Practice CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs Set B provided below. The MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics with answers and follow the latest CBSE/ NCERT and KVS patterns. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids
Class 11 Physics students should review the 50 questions and answers to strengthen understanding of core concepts in Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids
Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQ Questions Class 11 Physics with Answers
Question: The approximate depth of an ocean is 2700 m.The compressibility of water is 45.4 × 10–11 Pa–1 and density of water is 103 kg/m3. What fractional compression of water will be obtained at the bottom of the ocean?
a) 1.2 × 10–2
b) 1.4 × 10–2
c) 0.8 × 10–2
d) 1.0 × 10–2
Answer: a
Question: A body of mass 10 kg is attached to a wire of radius 3 cm. It’s breaking stress is 4.8 × 107 Nm–2, the area of cross-section of the wire is 10–6 m2. What is the maximum angular velocity with which it can be rotated in the horizontal circle ?
a) 1 rad sec–1
b) 2 rad sec–1
c) 4 rad sec–1
d) 8 rad sec–1
Answer: c
Question: The ratio of shearing stress to the corresponding shearing strain is called
a) bulk modulus
b) Young’s modulus
c) modulus of rigidity
d) None of the options
Answer: c
Question: The following four wires of length L and radius r are made of the same material. Which of these will have the largest extension, when the same tension is applied?
a) L = 100 cm, r = 0.2 mm
b) L = 200 cm, r = 0.4 mm
c) L = 300 cm, r = 0.6 mm
d) L = 400 cm, r = 0.8 mm
Answer: a
Question: Which of the following affects the elasticity of a substance?
a) hammering and annealing
b) change in temperature
c) impurity in substance
d) All of the options
Answer: d
Question: The radii and Young’s moduli of two uniform wires A and B are in the ratio 2 : 1 and 1 : 2 respectively. Both wires are subjected to the same longitudinal force. If the increase in length of the wire A is one percent, the percentage increase in length of the wire B is
a) 1.0
b) 1.5
c) 2.0
d) 3.0
Answer: c
Question: Two wires A and B have the same length and area of cross-section. But Young’s modulus of A is two times the Young’s modulus of B. Then the ratio of force constant of A to that of B is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 1/2
d) √2
Answer: b
Question: The volume change of a solid copper cube 10 cm on an edge, when subjected to a pressure of 7 MPa is (Bulk modulus of copper = 140 GPa)
a) 5 × 10–2 cm3
b) 10 × 10–2 cm3
c) 15 × 10–2 cm3
d) 20 × 10–2 cm3
Answer: a
Question: When a pressure of 100 atmosphere is applied on a spherical ball, then its volume reduces to 0.01%. The bulk modulus of the material of the rubber in dyne/cm2 is
a) 10 × 1012
b) 100 × 1012
c) 1 × 1012
d) 10 × 1012
Answer: c
Question: Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume. However wire 1 has cross-sectional area A and wire 2 has crosssectional area 3A. If length of wire l is increased by Δx on applying force F, how much force is needed to stretch wire 2 by the same amount?
a) 4F
b) 6F
c) 9F
d) F
Answer: c
Question: Two wires of same material and length but cross-sections in the ratio 1 : 2 are used to suspend the same loads. The extensions in them will be in the ratio
a) 1 : 2
b) 2 : 1
c) 4 : 1
d) 1 : 4
Answer: b
Question: The Young’s modulus of a perfectly rigid body is
a) unity
b) zero
c) infinity
d) some finite non-zero constant
Answer: c
Question: The following four wires are made of the same material. Which of these will have the largest extension when the same tension is applied?
a) length = 200 cm, diameter = 2 mm
b) length = 300 cm, diameter = 3 mm
c) length = 50 cm, diameter = 0.5 mm
d) length = 100 cm, diameter = 1 mm
Answer: c
Question: A mild steel wire of length 2L and crosssectional area A is stretched, well within elastic limit, horizontally between two pillars as shown in the figure. A mass m is suspended from the mid‑point of the wire. Strain in the wire is
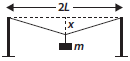
a) x2/2L2
b) x/L
c) x2/L
d) x2/2L
Answer: a
Question: Which one of the following affects the elasticity of a substance ?
a) Change in temperature
b) Hammering and annealing
c) Impurity in substance
d) All of the options
Answer: d
Question: A wire of length L and radius r fixed at one end and a force F applied to the other end produces an extension l. The extension produced in another wire of the same material of length 2 L and radius 2r by a force 2F, is
a) ∫
b) 2∫
c) 4∫
d) ∫/2
Answer: a
Question: Copper of fixed volume V is drawn into wire of length l. When this wire is subjected to a constant force F, the extension produced in the wire is Dl. Which of the following graphs is a straight line?
