Read and download the CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Wave Optics. Designed for the 2025-26 academic year, these Value Based Questions (VBQs) are important for Class 12 Physics students to understand moral reasoning and life skills. Our expert teachers have created these chapter-wise resources to align with the latest CBSE, NCERT, and KVS examination patterns.
VBQ for Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics
For Class 12 students, Value Based Questions for Chapter 10 Wave Optics help to apply textbook concepts to real-world application. These competency-based questions with detailed answers help in scoring high marks in Class 12 while building a strong ethical foundation.
Chapter 10 Wave Optics Class 12 Physics VBQ Questions with Answers
Question. In Young’s double-slit experiment, if there is no initial phase difference between the light from two slits,a point on the screen corresponding to the fifth minimum has path difference
(a) 5 λ/2
(b) 10λ/2
(c) 9λ/2
(d) 11λ/2
Answer. C
Question. A linear aperture whose width is 0.02 cm is placed immediately in front of a lens of focal length 60 cm.
The aperture is illuminated normally by a parallel beam of wavelength 5 x 10-5 cm. The distance of the first dark band of the diffraction pattern from the centre of the screen is:
(a) 0.20 cm
(b) 0.15 cm
(c) 0.10 cm
(d) 0.25 cm
Answer. B
Question. Two slits in young’s double slit experiment have widths in the ratio 81 :1. The ratio of the amplitudes of light waves is
(a) 3 :1
(b) 3 : 2
(c) 9 :1
(d) 6:1
Answer. C
Question. The colour of bright fringe nearest to central achromatic fringe in the interference pattern with white light will be
(a) violet
(b) red
(c) green
(d) yellow
Answer. B
Question. State essential condition for diffraction of light to take place.
Answer : Size of slit is comparable to the size of wavelength.
Question. The angle between the pass axes of a polarizer and analyser is 45°. Write the ratio of the intensitiesof original light and the transmitted light after passing through the analyser.of original light and the transmitted light after passing through the analyser.
Answer : 1/4
Question. The polarizing angle of medium is 600. What is the refractive index of the medium?
Answer : μ = tan ip = tan 600 = √3 = 1.732
Question. At what angle of incidence should a light beam strike a glass slab of refractive index √3, such that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other?
Answer : ip =tan -1μ = tan-1 (√3) = 600
Question. The refractive index of a material is 1/ √3. What is the angle of refraction if the unpolarised light is incident on it at the polarizing angle of the medium?
Does the poplarising angle for any transparent medium depend on the wavelength of light?
Answer : ip = tan-1 μ = tan-1(1/√3) = 300
, ip + r = 900 therefore r = 600
Question. Does the poplarising angle for any transparent medium depend on the wavelength of light?
Answer : Yes, since ip = tan−1μ = tan−1(λa⁄λm) since μ = λa⁄λm as refractive index depends upon wavelength.
Question. What type of wavefront will emerge from a (i) point source, and (ii) distant light source?
Answer. (i) Point source – Spherical wavefront (ii) Distant light source – Plane wavefront.
Question. In a single slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is reduced to half its original width. How would this affect the size and intensity of the central maximum?
Answer. Β=λD/d=2β ,when d=d/2 Iα(width)2 Hence, I=I/4
Question. Define the term ‘coherent sources’ which are required to produce interference pattern in Young’s double slit experiment.
Answer. Two monochromatic sources, which produce light waves, having a constant Phase difference are defined as coherent sources.
Question. Define the term ‘wavefront’
Answer. The wavefront is defined as the locus of all particles of a medium, which are vibrating in the same phase.
Question. Two independent monochromatic sources of light cannot produce a sustained interference pattern. Give reason.
Answer. The phase difference between the light waves originating from two on dependent monochromatic sources will change rapidly with time. The two sources will not be coherent and therefore will not produce a sustained interference pattern.
TWO MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Why clouds are white?
Answer : The clouds are at much lower heights. They are seen due to scattering of light from lower parts of the atmosphere, which contains large dust particles, water droplets, ice particles etc. all colours scattered equally merge to give us the sensation of white. Hence, clouds appear white.
Question. In Young’s double slit experiment, how is the fringe width altered if the separation between the slits is doubled and the distance between the slits and the screen is halved?
Answer : The fringe width is given by the relation β = λD/d,
Where λ, D and d are the wavelength of light, distance of the screen from the slits and the separation between the slits respectively.
Now, according to the question, d1 =2d and D1 =D/2
Therefore β1 =λD1/d 1 = (λ/2 × 2d) × (β/4) = ( 1/ 4)
Hence, the fringe width decreases to of its value.
