Read and download the CBSE Class 11 Economics Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet Set B in PDF format. We have provided exhaustive and printable Class 11 Economics worksheets for Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues, designed by expert teachers. These resources align with the 2025-26 syllabus and examination patterns issued by NCERT, CBSE, and KVS, helping students master all important chapter topics.
Chapter-wise Worksheet for Class 11 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues
Students of Class 11 should use this Economics practice paper to check their understanding of Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues as it includes essential problems and detailed solutions. Regular self-testing with these will help you achieve higher marks in your school tests and final examinations.
Class 11 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet with Answers
CASE STUDY-1
Over the last for decades, there has been considerable shift of workforce from self –employed and regular salaried employment to casual wage work .Scholars termed this process of movement from self employment and regular salaried employment to casual work as Casualisation of workforce. Although self employment continues to be the major employment provider, but its share is declining and the share of casual workers in employment is increasing.
Questions:
Question: Define casualisation of workforce.
Answer: The process of movement from self employment regular salaries to casual wage work is casualisation of workforce.
Question: Casual worker get lower _______.
Answer: Incomes
Question: Which is share is major in employment? (Self Employment and Casual Worker)
Answer: Casual Worker
Question: Give two reasons of casualisation of workforce.
Answer: Reasons:
(i). Slow growth of employment in organized sector.
(ii). Decreasing scope of earnings from agricultural activities
CASE STUDY-2
Mohan lived in a joint family. As he grew up, he started working with his father, uncles and cousins in their farm. They worked and earned well but Mohan thought that the people working on the farm were more than what were actually required. He moved to the city soon after, he did not get a job because he did not have the required degree. He enrolled himself in a college where he studied hard and after that, he got a well paid job, he felt satiated.
Questions:
Question: In the first part, which type of unemployment is being reflected?
Answer: Disguised unemployment
Question: Due to which type of urban unemployment, Mohan could not get a job?
Answer: Lack of skill and education
Question: __________ is a situation in which a worker does not get a full time job.
Answer: Unemployment
Question: State whether the following is true or false:
“Cyclic unemployment occurs due to imperfections in the mobility of labour across different occupations.”
Answer: False
CASE STUDY-3
In the course of economic development of a country, labour flows from agriculture and other related activities to industry and services. In this process, workers migrate from rural to urban areas. Eventually, the industrial sector begins to lose its share of total employment as the service sector enters a period of rapid expansion. In the last four decades, people have moved from self-employment to casual wage work. Yet, self-employment continues to be the major employment provider. Scholars calls the process of moving from self-employment and regular salaried employment to casual wage work as casualization of workforce. This makes workers highly vulnerable.
Questions:
Question: The newly emerging jobs are mostly found in the _________ sector.
Answer: Service
Question: __________ of workforce is moving from self-employment and regular salaried employment to casual wage work.
Answer: Casualisation
Question: An establishment, with four hired workers is known as ____________.
Answer: Informal
Question: The construction workers are known as __________.
Answer: Casual wage labourers
CASE STUDY-4
Unemployment is a very serious issue not only in India but in the world .There are hundreds and thousands of people out there who do not have employment.Besides the problem of unemployment are very severe in India because of the growing population and demand for jobs. More over, if the country neglect this problem then it will be going to become the reason for the doom of the nation. Unemployment refers to a situation in which skilled and talented people wanted to do a jobs but cannot find the proper job due to several reasons for various type of unemployment in the country including disguised unemployment, open unemployment, technological unemployment and seasonal unemployment etc. Worker population ratio s an indicator which is used for analysing the employment situation in the country. ln India the proportion of work force in the formal Sector to total workforce is very high population growth slow economic growth ,seasonal occupation, slow growth of economic sector and fall in the cottage industry are major reason for unemployment in India in last portion of the population is engaged in the agriculture sector and the sector provides employment in harvest or plantation time only.
