Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 12 Political Science. Our expert-created answers for Class 12 Political Science are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science
For Class 12 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 12 Political Science solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power NCERT Solutions PDF
Question: Arrange the following in chronological order:
(a) China’s accession to WTO
(b) Establishment of the EEC
(c) Establishment of the EU
(d) Birth of ARF
Answer: (b)
Question: The ASEAN WAY:
(a) Reflects the lifestyle of ASEAN members.
(b) A form of interaction among ASEAN members that is informal and cooperative.
(c) The defence policy followed by the ASEAN members.
(d) The road that connects all the ASEAN members.
Answer: (b)
Question: Which of the following is a supranational organisation?
(a) ASEAN
(b) SAARC
(c) EU
(d) EEC
Answer: (c)
Question: Who among the following adopted on open door Policy?
(a) China
(b) EU
(c) Japan
(d) USA
Answer: (b)
Question: The Currency Union is-
(a) Dollar
(b) Rupees
(c) Euro
(d) Yuan
Answer: (c)
Question: The OEEC was established in -
(a) 1946
(b) 1977
(c) 1948
(d) 1949
Answer: (c)
Question: Which of the following is not the founder member of ASEAN?
(a) Indonesia
(b) Malaysia
(c) India
(d) Thailand
Answer: (c)
Fill in the Blanks:
Question:The border conflict between China and India in 1962 was principally over……..and……..region.
Answer: Arunachal Pradesh , Aksai Chin,
Question: ARF was established in the year……..
Answer: 1994
Question: China entered into bilateral relations with ………(a major country) in 1972.
Answer: the US
Question: ………..plan influenced the establishment of the organisation for European Economic Cooperation in 1948.
Answer: Marshall
Question:……….. is the organisation of ASEAN that deals with security.
Answer: Asian Regional Forum
Question: _______________ is the organisation of ASEAN that deals with security.
Answer: ARF
Question: China entered in to bilateral relations with _______________ (a major country) in 1972.
Answer:India
Very short answer type question:
Question: What are the objectives of establishing regional organisations?
Answer: The regional organisations are established with the following objectives:
1. To make regional development at par the fast growing global economy.
2. To accelerate economic growth through the social progress and cultural development.
3. To promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of United Nations Charter.
Question: What led to the establishment of „ASEAN??
Answer: Efforts at Asian and third world unity such a Bandung Conference and the Non Aliged movement were ineffective in establishing the conventions for informal cooperation and interaction, Hence, the Southeast, Asian nations sought an alternative by establishing the Association for South East Asia Nations (ASEAN).
Question: What are the components of „ASEAN? vision 2020?
Answer: „ASEAN? is rapidly growing in to a very important regional organisation. Its vision 2020 has defined an outward looking role for „ASEAN? in the international community. This builds on the existing ASEAN policy to encourage negotiation over conflicts in the region. Thus ASEAN has mediated the end of the Cambodian conflict the east Timor crisis and meets annually to discuss East ASEAN cooperation.
Question: Name the pillars and the objective of Asian Community?
Answer: Indonesia, Malaysia the Philippines Singapore and Thailand are the pillars of the ASEAN Community. The objectives of ASEAN were primarily to accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development. A secondary objective was to promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations charter.
Question: What is unique about „ASIAN??
Answer: There is little desire in Asian for supranational structure and institutions. ASEAN countries have celebrated. What has become known as the „ASEAN WAY?, a form of interaction that is informal, non-confrontationist and co-operative? The respect for national sovereignty is critical to the functioning of ASEAN.
Question: What was the marshal plan?
Answer: Under the marshal plan, the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was established in 1948 to channel aid to the West European States. It becomes a forum where the Western European States began to cooperate on trade and economic issues.
Question: Name of the countries which established ASEAN?
Answer: ASEAN was established in 1967 by five countries of this region – Indonesia, Malaysia the Philippines Singapore and Thailand by singing the Bangkok Declaration.
Question: Though the Chinese ecomo my has improved dramatically there are areas where development is still to reach mention those areas?
Answer: (i) unemployment has Rison in china with nearly 100 million people looking for jobs.
(ii) Female employment and conditions of work are very bed.
(iii) Corruption has increased.
(iv) Environmental degradation have increased.
