Download the latest Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes in PDF format. These Class 7 Science revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 7 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 7 Science Our Environment
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 7 Science Our Environment notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Our Environment Revision Notes for Class 7 Science
Ecology:- Ecology is the scientific study of the interaction of living organisms and their environment. These interactions are studied with a view to discover the principles which govern them.
Ecosystem: Ecological system or ecosystem is an open space built by physical and biological components of an environment. Ecosystem is result of an active interaction between living and non- living components. Ecosystem is where community of plants, animals and their environment function as a whole, and relationship between organism and environment thrives blissfully.
Ecosystems have no particular size. An ecosystem can be as large as a desert or lake or as small as a tree or a puddle. If you have a terrarium, gardens or crop field that is an artificial ecosystem.
Structure of Ecosystem:- Ecosystem is composed of two components –
1. Abiotic components: It includes inorganic, organic and climatic factors like air, water, soil
and sunlight etc.
(i) Inorganic substances:
These include nutrient elements and compounds like- carbon, nitrogen, Sulphur, phosphorus, carbon dioxide and water. All these substances undergo cycling in ecosystem.
(ii) Organic compounds:
These include proteins, fats, carbohydrates and humic substances. They usually belong to the living body of organisms and link compounds of abiotic (non- living) and biotic (living) origin.
(iii) Climatic factors: These are of two types:-
(a) Atmospheric factors: For examples- light, temperature, humidity, precipitation etc.
(b) Edaphic factors: For example- topography, soil texture etc. These factors influence the distribution of number, metabolic processes and behavior of organisms.
2. Biotic components: They are divided in following parts:
(i) Producers:
They are chlorophyll containing plants which include algae, grasses and plants. They convert solar energy into chemical energy by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the source of food for majority of animals. Green plants are also called autotrophs since they synthesize their own food.
(ii) Consumers:
Those organisms which cannot synthesize their own food but depend on others for the same are called Heterotrophs. They are mostly animals. Those animals which are directly dependent on plants for food are called herbivores e.g. locust, goat, sheep, rabbit. Those animals which depend on herbivores for food are called carnivores e.g. lion, cat. The carnivores can be predators or parasites. Those organisms which depend on both plants as well as animals for food are called omnivores e.g. cockroach, man.
(i) Decomposers:
They include mostly bacteria and fungi. In ecosystem generally bacteria attack or act on animal tissues and fungi on plant tissues. They digest dead tissues by the secretion of enzymes liberating their basic elements of protoplasm in enviro nment. The liberating elements are utilised by producer s.
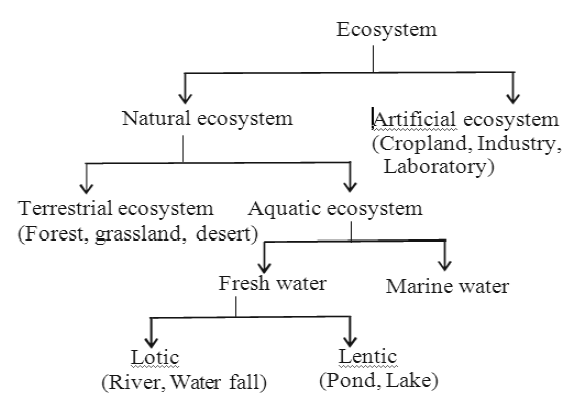
Types of Ecosystem:-
There are two main types of ecosystems:
1. Natural ecosystem: They are self controlled in natural conditions. The interference of human being is minimum; These can be further classified as follows on the basis of specific type of habitats.
(a) Terrestrial ecosystem: For example- forests, grasslands, deserts etc.
(b) Aquatic ecosystem: It is of two types- fresh water ecosystem and marine water ecosystem. Fresh water is again of two types- Lotic e.g. river, water fall etc.and Lentic e.g. pond, lake etc.
2. Artificial ecosystem: They are completely controlled by man, e.g. cropland which includes fields of wheat, bajra, rice etc. In this type man controls the biotic community and physicochemical atmosphere of the ecosystem.
In addition to the above two main types a third type ‘space ecosystem’ has also been recognized.
There are four main cycles that occur in ecosystem:
1. The water cycle: Liquid water from the ocean evaporates, condenses to form clouds, falls to the Earth as precipitation, and returns to the ocean as runoff.
