NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science C++ Revision Tour have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Computer Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Computer Science are an important part of exams for Class 12 Computer Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Computer Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. C++ Revision Tour is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
C++ Revision Tour Class 12 Computer Science NCERT Solutions
Students of Class 12 studying Computer Science are advised to carefully go through the NCERT questions and their detailed answers provided here for the chapter C++ Revision Tour. The questions in the NCERT textbook for Class 12 Computer Science form an important part of school exams. These solutions for Class 12 follow a step-by-step approach and are highly beneficial for exam preparation. Scroll down to view detailed, chapter-wise solutions for C++ Revision Tour and explore more NCERT solutions and free study materials for Computer Science and other subjects of Class 12.
C++ Revision Tour NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science
Question 1: Write the related library function name based upon the given information in C++.
1. Get single character using keyboard. This function is available in stdio.h file.
2. To check whether given character is alpha numeric character or not. This function is available in c type.h file.
Answer:
1. getchar( )
2. isalnum( )
Question 2: Observe the following program very carefully and write the names of those header file(s), which essentially needed to compile and execute the following program successfully :
Type def char TEXT[80];
void main()
{
TEXT Str[] = "Peace is supreme";
int Index = 0;
while(Str[Index]! = '\0')
if(isupper(Str[Index]"
Str[Index ++] = ? '#';
else
str[Index ++] = '*';
puts(Str);
}
Answer:
<ctype.h>, <stdio.h>
Question 3: Name the header files that shall be needed for ‘ successful compilation of the following C+ + code :
void main()
char str[20],str[20];
gets(str);
strcpy(str1,str);
strrev(str);
puts(str);
puts(str1);
}
Answer:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
Question 4: Observe the following C++ code and write the name(s) of the header file(s), which will be essentially required to run it in a C + + compiler :
void main()
{
char CH, STR[20];
cin>>STR;
CH=toupper(STR[0]);
cout<<STR<<"starts with"<<CH<<endl;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
Question 5: Observe the following C++ code and write the name(s) of the header file(s), which will be essentially required to rim it in a C++ compiler :
void main()
{
char Text[20],C;
cin>>Text;
C=tolower(Text[0]);
cout<<C<<"is the first char of"<<Text<<endl;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
Question 6: Name the header file(s), which are essentially required to run the following program segment :
void main()
{
char A='K',B;
if(islower(A))
B=toupper(A);
else
B= '*';
cout<<A<<"turned to"<<B<<endl;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
Question 7: Observe the following C+ + code and write the name(s) of header files, which will be essentially required to run it in a C + + compiler
void main()
{
float Area, Side;
cin>>Area;
Side = sqrt(Area);
cout<<"one side of the square<<side<<end1;
}
Answer:
Header files required:
1. math.h
2. iostream.h
Question 8: Write the names of header files used :
void main()
{
int number;
cin>>number;
if(abs(number) == number)
cout<<"Positive"<<endl;
}
Answer:
iostream.h, math.h
Question 9: Write the names of header files, which are NOT NECESSARY to run the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
void main()
{
char STR[80];
gets(STR);
puts(strrev(STR));
}
Answer:
Header files not required are :
iostream.h,math.h.
Question 10: Which C++ header file(s) are essentially required to be included to run/execute the following C++ source code ?
void main()
{
char TEXT[] = "Something";
cout<<"Remaining SMS Chars :"<<160-
strlen(TEXT)<<endl;
}
Answer:
1. <string.h>
2. <iostream.h>
Question 11: Which C++ header file(s) are essentially required to be included to run/execute the following C++ source code (Note : Do not include any header file, which is/are not required)
?
void main()
{
char STRING[] = "SomeThing";
cout<<"Balance Characters:"<<160-
strlen(STRING)<<endl;
}
Answer:
<iostream.h>,<string.h>
Question 12: Ahmed has started learning C++ and has typed the following program. When he compiled the following code written by him, he discovered that he needs to include some header files to successfully compile and execute it. Write the names of those header files, which are required to be included in the code.
void main()
{
float Radians,Value;
cin>>Radians;
Value=sin(radians);
cout<<Value<<endl;
}
Answer:
iostream.h
string.h
Question 13: Which C++ header file(s) are essentially required to be included to run/execute the following C++ code:
void main()
{
char*word1="Hello".word2="Friends";
strcat(word1,word2);
cout<<word1;
}
Answer:
iostream.h
string.h
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question 1: Define Macro with suitable example.
Answer:
Macro are pre processor directive created using # define that serve as symbolic constants.They are created to simplify and reduce the amount of repetitive coding.
For instance,
#define max (a, b) a > b ? a : b
Define the macro max, taking two arguments a and b. This macro may be called like any C
function with similar syntax. Therefore, after preprocessing.
A = max (x, y);
Becomes A = x>y ?x:y;
Question 2: Write the output of the following C+ + program code :
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
class Calc
{
char Grade;
int Bonus;
public:
Calc (){Grade = 'E'; Bonus = 0;}
void Down(int G)
{
Grade(-) = G;
}
void Up(int G)
{
Grade += G;
Bonus ++;
}
void Show()
{
cout<<Grade<<"#"<<Bonus<<endl
}
};
void main()
{
Calc c;
C.Down(2);
C.Show();
C.Up(7);
C.Show();
C.Down(2);
C.Show();
}
Answer:
C#0
J#1
H#1
Question 3: Rewrite the following program after removing any syntactical errors. Underline each correction made.