(v) There is a rise in economic inequality between rural and urban residents and coastal and inland provinces.
Question: Write about the relations between India and ASEAN?
Answer: During the cold war year?s Indian foreign policy did not pay adequate attention to „ASEAN?. But in recent years, India has tried to make amends. It signed „FTA?s with two ASEAN members. Singapore and Thailand it is trying to sign an FTA with ASEAN itself.
Question: Which four common symbols make the European Union look like a nation state?
Answer: The European Union has its own flag, anthem, founding date and currency.
Question: Mention any two steps taken by China to improve its economy.
Answer: 1. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) were created to invite foreign investors to set up their own enterprises.
2. The privatisation of agriculture and industry in 1982 and 1998.
Question: Mention the agreements signed between India and ASEAN.
Answer: 1. India signed Free Trade Areas (FTAs) with two ASEAN members, Singapore and Thailand.
2. India is trying to sign on FTA with ASEAN itself.
Question: What are the odds which limit the ability of EU?
Answer: European Union is a supernational organisation but in many areas its member states have their own foreign relations and defence policies that are often at odds as-
1. British Prime Minister Tony Blair supported the US’s Iraq invasion and many new members made US led ‘coalition of willing’ while Germany and France opposed it.
2. Denmark and Sweden have resisted the Maastricht treaty and the adoption of the Euro.
Question: “The European Union is a nation state more than a Economic Union”. Justify the statement.
Answer: The European Union has now started to act more as a nation state because:
1. European Union has its own flag, anthem, founding date and common currency.
2. European Union bears common foreign and security policy.
3. The EU has made efforts to expand areas of cooperation while acquiring new members especially from Soviet bloc.
Question: How can we say that ASEAN is an economic association?
Answer: To more extent it can be said that ASEAN is an economic association:
1. ASEAN Economic Community aims at to create open market and production based activities within ASEAN states.
2. ASEAN has created Free Trade Areas (FTAs) for investment, labour and services.
3. The current economic strength of ASEAN as a trading and investment partner to the growing Asian economies as India and China make this attractive proposition.
Question: What are the objectives of ASEAN Economic Community?
Answer: The objectives of ASEAN Economic Community are as follows:
1. To create common market and production based activities within ASEAN states.
2. To aid social and economic development.
3. To resolve economic disputes, the existing dispute settlement mechanism has been improved.
4. Free Trade Areas for investment, labour and services have also been created.
Question: How do ASEAN members commit to uphold peace and neutrality?
Answer: ASEAN members commit to uphold peace and neutrality-
1. ASEAN security community is based on the conviction that territorial disputes should not escalate into armed confrontation.
2. By 2003, ASEAN had several agreements among members states to uphold peace,neutrality, cooperation, non-interference, respect for national differences and sovereign rights.
3. ASEAN Regional Forum was established in 1994 to coordinate security and foreign policy.
Question: What are economic challenges of China despite its economic development?
Answer: Though the Chinese economy has improved dramatically, still everyone in China has not been benefitted by the reforms which can be judged by the following facts-
1. Unemployment has risen. About 100 million people are looking for jobs.
2. Female employment and conditions are bad as in Europe of 18th and 19th centuries.
3. Increasing environmental degradation and corruption.
4. Rising economic inequality between rural and urban residents.
Question: How did relations improve after the conflict of 1962 between India and China?
Answer: Indo-China war of 1962 had complicated Indo-China relations. After 1976 the relations began to improve slowly because:
1. China’s policy became more pragmatic and less ideological due to change in China’s political leadership in the late 1970s when China got ready to settle the contentious issues.
2. A series of talks to resolve the border issues were also initiated to develop harmonious relations.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: What is meant by ‘ASEAN WAT?
Answer: ‘ASEAN WAY’ is an interaction that is informal, confrontationist and cooperative to promote supernational structures in the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN).
Question: Correct the following statement and rewrite ASEAN stands for Association of South East African Nations.
Or
What does ASEAN stand for?
Answer: ASEAN stands for Association of South East Asian Nations.
Question: In which year the European Union was established?
Answer: 1992
Question: What is the common currency of EU?
Answer: EURO
Question: Name any two older members of EU.
Answer: Austria and Denmark
Question: Name any two new members of EU.
