Download the latest Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Notes Set B in PDF format. These Class 7 Science revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 7 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Revision Notes for Class 7 Science
Reproduction is a process by which every living organism produce an organism like their own.
- Types of reproduction :
(a) Asexual reproduction : In this type of reproduction only one parent organism either mother or father produces new organism.
(b) Sexual reproduction : In this type of reproduction both parent are involved & produces new organisms.
- Asexual reproduction in unicellular organism :
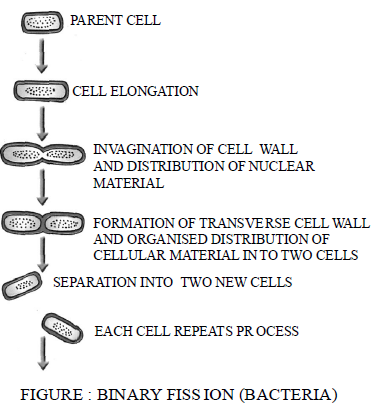
1. Binary fission : During this process, two daughter organisms of equal sizes are formed from one parent by the division of the parent body. This is the most common method of reproduction in algae, fungi and bacteria (fig.).
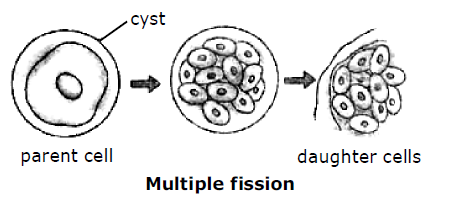
Multiple fission: Sometimes the nucleus divides into many daughter nuclei. The daughter nuclei arrange at the periphery of the parent cell, and a bit of cytoplasm around each daughter nuclei is present. Nucleus develops an outer membrane. Finally, the multinucleated body divides into many daughter cells. e.g. Blue green algae.
(2) Budding : In this type of reproduction, a small outgrowth appears on the body of the organism. This outgrowth is called a bud. The buds grow and finally detach from the parent body and begin to live as independent organisms.
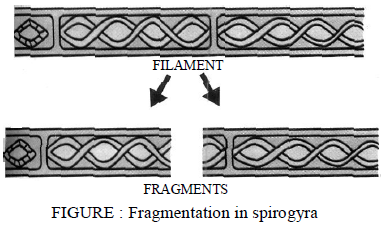
(3) Fragmentation : This takes place in algae like spirogyra and oscillatory. The filament of the alga breaks into two or more pieces called fragments, and the process is known as fragmentation. Each fragment the grows into a new plant.
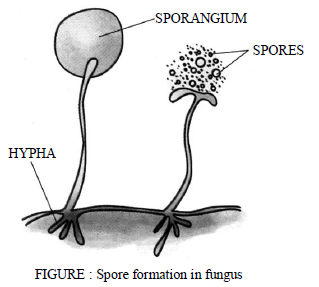
(4) Spore formation : Some lower plants such as ferns, mosses, lichens and fungi reproduce through spore formation under unfavourable conditions. Spores are tiny, microscopic bodies, which are covered by hard protective coats. The protective coats enable them to tide over adverse environmental conditions. When favourable conditions return, each spore gives rise to a new individual.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
When reproduction takes place only from the vegetative parts of plant known as vegetative reproduction.
(a) Natural vegetative propagation.
(b) Artificial vegetative propagation.
→ Natural vegetative propagation :
- Natural propagation by leaf : Vegetative propagation by leaves can be seen in very few plants like bryophyllum and begonia. In these plants buds are produced on leaf margins. These buds after falling on the ground grow into new plants.
- Natural propagation by stem : Underground stems are modified for storage of food. ?These
underground stems produce several new plants from their buds. Modified stems like tuber, bulb, rhizome and corm help the plants to multiply.
- Natural propagation by root : Roots also help in vegetative propagation. For example, sweet
potato and dahlia give rise to new plants from their fleshy roots. (figure)
→ Artificial vegetative propagation :
- Grafting : In this commonly practiced method a new variety is obtained from the mother plant (figure). In this process a detached part of one plant is inserted into the stem or the root system of another plant.
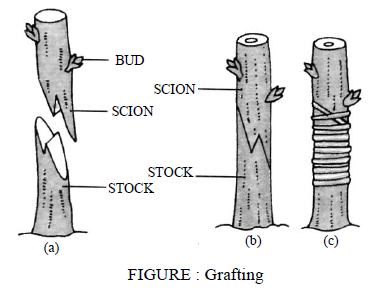
The short piece of detached shoot containing several buds is called scion. The lower portion of the plant that is fixed to the soil by its roots system is called the stock. They establish vascular connection with each other after a few days.