Questions:
Question: The proportion of population that is actively contribute to the production of goods and service of a country is called___________. (Worker population/Head count ratio)
Answer: Worker population ratio
Question: _____________ (Disguised/Open)unemployment is a kind of unemployment in which there are people who are visibly employed but are actually unemployed.
Answer: Disguised
Question: __________ (Agriculture/service) sector is a major source of liveli hood for Indian workers.
Answer: Agriculture
Question: _____________ (Casualisation/Brain drain) of workforce is the process of moving from self employment and regular salaries employment to unorganized wage work.
Answer: Casualisation
CASE STUDY-5
In urban areas, the workforce participation rate is about 30% whereas in rural India, it is about 40%. The reason is that people in rural areas have limited resources to earn a higher income and participate more in the employment market. Many do not go to schools, colleges and other training institutions. In rural India, people cannot stay at home as their economic condition may not allow them to do so.
Questions:
Question: ___________ is a major source of livelihood for both men and women as this category accounts for more than 50%.
(a) Self employment
(b) Casual wage labour
(c) Regular salaried employment
(d) none of these
Answer: A
Question: ____________ is the main source of employment for majority workers in India. (Primary sectors/ Secondary sectors)
Answer: Primary sectors
Question: Informal sectors include all those private enterprises which hire less than 10 Workers. (True / False)
Answer: True
Question: Why in urban areas, the workforce participation rate is less than rural areas ?
Answer: In rural areas, people cannot stay at home as their economic condition do not allow them.They do not have a variety of mployment opportunities so they are ready to work in primary sectors even at low wages.
CASE STUDY-6
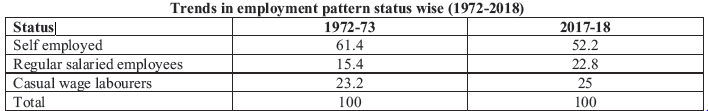
Questions:
Question: Compare the trends in employment pattern status wise
Answer: People have moved from self employment and regular salaried jobs to casual workers. Self employment is maximum.
Question: Define term casualisation.
Answer: The process in which the percentage of casually hired workers in the total work force tends to rise over time.
Question: What does above trend is indicating?
Answer: above trend is indicating moving of self employed and regular salaried employment to casual wage work.
Question: Supply of labour can increase or decrease even when the number of workers remains constant.(True/ False)
Answer: True
CASE STUDY-7
India’s unemployment rate stood at 7.8% for the week ended November 22 and the labour participation rate at 39.3% resulting in a sharp fall in employment rate at 36.24%. While this is a sign of weakening labour markets over the last four week, it also reflects the inability of the labour markets to absorb adequate proportions of the working age population during the festive season of 2020.
Questions:
Question: What is meant by unemployment?
Answer: Unemployment refers to a situation in which people are able and willing to work at the existing wage rate but do not get work.
Question: Who all are included in labour force?
Answer: All persons, who are working and though not working, are seeking and are available for work, are deemed to be in the labour force.
Question: Define worker-population ratio.
Answer: Worker-population ratio is the percentage of total population engaged in work.
Question: Higher worker-population ratio indicates that less people are involved in economic activities. (T/F)
Answer: False
CASE STUDY-8
G D P growth in India happens to be faster than employment growth. In other words, even when production activity is expanding, job opportunities continue to be low. This is a situation of ‘jobless growth’. This occurs when we rely more and more on labour-saving western technology. Such a technology (using more of capital and less of labour) does not suit the needs and means of country where unemployment is an alarming social challenge. But, given the fact that the country lacks investment capital, we are forced to depend more and more on FDI (foreign direct investment). Foreign investment in India is linked with foreign technology which is efficient but the one which uses less and less of labour.
Questions:
Question: Reliance on FDI cannot be_____________ (minimized/maximized).Implying that the reliance on labour-saving western technology cannot be _____________ (minimized/ maximized).
Answer: Minimized, minimized
Question: Using more of capital and less of labour does not suit the needs and means of country where unemployment is an alarming social challenge. (True/False)
Answer: True
Question: Define jobless growth.