Answer: Estonia and Poland.
Question: What does the circle with golden stars on the European Union flag stand for?
Answer: The circle with golden stars on the European Union flag stands for solidarity and harmony between the people of Europe.
Question: Mention the major challenges faced in Europe after Second World War.
Answer: 1. Shattered many assumptions and structures on which European states maintained their relations.
2. The European states confronted the ruin of economies and the destruction on which Europe had been founded.
Question: What is European Union?
Answer: European Union is a group of European capitalist countries established in 1992 for common goal of foreign and security policy, cooperation and home affairs.
Question: What was Marshall Plan?
Answer: Marshall Plan was introduced by America to provide financial help for revival of European economy.
Question: Name two countries of European Union who opposed America’s Iraq invasion.
Answer: Germany and France.
Question: What is ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF)?
Answer: ASEAN Regional Forum was established in 1994 to carry out coordination and foreign policy among ASEAN members.
Question: What is the significance of ASEAN flag?
Answer: In the ASEAN logo, the ten stellas of paddy (rice) represent the ten South East Asian countries bound together in friendship and solidarity. The circle symbolises the unity of ASEAN.
Question: When did China get independence?
Answer: 1949
Question: What is SEZs (Special Economic Zones)?
Answer: Special Economic Zones are created to set up their own enterprises by foreign investors.
Question: Mention the three pillars formed in ASEAN.
Answer: 1. The ASEAN Security Community
2. The ASEAN Economic Community
3. The ASEAN Socio-Cultural Com-munity.
Short answer type question:
Question: Point out some irritants between China and India.
Answer: (i) When China attacked on Tibet in 1950-51 Dalai Lama The Political and religious leader of Tibet, took shelter in India. As a result the relations between the two countries became strained.
(ii) India and China also have a controversy over the mecmohan line, the border line between India and China
(iii) China occupied a large territory in Ladakh and even built a road there in 1959
(iv) In October 1962 China invaded Indian frontier like NEFA and Ladakh and also occupied a considerable part of our territory.
(v) Most of the occasions China supports Pakistan against India. Yet India is trying her best to normalise the relations between the two countries.
Question: What are the objectives of establishing regional organisation?
Answer: The objective of establishing regional organisation are as follows-
(i) To accelerate economic growth.
(ii) To accelerate social progress and cultural development through economic growth.
(iii) To promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of United Nations charter.
(iv) To acquire political cooperation.
(v) To have a common foreign and security policy, cooperation on Justice and home affairs etc.
(vi) To have military influence.
Question: Describe the position of China in the International System?
Answer: Position of China in the international system: - After the disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1990. It looked as if, the world has become unipolar. But it is not so. China is slowly emerging as an alternative power center. Deng Ziaoping had a remarkable role in making China to reach Such heights. In the Last decade of twentieth century. China has increased the budget on militia greatly China is speedily modernizing her armed forces, guided missile system and ordinances. China has great achievements in the field of aerial, Inter continental and distant war sophistication. Briefly if Stated China today has acquired and strengthened her economic and security system to such an extent that she does not even fear the wrath of the all powerful country like the US. She has acquired the guts to retaliate with statements to statements issued against her by any other country.
Question: Write a note on „ASEAN?. Regional form?
Answer: The ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) was established in 1994. It is an informal multilateral dialogue of 25 members whose objectives are to foster dialogue and consultation and promote confidence building and preventive diplomacy in the region. The current participants in the ARF are as follows. ASEAN, Australia, Canada, People?s Republic of Chine, European Union India Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Russia East times and the United States Bangladesh was added to ARF as the 26th member, starting from July 28, 2006.
Question: How has the European Union evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one?
Answer: The European Union has evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one. The EU has started to act more as a nation state. While the attempts to have a constitution for the EU have failed, it has its own flag, anthem, founding date, and currency. It also has some form of a common foreign and security policy in its dealings with other nations. The European Union has tried to expand areas of cooperation while acquiring new members, especially from the erstwhile Soviet bloc. The process has not proved easy, for people in many countries are not very enthusiastic in giving the EU powers that were exercised by the government of their country. There are also reservations about including some new countries within the European Union.
Question: Explain the political, diplomatic influence of European Union as a supernational organisation.