2. The carbon cycle: Plants convert the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into carbon compounds, which are used by animals that consume the plants.
3. The nitrogen cycle: Nitrogen from the atmosphere is fixed by bacteria and made available to plants.
4. The phosphorus cycle: Phosphate dissolves in water, making phosphate ions available to plants. Plants convert the phosphorus into biological molecules, which are then passed through the ecosystem’s food chain.
Productivity in Ecosystem:-
The flow of energy through an ecosystem is not an efficient process. Only around 1 percent of the solar energy that reaches a plant is used to produce food. From there, at each level that organisms consume each other for food, energy is lost as heat. Scientists use three calculations for measuring plant productivity in an ecosystem: Primary productivity measures how much energy is produced by the photosynthetic organisms in an ecosystem. Gross primary productivity measures the total amount of organic matter produced by the photosynthetic organisms in the ecosystem. Plants also use some of the matter they produce for respiration. The remainder is available for heterotrophs.
Net primary productivity (NPP) measures the amount of matter produced that is available for heterotrophs. NPP for an ecosystem is generally measured in grams per square meter (g/ m 2).
- Biomass is the total weight of all an ecosystem’s organisms. Biomass increases as net primary productivity increases. Secondary productivity is a measure of the rate of biomass production by an ecosystem’s heterotrophs. Only around 10 percent of the energy available at one trophic level is available to the next. Energy may be lost as feacal matter or converted to heat. As energy passes from consumer to consumer down the food chain, the amount of available energy is continuously diminished, limiting the number of steps a given ecosystem’s food chain can sustain the energy.
- Biomes are ecosystems that have similar climates and organisms. There are eight major
biomes: trophic rainforest, savanna, desert, temperate grassland, temperate deciduous forest, temperate evergreen forest, taiga , and tundra.
Marine Ecosystem:-
Marine ecosystems are characterized based on water depth and light levels.
The neritic zone is the relatively shallow region along the edges of continents and islands.
It stretches to a depth of 300 meters.
The pelagic zone is the area of water above the ocean floor, stretching from the surface to depth approaching 1,000 meters.
The benthic zone is the ocean floor.
Food chain and Food web:-
A food chain shows how each living thing gets its food. Some animal eat plants and some animals eat other animals. For example, a simple food chain links the trees & shrubs, the giraffes (that eat trees & shrubs), and the lions (that eat the giraffes). Each link in this chain is food for the next link. A food chain always starts with plant life and ends with an animal.
Following are some more examples of food chain.
(i) grains sparrows cats
(ii) Algae, moss and food crumbs in the drains → cockroach → lizard → birds
(iii) grass → rabbit → hawks (garden and parks)
(iv) bark of a tree → wood house → spider → shrew → fox (woodland)
(v) cacti → ants / locusts → spiders → lizards → snakes (desert)
Food chains can be long or short depending upon the number of trophic level involved.
There are several different kinds of food chains, including
- predator chain : plant herbivore, carnivore, larger carnivore.
- parasite chain: various organisms sequentially parasitize one another
- saprophyte chain: decomposers, especially fungi, which feed an dead organic matter,
including the body of other decomposers.
Food web:-
A food web consists of many food chains. A food chain only follows just one path as animals find food. e.g: A hawk eats a snake, which has eaten a frog, which has eaten a grasshopper, which has eaten grass. A food web shows the many different paths plants and animals are connected. E.g. : A hawk might also eat a mouse, a frog or some other animal. The snake may eat a beetle, a caterpillar, or some other animal. And so on for all the other animals in the food chain. A food web is several food chains connected together.