#include <isotream.h>
void main()
int A[10];
A = [3, 2, 5, 4, 7, 9, 10];
for(p = 0; p <= 6; p++)
{
if(A[p]%2=0)
int S = S + A[p]];
}
cout<<S;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{
int A[10] = {3, 2, 5, 4, 7, 9, 10};
int S = 0, p;
for(p = 0; p <= 6; p++)
{
if(A[p]%2 == 0)
S = S + A[p];
}
cout<<S;
}
Question 4: Observe following C++ code very carefully and rewrite it after removing any/all syntactical errors with each correction underlined.
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the porgram.
#Define float Max = 70.0;
Void main)
{
int Speed
char Stop = 'N';
cin >> Speed;
if Speed > Max
Stop = 'Y' ;
cout <<stop<<end;
}
Answer:
#define float Max 70.0 //Error 1,2,3
void main() //Error 4
{
int Speed; //Error 5
char Stop = 'N';
cin>>Speed;
if(Speed>Max) //Error 6
Stop = 'Y';
cout<<Stop<<endl; //Error 7
}
Question 5: Write the output of the following C+ + program – code :
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
void Position(int & C1, int C2 = 3)
{
C1+ = 2;
C2+ = Y;
void main()
int P1 = 20, P2 = 4;
position(P1);
cout<<P1<<","<<P2<<endl;
position(P2, P1);
cout<<P1<<","<<P2<<endl;
}
Answer:
22,4
22,6
Question 6: Study the following program and select the posssible output(s) from the options (i) to (iv) following it. Also, write the maximum and the minimum. values that can be assigned to the variable NUM.
Note :
— Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
— random(n) function generates an integer between 0 and n -1.
void main()
{
randomize();
int NUM;
NUM = random(3)+2;
char TEXT[] = "ABCDEFGHIJK";
for(int I=1; I <= NUM; I++)
{
for(int J = NUM; J <= 7;J++)
cout<<TEXT[J];
cout<<endl;
}
}
(i)FGHI
FGHI
FGHI
FGHI
(ii)BCDEFGH
BCDEFGH
(iii)EFGH
EFGH
EFGH
EFGH
(iv)CDEFGH
Answer:
(iii) and (iv)
Minimum value of NUM = 2
Maximum value of NUM = 4
Question 7: Rewrite the following C++ program after removing all the syntactical errors (if any),underlining each correction :
includeciostream.h>
#define PI=3.14
void main()
{
float r,a;
cout<<'enter any radius';
cin>>r;
a=PI*pow(r,2);
cout<<"Area="<<a;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h> // Error 1: Declaration Syntax error
#include<math.h>
#define PI=3.14 // Error 2: Macro declaration does not allow assignment
void main()
{
float r,a; // Error 3:Undefined Symbol a
cout<<"enter any radius"; //Error 4 : Character Constant must be one or two characters
long
cin>>r;
a=PI*pow(r,2) //Error 5 : Expression Syntax
cout<<"Area="<<a;
}
Question 8: Rewrite the following C++ code after removing all the syntax error(s), if presents in the code.
Make sure that you underline each correction done by you in the code.
Important Note:
- Assume that all the required header files are already included, which are essential to run this code.
- The corrections made by you do not change the logic of the program.
typedef char STR[80];
void main()
{
STR Txt;
cin (Txt);
cout<<Txt<<endline;
}
Answer:
typedef char STR[80];
void main()
{
STR Txt;
gets(Txt);
cout<<Txt<<endl;
}
Question 9: Rewrite the following C+ + code after removing all the syntax error(s), if present in the code.
Make sure that you underline each correction done by you in the code.
Important Note :
- Assume that all the required header files are already included, which are essential to run this code.
- The corrections made by you do not change the logic of the program.l
typedef char STRING[50];
void main()
{
City STRING;
cin (City);
cout<<City<<endline ;
}
Answer:
typedef char STRING[50];
void main()
{
STRING City;
gets(City);
cout<<City<<endl;
}
Question 10: Out of the following, find those identifiers, which cannot be used for naming Variable,Constants or Functions in a C + + program : Total*Tax, double, case, My Name, New switch,Column31, _Amount
Answer: Total * Tax, double, case, My name, New switch
Question 11: Ronica Jose has started learning C++ and has typed the following program. When she compiled the following code written by her, she discovered that she needs to include some header files to successfully compile and execute it. Write the names of those header files,which are required to be included in the code.
void main()
{
double X,Times,Result;
cin>>X>>Times;
Result=pow(X,Times)
cout<<Result<<endl;
}
Answer:
<iostream.h>for cout and cin
<math.h>for pow()
Question 12: Rewrite the following C+ + code after removing any/all syntactical error with each correction underlined.
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
#define Formula(a,b)= 2*a+b
void main()
{
float x=3.2; Y=4.1;
Z=Formula(X,Y);
cout<<'Result='<<Z<<endl;
}
Answer:
# define Formula(a.b)2*a+b
void main()
{
float X=3.2, y=4.1;
float Z = Formula(X,Y);
cout<<"Result="<<Z<<endl;
}
Question 13: Find and write the output of the following C+ + program code :
Note ; Assume all required header files are already included in the program.
typedef char TexT[80];
void JumbleUp(TexT T)
{
int L=strlen(T);
for(int C=0;C<L-1;C+=2)
{
char CT=T[C];
T[C] = T[C+l];
T[C+l]=CT;
}
for(C=l;C<L;C+=2)
if(T[C]>='M'&& T[C]<='U')
T[C] = '@';
void main()
{
TEXT Str = "HARMONIOUS";
JumbleUp(Str);
cout<<Str<<endl;
}
Answer:
AHM@N@OIS@
Question 14: Look at the following C++ code and find the possible output(s) from the options (i) to (iv) following it. Also, write the maximum and the minimum values that can be assigned to the variable PICKER.