Answer:G D P growth in India happens to be faster than employment growth. In other words, even when production activity is expanding, job opportunities continue to be low. This is a situation of ‘jobless growth’
Question: (Foreign investment / Landlords) ____________ in India is linked with foreign technology which is efficient but the one which uses less and less of labour.
Answer: Foreign investment
CASE STUDY-9
Economic Survey 2020: The survey said the number of self-employed, regular wage earners and casual labourers have come down by 17 lakh in six years till 2017-18. Quoting various government sources, it pegged India’s workforce at 47.12 crore in FY18 compared with 47.29 crore in FY12, even as employment was getting more formal in nature. There was also a drop in female employment in the overall job space. From 12.91 crore in 2011-12, their number came down to 10.85 crore in 2017-18. Stressing on the need to set things right, the survey said, “In an era of globalisation, no country can develop and achieve its full potential if half of its population is locked in non-remunerative, less productive and noneconomic activities”. The survey also found that the number of self-employed people, too, came down during the period to 24.21 crore from 24.54 crore; but that is mostly due to a significant drop in the number of ‘unpaid family labour’ category.
Questions:
Question: A situation where percentage of workforce in the formal sector tends to decline and that in the informal sector tends to rise is known as:
(a) Informalisation
(b) Casualisation
(c) Jobless growth
(d) none of these
Answer: A
Question: An arrangement where a worker uses his own resources to make a living is known as:
(a) Wage employment
(b) Regular employment
(c) Casual employment
(d) Self employment
Answer: D
Question: All non-farm casual wage labourers who work for more than one employer such as construction workers and head-load workers are _______ . (formal/informal) sector workers.
Answer: informal
Question: Less employment of females in comparison to males is an indication of:
(a) Economic backwardness
(b) Social backwardness
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer: B
CASE STUDY-10
In urban areas, the worker-population ratio is about 36 whereas in rural India, the ratio is about 40. People in rural areas have limited resources to earn a higher income and participate more in the employment market. Many do not go to schools, colleges and other training institutions. Even if some go,they discontinue in the middle to join the workforce. People cannot stay at home as their economic condition may not allow them to do so.
Questions:
Question: The number of persons employed per hundred persons is termed as:
a) Worker- population ratio.
b) Head- Count ratio.
c) Capital-Gain ratio.
d) Legal reserves ratio.
Answer: A
Question: In Urban areas, the Worker-population ratio is about______ whereas in rural Indian, the ratio is about _____
Answer: 36,40
Question: Women workers account for———— of the rural workforce;whereas in urban areas, they are just __________ of the workforce.
Answer: one third, one fifth
Question: The worker- population ratio in rural India is higher than that in Urban areas. Give reason.
Answer: People in rural areas have limited resources to earn a higher income. So they participate more in the employment market.
Learning Objectives:-
1. Introduction
2. Basic Concepts
a. Meaning of worker
b. Labour force and work force
c. Meaning of employment
d. Wage employment
e. Regular workers(Regular Salaried employees)
f. Casual Workers
3. Participation of people in employment
a. Worker-population ration on the basis of region
b. Distribution of employment by gender
c. Distributions of employment by region
d. Distributions of employment in different sectors
e. Distributions of rural-urban employment in different sectors
4. Growth of employment and Gross Domestic Product(GDP)
5. Changing structure of employment
a. Casualization of work force.
6. Informalisation of Indian workforce
a. Formal or Organized sector.
b. Informal or unorganized sector.
Worker: A worker is an individual who is involved in some productive activities to earn a living.
Who and all included in workers?
It is not only people those who are paid workers also includes self-employed people like shopkeepers, barbers, cobblers etc.. Workers include all those people who are engaged in work whether for others (paid workers or self-employed)
Difference between labour force and work force?
Labour Force: All persons, who are working (who have a job) and though not working, are seeking and are available for work, are dram to be in the labour force.