Answer: Political and Diplomatic Influences:
(a) Two members of the EU — Britain and France hold permanent seats in the Security Council to influence the UN policies.
(b) The EU also includes various non-permanent members of the UNSC.
(c) The European Union plays an influential role in diplomacy and negotiations except the military force i. e. the EU’s dialogue with China on human rights and environmental degradation is remarkable.
Question: What led to the evolution of the EU from an economic union to an increasingly political one?
Answer: The European Union has now started to act more as a nation state because-
(i) European Union has its own flag, anthem, founding date and common currency.
(ii) European Union bears common foreign and security policy.
(iii) The EU has made efforts to expand areas of cooperation while acquiring new members especially from Soviet bloc.
Question: What are the objectives behind the formation of ASEAN?
Answer: The objectives behind the formation of ASEAN are as follows:
1. Territorial disputes should not escalate into armed confrontations.
2. To accelerate economic growth through social progress and cultural development.
3. To promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of United Nations ; charter.
4. To establish Dispute Settlement Mechanism to resolve economic disputes.
5. To create Free Trade Areas for investment, labour and services.
Question: Describe any four significant characteristics of ASEAN.
Answer: 1. To create common market and production based activities within ASEAN States.
2. To aid social and economic development.
3. To resolve economic disputes, the existing dispute settlement mechanism has been improved.
4. Free Trade Areas for investment, labour and services have also been created.
Question: What role has been played by European Union in solving the problems of the European countries?
Answer: 1. The EU functions as an important bloc in international organisation as World Trade Organisation to intervene in economic areas.
2. The EU has expanded areas of cooperation while acquiring new members especially from Soviet bloc.
3. The EU has an influential role in the UN policies because its two members—Britain and France hold permanent seats in the UN Security Council.
4. The EU is influential in the areas of diplomacy, economic investments and negotiation.
Question: Why India and China both view themselves as rising powers in global politics in spite of tensions between them? Substantiate your answer by giving any four events that have brought cordiality in their relationship.
Answer: Due to Indian initiatives, Indo-China relations improved. In 1954, India signed famous Panchsheel starting a new era of Indo-China friendship. But after 1957 some contentious issues had been arisen between them:
(i) Tibet Problem
(ii) Border Issues
(iii) Chinese Attack in 1962
(iv) Chinese Assistance to Pakistan.
Gradually, both the countries came together to develop harmonious relations between themselves:
1. Attempt to normalise relations were restored by exchange of ambassadors.
2. Joint Working Group was set up by both the countries to resolve border dispute.
3. Both of them committed to reduce the forces on Indo-China border.
4. Indian and Chinese leadership and official visits with great frequency.
5. Increasing transportation and communication links, common economic interests and global concerns.
Question: Why was European Union founded? What were its objectives and significance?
Answer: The European Union was founded in 1992 for a common foreign and security policy, cooperation on justice and home affairs and to create a single currency.
Objectives:
1. The circle of gold stars on the flag stands for solidarity and harmony between European Union States.
2. To expand areas of co-operation while acquiring new members especially from Soviet bloc.
Question: Why ASEAN was established?
Answer: ASEAN is the regional association to provide a political forum to discuss political and security concerns-
1. Before and during the Second World War, the southeastern region of Asia suffered the economic and political consequences of repeated colonialism, both European and Japanese.
2. At the end of war it confronted problems of nation building, the progress of poverty and economic backwardness and the pressure to align with one great power or another during cold war.
Question: “China has emerged as third alternative to world power”. Examine.
Answer: China emerged as the third alternative to world power since its economic reforms of 1978 as China has been the fastest growing economy since the reforms first began there-
1. China is projected to overtake the US as the world’s largest economy by 2040.
2. Its economic integration into the region makes it drive of East Asian growth.
3. Its strength of economy are population, landmass, resources, regional location, political influence, added to its power.
Question: How did China end its political and economic isolation?
Answer: China had adopted Soviet model of economy. Despite development, China faced economic crisis as industrial production was not growing fast, international trade was minimal. Under these situations some major policy decisions were taken-
1. China established relations with the US in 1972.
2. China proposed four areas of modernisation as agriculture, industry, science and technology in 1973.
3. Open door policy was introduced to generate higher productivity by investment of capital and technology from abroad.
4. Privatisation of agriculture and industry in 1982 and 1998.
5. China set Special Economic Zones to remove trade barriers.
Question: “Chinese economy has been recognised at the global level”. Justify.