Note :
- Assume all the required header files are already being included in the code.
- The function random(n) generates an integer between 0 and n -1
void main()
{
randomize();
int PICKER;
PICKER=random(3);
char COLOUR[][5]={"BLUE","PINK","GREEN","RED"};
for(int 1=0;I<=PICKER;I++)
{
for(int J=0;J<=I;J++)
cout<<COLOR[J];
cout<<endl;
}
}
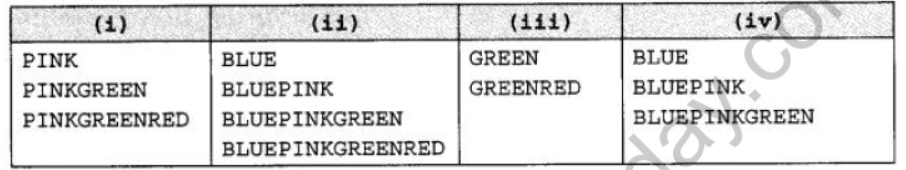
Answer:
Maximum value : 3
Min value : 1
Question 15: Out of the following, find those identifiers, which cannot be used for naming Variable,Constants or Functions in a C + + program : _Cost, Price*Qty, float, Switch, Address one,Delete, Numberl2, do
Answer: Price* Qty, float, Address one, do
Question 16: Jayapriya has started learning C+ + and has typed the following program. When she compiled the following code written by her, she discovered that she needs to include some header files to successfully compile and execute it. Write the names of those header files,which are required to be included in the code.
void main()
{
float A, Number, Outcome;
cin>>A>>Numbers;
Outcome = pow(A, Number);
cout<<outcome<<endl;
}
Answer:
<iostream. h> for cout and cin
<math. h> for Pow()
Question 17: Rewrite the following C+ + code after removing any/all syntactical error with each correction underlined.
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
#define Equation(p,q)=p+2*q
void main()
{
float A=3.2;B=4.1;
C=Equation (A,B);
cout<<’Output='<<C<<endl;
}
Answer:
#define Equation(p,q)g+2*q
void main()
{
float A=3.2,B=4.1;
float C=Equation(A,B);
Cout<<"Output"<<C<<endl;
}
Question 18: Find and write the output of the following C++ program code:
Note : Assume all required header files are included in the program,
typedef char STRING[80];
void MIXITNOW(STRING S)
{
int Size=strlen(S);
for(int 1=0;I<Size-l;I+=2)
{
char WS=S[I];
S[I]=S[I+1];
S[1+1]=WS;
}
for(1=1;I<Size;I+=2)
If(S[I]>='M1&&S[I]<='U')
S[I]=;
void main()
{
STRING Word = "CRACKAJACK";
MIXITNOW(Word);
cout<<Word<<endl;
}
Answer: RCCAAKAJKC.
Question 19: Find and write the output of the following C+ + program code :
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
class stock
{
long int ID;
float Rate;
int Date;
public:
Stock()
{ID=1001;Rate=200;Date=l;}
void RegCode(long int I, float R)
{
ID=I;
Rate=R;
}
void Change(int New, int DT)
Rate+=New;
Date=DT;
}
void Show()
{
cout<<"Date:"<<Date<<endl;
cout<<ID<<"#"<<Rate<<endl;
}
};
void main()
{
stock A,B,C;
A.RegCode(1024,150);
B.RegCode(2015,300);
B.Change(100,29);
C.Change(-20,20);
A.Show();
B.show();
C.Show();
}
Answer:
Date:1
1024 # 150
Date : 29
2015 # 400
Date : 20
1001 # 180
Question 20: Look at the following C+ + code and find the possible output(s) from the options (i) to (iv) following it. Also, write the maximum and the minimum values that can be assigned to the variable CHANGER.
Note :
- Assume all the required header files are already being included in the code.
- The function random(n) generates an integer between 0 and n -1
void main()
{
randomize();
int CHANGER;
CHANGER=random(3);
char CITY[][25]={"DELHI","MUMBAI","KOLKATA","CHENNAI"};
for(int 1=0;I<=CHANGER;I++)
{
for (int J=0;J<=I;J++)
cout<<CITY[J];
cout<<endl;
}
}
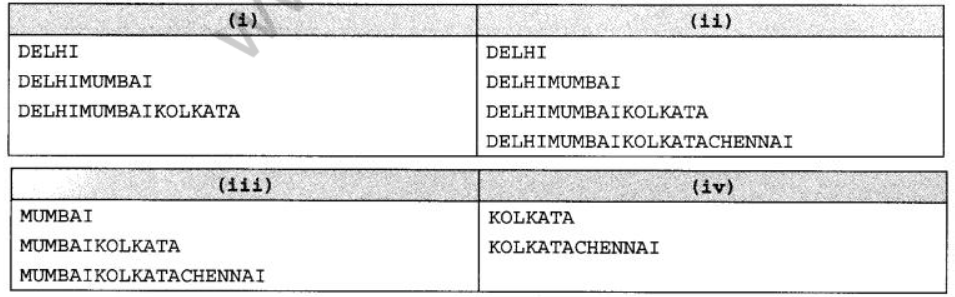
Answer:
DELHI
DELHIMUMBAI
DELHIMUMBAIKOLKATA
Minimum Value of CHANGER = 0
Maximum Value of CHANGER = 2
Question 21: Out of the following, find those identifiers, which can not be used for naming Variable,Constants or Functions in a C + + program :
Days*Rent, For, A+ Price, Grand Total
double, 2Members, . Participantl, MyCity
Answer:
Days * Rent
For
Grand Total
double
Question 22: Rewrite the following C+ + code after removing any/all syntactical errors with each correction underlined.