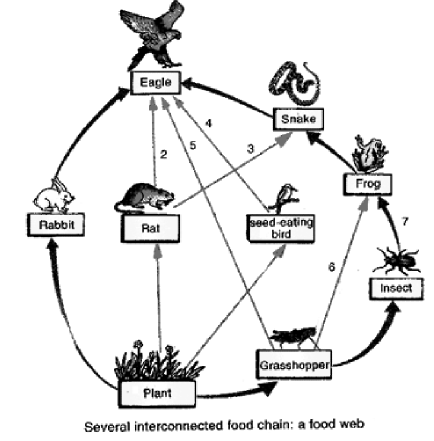
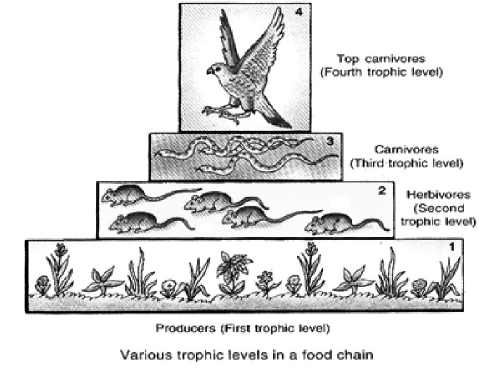
Trophic Levels and Food Chains:-
The trophic level of an organism is its position in a food chain, the sequence of consumption and
energy transfer through the environment.
For example, a simple grazing food chain is comprised of Plant → herbivore
→ carnivore
At the base of the food chain lies the primary producers.
Primary producers:-
Autotrophs (usually photosynthetic) are the organisms that support all other trophic levels either directly or indirectly by synthesizing sugars and other organic molecules using light energy. Some examples of these include terrestrial plants, aquatic photosynthetic protists, and cyanobacteria. An exception is communities of organisms living around hot water, deep sea vents where producers are cheomosynthetic bacteria that oxidize H 2S (driven by geothermal energy).
Primary consumers:-
These are herbivores that consume primary producers. Some examples are terrestrial insects, snails, grazing mammals, seed- eating birds, aquatic zoo- plankton, and some fish.
Secondary consumers:-
These are the carnivores that eat herbivores. This group include terrestrial spiders, frogs, insects- eating birds, lions, many fish, and sea- stars.
Tertiary consumers:-
These are the carnivores that eat other carnivores. eg. Eagle, etc.
Detritivores:-
These are the consumers that derive energy from organic wastes and dead organisms some examples include the bacteria and fungi. Also include scavengers such as cockroaches and bald eagles. This level often forms a major link between primary producers and higher- level consumers, and is important components of the recycling process.
Fungi are important components of the decomposers
Ecological efficiency:-
Ecological efficiency is the ratio of net productivity at one trophic level compared to net productivity at the level below. It can vary greatly depending on the organisms involved, but is roughly 10%. This means that 90% of the energy available at one trophic level never transfers to the next.
Habitat Destruction and the Biodiversity Crisis:-
The destruction of natural systems due to human encroachment has resulted in only a small proportion of natural, undisturbed habitat remaining in existence. Over 75% of the Earth’s original forests have been cleared or severely disrupted.
One result of the destruction of natural habitat will be the exitinction of many species as their ecosystem disappear. This biodiversity crisis has many aspects that must be considered in order to protect endangered species. Not only is localized protection necessary, but many migratory species are facing habitat destruction in both their northern breeding grounds and their tropical wintering grounds.
Ecological pyramids:
- Ecological pyramids are diagrammatic are representation that show the relationships between the trophic levels of an ecosystem. The pyramid shape reflects the loss of energy that occurs from one trophic level to the next. There will generally be many individuals at the lowest trophic level, where energy levels are more abundant. Since only 10 percent of the energy is passed on to the next level, there will be fewer individuals at the second level, and even fewer at the third.
Ecological pyramids can be represented in three ways:
1. A pyramid of numbers shows the number of individuals at each level.
2. A pyramid of biomass shows the amount of biomass produced at each level.
3. A pyramid of energy shows the amount of energy available at each level.
- A population is a group of individuals of the same species occupying a given area. It has a characteristic size, density, distribution, and age structure as well as characteristic ranges of heritable traits.
