Practice CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs Set C provided below. The MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics with answers and follow the latest CBSE/ NCERT and KVS patterns. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids
Class 11 Physics students should review the 50 questions and answers to strengthen understanding of core concepts in Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids
Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQ Questions Class 11 Physics with Answers
Question: The Young’s modulus of brass and steel are respectively 1010 N/m2. and 2 × 1010 N/m2. A brass wire and a steel wire of the same length are extended by 1 mm under the same force, the radii of brass and steel wires are RB and RS respectively. Then
a) RS = √2 RB
b) RS = RB /√2
c) RS = 4RB
d) RS = RB / 4
Answer: b
Question: A steel bar ABCD 40 cm long is made up of three parts AB, BC and CD, as shown in figure. The rod is subjected to a pull of 25 kN. Diamerter of parts AB and CD is 50 mm while diametre of port BC is 25 mm. The total extension of the rod is (Young’s modulus for steel = 2 × 1011 N m–2)
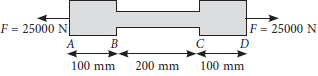
a) 0.0637 mm
b) 0.0647 mm
c) 0.0657 mm
d) 0.0667 mm
Answer: a
Question: Hooke’s law defines
a) stress
b) strain
c) modulus of elasticity
d) elastic limit
Answer: c
Question: Uniform rod of mass m, length l , area of cross-section A has Young’s modulus Y. If it is hanged vertically, elongation under its own weight will be
a) mgl /2AY
b) 2mgl /AY
c) mgl /AY
d) mgY/Al
Answer: c
Question: A polyster fibre rope of diameter 3 cm has a breaking strength of 150 kN. If it is required to have 600 kN breaking strength. What should be the diameter of similar rope?
a) 12 cm
b) 6 cm
c) 3 cm
d) 1.5 cm
Answer: b
Question: Assuming that shear stress at the base of a mountain is equal to the force per unit area due to its weight. Calculate the maximum possible height of a mountain on the earth if breaking stress of a typical rock is 3 × 108 N m–2 and its density is 3 × 103 kg m–3.
(Take g = 10 m s–2)
a) 4 km
b) 8 km
c) 10 km
d) 16 km
Answer: c
Question: A wire of cross-section 4 mm2 is stretched by 0.1 mm by a certain weight. How far (length) will the wire of same material and length but of area 8 mm2 stretch under the action of same force?
a) 0.05 mm
b) 0.10 mm
c) 0.15 mm
d) 0.20 mm
Answer: a
Question: The length of an iron wire is L and area of corss-section is A. The increase in length is l on applying the force F on its two ends. Which of the statement is correct?
a) Increase in length is inversely proportional to its length
b) Increase in length is proportional to area of crosssection
c) Increase in length is inversely proportional to area of cross-section
d) Increase in length is proportional to Young’s modulus
Answer: c
Question: What per cent of length of wire increases by applying a stress of 1 kg weight/mm2 on it? (Y = 1 × 1011 N/m2 and 1 kg weight = 9.8 newton)
a) 0.0067%
b) 0.0098%
c) 0.0088%
d) 0.0078%
Answer: b
Question: A steel wire is suspended vertically from a rigid support.When loaded with a weight in air, it extends by la and when the weight is immersed completely in water, the extension is reduced to lw. Then the relative density of material of the weight is
a) la /lw
b) la / la – lw
c) lw / la – lw
d) lw – la
Answer: b
Question: The compressibility of water is 6 × 10–10 N–1m2. If one litre is subjected to a pressure of 4 × 107 N m–2, the decrease in its volume is
a) 10 cc
b) 24 cc
c) 15 cc
d) 12 cc
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following relation is true ?
a) 3Y = K(1- σ )
(b K = 9ηY /Y+η
c) σ = (6K + η)Y
d) σ = 0.5Y – η / η
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following has no dimensions ?
a) strain
b) angular velocity
c) momentum
d) angular momentum
Answer: a
Question: The pressure of a medium is changed from 1.01 × 105 Pa to 1.165 × 105 Pa and change in volume is 10% keeping temperature constant.
Find the bulk modulus of the medium.
a) 1 × 103 Pa
b) 3 × 105 Pa
c) 2 × 104 Pa
d) 1.55 × 105 Pa
Answer: d
Question: A and B are two wires. The radius of A is twice that of B. If they are stretched by the same load, then the stress on B is
a) equal to that of A
b) two times that of A
c) four times that of A
d) half that of A.
Answer: c
Question: In case of steel wire (or a metal wire), the limit is reached when
a) the wire just break
b) the load is more than the weight of wire
c) elongation is inversely proportional to the tension
d) None of the options
Answer: d
Question: Two wires of equal length and cross-section area are suspended as shown in figure. Their Young’s modulus are Y1 and Y2 respectively.
