Air pollution is caused by the presence of high proportion of sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide and adversely affects human health, animals, plants, buildings, and the atmosphere as a whole.
- Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants are drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
- Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents discharged into rivers.
- Dumping of wastes like glass, harmful chemicals, industrial effluents, packaging, salts, and other garbage render the soil useless.
- Noise pollution is caused due to industrial and construction activities, factory equipment, generators, electric saws, drills, etc.
Question. Discuss the steps to be taken to minimize environmental degradation by industry?
Answer: The steps to be taken to minimize environmental degradation by industry are:
- To control water pollution, industrial effluents need to be treated on primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- The use of water for processing should be minimized via reuse and recycling; rainwater can be harvested to meet water requirements.
- For the minimization of air pollution, smoke stacks should be fitted in factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators.
- To control noise pollution, generators should be fitted with silencers and using earplugs and earphones besides other noise absorbing material.
Activity
Give one word for each of the following with regard to industry. The number of letters in each word are hinted in brackets.
(i) Used to drive machinery (5)P..............
(ii) People who work in a factory (6) W............
(iii) Where the product is sold (6) M..............
(iv) A person who sells goods (8) R..........
(v) Thing produced (7) P............
(vi) To make or produce (11) M...........
(vii) Land, Water and Air degraded (9) P.......
Answer:
(i) Power
(ii) Worker
(iii) Market
(iv) Retailer
(v) Product
(vi) Manufacture
(vii) Pollution
ACTIVITY
Question. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
1. Textiles, sugar, vegetable oil and plantation industries deriving raw materials from agriculture are called…
2. The basic raw material for sugar industry.
3. This fibre is also known as the ‘ Golden Fibre’.
4. Iron-ore, coking coal, and limestone are the chief raw materials of this industry.
5. A public sector steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
6. Railway diesel engines are manufactured in Uttar Pradesh at this place.
Answer:
1. Agrobased
2. Sugarcane
3. Jute
4. Ironsteel
5. Bhilai
6. Varanshi
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Objective Questions
Question. Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system and liquid relates to
(a) waste management
(b) work done by NTPC
(c) providing employment
(d) All of these
Answer: B
Question. In which of the following states is Kalpakkam nuclear power plant located?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Odisha
(c) Kerala
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer: D
Question. Match the following items given in Column A with those in Column B.
| Column A (Mill/Plant) |
Column B (Year of Establishment) |
| A. First Textile Mill | 1. 1904 |
| B. First Jute Mill | 2. 1854 |
| C. First Cement Plant | 3. 1859 |
Codes
A B C
(a) 2 3 1
(b) 1 3 2
(c) 3 2 1
(d) 2 1 3
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is not correct ?
(a) Agriculture and industries are dependent on each other.
(b) India is largest producer of raw jute and jute goods
(c) Sugar and textile industry are examples of mineral industry.
(d) Chemical industry has two sectors i.e. organic and inorganic.
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following groups of states have the largest number of cotton textile centers? Identify the correct option.
(a) Gujarat and Maharashtra
(b) Karnataka and Tamil Nadu
(c) Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh
(d) Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat
Answer: A
Question. Which one of the following agencies markets steel for the Public Sector plants?
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC
Answer: B
Question. Most of the integrated steel plants in India are located in ………… . Choose the correct option.
(a) Malwa Plateau
(b) Chota Nagpur Plateau
(c) Bundelkhand Plateau
(d) Meghalaya Plateau
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is jointly owned by public and private sectors?
(a) Bajaj Auto Ltd
(b) TISCO
(c) BHEL
(d) Oil India Ltd
Answer: D
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about Industries and their challenges.
(a) Cotton Textile Industry – Seasonal Nature of Industry
(b) Jute Textile Industry – Lower Labour Productivity
(c) Iron and Steel Industry- Irregular supply of Energy
(d) Sugar Industry- Less Demand
Answer: C
Question. Match the following items given in Column A with those in Column B.
| Column A (Types of Industries) | Column B (Location) |
| A. Aluminium Smelting Plants | 1. Bihar |
| B. Fertiliser Industry | 2. Jamshedpur |
| C. Automobile Industry | 3. Gujarat |
| D. Sugar Industry | 4. Odisha |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 3 4 1
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 1 4 3 2
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following group of factors is a prime group for the location of aluminium smelting plant?
