Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 10 Science. Our expert-created answers for Class 10 Science are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 5 Life Processes NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
For Class 10 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 10 Science solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 5 Life Processes solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes NCERT Solutions PDF
Question : Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans?
Answer: Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs. They have specialised cells and tissues for performing various necessary functions of the body such as intake of food and oxygen. Unlike unicellular organisms, multicellular cells are not in direct contact with the outside environment. Therefore, diffusion cannot meet their oxygen requirements.
Question : What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Answer: Any visible movement such as walking, breathing, or growing is generally used to decide whether something is alive or not. However, a living organism can also have movements, which are not visible to the naked eye. Therefore, the presence of life processes is a fundamental criterion that can be used to decide whether something is alive or not.
Question : What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Answer: An organism uses outside raw materials mostly in the form of food and oxygen. The raw materials required by an organism can be quite varied depending on the complexity of the organism and its environment.
Question : What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Answer: Life processes such as nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, etc. are essential for maintaining life.
Question : What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer: Autotrophic nutrition Heterotrophic nutrition
(i) Food is synthesised from simple inorganic raw materials such as CO2 and water.
(i) Food is obtained directly or indirectly from autotrophs. This food is broken down with the help of enzymes.
(ii) Presence of green pigment (chlorophyll) is necessary.
(ii) No pigment is required in this type of nutrition.
(iii) Food is generally prepared during day time.
(iii) Food can be prepared at all times.
(iv) All green plants and some bacteria havethis type of nutrition.
(iv) All animals and fungi have this type of nutrition.
Question : Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer: The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis:
• The raw material CO2 enters from the atmosphere through stomata.
• Water is absorbed from the soil by the plant roots.
• Sunlight, an important component to manufacture food, is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plants.
Question : What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Answer: The hydrochloric acid present in our stomach dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this acidic medium, enzyme pepsinogen is converted to pepsin, which is a proteindigesting enzyme.
Question : What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer: Digestive enzymes such as amylase, lipase, pepsin, trypsin, etc. help in the breaking down of complex food particles into simple ones. These simple particles can be easily absorbed by the blood and thus transported to all the cells of the body.
Question : How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Answer: The inner lining of small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption. The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels which transport the absorbed food to each and every cells of the body. Where, it is utilized to obtaining energy and repair of old tissues.
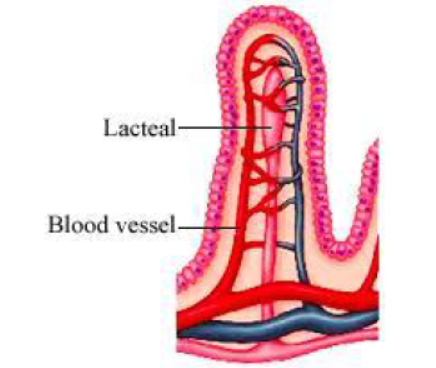
Question : What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer: Terrestrial organisms take up oxygen from the atmosphere whereas aquatic animals need to utilize oxygen present in the water. Air contains more O2 as compared to water. Since the content of O2 in air is high, the terrestrial animals do not have to breathe faster to get more oxygen. Therefore, unlike aquatic animals, terrestrial animals do not have to show various adaptations for better gaseous exchange.
Question : What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer: Glucose is first broken down in the cell cytoplasm into a three carbon molecule called pyruvate. Pyruvate is further broken down by different ways to provide energy. The breakdown of glucose by different pathways can be illustrated as follows.
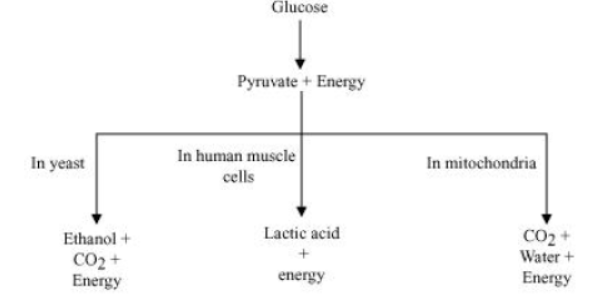
In yeast and human muscle cells, the breakdown of pyruvate occurs in the absence of oxygen whereas in mitochondria, the breakdown of pyruvate occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Question : How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer: Haemoglobin transports oxygen molecule to all the body cells for cellular respiration.The haemoglobin pigment present in the blood gets attached to four O2 molecules that are obtained from breathing. It thus forms oxyhaemoglobin and the blood becomes oxygenated. This oxygenated blood is then distributed to all the body cells by the heart. After giving away O2 to the body cells, blood takes away CO2 which is the end product of cellular respiration. Now the blood becomes de-oxygenated.
Since haemoglobin pigment has less affinity for CO2, CO2 is mainly transported in the dissolved form. This de-oxygenated blood gives CO2 to lung alveoli and takes O2 in return.