Note : Assume all required header files are already included in the program.
Days*Rent, For, A+Price, Grand Total
double, 2Members, Participantl, MyCity
Answer:
#define formula (a,b,c)a+2*b+3*c
void main()
{
int L=1,M=2,N=3;
int J=formula(L,M,N);
cout<<"Output="<cj<<endl;
}
Question 23: Look at the following C+ + code and find the possible output(s) from the options (i) to (iv) following it. Also, write the maximum and the minimum values that can be assigned to the variable P_Holder.
Note :
- Assume all the required header files are already being included in the code.
- The function random (n) generates and integer between 0 and n-1.
void main()
{
randomize();
int P_Holder;
P_Holder=random(3);
char place [][25]={"JAIPUR","PUNA","KOCHI","GOA" };
for(int P=0;P<=P_Holder;P++)
{
for (int C=0;C<P;C++)
cout<<Place[C];
cout<<endl;
}
}

Answer:
JAIPUR
JAIPUR PUNA
JAIPUR PUNA KOCHI
MINIMUM VALUE of P_Holder = 0
Maximum Value of P_Holder = 2
Question 24: Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical erros (if any). Underline each correction.
#include<conio.h>
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
Class product
{
int product_code,qty,price;
char name[20];
public:product()
{
product_code=0;qty=0;price=0;
name=NULL;
}
void entry()
{
cout<<"\n Enter code,qty(price";
cin>>product_code>>qty>>price;
gets(name);
}
void tot_price(){return qty*price;}
}
void main()
{
p product;
p.entry();
cot<<tot_price();
}
Answer:
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
class product
{
int product_code,qty,price;
char name[20];
public;
product()
{
product_code=0;qty=0;price=0;
strcpy(name.NULL);
}
void entry()
{
cout<<"\n Enter code, qty, price";
cin>>product_code>>qty>>price;
gets(name);
}
int tot_price(){return qty*price;}
};
void main()
{
product p;
p.entry();
cot<<p.tot price();
}
Question 25: Explain conditional operator with suitable example ?
Answer: Conditional operator is also known as ternary operator because it requires three operands and can be used to replace simple if- else code. It is used to check the condition and execute first expression if condition is true: else execute other.
Syntax :
Conditional expression ?
Expression 1 : Expression 2 :
Explanation : If the conditional expression is true then expression I executes otherwise expression 2 executes.
Example :
int y = 10, x;
x = y>10? 1:0;
cout<<X;
Output : 0
Short Answer Type Question-II
Question 1: Find and write the output of the following C+ + program code :
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
class Share
{
long int Code;
float Rate;
int DD;
public :
Share()
{Code=1001;Rate=100;DD=1;}
void GetCode(long int C, float R)
{
Code=C;
Rate=R;
}
void Update(int Change, int D)
{
Rate+=Change;
DD=D ;
}
void Status()
{
cout<<"Date:"<<DD<<endl;
cout<<Code<<"#"<<Rate<<endl;
}
void main()
{
Share S,T,U;
S.GetCode(1324,350);
T.GetCode(1435,250);
S.Update(50,28);
U.Change(-25,26);
S.Status();
T.Status();
U.Status();
}
Answer:
Date ; 28
1324 # 400
Date : 1
1435 #250
Date : 26
1000 # 75
TOPIC-2
Flow Control
Short Answer Type Questions-1
Question 1: Find syntax error(s), if any, in the following program : (Assuming all desired header file(s) are already included)
typedef char String[80];
void main
{
String S; int L;
for(L=0;L<26;C++)
S [L]=L+65;
cout<<S<<endl
}
Answer:
The given code has following errors:
1. Parenthesis () are missing after void main.
2. In for statement, the update expression should be L+ + but it is written as C + + .
Question 2: Read the following C++ code carefully and find out, which out of the given options (i) to (iv) are the expected correct outputs) of it. Also, write the maximum and minimum value that can be assigned to the variable Taker used in the code:
void main()
{
int GuessMe[4]= {100,50,200,20};
int Taker = random(2)+2;
for(int Chance=0;Chance<=Taker;Chance++)
cout<<GuessMe[Chance]<<"#";
}
(i)100#
(ii)50#200#
(iii)100#50#200#
(iv)100#50
Answer:
(iii) 100#50#200#
Max value : 350
Min value : 170
Question 3: Read the following C++ code carefully and find out, which out of the given options (i) to (iv) are the expected correct output(s) of it. Also, write the maximum and minimum value that can be assigned to the variable Start used in the code :
void main()
{
int
Guess [4]={200,150,20,250};
int Start=random(2)+2;
for (int C=Start;C<4;C++)
cout<<Guess[C]<<"#";
}
(i) 200#150#
(ii) 150#20#
(iii) 150#20#250#
(iv) 20#250#
Answer:
(iv) 20#250#
Max value : 470
Min value : 420
Question 4: Which C++ header file (s) will be include to run/execute the following C+ + code ?
void main()
{
int Last=26.5698742658;
cout<<setw(5)<<setprecision(9)<<Last;
}
Answer:
iostream.h
iomanip.h
Question 5: Find the correct identifiers of the following, which can be used for naming, variable, constants or functions in a C++ program :
For, while, INT, New, delete, IstName, Add + Subtract, namel
Answer: For, INT, New, namel
Question 6: Find correct identifiers out of the following, which can be used for naming variable,constants or function in a C++ program :
For, While, Float, new, 2ndName, A%B, Amount 2, Counter.