Question: Trophic levels are formed by –
a) only plants
b) only animals
c) only carnivores
d) organism linked in food chain
Answer: d
Question: Individuals of any species at a place form-
a) biotic community
b) ecosystem
c) population
d) biome
Answer: c
Question: An example of a producer in the aquatic food web would be –
a) Duckweed
b) Ducks
c) Fish
d) Insects
Answer: a
Question: The best source of energy in the environment is –
a) Water
b) Soil
c) Trees
d) Ponds
Answer: c
Question: When you were a child, you may have heard the old poem, “Fishy, fishy in the brook, daddy catch it with a hook, mamma fries it in pan, baby eats it like a man.” This poem illustrates the biological concept of –
a) Trophic levels in a food web
b) Primary productivity
c) The decomposition of organic matter
d) A poem that would be considered politically incorrect today
Answer: a
Question: The last chain of food is –
a) producers
b) decomposers
c) parasites
d) none
Answer: b
Question: Each step in a food chain is called a
a) trophic level
b) consumer level
c) food web
d) producer
Answer: a
Question: As energy is passed from one trophic level to another, the amount of usable energy –
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remain the same
d) Energy is not passed from one trophic level to another
Answer: b
Question: How do mountain ranges create deserts –
a) by lifting land up into colder, drier air
b) by completely blocking the flow of air into desert areas, thus preventing clouds from getting there
c) by forcing air to first rise and then fall, thus causing rain on one side of the mountains and desert on the other
d) by causing the global wind patterns that make certain latitudes very dry
Answer: c
Question: The part of earth comprising water is called an –
a) atmosphere
b) hydrosphere
c) lithosphere
d) none of the options
Answer: b
Question: Habitat together with functions of species constitute –
a) Trophic level
b) Boundary
c) Topography
d) Niche
Answer: d
Question: In an ecosystem green plants are known as
a) primary consumers
b) secondary consumers
c) producers
d) tertiary consumers
Answer: c
Question: Which of the following is the most important climatic factor
a) precipitation
b) soil
c) gradient of slope
d) atmosphere
Answer: a
Question: As a biologist, if you become very interested in the study of the interaction of organisms with each other and the environment your subspeciality would be –
a) Zoology
b) Ecology
c) Botany
d) Herpetology
Answer: b
Question: Which one of the following factors is biotic
a) Photoperiod
b) CO₂ extent to the soil
c) Texture and porosity
d) Rainfall
Answer: b
Question: As a black widow spider consumes her mate, what is the lowest trophic level she could be occupying –
a) third
b) first
c) second
d) fourth
Answer: d
Question: Term ‘ecology’ was proposed by –
a) William
b) Odum
c) Reiter
d) Daubenmier
Answer: c
Question: Sun gives radiations in the form of –
a) Infra-red radiation
b) Visible light
c) Ultra-violet
d) all of the options
Answer: d
Question: In the biosphere, which of the following is the ultimate source of energy –
a) Carbon
b) Water
c) Sunlight
d) Nitrogen
Answer: c
Question: Free services provided to humans by ecosystems include –
a) control of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration
b) prevention of soil erosion
c) filtering of pollutants from water and air
d) all of the options
Answer: d
Question: Organisms that feed on producers in the ecosystem are called
a) first level consumers
b) second level consumers
c) autotrophs
d) none of the options
Answer: a
Question: Which of the following constitute a food- chain ?
a) Grass, wheat and mango
b) Grass, goat and human
c) Goat, cow and elephant
d) Grass, fish and goat
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following organisms feeds on animal and plant material?
a) carnivores
b) herbivores
c) omnivores
d) autotrophs
Answer: c
Question: Pyramid of energy in a forest ecosystem is
a) Always inverted
b) Always upright
c) Both upright and inverted depending on ecosystem
d) First upright then inverted
Answer: b
Question: Which of the following would not be considered an autotroph?
a) plant
b) algae
c) photosynthetic bacteria
d) mushroom
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following would be considered a population?
a) all the insects in the world
b) all the birds in North America
c) all the bullfrogs in a pond
d) all the trees in a state park
Answer: c
Question: The physical location an organism lives is sometimes referred to as its
a) gene pool
b) biosphere
c) habitat
d) population
Answer: c
Question: In energy pyramids, which of the following trophic levels contains the largest amounts of usable energy?
a) producers
b) first level consumers
c) second level consumers
d) third level consumers
Answer: a
Question: The portion of the earth’s surface that supports life is known as
a) the biome
b) the atmosphere
c) the biosphere
d) the strata
Answer: c
Question: Which of the following is not correct concerning the nitrogen cycle?
