Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 9 Science. Our expert-created answers for Class 9 Science are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
For Class 9 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 9 Science solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules NCERT Solutions PDF
Class IX
Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules Science
Question 1: In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Sodium carbonate + ethanoic acid → sodium ethanoate + carbon dioxide + water
Answer: In the given reaction, sodium carbonate reacts with ethanoic acid to produce sodium ethanoate, carbon dioxide, and water.
Mass of sodium carbonate = 5.3 g (Given)
Mass of ethanoic acid = 6 g (Given)
Mass of sodium ethanoate = 8.2 g (Given)
Mass of carbon dioxide = 2.2 g (Given)
Mass of water = 0.9 g (Given)
Now, total mass before the reaction = (5.3 + 6) g
= 11.3 g
And, total mass after the reaction = (8.2 + 2.2 + 0.9) g
= 11.3 g
∴Total mass before the reaction = Total mass after the reaction
Hence, the given observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Question 2: Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1:8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?Answer:
It is given that the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen by mass to form water is 1:8. Then, the mass of oxygen gas required to react completely with 1 g of hydrogen gas is 8 g. Therefore, the mass of oxygen gas required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas is 8 × 3 g = 24 g.
Question 3: Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
Answer: The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory which is a result of the law of conservation of mass is:
Atoms are indivisible particles, which can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Question 4: Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
Answer: The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory which can explain the law of definitevproportion is: The relative number and kind of atoms in a given compound remains constant.
Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
Question 1: Define atomic mass unit.
Answer: Mass unit equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12 is called one atomic mass unit. It is written as ‘u’.
Question 2: Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
Answer: Thesize of an atom is so small that it is not possible to see it with naked eyes. Also, the atom of an element does not exist independently.
Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
Question 1: Write down the formulae of
(i) sodium oxide
(ii) aluminium chloride
(iii) sodium suphide
(iv) magnesium hydroxide
Answer:
(i) Sodium oxide →Na2O
(ii) Aluminium chloride → AlCl3
(iii) Sodium suphide → Na2S
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide → Mg(OH)2
Question 2: Write down the names of compounds represented by the following formulae:
(i) Al2(SO4)3
(ii) CaCl2
(iii) K2SO4
(iv) KNO3
(v) CaCO3
Answer:
(i) Al2(SO4)3 → Aluminium sulphate
(ii) CaCl2 → Calcium chloride
(iii) K2SO4 → Potassium sulphate
(iv) KNO3 → Potassium nitrate
(v) CaCO3 → Calcium carbonate
Question 3: What is meant by the term chemical formula?
Answer: The chemical formula of a compound means the symbolic representation of the composition of a compound. From the chemical formula of a compound, we can know the number and kinds of atoms of different elements that constitute the compound. For example, from the chemical formula CO2 of carbon dioxide, we come to know that one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms are chemically bonded together to form one molecule of the compound, carbon dioxide.
Question 4: How many atoms are present in a
(i) H2S molecule and
(ii) PO43− ion?
Answer: (i) In an H2S molecule, three atoms are present; two of hydrogen and one of sulphur.
(ii) In a PO43− ion, five atoms are present; one of phosphorus and four of oxygen.
Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
Question 1: Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, CO2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, NH3, CH3OH.
Answer:
Molecular mass of H2 = 2 × Atomic mass of H
= 2 × 1
= 2 u
Molecular mass of O2 = 2 × Atomic mass of O
= 2 × 16
= 32 u
Molecular mass of Cl2 = 2 × Atomic mass of Cl
= 2 × 35.5
= 71 u
Molecular mass of CO2 = Atomic mass of C + 2 × Atomic mass of O
= 12 + 2 × 16
= 44 u
Molecular mass of CH4 = Atomic mass of C + 4 × Atomic mass of H
= 12 + 4 × 1
= 16 u
Molecular mass of C2H6 = 2 × Atomic mass of C + 6 × Atomic mass of H
= 2 × 12 + 6 × 1
= 30 u
Molecular mass of C2H4 = 2 × Atomic mass of C + 4 × Atomic mass of H
= 2 × 12 + 4 × 1
= 28 u
Molecular mass of NH3 = Atomic mass of N + 3 × Atomic mass of H
= 14 + 3 × 1
= 17 u
Molecular mass of CH3OH = Atomic mass of C + 4 × Atomic mass of H + Atomic mass of O
= 12 + 4 × 1 + 16
= 32 u
Question 2:
Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2CO3, given atomic masses of Zn
= 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
Answer:
Formula unit mass of ZnO = Atomic mass of Zn + Atomic mass of O
= 65 + 16
= 81 u
Formula unit mass of Na2O = 2 × Atomic mass of Na + Atomic mass of O
= 2 × 23 + 16
= 62 u
Formula unit mass of K2CO3 = 2 × Atomic mass of K + Atomic mass of C + 3 × Atomic mass of O
= 2 × 39 + 12 + 3 × 16
= 138 u
Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
Question 1: If one mole of carbon atoms weighs 12 gram, what is the mass (in gram) of 1 atom of carbon?