Answer: While, float Amount 2, _Counter.
Question 7: Find out the expected correct output(s) from the options (i) to (iv) for the following C++ code. Also, find out the minimum and the maximum value that can be assigned to the variable Stop used in the code :
void main()
{
int Begin=3,Stop;
for(int Run=l;Run<4;Run++)
{
Stop=random(Begin)+6;
cout<<Begin++<<Stop<<"*";
}
}
(i) 36*46*57*
(ii) 37*46*56*
(iii) 37*48*57*
(iv) 35*45*57*
Answer:
The correct output will be:
(i) 36*46*57*
Maximum Value of Stop=8
Minimum Value of Stop=6
Question 8: Find the output:
int A [2] [3] = {{1,2,3}, {5,6,7}};
for (int i = 1; i<2; i+ +)
for (int j = 0; j<3; j + +)
cout << A [i] [j] <<endl;
Answer:
5
6
7
Question 9: Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical errors (if any). Underline each correction.
#include<iostream.h>
typedef char Text(80);
void main()
{
Text T = "Indian";
int Count = strlen(T);
cout<<T<<'has'<<Count<<'characters'
<<endl;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef char Text[80];
void main()
{
Text T = "Indian";
int Count=strlen(T);
cout<<T<<"has"<<Count<<"characters"<<endl;
}
Question 10: Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical errors (if any). Underline each correction.
#include<iostream.h>
typedef char[80] String;
void main()
{
String S = "Peace";
int L=strlen(S);
cout<<S<<'has'<<L<<'characters'<<endl;
}
Answer:
#include<string.h>
#include<<iostream.h>
typedef char String[80];
void main()
{
String S="Peace";
int L=strlen(S);
cout<<S<<"has"<<L<<"characters"<<endl;
}
Question 11: Based on the following C++ code, find out the expected correct output (s) from the options (i) to (iv). Also, find out the minimum and the maximum value that can be assigned to the variable Trick used in the code at the time when value of count is 3 :
void main()
{
char status[][10]={"EXCEL","GOOD", "OK"};
int Turn = 10, Trick;
for(int Count=1;Count<4;Count++)
{
Trick = random(Count);
cout<<Turn-Trick<<Status[Trick]<<"#";
}
}
(i) 10EXCEL#EXCEL#8OK#
(ii) 10EXCEL#8OK#9GOOD#
(in) 10EXCEL#9GOOD#10EXCEL#
(iv) 10EXCEL#10GOOD#8OK#
Answer:
None of the given output is correct.
The correct output is
10EXCEL#10EXCEL#9GOOD#
Minimum value = 0
Maximum Value = 3
TOPIC-3
Arrays and Functions
Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1: Observe the following program very carefully and write the names of those header file(s).
which are essentially needed to compile and execute the following program successfully :
typedef char STRING[80];
void main()
{
STRING Txt[]="We love peace";
int count=0;
while(Txt[count]! = ’\0 ')
if(isalpha(Txt Count)
Txt[count++] = 1@';
else
Txt[count++] = '#';
puts
Answer:
<ctype.h>, <stdio.h>
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question 1: Explain in brief the purpose of function prototype with the help of a suitable example.
Answer: The Function prototype serves the following purposes :
1. It tells the return type of the data that the function will return.
2. It tells the number of arguments passed to the function.
3. It tells the data types of each of the passed arguments.
4. Also it tells the order in which the arguments are passed to the function.
#include<iostream.h>
int timesTwo(int num); // function
prototype int main()
{
int number,response;
cout<<"Please enter a number:";
cin>>number;
response = timesTwo(number); //
function call
cout<<"The answer is"<<response;
return 0;
}
//timesTwo function
int timesTwo (int num)
{
int answer; //local variable
answer = 2*num;
return(answer);
}
Question 2: What is the difference between call by reference and call by value with respect to memory allocation ? Give a suitable example to illustrate using C+ + code.
Answer: Call By Value : In call by value method, the called function creates its own copies of original values sent to it. Any changes that are made, occur on the function’s copy of values are not reflected back to the calling function.
Call By Reference : In call by reference method, the called function accesses and works with the original values using their references. Any changes that occur, takes place on the original values and are reflected back to the calling code.