Answer: China has introduced open market economy which is moving China towards global economy due to following facts-
1. The integration of Chinese-economy and interdependencies has enabled China to have considerable influence with its trade partners.
2. The open door policy has stabilised the ASEAN economy.
3. China’s outward looking for investment and aid policies in Latin America and Africa are protecting China as a global player.
Question: How does the geographical proximity influence the formation of regional organisations?
Answer: The geographical proximity influences the formation of regional organisations because:
1. It is influenced by almost some historical enmities and weaknesses.
2. Sometimes the similar interests come together.
3. Even fruitful areas for regional economy are also the result of geographical proximity.
Question: What are the components of the ASEAN Visiong020?
Answer: The components of ASEAN Vision 2020 are:
• An outward looking role in the international community.
• To encourage negotiations over conflicts in tie region.
• Thus, ASEAN has mediated the end of the Cambodian conflict, the East Timor crisis, and meets annually to discuss East Asian cooperation.
Question: Name the pillars aid objectives of ASEAN community.
Answer: The ASEAN community established the following three pillars:
1. The ASEAN Security Community
2. The ASEAN Economic Community
3. The ASEAN Socio-cultural Community.
The objectives of ASEAN community are as follows:
1. Territorial disputes should not escalate into armed confrontations.
2. To accelerate economic growth through social progress and cultural development.
3. To promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter.
4. To establish dispute settlement mechanism to resolve economic disputes.
5. To create Free Trade Areas for investments, labour and services.
Question: In what ways does the present Chinese economy differ from its command economy?
Answer: The present Chinese economy has adopted the ‘open door policy’ to generate higher productivity by investments of capital and technology. It differed from its command economy in the following manner:
1. It broke stagnancy of command economy.
2.Command economy lagged behind the industrial production but Chinese economy recovered it by privatisation of agriculture and industry.
3. The present Chinese economy established new trading laws and created Special Economic Zones leading higher rise in foreign trade. During Command economy the international trade was minimal and per capita income was very low.
Question: How did the European countries resolve their Post Second World War problem? Briefly outline the attempts that led to the formation of the European Union.
Answer: After the end of Second World War in 1945, the European States confronted the ruin of their economies and the destruction of assumptions and structures on which Europe had been founded. European countries resolved their Post Second World War problems in the following manner:
1. Under the ‘Marshall Plan’ the USA provided financial help to revive European economy.
2. The US also created a new collective security structure under NATO.
3. Under the ‘Marshall Plan’ the organisation for European Economic Cooperation was established in 1948 to extend cooperation on trade and economic issues among the
Western European States.
4. European Union was founded in 1992 for a common foreign and security policy, cooperation on justice and home affairs and creation of a single currency. It evolved from an economic union to political one over time.
The following attempts led to the formation of European Union:
1. The Council of Europe was established in 1949 for political cooperation.
2. The process of economic integration of European Capitalist countries led to the formation of European Economic Community in 1957.
3. The above mentioned processes acquired a political dimension with the creation of European Parliament.
4. The collapse of Soviet bloc put Europe on a fast track and resulted in the establishment of European Union in 1992.
Question: What makes the European Union a highly influential regional organisation?
Answer: As a supranational organisation, the European Union bears economic, political diplomacy and military influence as a regional organisation in the following manner:
1. Economic Influence:
(а) Three times larger share in world trade than the US.
(b) Its currency Euro, can pose a threat to the dominance of the US dollar.
(c) The EU functions as an important bloc in the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
2. Political and Diplomatic Influences:
(a) Two members of the EU, Britain and France hold permanent seats in the Security Council to influence the UN policies.
(b) The EU also includes various non-permanent members of the UNSC.
(c) The European Union play an influential role in diplomacy and negotiations except the military force i.e. the EU’s dialogue with China on human rights and environmental degradation is remarkable.
3. Military Influence:
(o) The EU’s combined armed forces are second largest in the world.
(b) Its total expenditure on military is second to the US.
(c) Its two important members— Britain and France also experience nuclear ascends of 550 nuclear warheads.
(d) The EU is world’s second most important source of space and communications technology.
