Read and download the CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Data File Handling Worksheet in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 12 Computer Science worksheets for Data File Handling, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 12 Computer Science Data File Handling
Students of Class 12 should use this Computer Science practice paper to check their understanding of Data File Handling as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 12 Computer Science Data File Handling Worksheet with Answers
Object Oriented Programming in C++
Data File Handling In C++
File: - The information / data stored under a specific name on a storage device, is called a file.
Stream: - It refers to a sequence of bytes.
Text file: - It is a file that stores information in ASCII characters. In text files, each line of text is terminated with a special character known as EOL (End of Line) character or delimiter character. When this EOL character is read or written, certain internal translations take place.
Binary file:- It is a file that contains information in the same format as it is held in memory. In binary files, no delimiters are used for a line and no translations occur here.
Classes used for different file related operation
ofstream:Object of ofstream class used to write data to the files.
ifstream: Object of ifstream class used to read data from files
fstream: Object of fstream class used to both read and write from/to files.
Opening a file
Opening file using constructor
ofstream outFile("sample.txt"); //output only
ifstream inFile(“sample.txt”); //input only
Opening File Using open ()
StreamObject.open(“filename”, [mode]);
ofstream outFile;
outFile.open("sample.txt");
ifstream inFile;
inFile.open("sample.txt");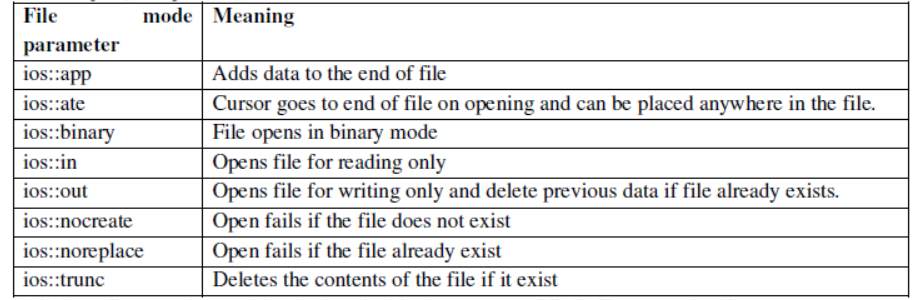
All these flags can be combined using the bitwise operator OR (|). For example, if we want to open the file example.dat in binary mode to add data we could do it by the following call to member
function open():
fstream file;
file.open ("example.dat", ios::out | ios::in | ios::binary);
Closing File
outFile.close();
inFile.close();
Input and output operation
put() and get() function
the function put() writes a single character to the associated stream. Similarly, the function get()
reads a single character from the associated stream.
example :
file.get(ch);
file.put(ch);
write() and read() function
write() and read() functions write and read blocks of binary data.
example:
file.read((char *)&obj, sizeof(obj));
file.write((char *)&obj, sizeof(obj));
Determining End of File.
eof():-returns true (non zero) if end of file is encountered while reading; otherwise return false(zero)
File Pointers And Their Manipulation
All I/O stream objects have, at least, one internal stream pointer:
ifstream has a pointer known as the get pointer that points to the element to be read in the next input operation.ofstream has a pointer known as the put pointer that points to the location where the next element has to be written.fstream, inherits both, the get and the put pointers.
These internal stream pointers that point to the reading or writing locations within a stream can be manipulated using the following member functions: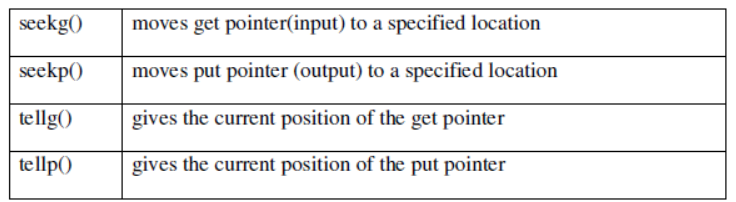
The other prototype for these functions is:
seekg(offset, refposition );
seekp(offset, refposition );
The parameter offset represents the number of bytes(any negative or positive integer value for backward or forward movement) the file pointer is to be moved from the location specified by the parameter refposition. The refposition takes one of the following three constants defined in the ios class.
ios::beg start of the file
ios::cur current position of the pointer
ios::end end of the fil


Short Answer Type Questions
1.Write a function in a C++ to count the number of lowercase alphabets present in a text file
“BOOK.txt”.