The equivalent Young’s modulus will be
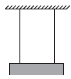
a) Y1 + Y2
b) Y1 + Y2 / 2
c) Y1Y2 / Y1 + Y2
d) √Y1Y2
Answer: b
Question: One end of a horizontal thick copper wire of length 2L and radius 2R is welded to an end of another horizontal thin copper wire of length L and radius R. When the arrangement is stretched by applying forces at two ends, the ratio of the elongation in the thin wire to that in the thick wire is
a) 0.25
b) 0.50
c) 2.00
d) 4.00
Answer: c
Question: According to Hooke’s law of elasticity, if stress is increased, then the ratio of stress to strain
a) becomes zero
b) remains constant
c) decreases
d) increases
Answer: b
Question: How much pressure should be applied on a litre of water if it is to be compressed by 0.1%? (Bulk modulus of water = 2100 MPa)
a) 2100 kPa
b) 210 kPa
c) 2100 MPa
d) 210 MPa
Answer: a
Question: A steel cable with a radius 2 cm supports a chairlift at a ski area. If the maximum stress is not to exceed 108 N m–2, the maximum load the cable can support is
a) 4π × 105 N
b) 4π × 104 N
c) 2π × 105 N
d) 2π × 104 N
Answer: b
Question: If Y and B represent Young’s modulus and bulk modulus for a material, then in practice
a) Y < 3B
b) Y = 3B
c) Y > 3B
d) B = 3Y
Answer: a
Question: A steel ring of radius r and cross sectional area A is fitted onto a wooden disc of radius R (R > r). If the Young’s modulus of steel is Y, then the force with which the steel ring is expanded is
a) A Y (R/r)
b) A Y (R – r)/r
c) (Y/A)[(R – r)/r]
d) Y r/A R
Answer: b
Question: For a perfectly rigid body
a) Young’s modulus is infinite and bulk modulus is zero.
b) Young’s modulus is zero and bulk modulus is infinite.
c) Young’s modulus is infinite and bulk modulus is also infinite.
d) Young’s modulus is zero and bulk modulus is also zero.
Answer: c
Question: The area of a cross-section of steel wire is 0.1 cm2 and Young’s modulus of steel is 2 × 1011 N m–2. The force required to stretch by 0.1% of its length is
a) 2000 N
b) 1000 N
c) 1500 N
d) 1700 N
Answer: a
Question: For a constant hydraulic stress on an object, the fractional change in the object volume (ΔV /V) and its bulk modulus b) are related as
a) ΔV /V ∝ B
b) ΔV /V ∝ 1/B
c) ΔV /V ∝ B2
d) ΔV /V ∝ B–2
Answer: b
Question: The length of an iron wire is L and area of cross-section is A. The increase in length is l on applying the force F on its two ends. Which of the following statements is correct ?
a) Increase in length is inversely proportional to its length L.
b) Increase in length is proportional to area of cross-section A.
c) Increase in length is inversely proportional to cross-section A.
d) Increase in length is proportional to Young’s modulus.
Answer: c
Question: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and crosssectional area 3.0 × 10–5 m2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 × 10–5 m2 under a given load. What is the ratio of the Young’s modulus of steel to that of copper?
a) 1.8 : 1
b) 2.8 : 1
c) 3.8 : 1
d) 4.8 : 1
Answer: a
Question: When an elastic material with Young’s modulus Y is subjected to stretching stress S, elastic energy stored per unit volume of the material is
a) YS / 2
b) S2Y / 2
c) S2 / 2Y
d) S / 2Y
Answer: c
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Work Energy and Power MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Gravitation MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Thermodynamic MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set C |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Waves MCQs Set D |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 1 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 2 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 3 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 4 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics MCQs Set 5 |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Physical World MCQs Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Physical World MCQs Set B |
More free study material for Physics
MCQs for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics Class 11
Students can use these MCQs for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids to quickly test their knowledge of the chapter. These multiple-choice questions have been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Physics released by CBSE. Our expert teachers suggest that you should practice daily and solving these objective questions of Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids to understand the important concepts and better marks in your school tests.
Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids NCERT Based Objective Questions
Our expert teachers have designed these Physics MCQs based on the official NCERT book for Class 11. We have identified all questions from the most important topics that are always asked in exams. After solving these, please compare your choices with our provided answers. For better understanding of Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11 Physics created by our team.
Online Practice and Revision for Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
To prepare for your exams you should also take the Class 11 Physics MCQ Test for this chapter on our website. This will help you improve your speed and accuracy and its also free for you. Regular revision of these Physics topics will make you an expert in all important chapters of your course.
You can get most exhaustive CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs Set C for free on StudiesToday.com. These MCQs for Class 11 Physics are updated for the 2025-26 academic session as per CBSE examination standards.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs Set C include the latest type of questions, such as Assertion-Reasoning and Case-based MCQs. 50% of the CBSE paper is now competency-based.
By solving our CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs Set C, Class 11 students can improve their accuracy and speed which is important as objective questions provide a chance to secure 100% marks in the Physics.
Yes, Physics MCQs for Class 11 have answer key and brief explanations to help students understand logic behind the correct option as its important for 2026 competency-focused CBSE exams.
Yes, you can also access online interactive tests for CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids MCQs Set C on StudiesToday.com as they provide instant answers and score to help you track your progress in Physics.