Example:

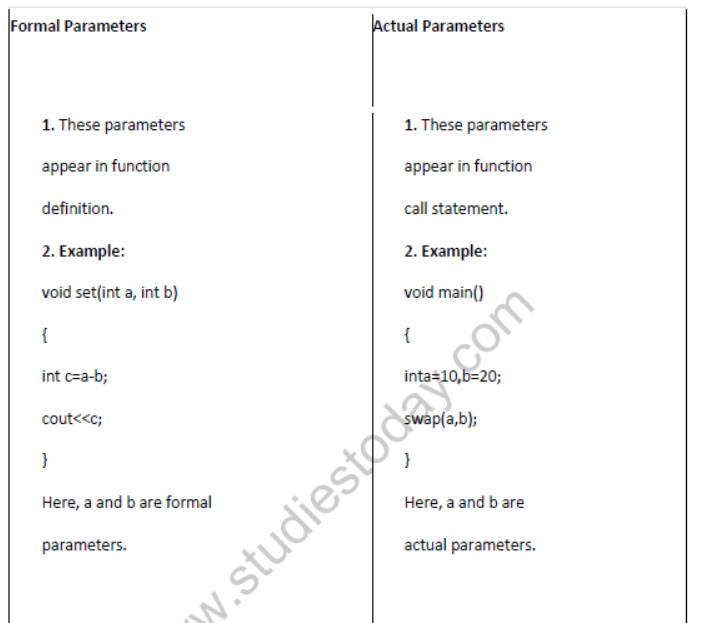
Question 3: What is the difference between Actual Parameter & Formal Parameter ? Give a suitable example to illustrate both in a C++ code.
Answer:
Question 4: Deepa has just started working as a programmer in STAR SOFTWARE company. In the company she has got her first assignment to be done using a C++ function to find the smallest number out of a given set of «numbers stored in a one-dimensional array. But she has committed some logical mistakes while writing the code and is not getting the desired result. Rewrite the correct code underlining the corrections done. Do not add any additional statements in the corrected code.
int find(int a[],int n)
{
int s=a[0] ;
for(int x=l;x<n,-x++)
if(a[x]>s)
a[x]=s;
return(s);
}
Answer:
int find(int a[],int n)
{
int s=a[0];
for(int x=l;x<n;x++)
{
if(a[x]<=s)
s=a[x];
}
return(s);
Question 5: What is the benefit of using default parameter/ argument in a function ? Give a suitable example to illustrate it using C++ code.
Answer: The benefit of using default arguments is that whenever there is no value supplied to the parameter within the program, its default value can be used.
Example :
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b=20,c;
a=change(c,b);
return a ;
}
int change(int a=10,b)
{
int temp;
temp=a;
a=b;
return temp;
}
In the above example, change () assigns a value 10 to a because it is defined by default.
Question 6: What is the benefit of using function prototype for a function? Give a suitable example to illustrate it using C++ code.
Answer:
The benefit of using a function prototype is to have a clear representation of the type of value that the function would return and type of argument the function needs.
Example :
int function (int a, int b);
The above is a prototype for a function named ‘function’ that has two integer arguments a & b which returns as integer value.
Question 7: Write a prototype of a function named percent, which takes an integer as value parameter & return a float type value. The parameter should have default value of 10.
Answer: float percent(int a=10) ;
Question 8: Observe the following C++ code carefully and write the same after removing syntax errors.
#define change(A,B)2*A+B;
void main()
{
float X,Y,F;
cin>>X>>Y;
F=Change(X,Y);
cout<<"result:<<F<<endline;
}
Answer:
The corrected code is :
#define change(A,B)2*A B;
void main()
{
float X,Y,F;
cin>>X>>Y;
F=change(X,Y);
cout<<"result:<<F<<endl;
}
Question 9: Write a function in C++ to accept two integers as parameters and returns the greater of these numbers.
Answer:
int max (int a, int b)
{
if(a>b)return a;
else
return b;
}
Question 10: Write the output from the following C+ + program code :
#include<iostream.h>
includecctype.h>
void strcon(char s[])
{
for(int i=0,1= 0;s[i]! = '\0' ;i++,1++) ;
for(int j=0;j<l;j++)
{
if (isupper(s[j]))
s[j]=tolower(s[j])+2;
else if(islower(s[j]))
s[j]=toupper(s[j])-2;
else
s[j]='@';
}
}
void main()
{
char *c="Romeo Joliet";
strcon(c);
cout<<"Text= "<<c<<endl;
c=c+3;
cout<<"New Text= "<<c<<endl;
c=c+5-2;
cout<<"last Text= "<<c
}
Answer:
Text = @tMKCM@lMJGCR
New Text = <KCM@1MJGCR
Last Text = @1MJGCR
Question 11: Study the following C++ program and select the possible output(s) from it : Find the maximum and minimum value of L.
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
randomize();
char P[]="C++PROGRAM";
long L;
for(int 1=0;P[I]!='R';I++)
{
L=random(sizeof(L))+5;
cout<<P[L]<<";
}
}
(i) R-P-O-R
(ii) P-0-R-+-
(iii) O-R-A-G
(iv) A-G-R-M
Answer:
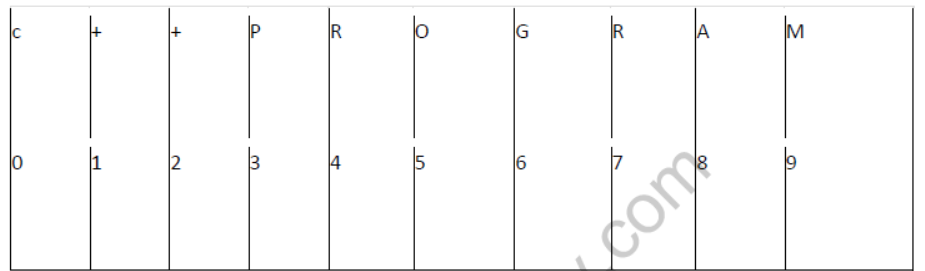
Possible Values:
Possible Output is (iii) O-R-A-G
Minimum value of L = 5
Maximum Value of L = 8
Question 12: Write a user defined function DIVTQ which takes an integer as parameter and returns whether it is divisible by 13 or not. The function should return 1 if it is divisible by 13,otherwise it should return 0.