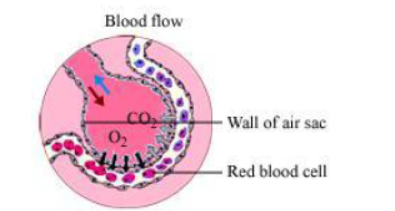
Transportation of O2 and CO2 in blood
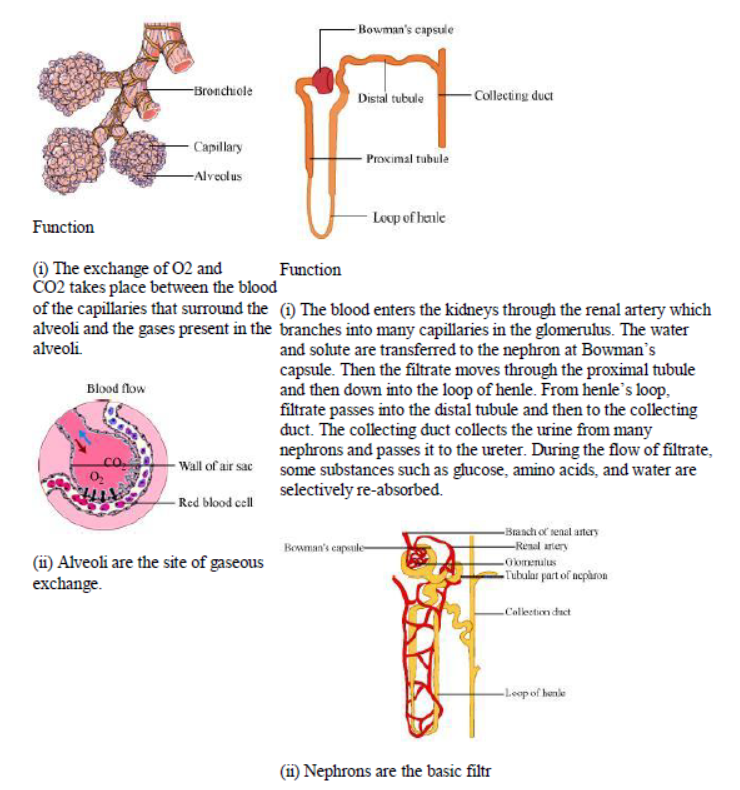
Question : How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for exchange of gases?
Answer: The exchange of gases takes place between the blood of the capillaries that surround the alveoli and the gases present in the alveoli. Thus, alveoli are the site for exchange of gases. The lungs get filled up with air during the process of inhalation as ribs are lifted up and diaphragm is flattened. The air that is rushed inside the lungs fills the numerous alveoli present in the lungs.Each lung contains 300-350 million alveoli. These numerous alveoli increase the surface area for gaseous exchange making the process of respiration more efficient.
Question : What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Answer: The main components of the transport system in human beings are the heart, blood, and blood vessels.
Heart pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body. It receives deoxygenated blood from the various body parts and sends this impure blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
Being a fluid connective tissue, blood helps in the transport of oxygen, nutrients, CO2, and nitrogenous wastes.
The blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) carry blood either away from the heart to various organs or from various organs back to the heart.
Question : Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Answer: Warm-blooded animals such as birds and mammals maintain a constant body temperature by cooling themselves when they are in a hotter environment and by warming their bodies when they are in a cooler environment. Hence, these animals require more oxygen (O2) for more cellular respiration so that they can produce more energy to maintain their body temperature.Thus, it is necessary for them to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood, so that their circulatory system is more efficient and can maintain their constant body temperature.
Question : What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plants?
Answer: The transport system of higher plants consists of xylem and phloem. Xylems have vessels and trachieds to transport water and minerals from root to other part of the plants.
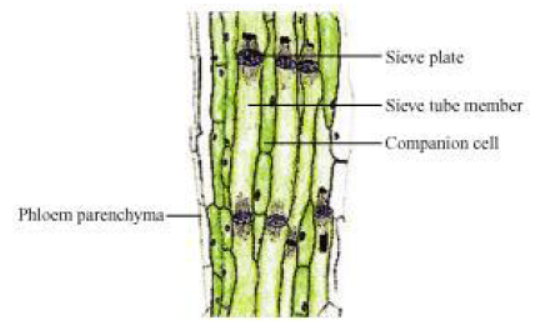
Phloem, which consists of sieve tubes and companion cells, transport food from leaves to storage organs and other parts of plant.
Question : How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Answer: The components of xylem tissue (tracheids and vessels) of roots, stems, and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels that reaches all parts of the plant. Transpiration creates a suction pressure, as a result of which water is forced into the xylem cells of the roots. Then there is a steady movement of water from the root xylem to all the plant parts through the interconnected water-conducting channels.