Answer:
One mole of carbon atoms weighs 12 g (Given)
i.e., mass of 1 mole of carbon atoms = 12 g
Then, mass of 6.022x1023 number of carbon atoms = 12 g
Therefore, mass of 1 atom of carbon = 12/6.022x1023g = 1.9926 x 10-23g
Question 2: Which has more number of atoms, 100 grams of sodium or 100 grams of iron (given, atomic mass of Na = 23 u, Fe = 56 u)?
Answer:
Atomic mass of Na = 23 u (Given)
Then, gram atomic mass of Na = 23 g
Now, 23 g of Na contains 6.022x1023 = number of atoms
Thus, 100 g of Na contains 6.022x1023/23 x 100 number of atoms
= 2.61826 x 1024number of atoms
Again, atomic mass of Fe = 56 u(Given)
Then, gram atomic mass of Fe = 56 g
Now, 56 g of Fe contains 6.022x1023= number of atoms
Thus, 100 g of Fe contains 6.022x1023/56 x 100 number of atoms
= 1.0753 x 1024number of atoms
Therefore, 100 grams of sodium contain more number of atoms than 100 grams of iron.
Chapter 3 – Atoms and Molecules
Question 1: A 0.24 g sample of compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Answer:
Mass of boron = 0.096 g (Given)
Mass of oxygen = 0.144 g (Given)
Mass of sample = 0.24 g (Given)
Thus, percentage of boron by weight in the compound = 0.096 /0.24 x 100%
= 40%
And, percentage of oxygen by weight in the compound = 0.144/0.24 x 100%
= 60%
Question 2: When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combinations will govern your answer?
Answer: Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
3 g of carbon reacts with 8 g of oxygen to produce 11 g of carbon dioxide.
If 3 g of carbon is burnt in 50 g of oxygen, then 3 g of carbon will react with 8 g of oxygen. The remaining 42 g of oxygen will be left un-reactive.
In this case also, only 11 g of carbon dioxide will be formed.
The above answer is governed by the law of constant proportions.
Question 3: What are polyatomic ions? Give examples?
Answer: A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms carrying a charge (positive or negative). For example, ammonium ion (NH+4) , hydroxide ion (OH−), carbonate ion (CO2-3) sulphate ion (SO2-4)
Question 4: Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate
Answer:
(a) Magnesium chloride → MgCl2
(b) Calcium oxide → CaO
(c) Copper nitrate → Cu (NO3)2
(d) Aluminium chloride → AlCl3
(e) Calcium carbonate → CaCO3
Question 5: Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(a) Quick lime
(b) Hydrogen bromide
(c) Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulphate
Answer:
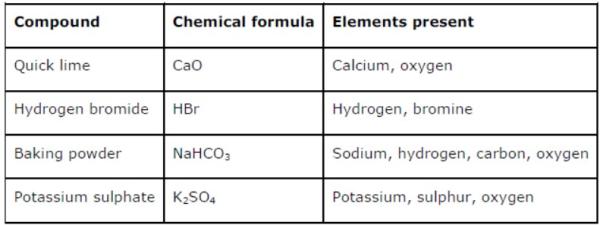
Question 6: Calculate the molar mass of the following substances:
(a) Ethyne, C2H2
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 (atomic mass of phosphorus = 31)
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3
Answer:
(a) Molar mass of ethyne, C2H2 = 2 × 12 + 2 × 1 = 28 g
(b) Molar mass of sulphur molecule, S8 = 8 × 32 = 256 g
(c) Molar mass of phosphorus molecule, P4 = 4 × 31 = 124 g
(d) Molar mass of hydrochloric acid, HCl = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5 g
(e) Molar mass of nitric acid, HNO3 = 1 + 14 + 3 × 16 = 63 g
Question 7: What is the mass of−−
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms?
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms (Atomic mass of aluminium = 27)?
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3)?
Answer:
(a) The mass of 1 mole of nitrogen atoms is 14 g.
(b) The mass of 4 moles of aluminium atoms is (4 × 27) g = 108 g
(c) The mass of 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) is
10 × [2 × 23 + 32 + 3 × 16] g = 10 × 126 g = 1260 g
Question 8: Convert into mole.