Question. A narrow monochromatic beam of light of intensity I is incident a glass plate. Another identical glass plate is kept close to the first one and parallel to it. Each plate reflects 25% of the incident light and transmits the reaming. Calculate the ratio of minimum and maximum intensity in the interference pattern formed by the two beams obtained after reflection from each plate.
Answer : Let I be the intensity of beam I incident on first glass plate.
Each plate reflects 25% of light incident on it and transmits 75%.
Therefore, I1 =I; and I2 = 25/100I = I/4; I3 =75/100 I = 3/4I; I4 = 25/100 I3 = 1⁄4 x 3⁄4 I = 3/16 I
I5= 7/100 I4= 3⁄4 x 3/16 I = 9/64 I
Amplitude ratio of beams 2 and 5 is R = √ I2/I5 = √I/4 x 64/91 = 4/3 Imin/ Imax = [r-1/r+1]2 = [4/3-1 /4/3+1]2 = 1/49 = 1:49
Question. In a two slit experiment with monochromatic light, fringes are obtained on a screen placed at some distance D from the slits. If the screen is moved 5 x 10-2 m towards the slits, the charge in fringe width is 3 x 10 -5 m. If the distance between the slit is 10-3 m. Calculate the wavelength of the light used.
Answer : The fringe width in the two cases will be β = Dλ/d; β ‘= D’λ/d
β - β’ = (D-D’)λ/d;
λ = (β - β’ )d / (D-D’)
But D-D’ = 5 x 10-2 m β - β’ = 3 x 10-5 m , d= 10-3 m;
λ = 3 x 10-5 x 10-3 / 5 x 10-2 = 6 x 10-7m= 6000A
Question. A screen is placed 50m from a single slit, which is illuminated with 6000Å light. If the distance between the first and third minima in the diffraction pattern is 3.00mm, what is the width of the slit?
Answer : Here, D=50 cm = 1⁄2 m, λ =6000Å=6×10-7 m
X=3.00 mm = 3×10-3 m, a=?
For the diffraction minima , a sinθ =nλ, when θ is small
Or ax/D=n λ . . . x=n λ D/a
Now x= x3 -x1 = 3 λ D/a-1λD/a=2λD/a . . . a =2 λ D/x=2×6×10-7 ×1/2/3×10-3 =2×10-4 m
Question. Two boys, on their way from school were discussing seriously about something. They both were blowing soap bubbles and were thrilled to watch the expanding bubble with spectacular colour rings. Shwetha, a class XII student, was watching them for a long time, walking behind them. Suddenly she realised that the kids did not look at the traffic in that junction area. She rushed to them and instructed them to be cautious while on the road. She also explained the importance of traffic rules and told them that obeying traffic rules not only makes us safe but also others safe.
a. What are the values highlighted by Shwetha?
b. Why are colours formed on bubbles?
Answers:
a. obeying road rules, alertness, concern in others’s life, clarity of knowledge.
b. due to superposition of incident and reflected waves of white light by thin film(interference)
Question. Ram and Suresh were going to their friend’s house by walk. It was a sunny day in the afternoon. It was very hot. Ram was finding it very difficult to see around him. He had to strain his eyes to see. Suddenly, Suresh took his cooling glasses from his pocket and asked him to wear them and later, Ram slowly managed to see. Suresh advised Ram on the necessity of wearing sun glasses during summer season.
a. What are the values shown by Suresh?
b. Name the phenomenon based on which cooling glasses reduce the glare.
c. What is the resultant intensity of light if both polariser and analyser are rotated through same angle?
Answers:
a. caring , sharing, concern
b. polarisation
c. no change in intensity of light
Question. Jimmy and Johnny were both creating a series of circular waves by jiggling their legs in water. The waves form a pattern. Their friend, Anitha , advised Jimmy and Johnny not to play with water for a long time. She then observed beautiful patterns of ripples which became very colourful. When her friend Latha poured an oil drop on it. Latha, a 12th standard girl, had explained the cause for colourful ripple patterns to Anitha earlier.
a. Identify any 2 values that could be related with Anitha and Latha?
b. Name the phenomenon involved in the above activity?
c. define wavefront
Answers:
a Caring and affectionate
b.Latha is creative and knowledgble
c.Definition of wavefront.
Question. Somya was watching her mother who was washing clothes. Coloured soap bubbles exciting Somya. She asked her mother as to why the soap bubbles appear coloured. Her mother did not know anything about this. In the evening, she talked with Somya’s father. He also did not know anything. Both father and mother went to a science teacher who lived nearby. The teacher explained everything to Somya’s parents. They were satisfied. They came home and explain everything to Somya. Somya was very happy and she expressed her gratitude to her parents.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Somya’s parents?
(b) Which concept of physics is involved in the formation of colures in soap bubbles?
Answers:
(a) Somya’s parents showed responsibility towards their daughter. They showed initiative in solving the problem.