a) nitrogen is an element needed to produce amino acids
b) atmosphere nitrogen is converted to ammonia by certain bacteria
c) denitrification is when atmospheric nitrogen is changed into ammonia
d) plants use nitrates in the soil to make proteins
Answer: c
Question: The burning of fossil fuels releases large amounts of
a) iron into the soil
b) carbon into the atmosphere
c) oxygen into the atmosphere
d) sulfur into the soil
Answer: b
Question: The study of the relationship between living things and the environment is called
a) evolution
b) paleontology
c) ecology
d) cytology
Answer: c
Question: The maximum energy is stored at following tropical level in any ecosystem –
a) Producers
b) Herbivores
c) Carnivores
d) Top carnivores
Answer: a
Question: Which organisms are responsible for removing carbon from the atmosphere and fixing this carbon into organic molecules?
a) autotrophs
b) plants
c) producers
d) all of the options
Answer: d
Question: An organism that cannot synthesize its own organic molecules is called a
a) producer
b) autotroph
c) heterotroph
d) A and B
Answer: c
Question: In an ecosystem the function of the producers is to
a) Convert organic compounds into inorganic compounds
b) Trap solar energy and convert it into chemical energy
c) Utilize chemical energy
d) Release energy
Answer: b
Question: All the living organisms and the nonliving environment in a particular location make up what is called a(n)
a) population
b) species
c) biotic factors
d) community
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
a) Carrying cloth bags to put purchases in while shopping
b) Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
c) Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter
d) all of the options
Answer: d
Question: For corrosion of metals, there should be –
a) Exposed surface of metal
b) Moisture
c) Air
d) all of the options
Answer: d
Question: Pyramids of energy are –
a) always upright
b) always inverted
c) mostly upright
d) mostly inverted
Answer: a
Question: Which of the following would best describe the niche of a rabbit?
a) its fur color
b) how many offspring it produces
c) the grass it eats in the environment
d) the enzymes present in its blood
Answer: c
Question: The first organism that will appear in an area experiencing primary succession is called a(n)
a) pioneer organisms
b) secondary consumer
c) parasites
d) heterotroph
Answer: a
Question: Which of the following biomes receives the highest annual rainfall?
a) taigas
b) deserts
c) grasslands
d) tropical rainforests
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following biomes contains many trees that lose their leaves in the colder months of the year?
a) tropical rainforest
b) grasslands
c) temperate deciduous forest
d) tundra
Answer: c
Question: In the process of ecological succession, the final community or group of organisms that will exist in the ecosystem are called
a) pioneer organisms
b) climax community
c) secondary consumers
d) none of the options
Answer: b
Question: What characteristic is usually used as the major identifying factor of a particular biome?
a) latitude
b) longitude
c) rock formations
d) climax plant life
Answer: d
Question: Commensalism is
a) an interaction among two species where both species benefit from the relationship
b) an interaction among two species where one species benefits and the other species is unaffected
c) an interaction among two species where one species benefits and the other species is harmed
d) when two organisms do not interact at all in an environment
Answer: b
Question: Transpiration is when
a) atmospheric nitrogen is chemically fixed as ammonia
b) ice is changed directly into water vapor
c) liquid water that has entered a plant leaves as water vapor
d) water vapor is changed into liquid water
Answer: c
Question: Which of the following conditions would probably result in the most competition for food?
a) a lion and a zebra in a savannah
b) an elephant and an ant colony in a forest
c) a spider and a plant in someone’s backyard
d) a deer and a rabbit in a grass field
Answer: d
Question: Which of the following statements are true about secondary succession?
a) Secondary succession will begin in an area that has no soil.
b) Secondary succession occurs on a site where no previous community existed.
c) Secondary succession will begin in an area that has been disturbed by a condition, such as fire, that destroys the vegetation, but leaves the soil.
d) Secondary succession will cause all plant life in the area to die.
Answer: c
| Class 7 Science Cellular Level of Organisation Notes |
| Class 7 Science Control And Coordination Notes |
| Class 7 Science Crop Production & Management Notes |
| Class 7 Science Human And Health Disease Notes |
| Class 7 Science Microbial World Notes |
| Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes |
| Class 7 Science Skeleton System Notes |
Important Practice Resources for Free Printable Worksheets PDF
CBSE Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Our Environment to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 7. Our teachers always suggest that Class 7 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Our Environment Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 7 Science to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 7. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Science.
Our Environment Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Our Environment . All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Science exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 7 students get the best study material for Science.
Yes, our Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Science principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 7 is covered.
These notes for Science are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes, Class 7 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including Class 7 Science Our Environment Notes, are available for immediate free download. Class 7 Science study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