Answer. int countalpha()
{
ifstream Fin(“BOOK.txt”);
char ch;
int count=0;
while(!Fin.eof())
{ Fin.get(ch);
if (islower(ch))
count++;
}
Fin.close();
return count;
}
2. Write a function in C++ to count the number of line started with alphabet ‘a’ or ‘A’ in a text
file “LINES.TXT”.
Answer. void counter( )
{
char Aline[80];
int Count=0;
ifstream Fin (“LINES.TXT”);
while(!fin.eof())
{
Fin.getline(Aline,80, ‘\n’));
if (Aline[0]== ‘A’||Aline[0]==’a’)
Count++;
}
cout<<Count<<endl;
Fin.close( );
}
3. Write a function to count number of words whose word length is 8, in a file named “article.txt”.
Answer. void wordlen8( )
{
char word[20];
int count=0;
ifstream fin(“article.txt”);
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin>>word;
if(strlen(word)==8)
count++;
}
cout<<”Total number of words with word length 8 is=” << count; fin.close();
}
4. Given a binary file PHONE.DAT, containing records of the following structure type.
class phonlist
{ char Name[20] ;
char Address[30] ;
char AreaCode[5] ;
char PhoneNo[15] ;
public :
void Register( ) ;
void Show( ) ;
int CheckCode(char AC[ ])
{ return strcmp(AreaCode, AC) ;
}
} ;
Write a function TRANSFER( ) in C++, that would copy all those records which are having
AreaCode as “DEL” from PHONE.DAT to PHONBACK.DAT.
Answer. void transfer( )
{
ifstream Fin;
ofstream Fout;
Phonlist ph;
Fin.open(“PHONE.DAT”, ios::in | ios::binary);
Fout.open(“PHONBACK.DAT”, ios::out | ios:: binary);
while(Fin.read((char*)&ph, sizeof(ph)))
{
if(ph.check(“DEL”) == 0)
Fout.write((char*)&ph, sizeof(ph));
}
Fin.close();
Fout.close();
}
5.Given a binary file STUDENT.DAT, containing records of the following classStudent type
class Student
{
char S_Admno[l0]; //Admission number of student
char S_Name[30]; //Name of student
int Percentage; //Marks Percentage of student
public:
void EnterData()
{
gets(S_Admno);gets(S_Name);cin>>Percentage;
}
void DisplayData()
{
cout<<setw(12)<<S_Admno;
cout<<setw(32)<<S_Name;
cout<<setw(3)<<Percentage<<endl;
}
int ReturnPercentage(){return Percentage;}
};
Write a function in C++, that would read contents of file STUDENT.DAT and display the
details of those Students whose Percentage is above 75
Answer.
void Distinction()
{
Student S;
fstream Fin;
Fin.open(“STUDENT.DAT”, ios::binary|ios::in);
while(Fin.read((char*)&S, sizeof(Student))
if (S.ReturnPercentage()>75)
S.DisplayData( );
Fin.close();
}
6. Given a binary file STUINFO.DAT, containing records of the following structure type.
class STUDENT
{
int rollno;
char Name[20] ;
char Address[30] ;
char PhoneNo[15] ;
public :
void enter( )
{
cin>>rollno;
cin.getline(name,20);
cin.getline(address,30);
cin.getline(phoneno,15);
}
void display( )
{
cout<<”information of student is”;
cout<<rollno<<name<<address<<phoneno;
}
} ;
Write a function stu_write( ) in C++, that would write information of students in STUINFO.DAT
Very Short Questions
1. Observe the program segment given below carefully and fill the blanks marked as Line 1 and Line 2 using fstream functions for performing the required task.
#include <fstream.h>
class Library
{
long Ano; //Ano – Accession Number of the Book
char Title[20]; //Title – Title of the Book
int Qty; //Qty – Number of Books in Library
public:
void Enter(int); //Function to enter the content
void Display(); //Function of display the content
void Buy(int Tqty)
{
Qty+=Tqty;
} //Function to increment in Qty
long GetAno() {return Ano;}
};
void BuyBook (long BANo, int BQty)
//BANo is Accessionno of the book purchased
//BQty is Number of books purchased
{
fstream File;
File. open (“STOCK.DAT”, ios: : binary|ios: : in|ios: : out);
int Position=–1;
Library L;
while (Position = = –1 && File. read ((char*) &L, sizeof (L)))
if (L. GetAno() = =BANo)
{
L. Buy (BQty); //To update the number of Books
Positions=File. tellg()–sizeof (L);
//Line 1: To place the file pointer to the required position.