Identify the correct option.
(a) Capital and market
(b) Raw material and electricity
(c) Labour and raw material
(d) Capital and transport
Answer: B
Question. Which one of the following industries manufactures telephones, computer, etc?
(a) Steel
(b) Electronic
(c) Aluminium Smelting
(d) Information Technology
Answer: B
Question. Identify the type of industry with the help of informations given below.
• This industry comprises of both large scale and small scale manufacturing units.
• It consists of two sectors namely organic and inorganic sectors.
(a) Automobile Industry
(b) Fertiliser Industry
(c) Chemical Industry
(d) Cement Industry
Answer: C
Question. Identify the type of pollution with the help of given information.
• This occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling,
• Due to this pollution chemicals get absorb in the soil, making the soil useless.
(a) Air Pollution
(b) Water Pollution
(c) Thermal Pollution
(d) Noise Pollution
Answer: C
Question. Which type of pollution occurs when hot water from factories is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling?
(a) Thermal pollution
(b) Water pollution
(c) Air pollution
(d) Noise pollution
Answer: A
Question. Which one of the following industries uses bauxite as a raw material?
(a) Aluminium Smelting
(b) Cement
(c) Paper
(d) Steel
Answer: A
Question. Find the incorrectly matched pair from the given options.
(a) Public Sector – BHEL
(b) Private Sector – SAIl
(c) Joint Sector – Oil India Limited
(d) Manufacturing Sector – NMCC
Answer: B
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Assertion-Reason MCQs
Directions Each of these questions
contains two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) The Cement Industry has established its plant in Gujarat.
Reason (R) After Independence, cement industry has flourished in India.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion (A) India imports potash from other countries.
Reason (R) India does not have any of the commercially usable potash or potassium compounds in any form.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) is a major power providing corporation in India.
Reason (R) The major task of NTPC is to set up power plants by conserving the natural environment and resources like air, water, oil gas, coal and other fuels.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion (A) In recent years, there is a tendency for the sugar mills to concentrate in the Southern and Western States, especially in Maharashtra.
Reason (R) The cane produced in the Southern and Western states has higher sucrose content and cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) Aluminium has gained popularity as a substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in different industries.
Reason (R) Aluminium is the second most important metallurgical industry in India.
Answer: B
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Case Based MCQs
Read the case/source given and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option.
India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies the first place in the production of gur and khandsari. The raw material used in this industry is bulky, and in haulage its sucrose content reduces.
The mills are located in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh. Sixty per cent mills are in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. This industry is seasonal in nature so, it is ideally suited to the cooperative sector. Can you explain why this is so?
In recent years, there is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states, especially in Maharashtra; this is because the cane produced here has higher sucrose content. The cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season.
Moreover, the cooperatives are more successful in these states. Major challenges include the seasonal nature of the industry, old and inefficient methods of production, transport delay in reaching cane to factories and the need to maximise the use of bagasse.
Question. Why sugar mills are perfectly convenient for the sector in which industries owned by suppliers or producers of raw materials, workers or both? With reference to the above context, infer the appropriate option.
(a) Because this industry is seasonal in nature.
(b) Dueto its efficient methods of production.
(c) Due to better transport system.
(d) Because raw material are bulky.
Answer: A
Question. Why there is a high concentration of sugar mills in Uttar Pradesh? Select the best suitable option from the following in reference to the context.
(a) Because Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of sugarcane.
(b) Because labour is easily available in Uttar Pradesh.
(c) Due to high consumption in Uttar Pradesh.
(d) All of the above
Answer: A
Question. Fill in the blank from the given options:
India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies the first place in the production of gur and khandsari. Sugar industry comes under …………group of industries.
(a) Public sector
(b) Cooperative sector
(c) Private sector
(d) Joint sector venture
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following is not a major challenge for sugar industry? Select the best suitable option from the following.
(a) Traditional methods of production
(b) Need to maximise the use of bagasse
(c) Availability of water
(d) Seasonal nature of this industry
Answer: C
Question. Read the following statements about cooperative sector and find the incorrect from the given options.
I. Cooperative Sector is owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both.
II. This sector pools in the resources and share the profits or losses proportionately.
III. This sector is jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals.
Codes
(a) Only I
(b) Both I and II
(c) Only III
(d) Both I and III
Answer: C
Question. Why Sugar industries are shifting to the South and the West? Identify the best suitable reason from the given options.