(a) 12 g of oxygen gas
(b) 20 g of water
(c) 22 g of carbon dioxide
Answer:
(a) 32 g of oxygen gas = 1 mole
Then, 12 g of oxygen gas = 12/32 mole = 0.375 mole
(b) 18 g of water = 1 mole
Then, 20 g of water = 20/18 mole = 1.11 moles (approx)
(c) 44 g of carbon dioxide = 1 mole
Then, 22 g of carbon dioxide = 22/44 mole = 0.5 mole
Question 9: What is the mass of:
(a) 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms?
(b) 0.5 mole of water molecules?
Answer:
(a) Mass of one mole of oxygen atoms = 16 g
Then, mass of 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms = 0.2 × 16g = 3.2 g
(b) Mass of one mole of water molecule = 18 g
Then, mass of 0.5 mole of water molecules = 0.5 × 18 g = 9 g
Question 10: Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 16 g of solid sulphur.
Answer:
1 mole of solid sulphur (S8) = 8 × 32 g = 256 g
i.e., 256 g of solid sulphur contains = 6.022 × 1023 molecules
Then, 16 g of solid sulphur contains = 6.022 x 1023 /256 x 16 molecules
= 3.76 × 1022 molecules (approx)
Question 11: Calculate the number of aluminium ions present in 0.051 g of aluminium oxide.
(Hint: The mass of an ion is the same as that of an atom of the same element.
Atomic mass of Al = 27 u)
Answer:
1 mole of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) = 2 × 27 + 3 × 16 = 102 g
i.e., 102 g of Al2O3 = 6.022 × 1023 molecules of Al2O3
Then, 0.051 g of Al2O3 contains = 6.022 x 1023 /102 x 0.051 molecules
= 3.011 × 1020 molecules of Al2O3
The number of aluminium ions (Al3+) present in one molecule of aluminium oxide is 2.
Therefore, the number of aluminium ions (Al3+) present in 3.011 × 1020 molecules
(0.051 g ) of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) = 2 × 3.011 × 1020
= 6.022 × 1020
Question. A piece of zinc (Zn) - a reactive metal - was dropped into a test tube containing hydrochloric acid (HCl). The bubbling in the tube indicated that a gas was released. The gas could be which of these?
(a) Hydrogen H2
(b) Oxygen O2
(c) Methane CH4
(d) Carbon dioxide CO2
Answer : A
Question. The first four compounds in a chemical series are CH4,
C2H6
C3H8
C4H10,
Identify the fifth.
(a) C5H10
(b) C5H12
(c) C6H12
(d) C6H14
Answer : B
Question. What happens to the individual molecules in a vegetable when we eat the vegetable?
(a) Individual molecules are always broken down into their constituent atoms during the digestion proce
(b) Individual molecules are always completely destroyed during the process of eating and digestion
(c) Individual molecules are always unaffected and stay in their original form in our bodies.
(d) Individual molecules may stay unaffected or their atoms may recombine to form different
molecules.
Answer : D
Question. Which of these is/are conserved during a chemical reaction?
(a) mass only
(b) charge only
(c) both mass and charge
(d) neither mass nor charge
Answer : C
Question. The carbon atom forms a part of all the major molecules found in living things. Which of the following does not contain carbon?
(a) DNA
(b) HCl
(c) Plastics
(d) Diesel
Answer : B
Question. Do atoms have colour?
(a) Yes. Atoms have different colours depending on their atomic composition.
(b) Yes. Atoms have different colour depending on the state of substance.
(c) No. All atoms are colourless (that is, they are transparent.)
(d) (The question is meaningless as colour has no meaning at the atomic level)
Answer : D
Question. In 1911, the physicist Ernest Rutherford discovered that atoms have tiny, dense nucleii by shooting positively charged particles at a very thin gold foil, Which physical property of gold was used by Rutherford in his gold leaf experiment?
(a) non corrosive
(b) highly malleable
(c) highly ductile
(d) non reactive
Answer : B
Question. An ion with 13 protons, 14 neutrons, and a charge of 3+ has an atomic number of
(a) 10
(b) 13
(c) 14
(d) 27
Answer : B
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Force and Laws of Motion |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Gravitation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Work and Energy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Sound |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement in Food Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms |
Important Practice Resources for Class 9 Science
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 9 Science textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 9 Science chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 9 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Science Class 9 Solved Papers
Using our Science solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 9 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 9 Science are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Science concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 9 Science. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