—————————;
//Line 2: To write the object L on to the binary file
—————————;
}
if (Position==–1)
cout<<“No updation done as required Ano not found...”;
File. Close();
}
Answer. File. seekp (position, ios :: beg); // Line–1
File. write ((char *) & L, sizeof (L)); // Line–2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. If a text file is opened in w+ mode, then what is the initial position of file pointer/cursor?
a. Beginning of file
b. End of the file
c. Beginning of the last line of text file
d. Undetermined
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following statements are true?
a. When you open a file for reading, if the file does not exist, an error occurs
b. When you open a file for writing, if the file does not exist, a new file is created
c. When you open a file for writing, if the file exists, the existing file is overwritten with the new file
d. All of the mentioned
Answer. D
Question. To read the entire remaining contents of the file as a string from a file object myfile, we use
a. myfile.read(2)
b. myfile.read()
c. myfile.readline()
d. myfile.readlines()
Answer. B
Question. A text file is opened using the statement f = open(‘story.txt’). The file has a total of 10 lines. Which of the following options will be true if statement 1 and statement 2 are executed in order. Statement 1: L1 = f.readline( ) Statement 2: L2 = f.readlines( )
a. L1 will be a list with one element and L2 will be list with 9 elements.
b. L1 will be a string and L2 will be a list with 10 elements.
c. L1 will be a string and L2 will be a list with 9 elements.
d. L1 will be a list with 10 elements and L2 will be an empty list.
Answer. C
Question. Which function of a file object can be used to fetch the current cursor position in terms of number of bytes from beginning of file?
a. seek( )
b. bytes( )
c. tell( )
d. fetch( )
Answer. C
Question.What will be the output of the following code?
f = open(‘test.txt’, ‘w+’)
L = [‘First Line\n’, ‘Second Line\n’, ‘Third Line’]
f.writelines(L)
f.flush() f.seek(0)
O = f.readlines()
print(len(O))
a. 33
b. 31
c. 28
d. 3
Answer. D
Question. The contents of a text file named ‘quote.txt’ is as shown below:
All the kings horses and all the kings men
cannot fix what isn’t broken.
What will be the output of the following code?
fin = open('fracture.txt’) data = fin.read(10) print(data[0:3], end= ‘’)
data = fin.readline(5)
print(data[0:3] , end= ‘’) fin.seek(0)
data = fin.read(4)
print(data[0:3] , end= ‘’)
a. AllngsAll
b. AllcanAll
c. Allcancan
d. Allngscan
Answer. A
Question. What will be the most correct option for possible output of the following code, given that the code executes without any error.
f = open(‘cricket.txt’)
data = f.read(150)
print(len(data))
a. It will always be 150
b. 151
c. More than or equal to 150
d. Less than or equal to 150
Answer. D
Question. For the following python code, what will be the datatype of variables x, y, z given that the code runs without any error?
f = open(‘story.txt’)
x = f.read(1)
y = f.readline()
z = f.readlines()
a. string, list, list
b. None, list, list
c. string, string, list
d. string, string, string
Answer. C
Question. The contents of a text file named ‘fracture.txt’ is as shown below:
Do you dare stay out, Do you dare go in
How much can you lose, How much can you win
And if you go in, should you turn left or right
You will get so confused that you will start in to race
What will be the output of the following code?
fin = open('fracture.txt’)
x = 0 for line in fin:
words = line.split( )
for w in words:
if len(w)>x:
x = len(w)
print(x)
a. 12
b. 11
c. 13
d. 10
Answer. A
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Differentiate between file modes r+ and w+ with respect to python?
Answer: r+ opens a text file for reading and writing. w+ opens a text file for reading and writing. It overwrites the file if it exists, create a file if it doesn’t.
Question. Write a statement in Python to open a text file “ABC.TXT” in reading mode.
Answer: F=open("ABC.TXT","r")
Question. In ___________ files each line terminates with EOL or ‘\n’ or carriage return, or ‘\r\n’.
Answer: Text File
Question. Observe the following code and answer the questions that follow.
File=open(“MyData”,”a”)
_____________ #Blank1
File.close()
a) What type (text/binary) of file is MyData ?
b) Fill the Blank1 with statement to write “ABC” in the file “Mydata”
Answer: a) Text File
b) File.write(“ABC”)
Question. What are files?
