Practice CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermal Properties of Matter MCQs Set B provided below. The MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics with answers and follow the latest CBSE/ NCERT and KVS patterns. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter
Class 11 Physics students should review the 50 questions and answers to strengthen understanding of core concepts in Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter
Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter MCQ Questions Class 11 Physics with Answers
Question: The surface temperature of a body is 727°C and that of another body is 327°C. The ratio of total energies radiated by them is :
a) 625 : 81
b) 125 : 27
c) 8 : 27
d) 9 : 25
Answer: a
Question: The wavelength of maximum energy released during an atomic explosion was 2.93 × 10-10 m.
The maximum temperature attained must be, (Weins constant = 2.93 × 10-3 mK)
a) 5.86 × 107 K
b) 10-13 K
c) 10-7 K
d) 107 K
Answer: d
Question: If the temperature of the sun were to increase from T to 2T and its radius from R to 2R, then the ratio of the radiant energy received on earth to what it was previously will be
a) 32
b) 16
c) 4
d) 64
Answer: d
Question: The absolute zero is the temperature at which :
a) all substances exist in solid state
b) molecular motion ceases
c) water freezes
d) none of the options
Answer: b
Question: A black body, at a temperature of 227°C, radiates heat at a rate of 20 cal m-2s-1. When its temperature is raised to 727°C, the heat radiated by it in cal m-2s-1 will be closest to :
a) 40
b) 160
c) 320
d) 640
Answer: c
Question: Steam is passed into 22 g of water at 20°C . The mass of water that will be present when the water acquires a temperature of 90°C is (Latent heat of steam is 540 cal/gm)
a) 24.8 gm
b) 24 gm
c) 36.6 gm
d) 30 gm
Answer: a
Question: The value of coefficient of volume expansion of glycerin is 5 ×10-4 K-1. The fractional change in the density of glycerin for a rise of 40°C in its temperature, is
a) 0.025
b) 0.010
c) 0.015
d) 0.020
Answer: d
Question: Woolen clothes keep the body warm because the wool :
a) decreases the temperature of the body
b) is a good conductor of heat
c) increases the temperature of the body
d) is a bad conductor of heat
Answer: d
Question: A crystal has a coefficient of expansion 13×110-7 in one direction and 231 × 10-7 in every direction at right angles to it. Then the cubical coefficient of expansion is
a) 462 × 10-7
b) 244 × 10-7
c) 475 × 10-7
d) 257 × 10-7
Answer: a
Question: Driver of truck gets his steel petrol tank filled with 75 L of petrol at 10°°C. If asteel is 24 ×10-6/°°C and gpetrol is 9.9 × 10-4/°°C, the overflow of petrol at 30°C is
a) 1.35 L
b) 1.38 L
c) 1.45 L
d) 1.48 L
Answer: b
Question: The colour of a star indicates its :
a) velocity
b) temperature
c) size
d) length
Answer: b
Question: A sphere, a cube and a thin circular plate, all of same material and same mass are initially heated to same high temperature.
a) Plate will cool fastest and cube the slowest
b) Sphere will cool fastest and cube the slowest
c) Plate will cool fastest and sphere the slowest
d) Cube will cool fastest and plate the slowest
Answer: c
Question: A piece of iron is heated in a flame. It first becomes dull red then becomes reddish yellow and finally turns to white hot. The correct explanation for the above observation is possible by using
a) Wien’s displacement law
b) Kirchoff’s law
c) Newton’s law of cooling
d) Stefan’s law
Answer: a
Question: The density of a substance at 0°C is 10 g/cc and at 100°C, its density is 9.7 g/cc. The coefficient of linear expansion of the substance is
a) 10-2
b) 10-2
c) 10-3
d) 10-4
Answer: a
Question: Find the stress developed inside a tooth cavity filled with copper when hot tea at temperature of 57°C is drunk. (Take temperature of tooth to be 37°C, a = 1.7 × 10-5 °C-1 and bulk modulus for copper = 140 × 109 N m-2)
a) 1.43 × 108 N m-2
b) 4.13 × 108 N m-2
c) 2.12 × 104 N m-2
d) 3.12 × 104 N m-2
Answer: a
Question: An aluminium sphere is dipped into water. Which of the following is true?
a) Buoyancy will be less in water at 0 °C than that in water at 4 °C.
b) Buoyancy will be more in water at 0 °C than that in water at 4 °C.
c) Buoyancy in water at 0 °C will be same as that in water at 4 °C.
d) Buoyancy may be more or less in water at 4 °C depending on the radius of the sphere.