int DIVT(int x)
{
int f;
if(x%13 == 0)
f=1;
else f=0;
Return f;
}
Question 13: Find output of the following program segment :
#include<iostream.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void Mycode(char Msg[],char CH)
{
for(int cnt=0;Msg[cnt]!='\0';cnt++)
{
if(Msg[cnt]>='B'&& Msg [cnt]<='G')
Msg[cnt] =tolower(Msg[cnt]);
else
if(Msg[cnt]=='N'?Msg[cnt]=='n'?Msg[c nt]==' ')
Msg[cnt]=CH;
else
if(cnt%2==0)
Msg[cnt]=toupper(Msg[cnt]);
else
Msg[cnt]=Msg[cnt-1];
}
}
void main()
{
char MyText[]="Input Raw";
Mycode(MyText,'@');
cout<<"NEW TEXT:"<<MyText<<endl;
}
Answer: I@PPT@RRW
Question 14: Observe the following program and find out, which output(s) out of (i) to (iv) will not expected from the program ? What will be the minimum and the maximum value assigned to the variable chance ?
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdib.h>
void main()
{
randomize()
int Game[]=(10,16),P;
int Turns=random(2)+5;
for(int T=0;T<=2;T++)
{
P=random(2);
Cout<<Game[P]+Turn<<"*";
}
}
(i) 15*22*
(ii) 22*16*
(iii) 16*21*
(iv) 21*22*
Answer: Option 1:
None of the outputs are correct Variable named chance does not exist in the program, hence no minimum and maximum values for it.
OR
Option 2 :
Error in question OR
Option 3: Assuming
Cout<<Game[P]+Turn<<“#”; in place of cout << Game[P] + Turn <<“*”;

Since out of the above possible outputs only option (ii) is correct, hence The outputs not ! expected from the program are (i) (iii) and (iv)
Question 15: Observe the following program and find out which output (s) out if (i) to (iv) will not be f expected from the program ? What will be the minimum and the maximum value assigned to the variable Chance ?
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
randomize() ;
int Arr[]={9, 6},N;
int Chance = random(2)+10;
for(int C=0;C<2;C++)
{
N=random(2);
cout<<Arr[N]+Chance<"#";
}
}
(i) 9#6#
(ii) 19#17#
(iii) 19#16#
(iv) 20#16#
Answer:
The outputs not expected from the program are (i), (ii) and (iv)
Minimum Value of Chance = 10
Maximum Value of Chance = 11
Question 16: Find and write the output of the following C+ + program code :
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
typedef char WORD(80];
void CODEWORD(WORD W)
{
int LEN=strlen (W);
for(int 1=0;I<LEN-1;I+=2)
{
char SW=W[I];
W[I]=W[I+1];
W[1+1]=SW;
}
for(1=1;I<LEN;I+=2)
if(W[I]>=1M1&&W[I]<='U’)
W[I)='#';
}
void main()
{
WORD Wrd="EDITORIALS";
codeword(Wrd);
cout<<Wrd<<endl;
}
Answer:
DETIROAISL
Question 17: Correct the following code and rewrite
#define convert(P,Q)P+2*Q;
void main()
{
float A,B,Result;
cin>>A>>B;
result=Convert[A,B];
cout<<"output"<<Result<<;
endline;
}
Answer:
#define convert(P,Q)P+2*Q
void main()
{
float A,B,Result;
cin>>A>>B;
Result=convert(A,B);
cout<<"Output"<<Result<<endl;
}
Short Answer Type Questions-ll
Question 1: Observe the following C++ code very carefully and rewrite it after removing any/all syntactical errors with each correction underline.
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
#Define float MaxSpeed =60.5;
void main()
}
int MySpeed char Alert = 'N';
cin>>MySpeed;
if MySpeed>MaxSpeed
Alert = 'Y';
cout<<Alert<<endiline;
}
Answer:
#define float MaxSpeed_60.5; //Error 1, 2, 3
void main()
{
int MySpeed; //Error 4
char Alert='N';
cin>>MySpeed;
if(MySpeed>MaxSpeed) //Error 5
Alert='Y';
cout<<Alert<<endl; //Error 6
Question 2: Write the ouputs of the following C+ + program code :
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
void Location(int &X, int Y=4)
{
Y+=2;
X+=Y;
}
void main()
{
int PX=10, PY=2;
Location(PY):
cout<<PX<<","<<PY<<endl;
Location (PX,PY);
cout<<PX<<","<<PY<<end;
}
Answer:
10,8
20,8
Question 3: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
void in(int x, int y, int &z)
{
x+=y;
y--;
z*=(x-y);
}
void out(int z,int y, int &x)
{
x*=y;
y++;
z/=(x+y);
}
void main()
{
int a=20, b=30, c=10;
out(a,c,b);
cout<<a<<"#"<<b<<"#"<<c<<"#"<<endl;
in(b,c,a);
cout<<a<<"@"<<b<<"@"<<c<<"@"<<endl;
out(a,b,c);
cout<<a<<"$"<<b<<"$"<<c<<"$"<<endl;
}
Answer:
20#300#10#
620@300@10@
620$300$3000$
Question 4: Find the output of the following program segment :
int a = 3 ;
void demo(int x, int y, int &z)
{
a+= x+y; z=a+y; y+=X;
cout<<x<<'*'<<y<<'*'<<z<<endl;
}
void main()
{
int a=2,b=5;
demo( : : a, a, b):
demo( : : a, a, b);
}
Answer:
3 * 5 * 10
8 * 10 * 20
TOPIC-4
Structures
Short Answer Type Questions-ll
Question 1: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
void ChangeArray(int number, int ARR[], int Size)
{
for(int L=0;L<Size;L++)
if(L<number)
ARR[L]+=L;
else
ARR[L]*=L;
}
void Show (int ARR[], int Size)
{
for(int L=0;L<Size;L++)
(L%2==0)?