Question. Why do people work?
Answer. People work for earning a living which helps them and their families to survive.
Question. Who all are included in labour force?
Answer. All persons, who are working (have job) and though not working, are seeking and are available for work, are deemed to be in the labour force.
Question. Who is worker?
Answer. A worker is an individual, who is involved in some productive activity, to earn a living.
Question. why are regular salaried employees more in urban areas than in rural areas?
Answer. Regular salaried employees are more in urban areas as considerable section of urban people are able to study in various educational institution and it enables them to look for an appropriate job to suit their qualifications and skills. However, in rural areas, most of the people are illiterate and lack skills, which are needed for regular Employment.
Question. What is meant by Employment?
Answer: Employment is an activity which enables a person to earn means of living.
Question. Are the following workers- a beggar, a thief, a smuggler, a gambler? Why?
Answer. No, They are not workers because they are not doing any productive activity.
Question. Who is a Casual Wage Labourer?
Answer. Workers who are not hired by their Employers on a regular or permanent basis (i.e. do not have job security) and do not get social security benefits, are termed as casual wage labour.
Question. Why do we differentiate between Economic activity and production activity?
Answer. We differentiate between Economic activity and production activity to calculate the number of workers. People engaged only in production Economic activities are to be included in the category of workers.
Question. Define jobless growth?
Answer. Jobless growth refers to a situation when the Economy is able to produce more goods and service without a proportionate increase in Employment opportunities.
Question. Give the meaning of work force.
Answer. The number of persons, who are actually employed at a particular time are known as work force.
Question. What is meant by seasonal unemployment?
Answer. Unemployment that occurs at certain seasons of the year is known as Seasonal unemployment.
Question. What is meant by Casualisation of work force?
Answer. The process of moving from Self- Employment and regular salaried employment to casual wage work is known as Casualisation of Workforce.
Question. Who are regular workers?
Answer. Workers who are hired by their employers on a permanent basis and also get social security benefits (like pension, provident fund, etc.) are higher in regular workers.
Question. Why is the Self – Employed work force higher in rural areas?
Answer. In case of rural areas, Self Employed Workers are greater as majority of rural people are engaged in farming on their own plots of land.
Question. Compared to urban women, more rural women are found working. Why?
Answer. More rural women are found working because of their poor economic condition as compared to urban women.
Question. Why does rural work force migrate to urban areas during some part of the year?
Answer. people in rural areas are engaged mostly in agriculture, which is a seasonal activity. So, rural workforce migrates to urban areas during some part of the year.
Question. Name the two kinds of urban unemployment.
Answer.1. Industrial unemployment
2. Educated unemployment.
Question. What do you mean by Informal sector Establishment?
Answer. All those private enterprises which hire less than 10 workers are called Informal sectors.
Eg: Workers who work in farms, owners of Small Enterprises, Agriculture labourers. Here they do not get regular income. No protection or regulation by government can be dismissed at any time. Live in slums, use outdated technology, do not maintain accounts.
Question. Give the meaning of disguised unemployment.
Answer. Disguised unemployment refers to a state in which more people are engaged in work than are really needed.
Question. What do you mean by industrial unemployment?
Answer. It refers to the unemployment among the illiterates who wish to work in industrial establishment
Question. What is meant by wage employment?
Answer. An arrangement in which a worker sells his labour and earns wages in return.
Question. What is worker population ratio? How do we calculate Worker population ratio? What is its use?
Answer. WPR refers to participation of people in the employment. It is measured by calculating
Total number of workers in India
WPR = _________________________ x 100
No. of work population In India
It helps in knowing the proportion of population that is actively contributing to the production of goods and services of a country.
Question. what is meant by labour force participation rate?
Answer. The ratio of labour force to total participation is called labour force participation rate.
Question. Give the meaning of educated unemployment.
Answer. Educated unemployment refers to the unemployment among the Educated people.
Work forces: The number persons who are actually employed at a particular time are known as work force.
