Read and download the CBSE Class 11 Economics Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet Set B in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 11 Economics worksheets for Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 11 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours
Students of Class 11 should use this Economics practice paper to check their understanding of Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 11 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet with Answers
CASE STUDY-1
Absolutely not. True, 30 years ago the Indian and Chinese economies were roughly of the same sizes. And it’s also a fact that both countries have similarly large populations. But that’s where the comparisons end. India in 1947 and China in 1949 chose two very different paths. India went the secular democracy way, while China embarked on the road to Communism with Chinese characteristics. Seventy years later, China is a veritable superpower and has lifted 300 million people out of poverty. In contrast, India is a rising middle-power that has made comparatively moderate yet significant achievements in the various development sectors.
Questions:
Question: China introduced reform in the year ______ (1978/1979) and India introduced reforms in the year ______ (1991/1992).
Answer: 1978, 1991
Question: ________ (China/India) has more population living in urban areas.
Answer: China
Question: India has higher share of __________ (service/agriculture) than China in the GVA.
Answer: Agriculture
Question: Dual pricing model was introduced in ___________ (China/India) .
Answer: China
CASE STUDY-2
In 1950, Pakistan’s per person GDP was US$1268, which was almost 50 per cent greater than India that year. However, in the backdrop of sustained political uncertainty and upheaval, Pakistan stagnated throughout the 1950s while a politically stable India grew. As a result, by 1960, India had almost caught up with Pakistan in per capita GDP terms with the per capita income gap having shrunk to 15 per cent. Unfortunately, from 1964, India went into two decades of economic stagnation while Pakistan, under the military rule of Ayub Khan, opened up to foreign capital which funded a period of rapid industrialisation and economic growth, albeit at the cost of worsening inequality. By 1984, Pakistan’s per capita income was more than double that of India’s. Pakistan’s slowdown began in the 1980s during the military regime of Zia-u-Haq. Zia enabled and institutionalised Islamic nationalism in Pakistan.
Questions:
Question: What led to downfall of Pakistan economy after 1950?
Answer: Political Uncertainty.
Question: What were the reasons for economic stagnation of India in late 1960’s?
Answer: inward-looking,
Question: Openness to trade and private enterprise usually has positive effects on growth (T/F)
Answer: True
Question: What was the main reason of growth of Pakistan during 1980’s?
Answer: Foreign funding.
CASE STUDY-3
China has been the fastest growing economy in the world since the 1980s, with an average annual growth rate of 10% from 1978 to 2005, based on government statistics. Its GDP reached $USD 2.286 trillion in 2005. Since the end of the Maoist period in 1978, China has been transitioning from a state dominated planned socialist economy to a mixed economy. This transformation required a complex number of reforms in China’s fiscal, financial, enterprise, governance and legal systems and the ability for the government to be able to flexibly respond to the unintended consequences of these changes. Thistransformation has been accompanied by high levels of industrialization and urbanization, a process that has influenced every aspect of China’s society, culture and economy.
Questions:
Question: Reforms in China were introduced in the year _______________.
Answer: 1978
Question: Which type of economic system is followed in China?
a) Mixed economy
b) Socialist economy
c) Capitalist economy
d) None of these
Answer: B
Question: Name the sectors where reforms were initiated in the initial phase in China.
Answer: Agriculture, foreign trade& investment sectors
Question: In the late phase, enterprises owned by the government were made to face competition. (T/F)
Answer: True
CASE STUDY-4
In most areas of human development, China has performed better than India and Pakistan. This is true for many indicatorsper Capita GDP or proportion of population below poverty line, health indicators such as mortality rates, access to sanitation, literacy, life expectancy or malnourishment etc. Pakistan is ahead of India in reducing proportion of people below the poverty line and also its performance in transferring labour force from agricultural sector to industrial sector and access to water is better than India. Contrary to it, India is ahead of Pakistan in education sector and providing health services.India and Pakistan are ahead of China in providing improved water sources.