Question: The emerging economies of China and India have great potential to challenge the unipolar world. Do you agree with the statement? Substantiate your arguments.
Answer: The Indo-China relations experience strategically organised as rising economic
powers in global politics and to play a major role in Asian economy after the end of Cold War. It can be proved on the following grounds:
1. The new economic policies of India and China have broken their economy from stagnancy.
2. The creation of special economic zones led to a phenomenal rise in foreign trade.
3. China has become the most important destination for foreign direct investment anywhere in the world. Hence, it has large reserves for foreign exchange to allow it to make big investment in other countries.
4. At the global level also, India and China have adopted similar policies in World Trade Organisation to deepen integration with the world economy to challenge unipolar world.
Question: The peace and prosperity of countries lay in the establishment and strengthening of regional economic organisations. Justify this statement.
Answer: This statement represents the ASEAN Regional Forum and the European Union,where ASEAN Regional Forum is based on the notion not to escalate territorial disputes into armed confrontation:
1. The ASEAN is rapidly growing as a regional organisation with the Vision 2020 including an outward looking role in international community and to encourage negotiations over conflicts in the region.
2. ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) maintains coordination of security and foreign policy.
3. The EU has also been funded on the ground of common foreign and security policy, cooperation on justice and home affairs.
4. The European Union has also extended cooperation while acquiring new members especially from Soviet bloc.
Question: Identify the contentious issues between China and India. How could these be resolved for greater cooperation? Give your suggestions.
Answer: The relations with China experience friendly gestures from India as India signed popular ‘Panchsheel’ to develop Indo-China relations in 1954 and advocated China’s membership to the United Nations. Still, after 1957, various contentious issues arose in Indo-China relations:
1. In 1962, military conflict over a border dispute of MacMohan Line resulted on unwarranted claim by China which now lie in Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin region of Ladakh.
2. Differences arose from Chinese take over of Tibet in 1950 which was protested by India against China.
3. After Panchsheel, attack by China on India in 1962, to occupy larger territories of India, created humiliation.
4. China’s assistance to Pakistan’s nuclear programme also created differences.
5. China’s military relations with Bangladesh and Myanmar were viewed as hostile to Indian interests.
All the above mentioned differences/ disputes could be resolved for greater cooperation-
1. Both the countries should make some more efforts to revive harmonious attitude between themselves.
2. Both the countries should move hand-in-hand to fight against terrorism, nuclear race and economic disparities.
3. Both the countries should develop understanding and respect.
4. Hence, both of them have signed agreements on cultural exchange and cooperation in science and technology.
Long answer Question:
Question: Describe the „Open Door Policy” of China?
Answer: Open Door Policy – Before two decades till 1978, China. Which was a closed society for the rest of the world, was made a centre for investment of the entire world and the credit for this important function goes to Deng? For this the Chinese people will ever remain grateful to him. After strengthening his hold over the political power in 1978. When he placed the “open door policy” of China before the world in 1982, then some kind of irritation in the throat of Chinese conservative communists was felt but Deng remained firm in his resolve and Ideas to the extent to which his eyes were sharp becomes clean from what he told mao roughly three decades before that it does not matter whether the cat is black or white, so long as it catches mice but then he was declared as a follower of capitalist class. Even since he was continuously harassed. It was only his efficiency that in order to lead China towards the path of reform and fulfill his ever cherished goal that he has been bending like a bamboo according to the direction of the wind but in 1987 after the thirteenth congress according to the direction he started functioning. In order to give a real shape to his policy of open door. Therefore in 1978 when Deng came to power he laid the foundation of economic liberalism.
Question: How did China rise to be an economic superpower? Assess.
Answer: China had adopted Soviet model of economy. Despite development, China faced economic crisis as industrial production was not growing fast, international trade was minimal. Under these situations some major policy decisions were taken-
1. China established relations with the US in 1972.
2. China proposed four areas of modernisation as agriculture, industry, science and technology in 1973.
3. Open door policy was introduced to generate higher productivity by investment of capital and technology from abroad.
4. Privatisation of agriculture and industry in 1982 and 1998.
5. China set Special Economic Zones to remove trade barriers.
6. The integration of Chinese economy and inter-dependencies has enabled China to have considerable influence with its trade partners.