Answer: A named entity, usually stored on a hard drive that contains a stream of characters are called files.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Explain seek() method in python.
In Python, seek() function is used to change the position of the File Handle to a given specific position.
Syntax: fi.seek(offset, from_where), where fi is the file pointer
Offset: This is used for defining the number of positions to move forward.
from_where: This is used for defining the point of reference. It can take
0: beginning of the file. 1: current position of the file. 2: end of the file.
Q1. Define File .
Answer : A file is a bunch of bytes stored on some storage devices.
Q2. How are binary file differ from text files in c++?
Answer : When a file is opened in text mode, various character translations may take place, such as the conversion of carriage return and linefeed sequences into newlines. However, no such character translations occur in files opened in binary mode. Any file can be opened in either text or binary mode. The only difference is the occurrence of character translations in text mode.
Q3. What is a stream? Name the streams generally used for file I/O.
Answer : A stream is a sequence of bytes. Or in other words, a stream is a flow of bytes into or out of a program. Generally three streams are used for file I/O. These are:
(i) Ifstream: It is derived from istream class and it is used to associate a file with an input buffer so that the file can be read from.
(ii) Ofstream: It is derived from ostream class and it is used to associate a file with an output buffer so that the file can be written from.
(iii) fstream: It is derived from iostream class and it is used to associate a file with a buffer so that the file can be read from as well as written onto.
Q4. Differentiate between ifstream class and ofstream class.
Answer : The ifstream class is an input stream class, which provides input operations for file.
The ofstream class is an output stream class, which provides output operations for file.
Q5. Differentiate between functions read() and write().
Answer : The read() lets one read a unit of information from a file and a write() lets one write a unit of information to a file.
Q6. Differentiate between getline() and getc() functions.
Answer : getc() function can read one character at a time .On the other hand , getline() can read a line of text of specified size.
getc() is defined in stdio.h however getline() is defined in iostream.h
Q7. Name two member functions of ofstream class.
Answer : seekp() , tellp()
Q8. Distinguish between ios::out and ios::app.
Answer : The ios::out is the default file mode of ofstream. With the mode of the file does not exist, it gets created but if the file exists then its existing contents get deleted. On the other hand ios::app is also an output mode , which creates the file if it does not exist but if the file exists then its existing contents are retained and new information is appended to it.
Q9. What is the difference between the functioning of ios::ate and ios::app file modes.
Answer : Both ios::ate and ios::app place the file pointer at the end of the file just opened. The difference between two is that ios::app lets you add data to the end of the file only, while the ios::ate mode when opened with ofstream allows you to write data anywhere in the file, even over old data.
Q10. What is the need and usage of read() and write() functions when there are get() and put() functions for I/O.
Answer : The get () and put () function perform I/O byte by byte .On the other hand, read () and write () functions lets you read and write structures and objects in one go without creating the need for I/O for individual constituent fields.
Q11. What is the difference between get() and read()?
Answer : The read() declared under iostream.h extracts a given number of characters into an array.
The get() declared under iostream.h either extracts the next character or EOF or extracts characters into a char* until eof or delimiter encountered or specified(len-1) bytes have been read.
Q12. Write a C++ program, which reads one line at a time from the disk file TEST.TXT, and displays it to a monitor. Your program has to read all the contents of the file. Assume the length of the line does not exceed 70 characters.
Answer : #include<fstream.h>
void main()
{
char str[80];
ifstream fin(“Test.txt”);
if (!fin)
{ cout<<”Error in the opening”;
return –1;
}
while(fin)
{ fin.getline(str,70);
cout<<str<<endl;
}
fin.close();
}
Q13. Write a function to count the number of blanks present in text file named “PARA.TXT”;
Answer : void countblanks()
{
char ch;
int count=0;
ifstream fin(“PARA.TXT”,ios::in);
while(!fin.eof())
{ fin.get(ch)
if(fin.eof())
break;
if(ch==’ ‘)
count++; }
fin.close();
cout<<count; }
Q14. Write a Program to write and read a structure using write() and read() function using a binary file
#include<fstream.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<conio.h>
struct customer
{
char name[51];
float balance; };
void main()
{
clrscr();
customer savac;
strcpy(savac.name,”Tina Marshall”);
savac.balance=21310.75;
ofstream fout;
fout.open(“Saving” , ios::out|ios::binary);
if(!fout)
{ cout<<”File cant be opened \n”;
return 1; }
fout.write(char *)&savac ,sizeof(customer));
fout.close();
ifstream fin;
fin.open(“Saving”,ios::in|ios::binary);
fin.read(cahr *)&savac,sizeof(customer));
cout<<savac.name;
cout<<”has the balance Rs”<<savac.balance<<”\n”;
fin.close(); }
Answer : Tina Marshall has the balance Rs 21310.75
Q14. Write a program for reading and writing class objects.