(a) Due to cooler climate in these areas.
(b) Due to success of cooperative movement in these areas.
(c) Due to higher sucrose content in the sugarcanes cultivated in these areas.
(d) All of the above
Answer: D
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why was the cotton textile industry concentrated in the cotton growing belt in the early years? Explain.
Answer: In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat due to availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc.
This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton ball pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing.
The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as chemicals and dyes, mill stores, packaging materials and engineering works. All these factors determine location of cotton mill in early years.
Question. Explain any three problems faced by cotton textile industries in India.
Answer: Three problems faced by cotton textile industries in India are
(i) Power supply is erratic. Regular power supply without breaks is essential for this industry.
(ii) Output of labour is low because the machinery is outdated. Particularly in the weaving and processing sectors, the machinery needs to be upgraded.
(iii) This industry faces stiff competition from the synthetic fibre industry in terms of cost and convenience of use.
Question. What is manufacturing? How does manufacturing lead to value addition of the raw material? Explain with the help of examples.
Answer: Production of goods in large quantities by processing of raw materials to more valuable products is called manufacturing.
Manufacturing leads to value addition of the raw material as people employed in the secondary activities manufacture the primary materials into finished goods. These finished
goods are more useful, hence more in value. For example, paper is manufactured from wood, sugar from sugarcane, iron and steel from iron ore, aluminium from bauxite, etc.
Thus, raw materials are transformed into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value. Countries that transform in this way are prosperous.
Question. Why is iron and steel industry called the basic industry? What are the problems faced by this industry?
Or Explain any three problems faced by Iron and Steel industry in India.
Answer: Iron and steel industry is known as the basic industry because all the other industries (heavy, medium and light) depend on it for their machinery and products.
Problems faced by this industry are
(i) The finished goods of this industry are heavy and bulky that require heavy transportations costs.
(ii) There is limited availability of coking coal and productivity of labour is low. Other problems are irregular supply of energy and poor infrastructure.
Question. Mention any six factors responsible for the location of jute mills in the Hugli basin.
Answer: Factors responsible for location of jute mills in the Hugli basin are
(i) Proximity of the jute producing areas.
(ii) Inexpensive water transport, supported by a good network of railways and roadways.
(iii) Abundance of water for processing raw jute.
(iv) Availability of cheap labour from nearby areas.
(v) Facilities for export of jute goods.
(vi) Banking, insurance and other commercial facilities to jute industry.
Question. Mention any two factors that have contributed to a healthy growth of the automobile industry in India. Name two centres where this industry is located.
Answer: Two factors contributing to healthy growth of the automobile sector are
(i) Liberalisation is one of the major factors which provided boost in the growth of the automobile industry in India.With the introduction of new and contemporary models of automobiles in the country, the demand for these vehicles increased at a faster pace.
(ii) With the introduction of new technology in this sector, Indian industries are now capable to compete with the global technologies. This could happen by Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
Two major centres where this industry is located are Gurugram and Indore.
Question. What are mineral based industries? Give four examples.
Answer: Industries that use minerals and metals as raw materials are called mineral based industries.
Four examples of mineral based industries are
(i) The Iron and Steel Industry All other industries depend on it for their machinery.
(ii) Chemical Industry It contributes approximately 3 per cent of India’s GDP.
(iii) Fertiliser Industry It is centered around the production of nitrogenous, phosphatic, ammonium phosphate and complex fertiliser.
(iv) Cement Industry This requires limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum as raw materials.
Question. How do industries create thermal and noise pollution? Mention their consequences.
Answer: Industries create thermal and noise pollution in the following ways
• Thermal pollution of water bodies occurs when hot water from factories and thermal power plants is released into them before cooling.
The consequence of thermal pollution are that aquatic life in the water bodies can be killed. This includes plants as well as fish.
• Noise pollution is generated by the unbearable noise from industrial and construction activities, machinery, generators, pneumatic and electric tools.
The consequences of noise polutions create irritation, anger, stress, hearing impairment, increased heart rate and blood pressure among other physiological effects.
Question. “Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand.” Justify the statement by giving any three arguments.
Answer: Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand. For example,
(i) Industrialisation causes growth in available factory jobs.
As a result, employment rate increaseswhich pulls people fromvarious places towards the placeswhere industries are located.