7. The open door policy has stabilised the ASEAN economy.
8. China’s outward looking for investment and aid policies in Latin America and Africa are projecting China as a global player.
Question: Why is the EU considered a highly influential regional organisation in the economic, political and military fields?
Answer: Because-
1. Economic Influence:
(a) Three times larger share in World trade than the US.
(b) Its currency Euro can pose a threat to the dominance of US Dollar.
(c) The EU functions as an important bloc in World Trade Organisation (WTO).
2. Political Influence:
(а) Two members of the EU, Britain and France hold permanent seats in Security Council to influence UN policies.
(b) The EU also includes various non-permanent members of UNSC.
(c) The European Union plays an influential role in diplomacy and negotiations except military force i.e. EU’s dialogue with China on Human Rights and environmental degradation is remarkable.
3. Military Influence:
(a) The EU’s combined armed forces are second largest in world.
(b) Its total military expenditure is second to the US.
(c) Its two important members— Britain and France also experience nuclear arsenals of 550 nuclear warheads.
(d) The EU is world’s second most important source of space and communication technology.
Question: Discuss Indo-China relations.
Answer: The relations with China experienced friendly gestures from India as India signed popular ‘Panchsheel’ to develop Indo-China relations in 1954 and advocated China’s membership to the United Nations still, after 1957, various contentious issues arose in Indo- China relations-
1. In 1962, military conflict over a border dispute of MacMohan Line resulted an unwarranted claim by China which lies now in Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin regions of Ladakh.
2. Differences arose from Chinese take over of Tibet in 1950 which was protested by India against China.
3. After Panchsheel, attack by China on India in 1962, to occupy larger territories of India, created a humiliation.
4. China’s assistance to Pakistan’s nuclear programme also created differences.
5. China’s military relations with Bangladesh and Myanmar were viewed as hostile to Indian interests.
All the above mentioned differences/ disputes could be resolved for greater cooperation.
1. Both the countries should make some more efforts to revive harmonious attitude between themselves.
2. Both the countries should move hand-in-hand to fight against terrorism, nuclear race and economic disparities.
3. Both the countries should develop mutual understanding and respect.
4. Hence, both of them have signed agreements on cultural exchange and cooperation in science and technology.
1. Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions:
ASEAN was and still remains principally an economic association. While the ASEAN region as a whole is a much smaller economy compared to the US the EU, and Japan, its economy is growing much faster than all these. This accounts for the growth in its influence both in the region and beyond. The objectives of the ASEAN Economic Community are to create a common market and production base within ASEAN States and to aid social and economic development in the region. The Economic Community would also like to improve the existing ASEAN Dispute Settlement Mechanism to resolve economic disputes. ASEAN has focused on creating a Free Trade Area (FTA) for investment, labour, and services. The US and China have already moved fast to negotiate FTAs with ASEAN.
Questions
Question: What is the objective of ASEAN Economic Community?
Answer: To create common market and production based activities within ASEAN states itself and to aid social and economic development.
Question: Why did ASEAN establish Free Trade Areas (FTAs)?
Answer: Free Trade Areas have been established for investment, labour and services.
Question: How ASEAN Economic Community would resolve economic disputes?
Answer: By improving the existing ASEAN Dispute Settlement Mechanism.
Question: Which countries have already moved fast to negotiate FTAs with ASEAN and why?
Answer: ASEAN is rapidly growing into areas of regional organisation with its Vision 2020.
2. Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions:
The conflict of 1962, in which India suffered military reverses, had long-term implications for India-China relations. Diplomatic relations between the two countries were downgraded until 1976. Thereafter, relations between the two countries began to improve slowly. After the change in China’s political leadership from the mid to late 1970s, China’s policy became more pragmatic and less ideological. So it was prepared to, put off the settlement of contentious issues while improving relations with India. A series of talks to resolve the border issue were also initiated in 1981.
Questions
Question: Why did India suffer military reverses as a result of conflict of 1962?
Answer: Due to territorial claims principally in Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin region of Ladakh.
Question: When did the relations between India and China begin to improve?
Answer: From the mid to late 1970s.
Question: What was the change in the policy of China in the seventies?
Answer: China’s policy became more pragmatic and less ideological in the seventies.