(b) Interference.
Question. Rupesh often thought as to how the glare is reduced in headlights of automobiles he once talked to his maternal uncle Rajesh about this. Rajesh himself did not know anything about this. Rajesh went to a library and consulted many books. He could finally understand things. When he explained to Rupesh the details, Rupesh was very happy. Rupesh thanked his uncle Rajesh.
(a) What according to you, are the values displayed by Rajesh?
(b) How glare is reduced in headlights of automobiles?
Answers
(a) Rajesh loves his nephew and is ready to “run the extra mile” for his nephew. Rajesh also showed strong will to find out the details.
(b) Polaroids are used in headlights of automobiles to reduced glare.
Question. Kavita accompanied her mother an optician to buy sunglasses. The shopkeeper showed them a vast variety of sunglasses. The price varied from a few hundred to few thousands. The shopkeeper could not satisfactorily explain the vast difference in the prices of various sunglasses. Kavita’s mother postponed the decision to buy sunglasses. Before buying sunglasses, Kavita’s mother wanted to be sure that she gets the best for Kavita. She went to different shops talked to many peoples and finally bought Polaroid sunglasses for Kavita. Kavita was very happy and she thanked her mother for the best buy.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Kavita’s mother?
(b) What is the best about Polaroid sunglasses?
Answers:
(a) Kavita’s mother showed investigative skills. She also showed “perfectionist” attitude. She is a hardworking woman. She is very careful in taking decision.
(b) Polaroid sunglasses drastically red
Question. Laser light of wavelength 640 nm incident on a pair of slits produces an interference pattern in which the bright fringes are separated by 7.2 mm. Calculate the wavelength of another source of light which produces interference fringes separated by 8.1 mm using same arrangement. Also find the minimum value
of the order ‘n’ of bright fringe of shorter wavelength which coincides with that of the longer wavelength.
Answer. Distance between two bright fringes = Fringe width β=λD/d ,for same values of D and d,we get β1/β2=λ1/λ2 Substituting and solving we get ,λ2=720 nm Calculation of minimum value of order for n to be minimum (n + 1)th maxima of shorter wavelength should coincide with nth maximum of longer wavelength (n+1)640= n(720),n=8.Hence minimum order of shorter wavelength is (n+1)=8+1=9
Question. Define the term wavefront. State Huygen’s principle.
Answer. Wave front: Wavefront is locus of all points in which light waves are in same phase. Huygens’ Principle: Each point of the wavefront is the source of a secondary disturbance and the wavelets emanating from these points spread out in all directions. These travel with the same velocity as that of the original wavefront.
Question. Two slits are made 1mm apart and the screen is placed away. What should be the width of each slit to obtain 10 maxima of the double slit pattern within the central maximum of the single slit pattern.
Answer. As per question, width of central maxima of single slit pattern = width of10 maxima of double slit pattern 2λD/a=10(λD/d) a=0.2d , 0.2×10−3=0.2×10−3m=0.2mm
Question. Yellow light (λ = 6000Å) illuminates a single slit of width 1 x 10-4 m. Calculate (i)the distance between the two dark lines on either side of the central maximum, when the diffraction pattern is viewed on a screen kept 1.5 m away from the slit; (ii)the angular spread of the first diffraction minimum.
Answer. (i) Distance between two dark lines, on either side of central maximum is =2λD/a,
Substituting and solving we get,18mm
(ii)Angular spread of the first diffraction minimum (on either side) ϴ=λ/a
Substituting and solving we get ϴ=6x10-3 rad
Question. A parallel beam of light of 500 nm falls on a narrow slit and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1 m away. It is observed that the first minimum is at a distance of 2.5 mm from the centre of the screen. Calculate the width of the slit.
Answer. Path difference for nth minimum is asinϴ=nλ or aϴ=nλ
Also,ϴ=x/D From this we get, ax/D=nλ Substituting and solving we get. a=2x10-4 m
CASE BASED QUESTIONS
1) Refraction of a plane wave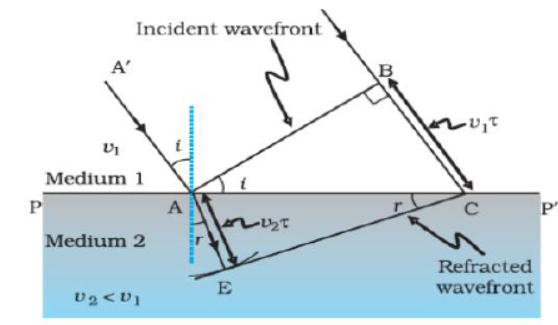
Question. What is the angle made by the ray of light on the wave front?
a) 90˚
b) 0˚
c) 45˚
d) None of the above
Answer. A
Question. Which parameter remains unchanged while a ray of light propagates from one medium to another?