#include<fstream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class Student
{
char name[40];
char grade;
float marks;
public:
void getdata(void);
void display(void);
};
void Student::getdat(void)
{
char ch;
cin.get(ch);
cout<<”Enter name”; cin.getline(name,40);
cout<<”Enter grade”; cin>>grade;
cout<<”Enter marks”; cin>>marks;
cout<<”\n”;
}
void Student::display(void)
{
cout<<”Name:”<<name<<”\t”
<<”Grade:”<<grade<<”\t”
<<”Marks:”<<marks<<”\t”<<”\n”;
}
void main()
{
clrscr();
Student arts[3];
fstream filin;
filin.open(“Stu.dat”,ios::in|ios::out);
if(!filin) {cout<<”Cannot open file \n”; return 1; } cout<<”Enter details for 3 students \n”; for(int i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
arts[i].getdata();
filin.write(char *) &arts[i],sizeof(arts[i]));
}
filin.seekg(0);
cout<<”the contents of stu.dat are shown below
for(int i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
filin.read(char *) &arts[i],sizeof(arts[i]));
arts[i].display();
}
filin.close();
}
CSV FILE
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question. CSV stands for :
a. Comma Separated Values
b. Comma Separated Variables
c. Comma Stored Values
d. Comma Stored Variables
Answer. A
Question. The separator character of CSV Files is called a
a. EOL
b. Delimiter
c. EOF
d. Default
Answer. B
Question. The default delimiter for a CSV file is :
a. Semi colon
b. Colon
c. Comma
d. Hyphen
Answer. C
Question. _____ module of Python provides the functionality to read and write tabular data in CSV file.
a. pickle
b. csv
c. file
d. ccv
Answer. B
Question. Which function is used to open a csv file ?
a. Open()
b. csv.open()
c. writer()
d. csv.writer()
Answer. B
Question. Name the function to read from CSV file.
a. read()
b. csv.reader()
c. csv.read()
d. readline()
Answer. B
Question. Which among the following is not a function of csv module?
a. reader()
b. read()
c. writer()
d. writerows()
Answer. B
Question. In Python, default newline character is :
a. \f
b. \t
c. \n
d. \v
Answer. C
Question. CSV module allows to write multiple rows using function.
a. writerows( )
b. writerow( )
c. writer( )
d. None of the above
Answer. A
Question. The opening function of a csv file is similar to the opening of:
a. Binary file
b. Text File
c. Both of them
d. None of them
Answer. B
Question. The _______argument of open function is to specify how Python handle the newline characters in csv file
a. newline
b. line
c. mode
d. char
Answer. A
Question. Which among the following is an iterable object ?
a. writer
b. file
c. reader
d. All of the above
Answer. C
Question. To specify a different delimiter while writing into a csv file, argument is used with writer object :
a. newline
b. separator
c. character
d. delimiter
Answer. D
Question. Which mode opens the file for exclusive creation, which fails in the case where file already exists
a. a
b. w
c. x
d. r
Answer. C
Question. The file mode to open a CSV file for reading as well as writing is .
a. a+
b. w+
c. r+
d. All the above.
Answer. D
Question. Identify the line number which may cause an error:
import csv #Line1 line=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]#Line 2
with open("sample.csv","w",newline="") as csvfile: #Line3
writer=csv.writer(csvfile,delimiter="|") #Line4
for line in writer: #Line5
writer.writerow(line)
a. Line1
b. Line2
c. Line 4
d. Line
Answer. D
Question. The CSV files are files.
a. Plain text file
b. Binary
c. Data
d. Python
Answer. A
Question. The writer() function has how many mandatory parameters?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following parameter needs to be added with open function to avoid blank row followed by each record in the CSV file?
a. quotechar
b. quoting
c. newline
d. skiprow
Answer. C
Question. Ajaikrishna wants to separate the values by a $ sign. Suggests him a pair of function and parameter to use it.