(ii) Many industries tend to come together to make use of advantages offered by the urban centres.
(iii) Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, which are needed by the industry.
Question. Examine how industrial pollution of freshwater can be reduced.
Or Suggest any three measures to reduce the industrial pollution of freshwater resources.
Answer: The industrial pollution of freshwater resources can be reduced in the following ways
(i) Restructuring the manufacturing processes in various industries to reduce or eliminate pollutants through pollution prevention methods.
(ii) Creating man-made cooling ponds designed to cool heated effluent waters of industries by evaporation, condensation and radiation.
(iii) Filtration of the sewage in water treatment plants before dumping it into water bodies.
Question. Mention the negative impacts of waste from the nuclear plant.
Answer: Negative impacts of waste from the nuclear plants are
• Waste from nuclear plants have radioactive properties and may cause cancers, birth defects and miscarriages.
• Nuclear wastes are generally dumped in deep sea-water.
In case of their unfortunate leakage, there will be severe threat to aquatic life.
• Radioactive contamination can easily spread throughout the environment and the air, land and water can all become polluted and harm humans and other life forms.
Question. Explain any five measures to control industrial pollution in India.
Or Suggest any three steps to minimise environmental degradation caused by industrial development in India.
Or Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry.
Answer: Five measures or steps to control or minimise industrial pollution in India are
(i) Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators.
(ii) Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
(iii) Updated machinery and equipment should be used that makes less noise and generators should be fitted with silencers.
(iv) Pollution check certificates should be made compulsory.
(v) Machineries used in the industries can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing materials may also be used.
Question. What is the contribution of industries to national economy of India? Compare this contribution with the East-Asian countries. What is the desired growth and present position of industry in GDP?
Answer: The contribution of industries to national economy of India has not been satisfactory for the last two decades. It has stagnated at 17 per cent of GDP out of a total of 27 per cent for the industries which includes 10 per cent of mining, quarrying, electricity and gas. In comparison to India’s 17 per cent share in the GDP, the manufacturing sector in
East-Asian countries have a contribution of 25 to 35 per cent of their GDP.
The desired growth rate over the next decade is 12 per cent. At present, growth rate is about 9 to 10 per cent and it is expected that we can achieve the growth rate of 12 per
cent by some efforts like setting up of the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC).
Question. ‘‘Sugar industry in India is facing challenges.’’
Analyse the statement with suitable arguments.
Answer: Sugar industry in India is facing lot of challenges which are
(i) This industry is seasonal as it is dependent on sugarcane which is an annual crop. Workers get employed only for a short period.
(ii) The machines and ways of producing sugar from sugarcane are old and inefficient.
(iii) The raw material i.e. sugarcane is bulky which increases the transportation cost and difficulty of transporting.
(iv) The sucrose content in sugarcane keeps on decreasing with time so transport delay in reaching sugarcane to factories results in losses.
(v) There is also the challenge of using the byproducts of sugarcane properly like bagasse.
Question. Mention any two challenges faced by the jute industry in India. State any one step taken by the government to stimulate its demand.
Answer: The two challenges faced by the jute industry in India are
(i) Stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes.
(ii) Supply competition from other jute producing nations like Bangladesh, Brazil, Philippines, Egypt and Thailand.
The step taken by the government to stimulate the demand for jute is that it has introduced a policy of mandatory use of jute packaging. The main markets of jute industries are USA, Canada, Ghana, Saudi Arabia, UK and Australia.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Which factor plays the most dominant role in the ideal location of an industry? Explain any three reasons in support of this factor.
Answer: Least cost factor plays the most dominant role for the ideal location of an industry due to the following reasons (i) Cost of obtaining raw material at the factory site should
be minimum i.e. raw materials should be available nearby or may be transported cheaply to the industrial location.
(ii) The factory should be located as such that the manufactured products may easily be distributed or transported to the market at the least cost by rail, road or water transport.
(iii) Cost of manufacturing at the factory site should be low.
This means that trained experienced labour should be readily available locally or in nearby areas, electric power supply should be readily available and cheap.
Also, land for locating the industry should be available at proper rates.
Question. Why does the textile industry occupy an important position in the Indian economy ? Explain.
Answer: Textile industry occupies unique position in Indian economy because
(i) Contribution to Industrial Production This industry is self-reliant and complete in the value chain, which means from production of cotton to processing of textiles, all the procedures are well developed and done in the country.