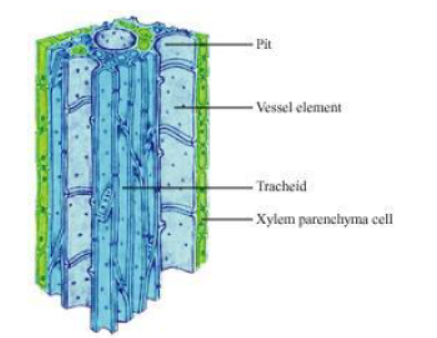
Question : How is food transported in plants?
Phloem transports food materials from the leaves to different parts of the plant body. The transportation of food in phloem is achieved by utilizing energy from ATP. As a result of this, the osmotic pressure in the tissue increases causing water to move into it. This pressure moves the material in the phloem to the tissues which have less pressure. This is helpful in moving materials according to the needs of the plant. For example, the food material, such as sucrose, is transported into the phloem tissue using ATP energy.
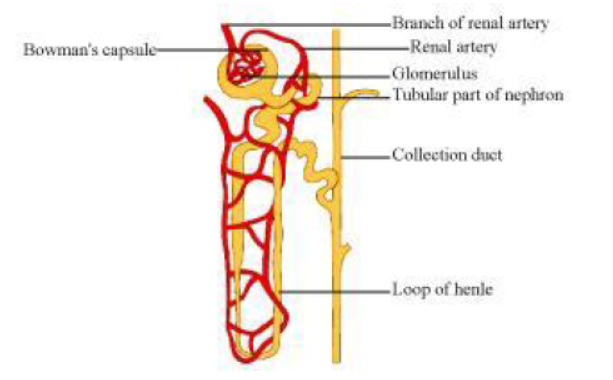
Question : Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Answer: Nephrons are the basic filtering units of kidneys. Each kidney possesses large number of nephrons, approximately 1-1.5 million. The main components of the nephron are glomerulus,Bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tubule.
Structure of a nephron
Functioning of a nephron:
The blood enters the kidney through the renal artery, which branches into many capillaries associated with glomerulus.
The water and solute are transferred to the nephron at Bowman’s capsule.
In the proximal tubule, some substances such as amino acids, glucose, and salts are selectively reabsorbed and unwanted molecules are added in the urine.
The filtrate then moves down into the loop of Henle, where more water is absorbed.
From here, the filtrate moves upwards into the distal tubule and finally to the collecting duct.
Collecting duct collects urine from many nephrons.
The urine formed in each kidney enters a long tube called ureter. From ureter, it gets transported to the urinary bladder and then into the urethra.
Question : What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Answer: Plants can get rid of excess of water by transpiration. Waste materials may be stored in the cell vacuoles or as gum and resin, especially in old xylem. It is also stored in the leaves that later fall off.
Question : How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Answer: The amount of urine produced depends on the amount of excess water and dissolved wastes present in the body. Some other factors such as habitat of an organism and hormone such as Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) also regulates the amount of urine produced.
Question : The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) nutrition.
(b) respiration.
(c) excretion.
(d) transportation.
Answer: (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of the system for excretion.
Question : The xylem in plants are responsible for
(a) transport of water.
(b) transport of food.
(c) transport of amino acids.
(d) transport of oxygen.
Answer: (a) In a plant, the xylem is responsible for transport of water.
Question : The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(a) carbon dioxide and water.
(b) chlorophyll.
(c) sunlight.
(d) all of the above.
Answer: (d) The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight.
Question : The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(a) cytoplasm.
(b) mitochondria.
(c) chloroplast.
(d) nucleus.
Answer: (b) The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in mitochondria.
Question : How are fats digested in our bodies?Where does this process take place?
Answer: Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine. The small intestine gets the secretions in the form of bile juice and pancreatic juice respectively from the liver and the pancreas. The bile salts (from the liver) break down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes can easily act on them. This is referred to as emulsification of fats. It takes place in the small intestine.
Question : What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products?
Answer: Autotrophic nutrition takes place through the process of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll pigment, and sunlight are the necessary conditions required for autotrophic nutrition. Carbohydrates (food) and O2 are the by-products of photosynthesis

Question : What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer:
Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration
1.It occurs in the presence of O2. 1.It occurs in the absence of O2.
2.It involves the exchange of gases between the organism and the outside environment.
2.Exchange of gases is absent.
3.It occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria. 3.It occurs only in cytoplasm.
4.It always releases CO2 and H2O. 4.End products vary.
5.It yields 36 ATPs. 5.It yields only 2 ATPs.
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the roots of some waterlogged plants, some parasitic worms, animal muscles, and some micro-organisms such as yeasts.