Questions:
Question: Pakistan is ahead of India in ________ proportion of people below the poverty line. (reducing /increasing)
Answer: Reducing
Question: India is ahead of Pakistan in _________ sector and providing health services. (service /education)
Answer: Education
Question: India and Pakistan are ahead of China in providing _______ water sources. (deteriorate/better)
Answer: Deteriorate
Question: Mortality rate is also known as __________ . (birth rate/death rate)
Answer: Death rate
CASE STUDY-5
The 1960s, Chinese Communist Party leader Mao Zedong came to feel that the current party leadership in China, as in the Soviet Union, was moving too far in a revisionist direction, with an emphasis on expertise rather than on ideological purity. Mao’s own position in government had weakened after the failure of his “Great Leap Forward” (1958-60) and the economic crisis that followed. Chairman Mao Zedong gathered a group of radicals, including his wife Jiang Qing and defense minister
Questions:
Question: The Great Leap Forward (GLF) campaign initiated in _____.
Answer: 1958
Question: Great Leap Forward (GLF) campaign:
a) aimed at trading on a massive scale
b) aimed at agriculture on a massive scale
c) aimed at industrialising the country on a massive scale
d) None of the above.
Answer: C
Question: Who introduced the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution?
Answer: In 1965 – Mao
Question: In the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution (1966–76) under which students and professionals were sent to work and learn from the countryside. (State whether true or false)
Answer: True
CASE STUDY-6
The basic reason for fast industrial growth in China can be traced back to the reforms introduced in phases 1978. China introduced reforms in phases. In the initial phase, reforms were initiated in in agriculture, foreign trade and investment sectors. In agriculture, commune lands were divided into small plots which were allocated (only for use and not as ownership) to the individual households. They were allowed to keep all income from the land after paying stipulated taxes. In the later phase, reforms were initiated in the industrial sector. Private Sector firms and township and village enterprises (enterprises which were owned and opened and operated by local collectives) were allowed to produce goods . At this stage, enterprises owned by government (known as State owned Enterprises or SOEs), were made to face competition.
Questions:
Question: Which type of economic system is followed in China?
a) Mixed Economy
b) Socialist Economy
c) Capitalist Economy
d) None of these
Answer: B
Question: Arrange the following events of China in chronological order and choose the correct alternative.
(i) Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
(ii) Great Leap Forward Campaign
(iii) Introduction of Economic Reforms
(iv) First Five Year Plan
a) ii, iv, iii, i
b) iv, ii, i, iii
c) ii, iv, i, iii
d) iv, i, ii, iii
Answer: B
Question: Name the other two reforms initiated by china other than the one mentioned in above extract.
Answer: Dual pricing and SEZ’s
Question: Which sector of the economy contributes the highest to China’s GDP?
Answer: Secondary sector
CASE STUDY-7
Human Development is a process of widening people’s choices as well as raising the level of well being achieved. HDI is regarded a very important indicator in this context. It measures the average achievements in three basic dimensions of human development are : a long and healthy life as measured by life expectancy at birth, knowledge as measured by adult literacyrate, A decent standard of living as measured by per capita GDP. HDI makes rating of different countries on a scale of 0,which represents lowest human development and 1 which represents hoighest human development.
Questions:
Question: What do you mean by HDI?
Answer: HDI is a process of widening people’s choices as well as raising the level of well being achieved.
Question: Who released Human Development Report and on what basis?
Answer: UNDP released Human Development report on basis of ranking of countries.
Question: Give three dimensions of HDI.
Answer: Three dimensions of HDI are
a) Life expectancy
b) Literacy rate
c) standard of living measured by per capita GDP.
Question: What is current ranking of INDIA acc. to HDI?
Answer: India has ranked 131 on the Human Development Report 2020 prepared by the United Nations Development programme.