a) Dl versus 1/l
b) Dl versus l 2
c) Dl versus 1/l 2
d) Dl versus l
Answer: b
Question: Two blocks of masses 1 kg and 2 kg are connected by a metal wire going over a smooth pulley as shown in figure. The breaking stress of the metal is (40/3π) × 106 N/m2. If g = 10 m s–2, then the minimum radius of the wire used if it is not to break is
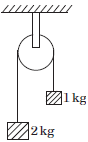
a) 0.5 mm
b) 1 mm
c) 1.5 mm
d) 2 mm
Answer: b
Question: K is the force constant of a spring. The work done in increasing its extension from l1 to l2 will be
a) K(l2 – l1)
b) K/2(l2 + l1)
c) K(l22 – l12)
d) K/2(l22 + l12)
Answer: d
Question: Minimum and maximum values of Possion’s ratio for a metal lies between
a) – ∞ to + ∞
b) 0 to 1
c) – ∞ to 1
d) 0 to 0.5
Answer: d
Question: In solids interatomic forces are
a) totally repulsive
b) totally attractive
c) both totally repulsive and totally attractive
d) None of the options
Answer: c
Question: A solid sphere of radius R, made of a material of bulk modulus K, is surrounded by a liquid in a cylindrical container. A massless piston of area A floats on the surface of the liquid. When a mass M is placed on the piston to compress the liquid the fractional change in the radius of the sphere dR/R, is
a) Mg/2AK
b) Mg/3AK
c) Mg/AK
d) 2Mg/3AK
Answer: b
Question: A and B are two wires. The radius of A is twice that of B.
They are stretched by the same load. Then the stress on B is
a) equal to that on A
b) four times that on A
c) two times that on A
d) half that on A
Answer: b
Question: The length of an elastic spring is a metres when a force of 4 N is applied, and b metres when the 5 N force is applied. Then the length of the spring when the 9 N force is applied is
a) a + b
b) 9b – 9a
c) 5b – 4a
d) 4a – 5b
Answer: c
Question: Elastomers are the materials which
a) are not elastic at all
b) have very small elastic range
c) do not obey Hooke’s law
d) None of the options
Answer: c
Question: The Young’s modulus of brass and steel are respectively 1.0 × 1011 N m–2 and 2.0 × 1011 N m–2. A brass wire and a steel wire of the same length are extended by 1 mm each under the same force. If radii of brass and steel wires are RB and RS respectively, then
a) RS = √2RB
b) RS = RB/√2
c) RS = 4RB
d) RS = RB/2
Answer: b
Question: The bulk modulus of water if its volume changes from 100 litre to 99.5 litre under a pressure of 100 atm is
(Take 1 atm = 105 N m–2)
a) 2 × 107 N m–2
b) 2 × 108 N m–2
c) 2 × 109 N m–2
d) 2 × 1010 N m–2
Answer: c
Question: Two wires A and B of the same material have their lengths in the ratio of 1 : 2 and their diameters in the ratio of 2 : 1. If they are stretched with the same force, the ratio of the increase in the length of A to that of B will be
a) 1 : 2
b) 4 : 1
c) 1 : 8
d) 1 : 4
Answer: c
Question: The bulk modulus of a spherical object is ‘B’. If it is subjected to uniform pressure ‘p’, the fractional decrease in radius is
a) B/3p
b) 3p/B
c) p/3B
d) p/B
Answer: c
Question: The Young’s modulus of steel is twice that of brass.Two wires of same length and of same area of cross section, one of steel and another of brass are suspended from the same roof. If we want the lower ends of the wires to be at the same level, then the weights added to the steel and brass wires must be in the ratio of
a) 4 : 1
b) 1 : 1
c) 1 : 2
d) 2 : 1
Answer: d
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set D |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 1 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 2 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 3 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 4 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 5 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Physical World MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Physical World MCQs Set B |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Physics
MCQs for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics Class 11
Students can use these MCQs for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids to quickly test their knowledge of the chapter. These multiple-choice questions have been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Physics released by CBSE. Our expert teachers suggest that you should practice daily and solving these objective questions of Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids to understand the important concepts and better marks in your school tests.
Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids NCERT Based Objective Questions
Our expert teachers have designed these Physics MCQs based on the official NCERT book for Class 11. We have identified all questions from the most important topics that are always asked in exams. After solving these, please compare your choices with our provided answers. For better understanding of Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11 Physics created by our team.
Online Practice and Revision for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
To prepare for your exams you should also take the Class 11 Physics MCQ Test for this chapter on our website. This will help you improve your speed and accuracy and its also free for you. Regular revision of these Physics topics will make you an expert in all important chapters of your course.
You can download the CBSE MCQs for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by CBSE for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids