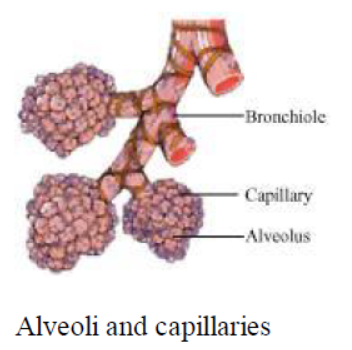
Question : How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer: The alveoli are the small balloon-like structures present in the lungs. The walls of the
alveoli consist of extensive network of blood vessels. Each lung contains 300−350 million alveoli,
making it a total of approximately 700 million in both the lungs. The alveolar surface when spread
out covers about 80 m2area. This large surface area makes the gaseous exchange more efficient.
Question : What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer: Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment that transports oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. Therefore, deficiency of haemoglobin in blood can affect the oxygen supplying capacity of blood. This can lead to deficiency of oxygen in the body cells. It can also lead to a disease called anaemia.
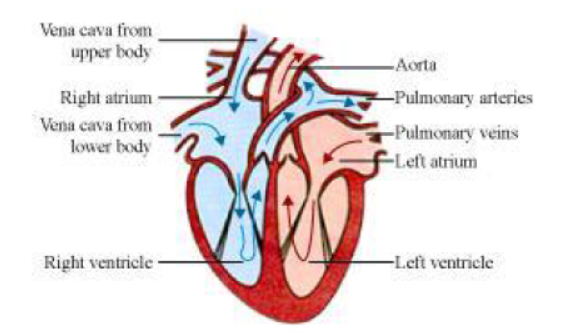
Question : Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer: The human heart is divided into four chambers − the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle.
Flow of blood in the heart:
The heart has superior and inferior vena cava, which carries de-oxygenated blood from the upper and lower regions of the body respectively and supplies this de-oxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart.
Flow of blood in the human heart
The right atrium then contracts and passes the de-oxygenated blood to the right ventricle,through an auriculo-ventricular aperture.
Then the right ventricle contracts and passes the de-oxygenated blood into the two pulmonary arteries, which pumps it to the lungs where the blood becomes oxygenated. From the lungs, the pulmonary veins transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart.
Then the left atrium contracts and through the auriculo-ventricular aperture, the oxygenated blood enters the left ventricle.
The blood passes to aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta gives rise to many arteries that distribute the oxygenated blood to all the regions of the body.
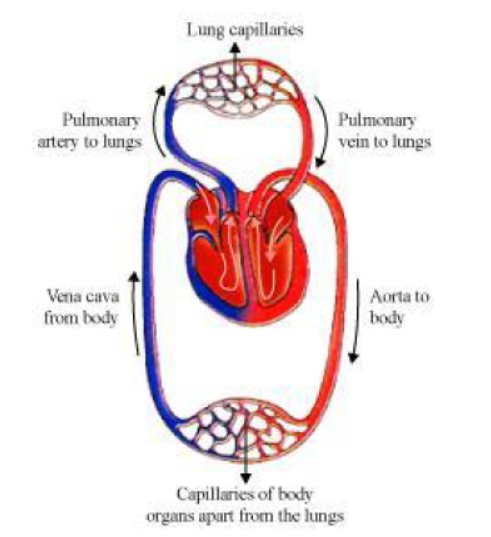
Schematic diagram of blood circulation in humans
Therefore, the blood goes twice through the heart. This is known as double circulation.
The separation of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood allows a more efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells. This efficient system of oxygen supply is very useful in warm blooded animals such as human beings.
As we know, warm-blooded animals have to maintain a constant body temperature by cooling themselves when they are in a hotter environment and by warming their bodies when they are in a cooler environment. Hence, they require more O2 for more respiration so that they can produce more energy to maintain their body temperature. Thus, the circulatory system of humans is more efficient because of the double circulatory heart.
Question : What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Answer:
Transport of materials in xylem Transport of materials in phloem
(i) Xylem tissue helps in the transport of water and minerals.
(i) Phloem tissue helps in the transport of food.
(ii) Water is transported upwards from roots to all other plant parts.
(ii) Food is transported in both upward and downward directions.
(iii) Transport in xylem occurs with the help of simple physical forces such as transpiration pull.
(iii) Transport of food in phloem requires energy in the form of ATP.
Question : Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Answer:
Alveoli Nephron
Structure Structure
(i) Alveoli are tiny balloon-like (i) Nephrons are tubular structures present inside the kidneys.
structures present inside the lungs.
(ii) The walls of the alveoli are one (ii) Nephrons are made of glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, and
cell thick and it contains an a long renal tube. It also contains a cluster of thin-walled capillaries.
extensive network of blood
capillaries.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non metals |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Electricity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric current |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Our Environment |
Important Practice Resources for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 5 Life Processes prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 10 Science textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 5 Life Processes
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 10 Science chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 10 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Science Class 10 Solved Papers
Using our Science solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 10 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 5 Life Processes to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 10 Science are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Science concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 10 Science. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

