NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Students of Class 10 studying Science are advised to carefully go through the NCERT questions and their detailed answers provided here for the chapter Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World. The questions in the NCERT textbook for Class 10 Science form an important part of school exams. These solutions for Class 10 follow a step-by-step approach and are highly beneficial for exam preparation. Scroll down to view detailed, chapter-wise solutions for Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World and explore more NCERT solutions and free study materials for Science and other subjects of Class 10.
Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
Question : What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
Answer: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant objects are clearly visible to the eyes. To see the nearby objects clearly, the ciliary muscles contract making the eye lens thicker. Thus, the focal length of the eye lens decreases and the nearby objects become visible to the eyes.
Hence, the human eye lens is able to adjust its focal length to view both distant and nearby objects on the retina. This ability is called the power of accommodation of the eyes.
Question : A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
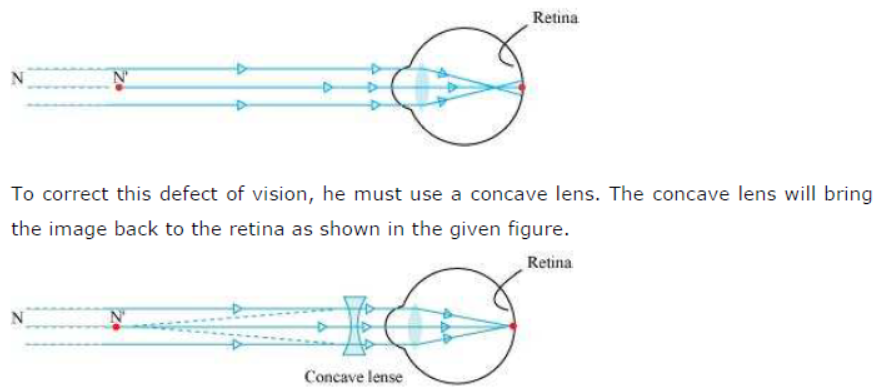
Answer: The person is able to see nearby objects clearly, but he is unable to see objects beyond 1.2 m. This happens because the image of an object beyond 1.2 m is formed in front of the retina and not at the retina, as shown in the given figure.
Question : What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Answer: The near point of the eye is the minimum distance of the object from the eye, which can be seen distinctly without strain. For a normal human eye, this distance is 25 cm.
The far point of the eye is the maximum distance to which the eye can see the objects clearly. The far point of the normal human eye is infinity.
Question : A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
Answer: A student has difficulty in reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. It shows that he is unable to see distant objects clearly. He is suffering from myopia. This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens.
Question : The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) presbyopia
(b) accommodation
(c) near-sightedness
(d) far-sightedness
Answer: (b) Human eye can change the focal length of the eye lens to see the objects situated at various distances from the eye. This is possible due to the power of accommodation of the eye lens.
Question : The human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) cornea
(b) iris
(c) pupil
(d) retina
Answer: (d) The human eye forms the image of an object at its retina.
Question :The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
(a) 25 m
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 2.5 m
Answer: (c) The least distance of distinct vision is the minimum distance of an object to see clear and distinct image. It is 25 cm for a young adult with normal visions.
Question : The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) pupil
(b) retina
(c) ciliary muscles
(d) iris
Answer: (c) The relaxation or contraction of ciliary muscles changes the curvature of the eye lens. The change in curvature of the eye lens changes the focal length of the eyes.
Hence, the change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of ciliary muscles.
Question : A person needs a lens of power −5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
Answer: For distant vision = −0.181 m, for near vision = 0.667 m
The power P of a lens of focal length f is given by the relation

Question : The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Answer: The person is suffering from an eye defect called myopia. In this defect, the image is formed in front of the retina. Hence, a concave lens is used to correct this defect of vision.
Object distance, u = infinity =
Image distance, v = −80 cm
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula,

A concave lens of power −1.25 D is required by the person to correct his defect.
Question : Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect?
Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
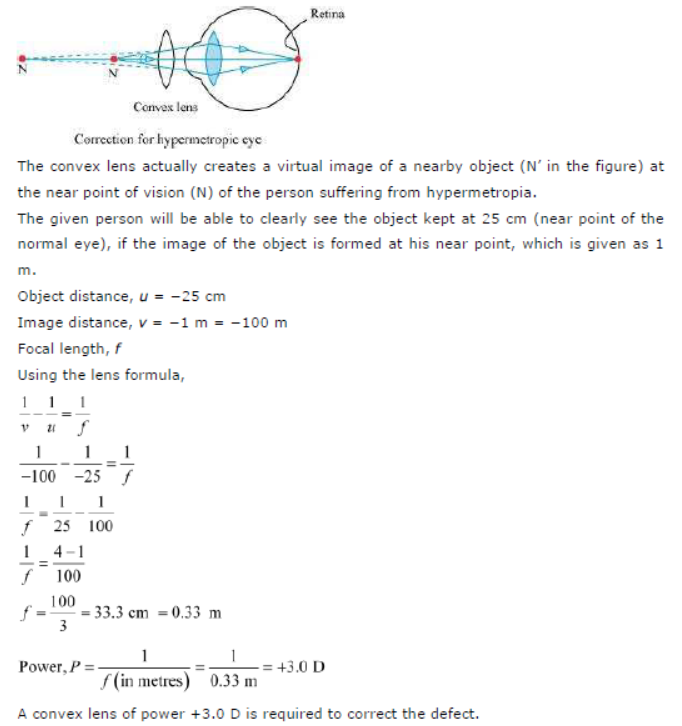
Answer: A person suffering from hypermetropia can see distinct objects clearly but faces difficulty in seeing nearby objects clearly. It happens because the eye lens focuses the incoming divergent rays beyond the retina. This defect of vision is corrected by using a convex lens. A convex lens of suitable power converges the incoming light in such a way that the image is formed on the retina, as shown in the following figure.
Question : What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Answer: Since the size of eyes cannot increase or decrease, the image distance remains constant.When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the image distance in the eye does not change. The increase in the object distance is compensated by the change in the focal length of the eye lens. The focal length of the eyes changes in such a way that the image is always formed at the retina of the eye.
Question : Why do stars twinkle?
Answer: Stars emit their own light and they twinkle due to the atmospheric refraction of light. Stars are very far away from the earth. Hence, they are considered as point sources of light. When the light coming from stars enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets refracted at different levels because of the variation in the air density at different levels of the atmosphere. When the star light refracted by the atmosphere comes more towards us, it appears brighter than when it comes less towards us. Therefore, it appears as if the stars are twinkling at night.
Question : Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
Answer: Planets do not twinkle because they appear larger in size than the stars as they are relatively closer to earth. Planets can be considered as a collection of a large number of point-size sources of light. The different parts of these planets produce either brighter or dimmer effect in such a way that the average of brighter and dimmer effect is zero.
Hence, the twinkling effects of the planets are nullified and they do not twinkle.
Question : Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer: During sunrise, the light rays coming from the Sun have to travel a greater distance in the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. In this journey, the shorter wavelengths of lights are scattered out and only longer wavelengths are able to reach our eyes. Since blue colour has a shorter wavelength and red colour has a longer wavelength, the red colour is able to reach our eyes after the atmospheric scattering of light. Therefore, the Sun appears reddish early in the morning.
Question : Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer: The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere in the outer space that can scatter the sunlight. As the sunlight is not scattered, no scattered light reach the eyes of the astronauts and the sky appears black to them.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non metals |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Electricity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric current |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Our Environment |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World of Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 chapter of Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World have been answered by our teachers