Answer: a
Question: Three objects colored black, gray and white can withstand hostile conditions upto 2800°C. These objects are thrown into a furnace where each of them attains a temperature of 2000°C. Which object will glow brightest?
a) the white object
b) the black object
c) all glow with equal brightness
d) gray object
Answer: b
Question: The instrument used to measure the temperature of the source from its thermal radiation is :
a) hydrometer
b) barometer
c) thermopile
d) pyrometer
Answer: c
Question: If the temperature of a black body increases from 7°C to 287°C then the rate of energy radiation increases by
a) (287/7 )4
b) 16
c) 4
d) 2
Answer: b
Question: The wavelength of radiation emitted by a body depends upon
a) the nature of its surface
b) the area of its surface
c) the temperature of its surface
d) All of the options
Answer: d
Question: A glass flask of volume 1 litre is fully filled with mercury at 0ºC. Both the flask and mercury are now heated to 100ºC. If the coefficient of volume expansion of mercury is 1.82 × 10-4/ºC, volume coefficient of linear expansion of glass is 10 × 10-6/ºC, the amount of mercury which is spilted out is
a) 15.2 ml
b) 17.2 ml
c) 19.2 ml
d) 21.2 ml
Answer: a
Question: The sun emits a light with maximum wave length 510 nm while another star emits a light with maximum wavelength of 350 nm. The ratio of surface temperature of sun and the star will be :
a) 0.68
b) 2.1
c) 1.45
c) 0.46
Answer: a
Question: A quantity of heat required to change the unit mass of a solid substance to its liquid state, while the temperature remains constant, is known as
a) latent heat of vaporation
b) latent heat of fusion
c) heat of condensation
d) specific heat
Answer: b
Question: A one litre flask contains certain quantity of mercury.If the volume of air inside the flask remains the same at all temperatures then the volume of mercury in the flask is (volume expansion coefficient of mercury is 20 times that of flask)
a) 100 cc
b) 50 cc
c) 200 cc
d) 150 cc
Answer: b
Question: Suppose the sun expands so that its radius becomes 100 times its present radius and its surface temperature becomes half of its present value. The total energy emitted by it then will increase by a factor of :
a) 104
b) 625
c) 16
d) 16
Answer: b
Question: A piece of ice (heat capacity = 2100 J kg-1 °°C-1 and latent heat = 3.36 × 105 J kg-1) of mass m grams is at -5°°C at atmospheric pressure. It is given 420 J of heat so that the ice starts melting. Finally when the ice-water mixture is in equilibrium, it is found that 1 g of ice has melted. Assuming there is no other heat exchange in the process, the value of m is
a) 4g
b) 6g
c) 8g
d) 10g
Answer: c
Question: On a new scale of temperature (which is linear) and called the W scale, the freezing and boiling points of water are 39°W and 239°W respectively. What will be the temperature on the new scale, corresponding to a temperature of 39°C on the Celsius scale ?
a) 200°W
b) 139°W
c) 78°W
d) 117°W
Answer: d
Question: As the temperature is increased, the time period of a pendulum
a) increases as its effective length increases even though its centre of mass still remains at the centre of the bob.
b) decreases as its effective length increases even though its centre of mass still remains at the centre of the bob.
c) increases as its effective length increases due to shifting of centre of mass below the centre of the bob.
d) decreases as its effective length remains same but the centre of mass shifts above the centre of the bob.