a) velocity
b) Wave length
c) frequency
d) None of the above
Answer. C
Question. According to the above given fig., identify the correct expression for Snell’s law.
a) n1 sin i = n2 sin r
b) n2 sin i = n1 sin r
c) n21 = sin r/ sin i
d) None of the above
Answer. A
Question. When a ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, it
a) it bends towards the normal
b) it travels in a straight line irrespective of angle of incidence.
c) it bends away from the normal
d) None of the above
Answer. C
Question. Which parameter changes while a ray of light propagates from one medium to another?
a) velocity
b) Wave length
c) frequency
d) both a and b
Answer. D
2) Diffraction at a single slit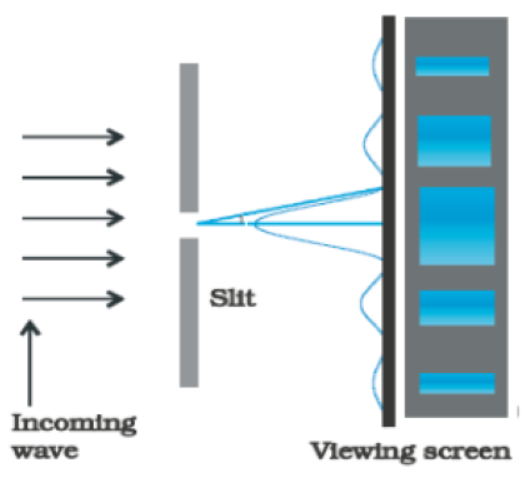
Question. In the phenomena of Diffraction of light when the violet light is used in the experiment is used instead of red light then,
(a) Fringe width increases
(b) No change in fridge width
(c) Fringe width decreases
(d) Colour pattern is formed
Answer. C
Question. Diffraction aspect is easier to notice in case of the sound waves then in case of the light waves because sound waves
(a) Have longer wavelength
(b) Shorter wavelength
(c) Longitudinal wave
(d) Transverse waves
Answer. A
Question. Diffraction effects show that light does not travel in straight lines. Under what condition the concepts of ray optics are vali(d) ( D = distance of screen from the slit).
(a) D < Zf
(b) D = Zf
(c) D > Zf
(d) D << Zf
Answer. D
Question. when 2nd secondary maxima is obtained in case of single slit diffraction pattern, the angular position is given by
(a) λ
(b) λ/2
(c) 3λ/2
(d) 5λ/2
Answer. D
Question. intensity of secondary maxima in diffraction has
(a) same intensity as central maxima
(b) less intensity than central maxima
(c) more intensity than central maxima
(d) None of these
Answer. C
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Electric Charges and Fields |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Potential and Capacitance |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Current Electricity |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Effect Of Current and Magnetism |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Magnetism and Matter |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Electromagnetic Induction |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Alternating Current |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Electromagnetic Waves |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Ray Optics |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Wave Optics |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Atoms and Nuclei |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Nuclei |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Semiconductor Devices |
| CBSE Class 12 Physics VBQs Communication System |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
VBQs for Chapter 10 Wave Optics Class 12 Physics
Students can now access the Value-Based Questions (VBQs) for Chapter 10 Wave Optics as per the latest CBSE syllabus. These questions have been designed to help Class 12 students understand the moral and practical lessons of the chapter. You should practicing these solved answers to improve improve your analytical skills and get more marks in your Physics school exams.
Expert-Approved Chapter 10 Wave Optics Value-Based Questions & Answers
Our teachers have followed the NCERT book for Class 12 Physics to create these important solved questions. After solving the exercises given above, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 12 Physics and read the answers prepared by our teachers.
Improve your Physics Scores
Daily practice of these Class 12 Physics value-based problems will make your concepts better and to help you further we have provided more study materials for Chapter 10 Wave Optics on studiestoday.com. By learning these ethical and value driven topics you will easily get better marks and also also understand the real-life application of Physics.
The latest collection of Value Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter Chapter 10 Wave Optics is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These questions are as per 2026 academic session to help students develop analytical and ethical reasoning skills.
Yes, all our Physics VBQs for Chapter Chapter 10 Wave Optics come with detailed model answers which help students to integrate factual knowledge with value-based insights to get high marks.
VBQs are important as they test student's ability to relate Physics concepts to real-life situations. For Chapter Chapter 10 Wave Optics these questions are as per the latest competency-based education goals.
In the current CBSE pattern for Class 12 Physics, Chapter 10 Wave Optics Value Based or Case-Based questions typically carry 3 to 5 marks.
Yes, you can download Class 12 Physics Chapter Chapter 10 Wave Optics VBQs in a mobile-friendly PDF format for free.