a. open, quotechar
b. writer, quotechar
c. open, delimiter
d. writer, delimiter
Answer. D
Question. Tejalakshmi of Class 12 have written the below code . Observe and fill in the given blanks so that it opens the file “data.csv” and read and print all the records.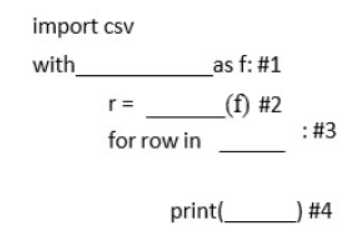
Question. What must be filled in line 1?
a. Open(“data.csv”,”r”)
b. open(“data.csv”)
c. “data.csv”
d. File
Answer. B
Question. What must be filled in Line 2?
a. csv.reader()
b. csv.read()
c. csv.write()
d. csv.writer()
Answer. A
Question. What must be filled in line 3?
a. data.csv
b. f
c. r
d. None
Answer. C
Question. What must be filled in line 4?
a. data
b. f
c. “File”
d. row
Answer. D
Question. What is the default data type of data read from this file?
a. List
b. String
c. Tuple
d. Integer
Answer. B
Question. Sudev, a student of class 12th, is learning CSV File Module in Python. During examination, he has been assigned an incomplete python code to create a CSV file ‘customer.csv’ .Help him in completing the code which creates the desired CSV file.
Question. Identify suitable code for the blank space in line marked as Statement-1.
a) include
b) add
c) Import
d) import
Answer. D
Question. Identify the missing code for the blank space in line marked as Statement-2.
a) Customer
b) reader
c) csvwriter
d) writer
Answer. C
Question. Identify the argument name for the blank space in line marked as Statement-3?
a) Row
b) Rec
c) row
d) rec
Answer. B
Question. Identify the missing file name for the blank space in line marked as Statement-4?
a) customer
b) customer.csv
c) customer.txt
d) customer.dat
Answer. B
Question. Identify the object name for the blank space in line marked as Statement-5?
a) i
b) Rec
c) row
d) rec
Answer. D
Data File Handling
1. Differentiate between :
(i) Text file and binary file
(ii) ios::out,ios::app and ios::ate
(iii) ios::nocreate and ios ::noreplace
(iv) seekg() and tellg()
(v) get() and getline()
2. Describe the two ways in which you can open files.
3. Find the errors :
(i) Ifstream inf;
Inf.open(“myfilr.tx”,ios::app);
(ii) Ifstream inf;
Inf.close(“myfile.txt”);
(iii) Ofstream fout;
Fout.open(“f.dat”,ios::in|ios::out|ios::ate);
Close(fout);
PROGRAMS
1. Write a program to count the number of blank spaces present in the text file.
2. Write the program that displays the size of the text file in bytes.
3. Write a program to count and display the number of lines starting with’T’ in a text file.
4. Given a binary file try.dat, write a C++ program to generate the following menu :
1. Input Data
2. Display Data
3. Modify
4. Delete
5. Exit
The class definition for the above program is :
Class Colour
{
int C_id;
char c_name[];
float price;
};
You can add member functions to the class as required.
5. To find the occurrence of word ‘the’ in a text file
6. To insert data in a sorted file
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Revision Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Revision Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Revision Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Boolean Algebra Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Boolean Algebra Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Computers Boolean Algebra Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science C++ Programming Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Case Study Based Questions |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Class And Objects Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Class And Objects Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Computers Classes And Objects Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Classes Objects Constructors And Destructors Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Communication And Network Concepts Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Computer Networking Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Constructors And Destructors Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computers Constructors And Destructors Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Data File Handling Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computers Data Structures Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Database Concepts And Sql Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Dbms And Structured Query Language Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Flow Of Control Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Function And Structures Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Function Overloading Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Fundamentals Of Computer Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Inheritance Extending Classes Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Linked Lists Stacks And Queues Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Network And Communication Technology Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computers Object Oriented Programming Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming In C++ Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Oop Classes And Objects Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Programming In C++ Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science SQL Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science SQL Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Stacks Queues And Linked List Worksheet |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Computer Science Class 12 Data File Handling Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Data File Handling to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 12. We suggest that Class 12 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Computer Science.
Data File Handling Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 12 Computer Science to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Computer Science to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 12 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 12 Computer Science study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Data File Handling difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 12 Computer Science. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter Data File Handling for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 12 Computer Science worksheets for Chapter Data File Handling focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter Data File Handling to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 12 Computer Science test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Data File Handling, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