Answer: a
Question: 0.1 m3 of water at 80°C is mixed with 0.3 m3 of water at 60°C. The final temperature of the mixture is
a) 65°C
b) 70°C
c) 60°C
d) 75°C
Answer: a
Question: Two identical bodies are made of a material for which the heat capacity increases with temperature. One of these is at 100°C, while the other one is at 0°C. If the two bodies are brought into contact, then, assuming no heat loss, the final common temperature is
a) 50°C
b) more than 50°C
c) less than 50°C but greater than 0°C
d) 0°C
Answer: b
Question: Certain quantity of water cools from 70°C to 60°C in the first 5 minutes and to 54°C in the next 5 minutes. The temperature of the surroundings is:
a) 45°C
b) 20°C
c) 42°C
d) 10°C
Answer: a
Question: Steam at 100°C is passed into 20 g of water at 10°C. When water acquires a temperature of 80°C, the mass of water present will be:
[Take specific heat of water = 1 cal g- 1 °C- 1 and latent heat of steam = 540 cal g- 1]
a) 24 g
b) 31.5 g
c) 42.5 g
d) 22.5 g
Answer: d
Question: On observing light from three different stars P, Q and R, it was found that intensity of violet colour is maximum in the spectrum of P, the intensity of green colour is maximum in the spectrum of R and the intensity of red colour is maximum in the spectrum of Q. If TP, TQ and TR are the respective absolute temperature of P, Q and R, then it can be concluded from the above observations that
a) TP > TR > TQ
b) TP < TR < TQ
c) TP < TQ < TR
d) TP> TQ > TR
Answer: a
Question: A Centigrade and a Fahrenheit thermometer are dipped in boiling water. The water temperature is lowered until the Fahrenheit thermometer registers 140°F. What is the fall in temperature as registered by the centigrade thermometer?
a) 80°C
b) 60°C
c) 40°C
d) 30°C
Answer: c
Question: On a temperature scale Y, water freezes at - 160°Y and boils at - 50°Y. On this Y scale, a temperature of 340 K would be read as : (colder freezes at 273 K and boils at 373 K)
a) - 106.3°Y
b) - 96.3°Y
c) - 86.3°Y
d) - 76.3°Y
Answer: c
Question: The figure shows a cross-section of a double glass unit of a window on a vertical wall. A graph of the temperatures at different points within the unit is given below. The temperature difference across the unit is 13 K. It has a cross-sectional area of 1.3 m2 and the rate of heat flow through it is 65 W. Then the correct statement is (Glass has a thermal conductivity of 1 W m-1 K-1)
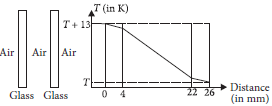
a) The unit is in steady state and in thermal equilibrium.
b) The unit is in steady state but not in thermal equilibrium.
c) The unit is not in steady state but is in thermal equilibrium.
d) The unit neither in steady state nor in thermal equilibrium.
Answer: b
Question: A vessel completely filled with a liquid is heated. If a and g represent coefficient of linear expansion of material of vessel and coefficient of cubical expansion of liquid respectively, then the liquid will not overflow if
a) g = 3 a
b) g > 3 a
c) g < 3 a
d) g £ 3 a
Answer: d
Question: A uniform metallic rod rotates about its perpendicular bisector with constant angular speed. If it is heated uniformly to raise its temperature slightly
a) its speed of rotation increases
b) its speed of rotation decreases
c) its speed of rotation remains same
d) its speed increases because its moment of inertia increases
Answer: a
Question: The triple point of carbon dioxide is 216.55 K the corresponding temperature on the celsius and Fahrenheit scale is
a) 56.45°C, -69.61°F
b) -56.45°C, 69.61°F
c) 56.45°C, 69.61°F
d) - 56.45°C, -69.61°F
Answer: d
Question: Two rods of different materials having coefficients of linear expansion a1 and a2 and Young’s modulus Y1 and Y2 respectively are fixed between two rigid massive walls. The rods are heated such that they undergo the same increase in temperature. There is no bending of rods. If a1 : a2 = 2 : 3,the thermal stress developed in the two rods are equal provided Y1 : Y2 equal to
a) 2 : 3
b) 4 : 9
c) 1 : 2
d) 3 : 2
Answer: d
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set D |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 1 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 2 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 3 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 4 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 5 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Physical World MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Physical World MCQs Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Physics
MCQs for Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics Class 11
Students can use these MCQs for Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter to quickly test their knowledge of the chapter. These multiple-choice questions have been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Physics released by CBSE. Our expert teachers suggest that you should practice daily and solving these objective questions of Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter to understand the important concepts and better marks in your school tests.
Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter NCERT Based Objective Questions
Our expert teachers have designed these Physics MCQs based on the official NCERT book for Class 11. We have identified all questions from the most important topics that are always asked in exams. After solving these, please compare your choices with our provided answers. For better understanding of Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11 Physics created by our team.
Online Practice and Revision for Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics
To prepare for your exams you should also take the Class 11 Physics MCQ Test for this chapter on our website. This will help you improve your speed and accuracy and its also free for you. Regular revision of these Physics topics will make you an expert in all important chapters of your course.
You can download the CBSE MCQs for Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by CBSE for Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter