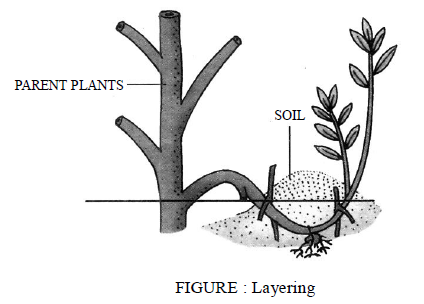
- Layering : In this method a young branch is bent towards the ground and covered with moist soil. After some days, new roots develop from the covered part, which is in contact with the soil. This is called a layer and the process is called layering. The branch is then separated from the parent plant and allowed to grow into a new independent plant.
- Cutting : In this method a healthy young branch of a plant having leaf buds is cut out and planted in moist soil (figure). The branch develops root and grows into a new plant. Bougainvillea, sugarcane, rose and grapes are grown from cuttings.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
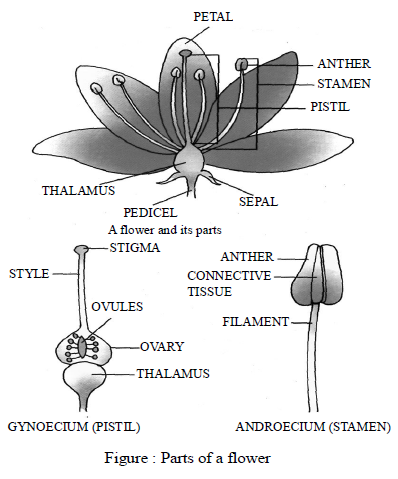
Flower is a reproductive part of plant. Which contain male & female sex organ & produce ovum & pollen grain. A normal flower consists of four whorls namely sepals, petals, androecium and gynoecium (figure).
The androecium is the male reproductive part of the flower. Androecium may consist of one or more tube-like stamens. Each stamen consists of thin stalk called filament and a two-lobed head called the anther. Anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes. The pistil or gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower. Each pistil consist of stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules.
POLLINATION
Pollination is the process by which pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same flower or another flower.
- Types of pollination :
There are two types of pollination which are described below :
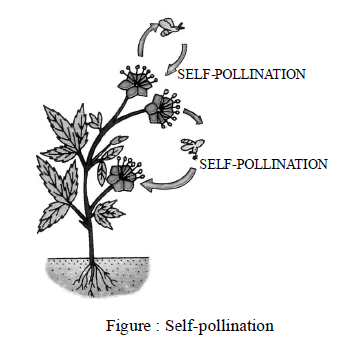
- Self-Pollination or Autogamy :
It is the process of transfer of pollen from anther to the stigma of the same flower or to the stigma of another flower of the same plant.
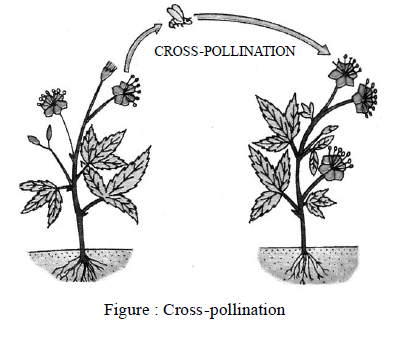
- Cross-pollination or Allogamy :
It is the process of transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower of another plant of the same species or sometimes of very closely related species.
FERTILISATION
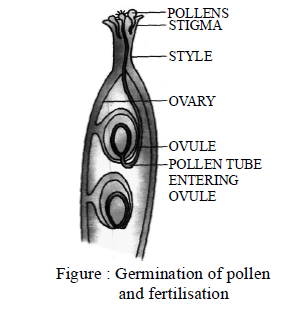
After successful pollination the stigma secretes nutrients for the lodged pollen grains. The pollen grains absorb these nutrients and grow to form a thin tube called pollen tube. This grows into the stigma in down the style (figure). It grows until it reaches the ovule and enters inside it. The pollen tube contains two male gametes. After reaching the ovule, it releases the male gametes, one of which fused with the egg to form the zygote. This process of fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete is called fertilization. The zygote develops into an embryo.
FRUIT & SEED FORMATION
After fertilization the ovary grows into a fruit and the ovules inside it become seeds. The other parts of the flower such as sepals, petals, and stamens fall off. A fruit is actually a biologically ripened ovary.
| Class 7 Science Cellular Level of Organisation Notes |
| Class 7 Science Control And Coordination Notes |
| Class 7 Science Crop Production & Management Notes |
| Class 7 Science Human And Health Disease Notes |
| Class 7 Science Microbial World Notes |
| Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes |
| Class 7 Science Skeleton System Notes |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 7. Our teachers always suggest that Class 7 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 7 Science to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 7. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Science.
Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Science exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Notes Set B from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 7 students get the best study material for Science.
Yes, our Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Notes Set B include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Science principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Notes Set B provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 7 is covered.
These notes for Science are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Notes Set B, Class 7 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plants Notes Set B, are available for immediate free download. Class 7 Science study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