(ii) Employment Generation This industry generates employment for large number of persons directly or indirectly.
(iii) Demand Creation Textile industries create demand for other industries such as chemicals, dyes, packaging materials, engineering works, handicrafts industry etc.
(iv) Foreign Exchange Earnings By exporting the products of this industry, the country earns foreign exchange.
(v) Supports Agriculture This is a major agro-based industry of India and supports agriculture in a big way both by buying agricultural output (cotton) and by providing agricultural inputs (hybrid cotton seeds, implements).
Question. Which states of India have the maximum extent of cotton textile growth? Give four reasons for its concentration in this state.
Answer: Maharashtra and Gujarat states have the maximum extent of cotton textile growth. The reasons for the concentration of cotton textile industry in these states are
(i) Availability of Raw Materials Due to favourable soil type and other climatic conditions, cotton is grown in a vast area in these states. So, raw materials are available in plenty.
(ii) Transport These states are well connected to the rest of the country by rail and road. Also, they have many large ports from where the finished products can be easily
exported.
(iii) Market They also enjoy well-developed markets where there is lot of demands for cotton textiles.
(iv) Labour Although they have locally available cheap labour force, they are supported by migrant labours from the other states.
(v) Moist Climate For cotton cultivation, moist climate is a must. These states have favourable climatic conditions.
Question. Why is the economic strength of a country measured by the development of manufacturing industries ? Explain with examples.
Answer: The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of manufacturing industries because
• Manufacturing industries help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy. For example, these provide tractors, thresher, irrigation pumping machines and other modern machineries for agricultural development.
• Manufacturing also reduces the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
• Industrial development helps in removal of unemployment and poverty. It also aims at bringing down regional differences by establishing industries in backward areas. For example, handloom industries in tribal regions.
• Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce and brings much needed foreign exchange.
• Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous.
Question. Explain any three physical factors and two human factors for the location of the industry.
Or Explain with examples any five factors that are responsible for industrial location.
Or Explain any three factors affecting the localisation of industries with suitable examples.
Answer: The physical and human factors that affect the location of industry are
Physical Factors
(i) Availability of Raw Materials The factory needs to be close to the location of raw material if they are heavy and bulky to transport. For example, iron and steel industry is located near the source of raw material.
(ii) Water Source Water is an important factor that determines the location of industries. Water is required for various industrial processes. River water and waterfalls can also be used to generate hydroelectricity.
(iii) Climate It plays a significant role in establishment of industries. Harsh climate is not much suitable for industries. Extremely hot, humid, dry or cold climate is not very conducive for industries.
For example, cotton textile industry requires humid climate because thread breaks in dry climate.
Human Factors
(i) Labour A large and cheap labour force is required for labour-intensive and manufacturing industries.
High-tech industries have to be located where suitable skilled workers are available.
(ii) Capital This is the money that is invested to start a business. The amount of capital will determine the size and location of the factor.
(iii) Government Policies Industrial development is encouraged in some areas and restricted in others.
Industries that are located in backward areas may receive financial incentives and assistance from the government in the form of low rent and tax rates.
Question. How are industries responsible for environmental degradation in India? Explain with examples.
Answer: Industries are responsible for environmental degradation in India as they pollute the environment by polluting air, water and land in following ways
(i) Air Pollution Industries cause air pollution by the emission of gases from industrial complexes and power generation units. Leakage of poisonous gases and chemicals and smoke from chemical industries also lead to air pollution.
(iii) Water Pollution It is caused when industrial effluents both organic and inorganic are discharged into rivers or other water bodies.
Industries like paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries and electroplating industries discharge detergents acids, salts and heavy metals like lead and mercury, pesticides, fertilisers, synthetic chemicals with carbon, plastic and rubber, etc. into water bodies.
(iii) Thermal Pollution This pollution occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling. It badly affects the aquatic life. For example, wastes from nuclear power plants, nuclear and weapon production causes cancers, birth defects, miscarriages etc. Rain water percolates to the soil carrying the pollutants to the ground and thus ground water also gets contaminated.
(iv) Noise Pollution Undesirable noise pollution from industries like construction, running of generators to generate power, electrical drills, etc. is responsible for disturbing our environment. Noise pollution not only irritates us, but it also causes hearing impairment, increased heart rate and blood pressure etc.
