Download the latest CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes in PDF format. These Class 11 Computer Science revision notes are carefully designed by expert teachers to align with the 2025-26 syllabus. These notes are great daily learning and last minute exam preparation and they simplify complex topics and highlight important definitions for Class 11 students.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes for Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 6 Flow of Control
To secure a higher rank, students should use these Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 6 Flow of Control notes for quick learning of important concepts. These exam-oriented summaries focus on difficult topics and high-weightage sections helpful in school tests and final examinations.
Chapter 6 Flow of Control Revision Notes for Class 11 Computer Science
Decision Making and branching (Conditional Statement)
Looping or Iteration
Jumping statements
4.1 DECISION MAKING & BRANCHING
Decision making is about deciding the order of execution of statements based on certain conditions. Decision structures evaluate multiple expressions which produce TRUE or FALSE as outcome.
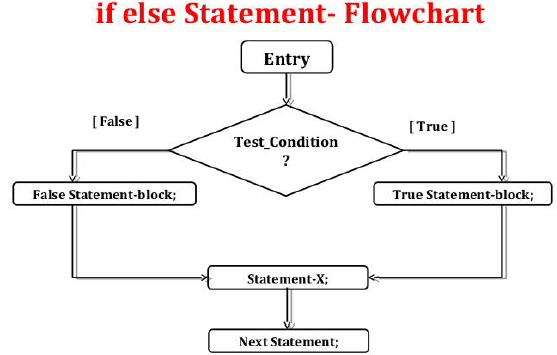
There are three types of conditions in python:
1.if statement
2.if-else statement
3.elif statement
4.if statement: It is a simple if statement. When condition is true, then code which is associated with if statement will execute.
Example:
a=40
b=20
if a>b:
print(“a is greater than b”)
5.if-else statement: When the condition is true, then code associated with if statement will execute, otherwise code associated with else statement will execute.
Example:
a=10
b=20
if a>b:
print(“a is greater”)
else:
print(“b is greater”)
elif statement: It is short form of else-if statement. If the previous conditions were not true, then do this condition”. It is also known as nested if statement.
Example:
a=input(“Enter first number”)
b=input(“Enter Second Number:”)
if a>b:
print(“a is greater”)
elif a==b:
print(“both numbers are equal”)
else:
print(“b is greater”)
4.2 LOOPS in PYTHON
Loop: Execute a set of statements repeatedly until a particular condition is satisfied.
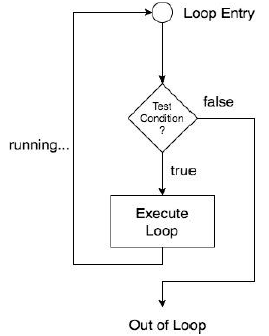
There are two types of loops in python:
1. while loop
2. for loop
while loop: With the while loop we can execute a set of statements as long as a condition is true. It requires to define an indexing variable.
Example: To print table of number 2
i=2
while i<=20:
print(i)
i+=2
for loop : The for loop iterate over a given sequence (it may be list, tuple or string).
Note: The for loop does not require an indexing variable to set beforehand, as the for command itself allows for this. primes = [2, 3, 5, 7]
for x in primes:
print(x)
The range( ) function:
it generates a list of numbers, which is generally used to iterate over with for loop. range( ) function uses three types of parameters, which are:
- start: Starting number of the sequence.
- stop: Generate numbers up to, but not including last number.
- step: Difference between each number in the sequence.
Python use range( ) function in three ways:
a. range(stop)
b. range(start, stop)
c. range(start, stop, step)
Note:
- All parameters must be integers.
- All parameters can be positive or negative.
a. range(stop): By default, It starts from 0 and increments by 1 and ends up to stop, but not including stop value. Example: for x in range(4): print(x)
Output:
0
1
2
3
b. range(start, stop): It starts from the start value and up to stop, but not including stop value.
Example: for x in range(2, 6): print(x)
Output:
2
3
4
5
c. range(start, stop, step): Third parameter specifies to increment or decrement the value by adding or subtracting the value.
Example: for x in range(3, 8, 2): print(x)
Output:
3
5
7
Explanation of output: 3 is starting value, 8 is stop value and 2 is step value. First print 3 and increase it by 2, that is 5, again increase is by 2, that is 7. The output can’t exceed stop-1 value that is 8 here. So, the output is 3, 5, 8.
Difference between range( ) and xrange( ):
| xrange( ) | ||
| returns the list of numbers | returns the generator object that can be used to display numbers only by looping | ||
| The variable storing the range takes more memory | variable storing the range takes less memory | ||
| all the operations that can be applied on the list can be used on it | operations associated to list cannot be applied on it | ||
| slow implementation | faster implementation |
4.3 JUMP STATEMENTS:
There are two jump statements in python:
break
continue
break statement : With the break statement we can stop the loop even if it is true.
Example:
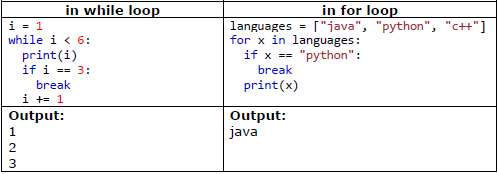
Note: If the break statement appears in a nested loop, then it will terminate the very loop it is in i.e. if the break statement is inside the inner loop then it will terminate the inner loop only and the outer loop will continue as it is.
continue statement : With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration, and continue with the next iteration.