Question: Which efforts were made to resolve the border issues between India and China?
Answer: 1. It prepared to put off settlements of contentious issues.
2. A series of talks to resolve the border issues were initiated in 1981.
Picture/Map Based Questions
1. Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follow:
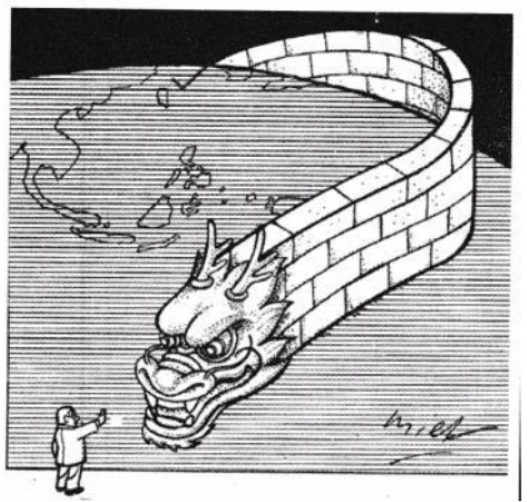
Question.
Question: The given cartoon is related to which country?
Answer: This cartoon is related to China.
Question: Which two symbols in this cartoon helped in identifying the country?
Answer: The Dragon and the Great Wall helped in identifying the country.
Question: What message does this cartoon convey to the world?
Answer: This cartoon conveys a message to the world that China is emerging as a great economic power.
2. Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follow:

question.
Question: What does the cartoon represent?
Answer: India’s policy towards ASEAN.
Question: Name the policy that is being represented in the cartoon.
Answer: ‘Look East’ Policy since 1991 to interact with ASEAN, China, Japan and South Korea.
Question: What does the ‘Competition’ refer to in the cartoon?
Answer: Competition among various countries to develop potential relations with ASEAN.
Question: “We’ll have to get used to it”. What does it denote?
Answer: It denotes India’s strategy towards using free trade areas with ASEAN
B. On a political outline map of world locate and label the following and symbolise them as indicated:
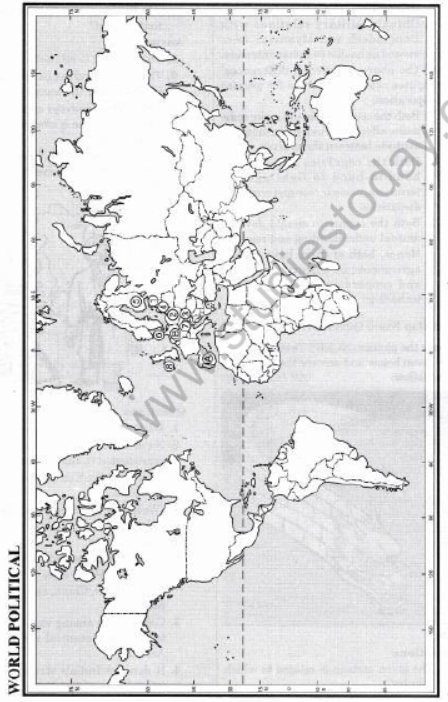
1. An older member of EU between Portugal and France. Symbolise (A)
2. An older member near Belgium and Netherlands. Symbolise (B)
3. The four new members of EU. Symbolise 1, 2, 3, 4.
4. Four old members of EU. Symbolise 5, 6, 7, 8.
Answer:
1. Spain
2. Germany
3. 1. Estonia 2. Poland
3. Hungary 4. Lithuania
4. 5. Finland 6. Denmark
7. Austria 8. Ireland
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 2 The End of Bipolarity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 5 Contemporary South Asia |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 6 International Organisations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 7 Security in the Contemporary World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 8 Environment and Natural Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Globalisation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 1 Challenges of Nation Building |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 2 Era of One Party Dominance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 3 Politics of Planned Development |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 Indias External Relations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 5 Challenges to and Restoration of Congress System |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 6 The Crisis of Democratic Order |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 8 Regional Aspirations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Recent Developments in Indian Politics |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 12 Political Science textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 12 Political Science chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 12 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Political Science Class 12 Solved Papers
Using our Political Science solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 12 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 4 Alternative Centres of Power to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 12 Political Science are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Political Science concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 12 Political Science. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