– What is the labour force participation rate?
The ratio of labour force to total population is called labour force participation rate.
– How can we calculate number of unemployed people?
Unemployed people = labour force – Work force.
Meaning of Employment
Employment is an activity which enables a person to earn his means of living.
Full employment
Full employment is a situation in which all the workers who are capable of working and willing to work get an employment at a prevailing wage rate.
Self-employment
When the worker uses his own resources to work and make a living then we call it as Self Employment.
Question. What do you mean by full employment?
Answer. Full employment refers to a situation in which all the workers who are capable of working and willing to work get an Employment in prevailing wage rates.
Question. Give the meaning of self-employment.
Answer. An arrangement in which a worker used his own resources, to make a living is knowing as self-employment.
Question. Define worker – population ratio.
Answer. Worker- population ration is the percentage of total population engaged in work.
Question. What is information of workforce?
Answer. Informalisation of workforce refers to a situation whereby the proportion of workforce in the informal sector to total workforce increases.
Question. Men are found in greater proportion than women in regular salaried employment. Why?
Answer. Rural unemployment is of two types:-
1. Disguised unemployment
2. Seasonal unemployment
Question. What do you mean by formal sector establishment?
Answer. All the public enterprises and private establishments, which Employ 10 or more hired workers are called formal sector establishments.
Question. What is meant by frictional unemployment?
Answer. Temporary unemployment, which exists during the period, wherein. Workers leave one role and join some other, are called frictional unemployment.
People those who are not working and are neither seeking nor available for work are consider to be outside the labour force.
Labour force = Person’s working + Persons seeking & available for work.
After 66 years & below 15 years not included labour force. A handicapped person not included. People those who are not interested not included. People are not available not included.
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Indian Economy On The Eve Of Independence Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Indian Economy On The Eve Of Independence Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Economic Indian Economy Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Economic Indian Economy Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Economic Indian Economy Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Topic Economic Reforms Since 1991 Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Human Capital Formation In India Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Human Capital Formation In India Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Rural Development Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Rural Development Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Sustainable Development Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Sustainable Development Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Comparative Development Experiences Of India and Its Neighbours Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Introduction To Statistics Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Collection Of Data Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Organization Of Data Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Presentation Of Data Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Measure Of Central Tendency And Positional Values Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Measures of Correlation Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 11 Economics Index Numbers Worksheet |
More free study material for Economics
CBSE Economics Class 11 Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Worksheet
Students can use the practice questions and answers provided above for Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues to prepare for their upcoming school tests. This resource is designed by expert teachers as per the latest 2026 syllabus released by CBSE for Class 11. We suggest that Class 11 students solve these questions daily for a strong foundation in Economics.
Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues Solutions & NCERT Alignment
Our expert teachers have referred to the latest NCERT book for Class 11 Economics to create these exercises. After solving the questions you should compare your answers with our detailed solutions as they have been designed by expert teachers. You will understand the correct way to write answers for the CBSE exams. You can also see above MCQ questions for Economics to cover every important topic in the chapter.
Class 11 Exam Preparation Strategy
Regular practice of this Class 11 Economics study material helps you to be familiar with the most regularly asked exam topics. If you find any topic in Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues difficult then you can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11 Economics. All revision sheets and printable assignments on studiestoday.com are free and updated to help students get better scores in their school examinations.
You can download the latest chapter-wise printable worksheets for Class 11 Economics Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues for free from StudiesToday.com. These have been made as per the latest CBSE curriculum for this academic year.
Yes, Class 11 Economics worksheets for Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues focus on activity-based learning and also competency-style questions. This helps students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
Yes, we have provided solved worksheets for Class 11 Economics Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues to help students verify their answers instantly.
Yes, our Class 11 Economics test sheets are mobile-friendly PDFs and can be printed by teachers for classroom.
For Chapter Indian Economic Development Chapter 6 Employment Growth Informalisation and other Issues, regular practice with our worksheets will improve question-handling speed and help students understand all technical terms and diagrams.