cout<<ARR[Ll<<"#": cout<<
ARR[L]<<endl;
}
void main()
{
int Array[]={30,20,40,10,60,50};
ChangeArray(3,Array,6);
Show(Array,6);
}
Answer:
Output:
30#21
42# 30
240#250
Question 2: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
void Switchover(int A[], int N, int split)
{
for(int K=0;K<N K++)
if(K<split)
A[K]+=K;
else
A[K]*=K;
}
void Display(int A[], int N)
{
for(int K=0;K<N;K++)
(K%2==0)?cout<<A[K]<<"%" :
cout<< A[K]<<endl;
}
void main()
{
int H[]={30,40,50,20,10,5};
Switchover(H,6,3);
Display(H,6);
}
Answer:
Output:
30%41
52%60
40% 25
Question 3: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
struct GAME
{
Int Score, Bonus,
};
void Play(GAME &g, int N=100)
{
g.score ++;
g.Bonus+=N;
}
void main()
{GAME G={110,50};
Play(G,10);
cout<<G.Score<<":"<<G.Bonus<<endl;
Play(G);
cout<<G.Score<<":"<<G.Bonus<<endl,
Play(G,15);
cout<<G.Score<<":"<<G.Bonus<<endl;
}
Answer:
Output:
111 : 60
112:160
113:175
Question 4: Rewrite the following program after removing the syntax errors (if any). Underline each correction.
#include<iostream.h>
struct Pixels
{int Color<<Style;}
void ShowPoint(Pixels P)
{
cout<<P.Color<<P.Style<<endl;
void main()
{
Pixels Pointl={5,3};
Show Point(Pointl);
Pixels Point2=Point1;
Color.Point1+=2;
Show Point(Point2) ;
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
struct Pixels
{int Color, Style};
void ShowPoint(Pixels P)
{
cout<<P.Color<<P.Style<<endl;) //
In cascading of Cout,<<to be used
void main()
{
Pixels Point1={5,3); //{} to be used to initialise of members of the object
ShowPoint(Point1);
Pixels Point2=Point1;
Point 1.Color+=2;
ShowPoint(Point2);
}
Question 5: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream. h>
struct POINT
{int X, Y, Z ;};
void Stepln(POINT &P, int Step=1)
{
P.X+=Step;
P.Y-=Step;
P.Z+=Step;
void Stepout(POINT&P, int Step=1)
P.X-=Step;
P.Y+=Step;
P.Z-=Step;
}
void main()
{
POINT Pl={15,25,5}, P2={10,30,20} ;
Stepln(P1);
StepOut(P2,4);
cout<<Pl.X<<","<<Pl.Y<<","<<Pl.Z<<endl;
cout<<P2.X<<","<<P2.Y<<","<<P2.Z<<endl;
Stepln(P2,12);
cout<<P2.X<<","<<P2.Y<<","<<P2.Z<<endl;
}
Answer:
Output:
16,24,6
6, 34,16
18,22,28
Question 6: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
struct Score
{
int Year;
float Topper;
};
void Change(Score*S, int x=20)
{S -> Topper = (S->Topper+25)-x;
S->Year++;}
void main()
{
Score Arr[]={ {2007, 100}, {2008, 95}};
Score * Point = Arr;
Change(Point,50);
cout<<Arr[0].Year<<'#'<<Arr[0].Topper<<endl;
Change(++Point);
cout<<Point->Year<<'#'<<Point->Topper<<endl;
}
Answer:
Output:
2008 # 75
2009 # 100
Question 7: Find the output of the following program :
#include<iostream.h>
struct THREE_D{int X,Y,Z;};
void Moveln(THREE_D & T, int Step=1)
{
T.X+=Step;
T.Y-=Step;
T.Z+=Step;
}
Void MoveOut(THREE_D & T, int Step = 1)
{
T.X-=Step ;
T.Y+=Step ;
T.Z-=Step ;
}
Void main()
{
THREE_D T1={10,20,5},
T2 ={30,10,40};
Moveln(Tl);
MoveOut(T2,5);
Cout<<Tl.X<<11,"<<T1.Y<<","<<T1.Z<<endl;
Cout<<T2.X<<","<<T2.Y<<","<<T2.Z<<endl;
Moveln(T2,10);
COUt<<T2.X<<","<<T2.Y<<","<<T2.Z<<endl;
}
Answer:
11,19,6
25,15,35
35, 5,45
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 3 Stack |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 4 Queue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science C++ Revision Tour
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science C++ Revision Tour is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Computer Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in C++ Revision Tour of Computer Science Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in C++ Revision Tour Class 12 chapter of Computer Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of C++ Revision Tour NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Computer Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Computer Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Computer Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Computer Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science C++ Revision Tour for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Computer Science C++ Revision Tour have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Computer Science C++ Revision Tour can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT C++ Revision Tour Class 12 Computer Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 C++ Revision Tour Computer Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter C++ Revision Tour have been answered by our teachers