Question. Why does the ‘Chota Nagpur Plateau region’ have the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries? Analyse the reasons.
Or Explain the reasons for concentration of iron and steel industries in and around Chotanagpur region.
Answer: The reasons/factors responsible for the concentration of iron and steel industries in and around the ‘Chotanagpur Plateau Region’ are
(i) Low Cost of Iron Ore Iron mines are located in the nearby areas. It helps to reduce the transportation cost of iron ore to the industries.
(ii) High Grade Raw Materials in Proximity Bulky raw materials like, coking coal, limestone are also available in proximity.
(iii) Availability of Cheap Labour From the adjoining areas of Bihar, Jharkhand and Odisha, cheap labour is available in abundance.
(iv) Dense Transport Network This region is well connected with roadways and railways that help in the swift movement of raw materials and finished goods to the industry and market areas, respectively.
(v) Port Facilities Kolkata is a well developed port that is near to this area.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Case Based Questions
1. Read the given cases/sources and answer the following questions
Source A Importance of Manufacturing Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary
sectors.
Question. Why it is said that it is rarely possible to find all the factors of industrial location available at one place?
State only one aspect.
Answer: It is rarely possible to find all the factors of industrial location available at one place because these factors are different in nature. For example, some factors are physical in nature like raw materials, water source and climate whereas some are human factors such as labour, capital, power and market places.
Question. To what extent do you agree that manufacturing industries are important for people? State only two reasons.
Answer: It is true that manufacturing industries are important for people because these industries create jobs for people and reduce heavy dependence of people on agricultural
income.
SourceB Contributionof Industry toNational Economy Over the last two decades, the share of manufacturing sector has stagnated at 17 per cent of GDP - out of a total of 27 per cent for the industry which includes 10 per cent for mining, quarrying, electricity and gas. This is much lower in comparison to some East Asian economies, where it is 25 to 35 per cent.
Question. Why it is said that manufacturing sector of Indian economy is much lower than the East Asian economics? What initiatives are taken by the government to deal with this situation?
Answer: Manufacturing sector of Indian economy is much lower than the East Asian economics because the manufacture sector of India has stagnated at 17% of GDP whereas East Asian economics have 25-35% GDP. In order to develop the sector of manufacturing industries, government has set up the National manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC). The objective is to bring appropriate policy to improve productivity to achieve desired growth rate.
Source C IndustrialLocation
Industrial locations are complex in nature. These are influenced by availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market, etc. It is rarely possible to find all these factors available at one place.
Consequently, manufacturing activity tends to locate at the most appropriate place where all the factors of industrial location are either available or can be arranged at lower cost.
2. Read the given case/source and answer the following questions.
In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contributed towards its localisation.
This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton ball pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, packaging materials and engineering works.
Question. To what extent do you agree that these places are suitable for the location of cotton textile industry?
State any two reasons.
Answer: Gujarat and Maharashtra are suitable for the location of cotton textile industry because
(i) Both states have favourable climate conditions for growing cotton.
(ii) Both states have well developed market, where there is a lot of demand for cotton textiles.
Question. To what extent do you agree that cotton textile industry has close links with agriculture and also supports other industries as well? State two reasons.
Answer: It is true that cotton textile industry has close links with agriculture and also supports industries as
(i) Cotton textile industry provides a living to farmers and cotton ball pluckers because they grow cotton which is the basic raw material of this industry.
(ii) This industry by creating demands supports many other industries. For example, chemicals and dyes, mill stores, packaging materials and engineering works.
Question. Which two places were important in early years for the concentration of textile industry in India? State any one challenge faced by cotton textile industries in India.
Answer: Gujarat and Maharashtra were important in early years for the concentration of textile industry in India.
The challenges faced by cotton textile industries in India is that this industry faces stiff competition from the synthetic fibre in terms of cost and convenience of use.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Resources and development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Water Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 Power Sharing |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Federalism |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 Gender Religion and Caste |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 Political Parties |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Outcomes of Democracy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 3 The Making of a Global World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialization |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Print Culture and Modern World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors Of The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money And Credit |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Globalization And The Indian Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 5 Consumer Rights |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Social Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries of Social Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 chapter of Social Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Social Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Social Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Social Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Social Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Social Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries have been answered by our teachers