CASE STUDY-8
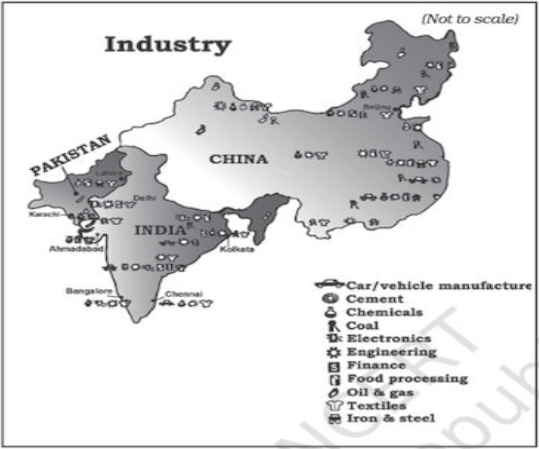
Questions:
Question: Which country has largest land area.
Answer: China
Question: Which country has largest density of population.
Answer: India
Question: Which country has higher contribution to GDP through industry?
Answer: China
Question: Which country has better HDI – India or Pakistan?
Answer: India
CASE STUDY-9
China traditionally has struggled to feed its large population. Even in the twentieth century, famines periodically ravaged China’s population. Great emphasis has always been put on agricultural production, but weather, wars, and politics often mitigated good intentions. With the onset of reforms in the late 1970s, the relative share of agriculture in the gross domestic product (GDP) began to increase annually. Driven by sharp rises in prices paid for crops and a trend toward privatization in agriculture, agricultural output increased from 30 percent of GDP in 1980 to 33 percent of GDP by 1983. Since then, however, agriculture has decreased its share in the economy at the same time that the services sector has increased. By 2004 agriculture (including forestry and fishing) produced only 15.2 percent of China’s GDP but still is huge by any measure. Some 46.9 percent of the total national workforce was engaged in agriculture, forestry, and fishing in 2004.
Questions:
Question: Relative share of agriculture in the GDP started to increase after reforms as small plots were allocated to individuals (T / F)
Answer: True
Question: The proportion of workforce in agriculture reduced and __________sector increased.
Answer: service
Question: Give one reason why the total cultivable area in China is less.
Answer: Topographic and Climatic condition
Question: When was reforms introduced in China?
Answer: 1978
CASE STUDY-10
On the basis of individual indices of these parameters, a Human Development Index (HDI) was constructed. … The rankings are accorded to the countries as per their HDI. China ranked 81, India 128th and Pakistan 136th. High ranking of China is due to the higher GDP per capital. In World Bank’s ease of doing business ranking 2020, Pakistan stands at 108 position while India is placed higher at the 63rd spot. India’s post-independence journey began as an agrarian nation. However, the manufacturing and services sector have emerged strongly over the years. The service sector is the fastestgrowing sector, contributing to more than 60 per cent to its economy and accounting for 28 per cent of the employment.
Questions:
Question: China’s growth is mainly attributed to _________ sector and India’s growth is led by ________ sector.
Answer: Manufacturing, service
Question: Structure of country’s growth refers to relative significance of different sectors of economy in terms of _____ and _____.
Answer: Output and Employment
Question: Mention any one similarity in the economic policies of India and Pakistan.
Answer: Heavy reliance on public sector and substantial expenditure on social development.
Question: _______ is prepared by UNDP on the basis of parameters like longevity, educational attainment, per capita real GDP etc.
Answer: Human Development Index (HDI)
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Indian Economy On The Eve Of Independence Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Indian Economy On The Eve Of Independence Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Economic Indian Economy Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Economic Indian Economy Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Economic Indian Economy Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Topic Economic Reforms Since 1991 Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Human Capital Formation In India Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Human Capital Formation In India Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Rural Development Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Rural Development Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Sustainable Development Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Sustainable Development Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Introduction To Statistics Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Collection Of Data Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Organization Of Data Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Presentation Of Data Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Measure Of Central Tendency And Positional Values Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Measures of Correlation Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Index Numbers Worksheet |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Economics
CBSE Economics Class 11 Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 11. We suggest that Class 11 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Economics.
Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 11 Economics to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Economics to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 11 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 11 Economics study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11 Economics. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 11 Economics Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 11 Economics worksheets for Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 11 Economics Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 11 Economics test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