Example:
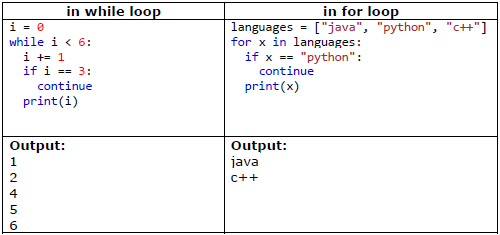
4.4 Loop else statement:
The else statement of a python loop executes when the loop terminates normally. The else statement of the loop will not execute when the break statement terminates the loop.
The else clause of a loop appears at the same indentation as that of the loop keyword while or for.

4.5 Nested Loop :
A loop inside another loop is known as nested loop.
Syntax:
for in :
for in :
statement(s)
statement(s)
Example:
for i in range(1,4):
for j in range(1,i):
print(“*”, end=” “)
print(” “)
Programs related to Conditional, looping and jumping statements
1.Write a program to check a number whether it is even or odd.
num=int(input(“Enter the number: “))
if num%2==0:
print(num, ” is even number”)
else:
print(num, ” is odd number”)
2.Write a program in python to check a number whether it is prime or not.
num=int(input(“Enter the number: “))
for i in range(2,num):
if num%i==0:
print(num, “is not prime number”)
break;
else:
print(num,”is prime number”)
3.Write a program to check a year whether it is leap year or not.
year=int(input(“Enter the year: “))
if year%100==0 and year%400==0:
print(“It is a leap year”)
elif year%4==0:
print(“It is a leap year”)
else:
print(“It is not leap year”)
4.Write a program in python to convert °C to °F and vice versa.
a=int(input(“Press 1 for C to F \n Press 2 for F to C \n”))
if a==1:
c=float(input(“Enter the temperature in degree celcius: “))
f= (9/5)c+32
print(c, “Celcius = “,f,” Fahrenheit”)
elif a==2:
f=float(input(“Enter the temperature in Fahrenheit: “))
c= (f-32)5/9
print(f, “Fahrenheit = “,c,” Celcius”)
else:
print(“You entered wrong choice”)
5.Write a program to check a number whether it is palindrome or not.
num=int(input(“Enter a number : “))
n=num
res=0
while num>0:
rem=num%10
res=rem+res*10
num=num//10
if res==n:
print(“Number is Palindrome”)
else:
print(“Number is not Palindrome”)
6.A number is Armstrong number or not.
num=input(“Enter a number : “)
length=len(num)
n=int(num)
num=n
sum=0
while n>0:
rem=n%10
sum=sum+rem**length
n=n//10
if num==sum:
print(num, “is armstrong number”)
else:
print(num, “is not armstrong number”)
7.To check whether the number is perfect number or not
num=int(input(“Enter a number : “))
sum=0
for i in range(1,num):
if(num%i==0):
sum=sum+i
if num==sum:
print(num, “is perfect number”)
else:
print(num, “is not perfect number”)
8.Write a program to print Fibonacci series.
n=int(input(“How many numbers : “))
first=0
second=1
i=3
print(first, second, end=” “)
while i<=n:
third=first+second
print(third, end=” “)
first=second
second=third
i=i+1
9.To print a pattern using nested loops
for i in range(1,5):
for j in range(1,i+1):
print(j,” “, end=” “)
print(‘\n’)
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Functions Notes Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Functions Notes Set B |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Computer Fundamentals Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Online Access And Computer Security Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Computing and Binary Operation Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Functions In C++ Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Introduction To C++ Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Introduction To Python Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science List in Python Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Programming In C++ Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Programming Methodology Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Structured Data Types Arrays And Structures Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Using C++ Constructs Notes |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Computer Science
CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 6 Flow of Control Notes
Students can use these Revision Notes for Chapter 6 Flow of Control to quickly understand all the main concepts. This study material has been prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 11. Our teachers always suggest that Class 11 students read these notes regularly as they are focused on the most important topics that usually appear in school tests and final exams.
NCERT Based Chapter 6 Flow of Control Summary
Our expert team has used the official NCERT book for Class 11 Computer Science to design these notes. These are the notes that definitely you for your current academic year. After reading the chapter summary, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 11. Always compare your understanding with our teacher prepared answers as they will help you build a very strong base in Computer Science.
Chapter 6 Flow of Control Complete Revision and Practice
To prepare very well for y our exams, students should also solve the MCQ questions and practice worksheets provided on this page. These extra solved questions will help you to check if you have understood all the concepts of Chapter 6 Flow of Control. All study material on studiestoday.com is free and updated according to the latest Computer Science exam patterns. Using these revision notes daily will help you feel more confident and get better marks in your exams.
You can download the teacher prepared revision notes for CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes from StudiesToday.com. These notes are designed as per 2025-26 academic session to help Class 11 students get the best study material for Computer Science.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes include 50% competency-based questions with focus on core logic, keyword definitions, and the practical application of Computer Science principles which is important for getting more marks in 2026 CBSE exams.
Yes, our CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes provide a detailed, topic wise breakdown of the chapter. Fundamental definitions, complex numerical formulas and all topics of CBSE syllabus in Class 11 is covered.
These notes for Computer Science are organized into bullet points and easy-to-read charts. By using CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes, Class 11 students fast revise formulas, key definitions before the exams.
No, all study resources on StudiesToday, including CBSE Class 11 Computer Science Flow of Control Notes, are available for immediate free download. Class 11 Computer Science study material is available in PDF and can be downloaded on mobile.

